Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conclusion Lab
Uploaded by
Patricia KCCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conclusion Lab
Uploaded by
Patricia KCCopyright:
Available Formats
QUESTIONS:
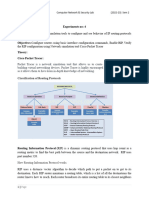
1.0 Obtain and analyze the graphs that compare the sent RIP traffic for the Failure and NO Failure scenarios. Make sure to change the draw style for the graphs to Bar. [5 marks]
In No failure scenario, it shows that routing table we created will build their routing table with no update tables as there is no link failure therefore, the routing table is smooth as show in the above figure. In Failure scenario, we created a link failure where more traffic is sent and set time is 0.00025 seconds to fail the simulation. In result the RIP in effected nodes send out an update of their routing table to place that failure.
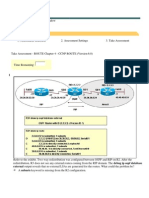
2.0 Change the Ping packet size to 5000 bytes (Hint: Edit the attributes of the Ping Parameters node). Run the simulation to generate a new Ping report. What is the effect of the new size on the ICMP packet response time? [5 marks]
The ICMP packet response time will be affected if the Ping packet size is changed. If the size of byte increases, so the time response is faster and also vice versa.
CONCLUSION [5 Marks]
In this experiment, we had done to configure and analyze the performance of Routing Information Protocol model. RIP (Routing Information Protocol) is a widely-used protocol for managing router information within a self-contained network such as a corporate local area network (LAN) or an interconnected group of such LANs. RIP is classified by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as one of several internal gateway protocols (Interior Gateway Protocol). Using RIP, a gateway host (with a router) sends its entire routing table (which lists all the other hosts it knows about) to its closest neighbor host every 30 seconds. RIP uses a hop count as a way to determine network distance. Each host with a router in the network uses the routing table information to determine the next host to route a packet to for a specified destination. RIP is intended for use within the IP-based Internet. The Internet is organized into a number of networks connected by special purpose gateways known as routers. The networks may be either point-to-point links or more complex networks such as Ethernet or token ring. Hosts and routers are presented with IP datagrams addressed to some host. Routing is the method by which the host or router decides where to send the datagram. It may be able to send the datagram directly to the destination, if that destination is on one of the networks that are directly connected to the host or router. In this experiment, we had test the performance of different scenarios.
You might also like
- Remember: Use The Pop Quiz Feature To Test Your Understanding Throughout This CourseDocument17 pagesRemember: Use The Pop Quiz Feature To Test Your Understanding Throughout This CourseSathis Kumar ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- Implement The Topology With Fully Functional Routers (I.E. Network Connecting The Two Vyos Routers)Document22 pagesImplement The Topology With Fully Functional Routers (I.E. Network Connecting The Two Vyos Routers)Denis McdenohNo ratings yet
- 166_exp4Document15 pages166_exp4neha.shroffNo ratings yet
- 263_exp3_CNSDocument15 pages263_exp3_CNSneha.shroffNo ratings yet
- Cisco ExamDocument109 pagesCisco ExamBart WetzelsNo ratings yet
- IGRPDocument9 pagesIGRPDion Odessy PaduaNo ratings yet
- Informe Redes 06Document4 pagesInforme Redes 06gamersonwayNo ratings yet
- Theory-: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Is A Routing Protocol For Internet Protocol (IP)Document4 pagesTheory-: Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) Is A Routing Protocol For Internet Protocol (IP)Saugat TripathiNo ratings yet
- RIP: Analyzing Routing Information Protocol Performance in Failure and No-Failure Network ScenariosDocument7 pagesRIP: Analyzing Routing Information Protocol Performance in Failure and No-Failure Network ScenariosahmedNo ratings yet
- RIP Basic IntroDocument8 pagesRIP Basic Introathartanveer31No ratings yet
- Ccna 2 Module 6Document9 pagesCcna 2 Module 6shkarkoddl100% (4)
