Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Secured Transactions Attack Outline
Uploaded by
mkelly2109Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Secured Transactions Attack Outline
Uploaded by
mkelly2109Copyright:
Available Formats
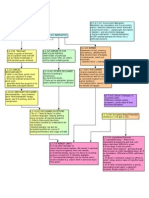
Secured Transactions Attack Outline 1. Scope (9-109) a. In i. 9-109(a)(1): SI (9-102(a)(35)) in P.P ii. 9-109(a)(2): Agricultural Lien iii.
9-109(a)(3): Sale of accts, chattel paper, pymt intangibles, or prom. notes iv. 9-109(a)(4): Consignments 10 factors + 9-102(a)(2) 1-7 v. Leases: (1) meet 1-203(b) + (2) meet 1-203 (b)(1-4) (need one) b. Out i. (c): Law that supersede Article 9 ii. (d): 13 situations may kick you out 2. Attachment (9-203) a. Enforceability i. (b)(1): Value (1-204) ii. (b)(2): Debtor has rights (2-501) when debtor gets rights iii. (b)(3): A security interest in writing, or oral (pledge) + description of the collateral (9-108)(a)+(b)(need one) 1. (A): Authenticated(7) and description of collateral 2. (B): Possession 3. (C): Security certificate delivered to secured party (stocks and bonds) 4. (D): Control iv. Debtor (28) v. Obligor (59)- Debtor is the one who must have their name on the S.A. b. After Acquired Clause (9-204) i. (b): SI under an AAC does not attach
1. Consumer goods unless debtor gets rights to them 10 days after value is given by the creditor 2. A Commercial Tort Claim c. Passing of Title (2-401) i. In a conditional sale the debtor does not really hold title, but merely holds a security interest d. When a new Debtor is Bound (9-203) i. (d): The party is bound by somebody elses security agreement if done by an outside law or by contract: 1. The S.A. becomes effective 2. Generally obligated for all the obligations of the other person 3. Perfection a. Define the Collateral (9-102(a)) i. Goods(44): 1. Consumer Goods (23) 2. Farm Products (34) 3. Inventory (48) 4. Equipment (33) ii. Intangible Property: 1. Accounts (2) 2. Deposit Accounts (29) 3. General Intangibles (42) 4. Payment Intangibles (61) iii. Quasi-Tangible Property: 1. Instrument (47) 2. Investment (49) 3. Documents (30)
4. Chattel Paper (11) b. What type of perfection is needed? i. Need attachment and one of the perfection steps ii. File: 1. Accounts 2. General Intangibles 3. Commercial Tort Claim iii. Possess: 1. Money iv. File or Possess: 1. Goods 2. Negotiable Documents 3. Instruments 4. Tangible Chattel Paper v. Control: 1. Deposit Accounts 2. Letter of Credit Rights vi. File or Control: 1. Electronic Chattel Papers 2. Investment Property (stocks) c. General Rule (9-310) i. (a): File a financing statement ii. (b): exceptions 9-308-9-314 d. Exception: Possession (9-313) i. The secured party may perfect a SI in negotiable documents, goods, instruments, money or tangible chattel paper by taking possession
ii. 9-313(d):perfection begins when the SP takes possession and only continues while the party retains possession iii. Exception: 9-312(f)-Temporary perfection for 20 days without a filing, only when possession is given back to prepare the goods for sale e. Exception: Automatic Perfection (9-309) i. 1. PMSI (9-103) in consumer goods ii. 2. Assignments of accounts or payment intangibles iii. 3+4. Sale of payment intangibles or promissory notes f. Exception: Control (9-312(b)) i. 1. SI in deposit accounts are perfected by control ii. 2. SI in LOC rights are perfected by control iii. 3. SI in money are perfected by possession g. Financing Statement i. 9-501(a)(2)- Office to file in ii. 9-502(a)- Sufficiency of a financing statement 1. Debtors name 2. Name of the secured party 3. Description of the collateral iii. 9-515(a)- Duration of FS effectiveness 1. 5 years, but cannot renew until 6 months before it lapses (d) iv. 9-516- Effectiveness of the filing 1. Communication of the record to the filing office 2. Tendering of the filing fee 3. Acceptance from the filing office v. 9-517- Filing office screw up 1. Even if the filing office screws up the filing is still effective