- Chapter 02 - TestDocument6 pagesChapter 02 - TestAlexandrosAristeridisNo ratings yet
- Network LayerDocument2 pagesNetwork Layer01fe21mca013No ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- Ccna 2 Module 3 v4.0Document7 pagesCcna 2 Module 3 v4.0ccnatrainingNo ratings yet
- Final ExamDocument13 pagesFinal Examcristiaan_schipper_147263100% (5)
- Week08 RoutingDocument30 pagesWeek08 RoutingSara El-GendyNo ratings yet
- G PDFDocument20 pagesG PDFokienaNo ratings yet
- EasyChair Preprint 2605Document10 pagesEasyChair Preprint 2605you1lawNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Routing (RIP) : 1. ObjectiveDocument11 pagesDynamic Routing (RIP) : 1. ObjectiveNouman SaleemNo ratings yet
- Lab 01: Basic Networking Commands: IpconfigDocument9 pagesLab 01: Basic Networking Commands: IpconfigBipin MasalNo ratings yet
- Clase 3 VRF, PBR & IpslaDocument58 pagesClase 3 VRF, PBR & IpslaOscar sanchezNo ratings yet
- 20.verification of Four Port Router For Network On Chip (Noc)Document5 pages20.verification of Four Port Router For Network On Chip (Noc)vijaykannamallaNo ratings yet
- Lab 12 CCN MUSTAFADocument3 pagesLab 12 CCN MUSTAFAAbdul ShakoorNo ratings yet
- ROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document12 pagesROUTE Chapter 4 - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS2205100% (5)
- Eng-Design and Implementation-Sarjeet Kaur BrarDocument6 pagesEng-Design and Implementation-Sarjeet Kaur BrarImpact JournalsNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 3 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolDocument5 pagesCHAPTER - 3 Introduction To Dynamic Routing ProtocolAlexandrosAristeridisNo ratings yet
- Understandig EIRP Part2Document12 pagesUnderstandig EIRP Part2Nour IbbaNo ratings yet
- Understand Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) - Design Guide - CiscoDocument117 pagesUnderstand Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) - Design Guide - Ciscojaymalaviya48No ratings yet
- OSPF Design GuideDocument70 pagesOSPF Design Guidespecific4xNo ratings yet
- ROUTE Exam Guide v3.3Document98 pagesROUTE Exam Guide v3.3hilbert69No ratings yet
- Semester II. - Chapter 3Document6 pagesSemester II. - Chapter 3KlokanNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration2 - Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 3 ExamDocument6 pagesCCNA Exploration2 - Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 3 Examchocolat4No ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration2: Routing Protocols - Chapter 3 Exam: Distance of EIGRP Is Lower Than RIPDocument5 pagesCCNA Exploration2: Routing Protocols - Chapter 3 Exam: Distance of EIGRP Is Lower Than RIPsayedahmedNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Network LabsDocument125 pagesComputer Communication Network LabsasadhppyNo ratings yet
- Ethernet CablingDocument8 pagesEthernet CablingOctav EnachiNo ratings yet
- DsmbISP Final Exam - CCNA Dicovery Working at A Small-To-Medium Business or ISP (Version 4.1) Final 2Document13 pagesDsmbISP Final Exam - CCNA Dicovery Working at A Small-To-Medium Business or ISP (Version 4.1) Final 2JesusforgivemeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Routing Protocol QuestionsDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Routing Protocol QuestionsYash RamlugunNo ratings yet
- CSE 4512 Computer Networks-Lab 07Document17 pagesCSE 4512 Computer Networks-Lab 07Ahmad MukaddasNo ratings yet
- Network(8-9)[1]Document7 pagesNetwork(8-9)[1]nirigik980No ratings yet
- Lab 5: Basics of Redistribution, Configure OSPF On A Multi-Access NetworkDocument14 pagesLab 5: Basics of Redistribution, Configure OSPF On A Multi-Access NetworkNguyễn Tiến HoàiNo ratings yet
- 3.1 IP Routing Part 2Document15 pages3.1 IP Routing Part 2trustyNo ratings yet
- CCNP Final Exam PDFDocument12 pagesCCNP Final Exam PDFMauro Di CesareNo ratings yet
- DCompNtwk Practice FinalDocument6 pagesDCompNtwk Practice Finalbelizean19930% (1)
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Sindhu TalrejaNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Discovery Final V4.1Document50 pagesCCNA 2 Discovery Final V4.1Sandra100% (5)
- IP Networks: Nasir Majeed Manager (Certification) Cisco Academy Support Centre (ASC) PTCL AcademyDocument41 pagesIP Networks: Nasir Majeed Manager (Certification) Cisco Academy Support Centre (ASC) PTCL AcademyMuhammad AsifNo ratings yet