vi. 9-520- Acceptance and Refusal to Accept the Record 1. (c)The filing is still good if the basics in 9-502 are met vii. 9-504- Indication of Collateral 1. Provides a description of the collateral + FS covers all assets or all P.P. viii. 9-506- Effect of Error or Omission 1. (a)- FS is good if it substantially satisfies the requirements 2. (b)- seriously misleading 3. (c)- not seriously misleading if they can find it (some courts=reasonableness, some courts=needs to be on the page that comes up using filing office search index) (burden is on the searcher) ix. 9-507(c)- Name Changes 1. (c)(1)- 4 month grace period FS is effective 2. (c)(2)- FS will remain effective if an amendment renders it not seriously misleading x. 9-513- Termination Statements 1. (a)- A secured creditor of Consumer Goods must file a termination statement if: a. 1. There is no further obligation or commitment by the financing statement 2. (b)- Need to file it within one month after there is no more obligations or the S.C. may be liable for damages xi. Bogus filings 1. 9-509(d)- A debtor may file a termination statement if the creditor doesnt (needs to be authorized) 2. 9-513(a)(2)- Debtor did not authorize the filing a. (b)(2)- 20 days after the creditor receives an authenticated demand from the debtor xii. Errors
1. 9-518- Person may file a correction statement 2. 9-512- States can choose alternatives to amendments to filings h. Multi-State Transactions i. 9-301- What state to file a FS 1. (1)-General rule- The jurisdiction where ever the debtor is located 2. (2)- for pledge purposes, wherever the collateral is located ii. 9-307- Determines the location of the debtor 1. (b)(1)- Individuals principle residence 2. (b)(2)- Place of business (if there is only one place of business) 3. (b)(3)- Chief Executive Office (if more than one place of business) iii. 9-316- Continued Perfection + Change in Governing Law 1. If you move, this governs perfection 2. (a) Earliest of: (usually 1+2 or 1+3) a. 1. Time of perfection would have ceased (FS good for 5 years) b. 2. 4 months after original debtor changes locations c. 3. 1 year after transfer of the collateral to a new debtor located in another jurisdiction i. Certificates of Title i. 9-303- Covers certificates of title 1. (b)- are valid if a valid application is submitted and the fee are delivered 2. (b)-cease to be covered under the earliest of: a. 1. Time it ceases to be effective in the issuing jurisdiction
b. 2. Time goods become covered by a COT issued by another jurisdiction ii. 9-316 (see above) 4. Priority a. General Rule i. 9-201- Secured Party wins b. 1. Classify your Parties i. Analyze attachment and perfection issues c. Secured Creditor vs. Third Party i. (a)(1)-SI loses to the rights of a person entitled to priority under 9-322 ii. (a)(2)-SI loses to a person that becomes a lien creditor before the earlier of 1. (A)- SI is perfected 2. (B)- attachment and FS for the collateral is filed iii. Judicial Lien Creditors 1. 9-333- Possessory lien (anything other than a SI or an agricultural lien)on goods wins over a SI in the goods unless the lien is created by a statute that says otherwise d. Priorities among Conflicting Security Interests i. 9-322(a) 1. Perfected v. Perfected- Race Rule first to file or perfect wins 2. Perfected v. Unperfected- perfected SI wins over an unperfected one 3. Unperfected v. Unperfected- First to attach has priority ii. Purchase Money Creditor (around the race rule) 1. 9-324(a)- general rule is a perfected PMSI in goods wins if PMSI is perfected when the debtor receives possession of the collateral or within 20 days thereafter
2. (b)- PMSI in inventory dont have 20 day grace period to perfect = must be perfected when the debtor possesses a. 9-103(d)- PMSI in inv. Defined b. 9-102(20)- Consignment 3. (g)- Conflicting PMSI- PM seller v. PM Lender = Seller wins e. Exception i. 9-317(e)- If a FS is filed for a PMSI before or within 20 days after debtor receives delivery of the collateral the SI wins over rights of a buyer, lessee, or lien creditor f. After Acquired Clauses i. 9-204(a)- SA may create/provide for a SI in after-acquired collateral ii. (b)- SI doesnt attach under an AAC to: 1. Consumer goods unless debtor acquires rights in them within 10 days after the secured party gives value 2. Commercial tort claims iii. (c)-Future advances are cool (future loan is secured by the same collateral (over-collateralized)) g. Future Advance Clauses i. 9-323(a)(1)- only when the advance is automatic or temporary ii. (a)(2)- not made pursuant to a commitment entered into before while SI is perfected 5. Disposition of Collateral and Continuation of SI a. 9-315(a)(1)- SI continues in collateral notwithstanding sale, lease, license, exchange Unless SP authorized the disposition free of the SI + SI attaches to identifiable proceeds b. Protections for Buyers in the Ordinary Course i. 9-320(a)- BOCB take free of a security interest created by the buyers seller, even if it is perfected + buyer knows of its existence ii. 1-201(9)-
1. Good Faith 2. Without Knowledge 3. Ordinary Course of Business 4. In the Business 5. Possession 6. New Value iii. 9-320(e)- Buyer does not receive protection if the goods are still in the possession of the creditor c. Protections for Buyers of Consumer Goods i. 9-320(b)- Buyer of consumer goods takes free of a SI if the buyer buys: 1. Without knowledge of the SI 2. For Value 3. Primarily for the Buyers family or personal purposes 4. Before the financing statement is filed ii. 9-320(e)- Buyer does not receive protection if the goods are still in the possession of the creditor d. Priority of Rights of Purchases of Instruments i. 9-331- Buyer of negotiable instruments + holder in due course is protected if they buy for new value + are innocent 6. Investment Property (Deposit Accounts) a. Definition i. 9-102(a)(29)- Demand, time, savings, passbook, or similar account maintained within a bank b. Perfection i. 9-310(b)(8)- Exception to 9-310(a)-Filing a FS statement is not needed to perfect a SI in: Deposit Accounts, elec. CP, elec. Docs, investment property, and letter of credit
ii. 9-312(b)(1)- SI in a deposit account may be perfected only by control c. Control of Deposit Accounts i. 9-104(a)-requirements for control ii. 9-104(b)- SP that satisfies (a), has control even if the debtor retains a right to disposition of funds. 7. Fixtures a. Definition i. 9-102(41)-Goods that have become so related to the particular real property that an interest in them arises under real property law b. Classification of a Fixture i. 1. Is the good physically annexed? ii. 2. Adapted iii. 3. Intent is for permanent attachment c. Look to state law to see when a good becomes a fixture d. Fixture Filing i. 9-501(b)- File in the same office as mortgages ii. 9-502(a)- Name of debtor, SP, and indicates the collateral to be covered iii. 9-502(b) 1-4 e. Priority in Fixtures i. 9-334(e)(1)- A9 creditor v. real property creditor- first to file or record wins (race rule) ii. 9-334(c)- General Rule: A real estate creditor wins if (d-h) dont apply iii. 9-334(d)- Perfected SI in fixtures wins over a conflicting owner of real property if the debtor has an interest of record or is in possession of the real property and 1. SI is a PMSI
2. Interest of the encumbrancer arises before goods become fixtures 3. SI is perfected by a fixture filing before the goods become fixtures or within 20 days after iv. 9-334(h)- A construction mortgage beats a SI in fixtures if: 1. Mortgage is recorded before goods become fixtures; and 2. Goods become fixtures before completion of the construction (h) trumps (d) f. Removal of Fixtures i. 9-604(c)- A priority holder in fixtures may remove the collateral from the real property ii. 9-604(d)- the secured party that is removing the collateral must properly reimburse the owner of the real property for the cost of repair and physical injury, but not for diminution in value 8. Tax Liens a. Definition i. 6321-Lien arises + covers everything owned b. Length of the Lien i. 6322- Lien arises upon assessment + lasts until you pay taxes, judgment or SOL runs out c. Priority i. 6323 1. SI must be perfected to win over a tax lien 2. Lien isnt valid against purchases, holder of SI until notice of lien is filed 3. SI beats tax liens unless lien is filed before SI comes along ii. 6323(c)-after-acquired collateral iii. 6323(d)- Future Advance