- ROUTE Final Exam - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document28 pagesROUTE Final Exam - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS220588% (40)
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- IPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1From EverandIPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1From EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1No ratings yet
- Carry Out Safety Assessment at Work AreaDocument2 pagesCarry Out Safety Assessment at Work AreaPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- RPP04 Bee32102Document4 pagesRPP04 Bee32102Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Standard Practice Hair Dresser - 1Document29 pagesStandard Practice Hair Dresser - 1Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Jadual Pmbahgian WIM AMALIDocument2 pagesJadual Pmbahgian WIM AMALIPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- 1 Intro Workshop Arduino 1dayDocument14 pages1 Intro Workshop Arduino 1dayPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Digital Modulation Signal of Data UsingDocument17 pagesDigital Modulation Signal of Data UsingPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Final Report Content MULTIMEDIADocument1 pageFinal Report Content MULTIMEDIAPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Borang Akaun Affin BankDocument2 pagesBorang Akaun Affin BankPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Report Osha CompleteDocument16 pagesReport Osha CompletePatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Siap - Analysis and Result - Lab5Document24 pagesSiap - Analysis and Result - Lab5Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- MOSFET - The Metal Oxide FETDocument1 pageMOSFET - The Metal Oxide FETPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Coa07 PDFDocument17 pagesCoa07 PDFPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Kalendar MUET 2014 (Ed. 19.09.2013) - BIDocument1 pageKalendar MUET 2014 (Ed. 19.09.2013) - BIPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Graph - Internet (n0 6 N No 7)Document4 pagesGraph - Internet (n0 6 N No 7)Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Lamp Iran NNNNDocument7 pagesLamp Iran NNNNPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Lamp Iran NNNNDocument7 pagesLamp Iran NNNNPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 CPU InstructionsDocument16 pagesLab 4 CPU InstructionsPatricia KC0% (1)
- Chapter 4 Isi EyeDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Isi EyePatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Answer Assigment 2Document1 pageAnswer Assigment 2Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Tda8551 T 2Document21 pagesTda8551 T 2Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Dcomm 0 IntroDocument5 pagesDcomm 0 IntroPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- BEC30403 Assignment1 v3Document3 pagesBEC30403 Assignment1 v3Eika MuhamadNo ratings yet
- Worker Injured By Forklift Load Fall At Brick FactoryDocument1 pageWorker Injured By Forklift Load Fall At Brick FactoryPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Minutes Meeting IDP1 Week 4Document2 pagesMinutes Meeting IDP1 Week 4Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- ns-2 Tutorial IntroductionDocument16 pagesns-2 Tutorial IntroductionSameer SalamNo ratings yet
- UNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA FINAL EXAMDocument9 pagesUNIVERSITI TUN HUSSEIN ONN MALAYSIA FINAL EXAMPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Bee 3223Document8 pagesBee 3223Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Motor Driver Circuit FlowchartDocument1 pageMotor Driver Circuit FlowchartPatricia KCNo ratings yet
- Bee 3223Document8 pagesBee 3223Patricia KCNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of Frequency Board GameDocument1 pageAdverbs of Frequency Board GameIsmi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Alphabet Bean BagsDocument3 pagesAlphabet Bean Bagsapi-347621730No ratings yet
- Ivan PavlovDocument55 pagesIvan PavlovMuhamad Faiz NorasiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC - 1 - Intro To Tourism PDFDocument16 pagesTOPIC - 1 - Intro To Tourism PDFdevvy anneNo ratings yet
- Modern Slavery Unveiled Training in Manila 2022 PrimerDocument13 pagesModern Slavery Unveiled Training in Manila 2022 PrimerRapplerNo ratings yet
- The Forum Gazette Vol. 2 No. 23 December 5-19, 1987Document16 pagesThe Forum Gazette Vol. 2 No. 23 December 5-19, 1987SikhDigitalLibraryNo ratings yet
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 1Document16 pagesEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 1Ryze100% (1)
- Merah Putih Restaurant MenuDocument5 pagesMerah Putih Restaurant MenuGirie d'PrayogaNo ratings yet
- CARET Programme1 Bennett-1Document10 pagesCARET Programme1 Bennett-1TerraVault100% (3)
- Classwork Notes and Pointers Statutory Construction - TABORDA, CHRISTINE ANNDocument47 pagesClasswork Notes and Pointers Statutory Construction - TABORDA, CHRISTINE ANNChristine Ann TabordaNo ratings yet
- Hidaat Alem The Medical Rights and Reform Act of 2009 University of Maryland University CollegeDocument12 pagesHidaat Alem The Medical Rights and Reform Act of 2009 University of Maryland University Collegepy007No ratings yet
- Syllabus For The Post of ASI - Traffic - WardensDocument2 pagesSyllabus For The Post of ASI - Traffic - WardensUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Swedenborg's Formative Influences: Jewish Mysticism, Christian Cabala and PietismDocument9 pagesSwedenborg's Formative Influences: Jewish Mysticism, Christian Cabala and PietismPorfirio MoriNo ratings yet
- HVDC PowerDocument70 pagesHVDC PowerHibba HareemNo ratings yet
- Full Download Ebook Ebook PDF Nanomaterials Based Coatings Fundamentals and Applications PDFDocument51 pagesFull Download Ebook Ebook PDF Nanomaterials Based Coatings Fundamentals and Applications PDFcarolyn.hutchins983100% (43)
- Tentative Seat Vacancy For CSAB Special Rounds-202Document92 pagesTentative Seat Vacancy For CSAB Special Rounds-202Praveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Second Year Memo DownloadDocument2 pagesSecond Year Memo DownloadMudiraj gari AbbaiNo ratings yet
- MAY-2006 International Business Paper - Mumbai UniversityDocument2 pagesMAY-2006 International Business Paper - Mumbai UniversityMAHENDRA SHIVAJI DHENAKNo ratings yet
- Polisomnografí A Dinamica No Dise.: Club de Revistas Julián David Cáceres O. OtorrinolaringologíaDocument25 pagesPolisomnografí A Dinamica No Dise.: Club de Revistas Julián David Cáceres O. OtorrinolaringologíaDavid CáceresNo ratings yet
- Coursebook 1Document84 pagesCoursebook 1houetofirmin2021No ratings yet
- Discover books online with Google Book SearchDocument278 pagesDiscover books online with Google Book Searchazizan4545No ratings yet
- BVOP-Ultimate Guide Business Value Oriented Portfolio Management - Project Manager (BVOPM) PDFDocument58 pagesBVOP-Ultimate Guide Business Value Oriented Portfolio Management - Project Manager (BVOPM) PDFAlexandre Ayeh0% (1)
- Final DSL Under Wire - FinalDocument44 pagesFinal DSL Under Wire - Finalelect trsNo ratings yet
- Price and Volume Effects of Devaluation of CurrencyDocument3 pagesPrice and Volume Effects of Devaluation of Currencymutale besaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Evidence-Based Practices in Online Learning: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Online Learning StudiesDocument93 pagesEvaluation of Evidence-Based Practices in Online Learning: A Meta-Analysis and Review of Online Learning Studiesmario100% (3)
- Derivatives 17 Session1to4Document209 pagesDerivatives 17 Session1to4anon_297958811No ratings yet
- Plo Slide Chapter 16 Organizational Change and DevelopmentDocument22 pagesPlo Slide Chapter 16 Organizational Change and DevelopmentkrystelNo ratings yet
- Planificación Semanal Maestro de Inglés RAE 2022-2023Document2 pagesPlanificación Semanal Maestro de Inglés RAE 2022-2023vanessabultron8804100% (1)
- ! Sco Global Impex 25.06.20Document7 pages! Sco Global Impex 25.06.20Houssam Eddine MimouneNo ratings yet
- Freeing Music Education From Schooling: Toward A Lifespan Perspective On Music Learning and TeachingDocument24 pagesFreeing Music Education From Schooling: Toward A Lifespan Perspective On Music Learning and TeachingRockyNo ratings yet






































![Network(8-9)[1]](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/719888260/149x198/084146ff98/1712204636?v=1)











































