1. 9-323(d)a. 9-323(e) 2. 9-323(b)iv. 6323(h)- Perfected SI: 1. (a)- Collateral Existing 2. (b)- Protected against JLC 3. (c)- Value Given 9. Bankruptcy a. Step 1: i. Bankruptcy petition is filed in federal court ii. 362- everything the debtor owns is frozen, and anything that comes in after is free and clear of bankruptcy b. Step 2 Strong Arm Statute: i. 544(a)- gives the debtor the status of a hypothetical judicial lien creditor, and destroys any unperfected security interests 1. 9-317(a)(2)- Secured creditor wins if the secured creditor was perfected before the lien arose ii. 544(b)-The trustee has the right to step into the shoes of a general creditor and exercise their rights against other creditors iii. 588- gives the trustee the debtors rights against other creditors iv. If the strong arm statute works go to 9-317 c. Step 3 Preferences: i. 547(b)- gives power to the trustee to remove a preferential transfer if 1-6 are not met 1. Transfer of Property 2. To a Creditor a. 101(10)- defines creditor claim against the debtor b. 101(5)- right to payment
3. Pursuant to an Antecedent debt a. Look when the transfer was made + see if it was on old debt b. 547(e)(2)- Transfer is on the date of perfection (not attachment) i. Creditor perfects within 30 days of attachment, then the date of transfer is moved back to the date of attachment (not a grace period) c. 547(c)- Weekend exception i. 1. Both Debtor and Creditor intended that the security interest + loan be transferred at the same time ii. 2. Transfer was a substantial contemporaneous exchange (with the loan) d. 547(c)(2)- Conventional debt payment, must meet 1-3 i. 1. Debt was created in ordinary course of partys affairs ii. 2. Payment was made in the ordinary course of affairs iii. 3. Payment be made according to ordinary business terms e. 547(c)(3)- PMSI creditor transfers, if perfected w/in 20 days after debtor gets property 4. Transfer must have been made while the debtor was insolvent a. 547(f)- within 90 days before the bankruptcy there is a presumption that the debtor is insolvent b. Debtor can rebut this presumption with evidence of solvency 5. Transfer has to be made within 90 days of the date of bankruptcy
a. Exception: transfer to an insider (101(31)), then 90 day period is extended to 1 year 6. More Than a. Does creditor get more with the transfer then he would without the transfer? i. Run debtor through bankruptcy w/o transfer (.08-.10 cents on the dollar) ii. Run debtor through bankruptcy w/ transfer b. If creditor gets more than it will be struck down 10. Proceeds a. Definition i. 9-102(a)(64)- Whatever is acquired upon a sale, lease, license, exchange, or other disposition of collateral b. Perfection i. 9-315(c)- SI interest in the proceeds is perfected if the SI in the original collateral was perfected ii. (d) - PMSI in proceeds becomes unperfected on the 21st day after the SI attaches to the proceeds unless: 1. All conditions are met a. FS covers the original collateral b. Properly filed at the correct office under 9-501 c. Proceeds were not acquired with cash proceeds 2. Proceeds are identifiable cash proceeds 3. SI in the proceeds is perfected other than under (c) when the SI attaches to the proceeds or within 20 days thereafter iii. 9-315(a)(2)- SI attaches to any identifiable proceeds of collateral 1. Are identifiable if the creditor can prove the cash went into a particular account of funds commingled- they are identifiable
2. Lowest Intermediate Balance Rule a. If the amount of money stays at or above the proceed amount then the proceeds are assumed to still be in the bank (debtor spends his money first) i. BOP on creditor to show 1. Wrongfully taken 2. Put into a comingled account, burden then shifts to debtor b. When the money drops below the proceeds, then the SI drops with it and any later deposits dont bring the SI back up c. Priority i. 1. Classify the parties ii. 2. 9-315(c)+(d) to see if it stays perfected iii. 3. Battle between Perfected v. Perfected (9-322(a)(1) first to file rule) d. Exception for Purchasers of Chattel Paper i. 9-330- Purchaser of CP wins over a SI in CP which are claimed as proceeds of inventory subject to a SI if: 1. In Good Faith and in the Ordinary Course of Business, purchaser gives new value and takes possession of the CP or obtains control of the CP under 9-105 (knowledge of the SI does not constitute Bad Faith)
You might also like
- Secured Transactions ChecklistDocument6 pagesSecured Transactions Checklistshacisa90% (10)
- Secured Transaction OutlineDocument43 pagesSecured Transaction Outlinecjd223100% (4)
- Secured Trans (Good Explanations)Document42 pagesSecured Trans (Good Explanations)JasonGershensonNo ratings yet
- Art. 9 UCC Priority AnalysisDocument22 pagesArt. 9 UCC Priority Analysistestacct00% (1)
- Secured Transaction Basic ModelsDocument5 pagesSecured Transaction Basic ModelsElissa Mckee100% (7)
- Outline - Secure Transactions - Harrell - PDPDocument36 pagesOutline - Secure Transactions - Harrell - PDPCaitlin Elizabeth100% (3)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument27 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineJ M100% (1)
- Secured-Transactions OutlineDocument43 pagesSecured-Transactions Outlinea thayn100% (2)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument22 pagesSecured Transactions Outlinetroberp100% (4)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument59 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineGabby ViolaNo ratings yet
- Secured Transaction OutlineDocument44 pagesSecured Transaction OutlinewgearharNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions, Governing Law: Law Essentials for Law School and Bar Exam PrepFrom EverandSecured Transactions, Governing Law: Law Essentials for Law School and Bar Exam PrepRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Secured Transaction Outline 2012Document45 pagesSecured Transaction Outline 2012Isabella L100% (10)
- Secured Transactions - LoPucki Casebook ProblemsDocument72 pagesSecured Transactions - LoPucki Casebook ProblemsEmmanuel Ulubiyo97% (36)
- CHANGES AND COMPETITIONS IN SECURED TRANSACTIONSDocument10 pagesCHANGES AND COMPETITIONS IN SECURED TRANSACTIONSAnonymous vXdxDlwKO89% (9)
- Secured TransactionsDocument28 pagesSecured Transactionspatrick88% (8)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument121 pagesSecured Transactions Outlinemaureen P100% (2)
- Secured Transactions Flow Chart (Collateral)Document10 pagesSecured Transactions Flow Chart (Collateral)Kathleen Alcantara94% (16)
- Secured Transactions RemediesDocument70 pagesSecured Transactions RemediesCarolina Jordan100% (1)
- Vela - Secured Transactions OutlineDocument90 pagesVela - Secured Transactions OutlineJonathan Vela100% (5)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument65 pagesSecured Transactions Outlinemasskonfuzion100% (3)
- Secured Transactions Outline From OnlineDocument59 pagesSecured Transactions Outline From Onlinektbabyo0650% (2)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument103 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineJason Henry100% (2)
- Sec Trans Outline MEE/UBEDocument8 pagesSec Trans Outline MEE/UBEArthur Shalagin100% (2)
- SECURED TRANSACTIONS GUIDEDocument9 pagesSECURED TRANSACTIONS GUIDEJustin CashNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument46 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineEric Shepherd100% (3)
- Secured Transactions Outline JDDocument176 pagesSecured Transactions Outline JDJesse Danoff92% (13)
- Secured Transactions PRINT2Document34 pagesSecured Transactions PRINT2seabreeze100% (1)
- Wills and Trusts - Attack SheetDocument4 pagesWills and Trusts - Attack SheetMissPardis100% (8)
- Remedies Outline - Modern American Remedies by LaycockDocument41 pagesRemedies Outline - Modern American Remedies by Laycockcordeliascarlette85% (13)
- Secured Transactions: Attachment and PerfectionDocument8 pagesSecured Transactions: Attachment and PerfectionJenna Alia100% (1)
- Secured Transactions ChecklistDocument1 pageSecured Transactions Checklistjsanoh100% (2)
- Sales Final OutlineDocument44 pagesSales Final OutlineCole Hoffmeister75% (8)
- Creation, Transfer and Termination of Private TrustsDocument4 pagesCreation, Transfer and Termination of Private TrustsJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- ST OutlineDocument103 pagesST Outlineam3ze100% (4)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument30 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineShelby Bullitt100% (1)
- WIlls and Trusts Essay RoadmapDocument18 pagesWIlls and Trusts Essay RoadmapCamille Walker100% (3)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument20 pagesSecured Transactions Outlineprentice brown100% (3)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument27 pagesSecured Transactions OutlineAlexandraMarie100% (6)
- Commercial Paper + Secured TransactionsDocument15 pagesCommercial Paper + Secured TransactionsDavid Shim100% (2)
- Secured Transations OutlineDocument153 pagesSecured Transations OutlineTara Patton100% (1)
- Secured Transactions Spring 2010Document81 pagesSecured Transactions Spring 2010Joshua Ryan Collums100% (1)
- Buyer Remedies ChartDocument1 pageBuyer Remedies Chartzmeth144100% (1)
- UCC Seller Remedies for Buyer Breach Under Sections 2-703, 2-706, 2-708 & 2-710Document1 pageUCC Seller Remedies for Buyer Breach Under Sections 2-703, 2-706, 2-708 & 2-710blade1111100% (1)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument31 pagesSecured Transactions Outlinekurt100% (1)
- UCC Warranties ChartDocument1 pageUCC Warranties Chartzmeth144100% (1)
- Probate Assets: Property Non-Probate Assets: Gifts Causa Mortis: 3805 ClaimsDocument4 pagesProbate Assets: Property Non-Probate Assets: Gifts Causa Mortis: 3805 ClaimsGavin Lacambra100% (3)
- Secured Transactions OutlineDocument148 pagesSecured Transactions Outlineinsane7100% (3)
- Secured TransactionsDocument41 pagesSecured TransactionsSom RasouliNo ratings yet
- Remedies Outline Very GoodDocument13 pagesRemedies Outline Very GoodMonte Bell100% (10)
- Secured Transactions OutlinexDocument38 pagesSecured Transactions Outlinexriffsong100% (2)
- Sec Trans AssignmentsDocument5 pagesSec Trans AssignmentsKaylynn NoethlichNo ratings yet
- Secured Transactions: UCC Title 9Document17 pagesSecured Transactions: UCC Title 9Rebel X86% (7)
- Sales Law OutlineDocument53 pagesSales Law Outlinepmariano_5100% (12)
- Trusts and Estates Altv1Document3 pagesTrusts and Estates Altv1zumieb100% (6)
- Bar Prep - Outline - Remedies - ShortDocument11 pagesBar Prep - Outline - Remedies - ShortAnonymous Cbr8Vr2SX100% (2)
- @ UCC Negotiable Instruments Outline - Masinter (Winter 2013)Document63 pages@ UCC Negotiable Instruments Outline - Masinter (Winter 2013)Kim BoSlice100% (9)
- Community Property Outline - Pepper Dine Law - Popovich - 2Document24 pagesCommunity Property Outline - Pepper Dine Law - Popovich - 2fredtv100% (1)
- Comparing intestacy systems and omitted spouse statutesDocument16 pagesComparing intestacy systems and omitted spouse statutesnblu100% (3)
- Con Law 1 Attack OutlineDocument6 pagesCon Law 1 Attack Outlinemkelly2109No ratings yet
- 1 Page Cheat Sheet - Quiz 2Document2 pages1 Page Cheat Sheet - Quiz 2mkelly2109No ratings yet
- Torts Immunity ChartDocument1 pageTorts Immunity Chartmkelly2109No ratings yet
- Evidence 2011 OutlineDocument14 pagesEvidence 2011 Outlinemkelly2109No ratings yet
- Business Associations - ChartDocument9 pagesBusiness Associations - Chartmkelly2109100% (1)
- Torts - Damaages - ChartDocument3 pagesTorts - Damaages - Chartmkelly2109No ratings yet
- Torts II Final Outline Spring 2011Document15 pagesTorts II Final Outline Spring 2011mkelly2109No ratings yet
- Torts Damages Flow ChartDocument3 pagesTorts Damages Flow Chartmkelly2109100% (2)
- Immunity Flow Chart - TortsDocument1 pageImmunity Flow Chart - Tortsmkelly2109No ratings yet
- Business Associations - ChartDocument9 pagesBusiness Associations - Chartmkelly2109100% (1)
- Torts II Final Outline Spring 2011Document15 pagesTorts II Final Outline Spring 2011mkelly2109No ratings yet
- Evidence 2011 OutlineDocument14 pagesEvidence 2011 Outlinemkelly2109No ratings yet
- Week 10 - Applied MicroeconometricsDocument10 pagesWeek 10 - Applied MicroeconometricsMuhibbuddin NoorNo ratings yet
- REQ-Mumbai MC1-11860967-5002214Document1 pageREQ-Mumbai MC1-11860967-5002214shreya arunNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter Worksheet KinderDocument63 pages4th Quarter Worksheet KinderROQUETA SONNo ratings yet
- Convertible Loan AgreementDocument30 pagesConvertible Loan AgreementBernard Chung Wei Leong86% (21)
- Trust Deed DetailsDocument12 pagesTrust Deed DetailsCA Sumanth AshokNo ratings yet
- SLL 2710 Property LawDocument4 pagesSLL 2710 Property LawSuditi TandonNo ratings yet
- Terms and Conditions for Spare Parts SalesDocument3 pagesTerms and Conditions for Spare Parts Salesshujad77No ratings yet
- Carondelet High School Sample Bequest LanguageDocument2 pagesCarondelet High School Sample Bequest Languageapi-25953150No ratings yet
- 06-20-23 Goba Capital LOI Factoring Zigma Comercializadora S.A.S - SignedDocument5 pages06-20-23 Goba Capital LOI Factoring Zigma Comercializadora S.A.S - SignedTechnology sports ColombiaNo ratings yet
- John E. White, D/B/A White & White Law Offices, P.C. v. TRW Real Estate Loan Services, Incorporated, 14 F.3d 599, 4th Cir. (1993)Document4 pagesJohn E. White, D/B/A White & White Law Offices, P.C. v. TRW Real Estate Loan Services, Incorporated, 14 F.3d 599, 4th Cir. (1993)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Disabled Toilet LayoutDocument1 pageDisabled Toilet LayoutVivix VivianaNo ratings yet
- MapansaDocument2 pagesMapansaJay Cabale AcevedoNo ratings yet
- PNCC Skyway Vs PNCC SkywayDocument3 pagesPNCC Skyway Vs PNCC SkywayTrixie PeraltaNo ratings yet
- Article 1482Document1 pageArticle 1482JAYBIE ENDAYANo ratings yet
- Termination of Employment Letter TemplateDocument4 pagesTermination of Employment Letter Templateprecious okpokoNo ratings yet
- 03 Promoters Law 3210 Company Law I Ii. DisclosureDocument3 pages03 Promoters Law 3210 Company Law I Ii. DisclosureYusra AliNo ratings yet
- Family LawDocument14 pagesFamily LawSuriya AadilaNo ratings yet
- Spouses Mallari vs. Prudential Bank DigestDocument2 pagesSpouses Mallari vs. Prudential Bank DigestkristofferNo ratings yet
- CenidoDocument26 pagesCenidoJennilyn TugelidaNo ratings yet
- Contract of Lease for GarageDocument2 pagesContract of Lease for GarageJohn ReyesNo ratings yet
- Discovering Jmp Zh 发现 JMPDocument192 pagesDiscovering Jmp Zh 发现 JMP1105195794No ratings yet
- OIC MigrationToolsDocument13 pagesOIC MigrationToolsCarlos Alexandre MansurNo ratings yet
- Negotiable Instrument Act 1881Document19 pagesNegotiable Instrument Act 1881Shaktikumar95% (19)
- in Re - Sycip, Salazar, Feliciano, Hernandez & CastilloDocument3 pagesin Re - Sycip, Salazar, Feliciano, Hernandez & Castilloczarina annNo ratings yet
- EasementsDocument18 pagesEasementsLarry Namukamba80% (5)
- PDP AGreementDocument6 pagesPDP AGreementMatthew JacobsNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2 Suggested AnswersDocument1 pageActivity No. 2 Suggested AnswersGabriel Adrian ObungenNo ratings yet
- Article 1815 1827 Partnership DIGESTDocument6 pagesArticle 1815 1827 Partnership DIGESTChristopher PhilipNo ratings yet
- Korean Polyester Filament Sale ContractDocument3 pagesKorean Polyester Filament Sale ContractQuo QingNo ratings yet
- Marginal Cost of CapitalDocument26 pagesMarginal Cost of CapitalSaeedNo ratings yet