Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy of The Heart
Uploaded by
Tim KuehneOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy of The Heart
Uploaded by
Tim KuehneCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy of the Heart
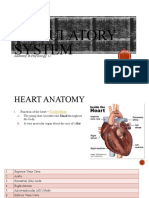
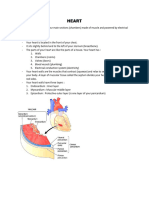
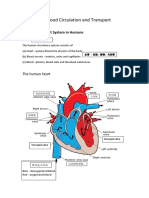
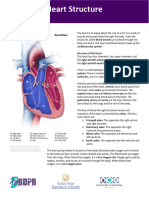
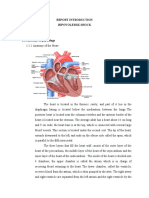
I. Chambers - 4
A. Atria Left and Right Atrium smaller than and superior to . . . B. Ventricles Left and Right Ventricles are larger with thicker cardiac muscle walls. The left is the most powerful pump in the heart C. Other points Septum: wall between chambers, Myocardium: muscle wall of the chambers, Endocardium: epithelial lining of chambers
II.
Major Blood Vessels
A. Superior Vena Cava drains blood from head, neck, and arms into the right atrium B. Inferior Vena Cava second longest vein in body, drains blood from everywhere else into the right atrium C. Pulmonary Trunk carries blood from the right ventricle. Divides into right and left pulmonary artery; blood flow continues toward lungs D. Pulmonary Veins two from each lung (total 4) return blood to left atrium E. Aorta largest body artery; carries blood for all parts of body except the lungs F. Coronary Arteries Shortly after the aorta leaves left ventricle, the coronary arteries send some blood back to heart tissue for its own O2 and nutrients
III.
Valves two pairs
A. AV (atrioventricular) valves between atria and ventricles i. Bicuspid (mitral) between atrium and ventricle on the left B. Tricuspid between atrium and ventricle on right C. Semilunar valves where the major artery exits from the ventricle on each side i. Pulmonary Semilunar Valve where the pulmonary trunk exits the right ventricle ii. Aortic Semilunar Valve where aorta exits left ventricle
You might also like
- Circulatory System AnatomyDocument15 pagesCirculatory System AnatomyVanesa VorpsiNo ratings yet
- 5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2Document29 pages5-Structure and Function of The Body Systems 2uxdan154No ratings yet
- Circulatory System Lesson Plan Explains Heart & Blood FlowDocument6 pagesCirculatory System Lesson Plan Explains Heart & Blood FlowYenny YenNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular AnatomyDocument5 pagesCardiovascular AnatomyDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Heart Structure, Function & Location in 40 CharactersDocument4 pagesHeart Structure, Function & Location in 40 CharactershahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- Quarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesQuarter1 Week2 Lesson2Blood and Gas ExchangeRicky RickyNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument34 pagesCardiovascular Systemkaz92100% (6)
- Functions of the Heart & Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesFunctions of the Heart & Circulatory SystemVeronica FrancisNo ratings yet
- HEARTDocument3 pagesHEARTShan ShanNo ratings yet
- Name: Jeremy F. Saycon Section:9-Boyle Explain How The Blood Flows Throughout The Body ReflectionDocument1 pageName: Jeremy F. Saycon Section:9-Boyle Explain How The Blood Flows Throughout The Body ReflectionAntonio Meneses ValdezNo ratings yet
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDocument46 pagesTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasNo ratings yet
- CVS IDocument7 pagesCVS Itemple samNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyClint-Marie LaxaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System ReviewDocument9 pagesCardiovascular System ReviewsenjicsNo ratings yet
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDocument3 pagesHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Document10 pagesLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςNo ratings yet
- Branching Blood VesselsDocument2 pagesBranching Blood VesselsMarjia TulyNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 - Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesLab 9 - Circulatory SystemClobelle Marie SiachuaNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsDocument47 pagesParts and Function of Heart: Group 5 9 - ActsJasmin GarciaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATORYDocument3 pagesCIRCULATORYSumbul ShoaibNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Word Circulatory SystemDocument26 pagesUnit 4 Word Circulatory SystemChandan Shah100% (2)
- Research Questions-: How The Blood FlowsDocument5 pagesResearch Questions-: How The Blood FlowsAasritha SenagapallyNo ratings yet
- Circolatory SystemDocument2 pagesCircolatory SystemGAIA BACCANINo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument2 pagesThe Cardiovascular SystembluewindNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.6Document5 pagesAnatomy Lec.6aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Anatomi JantungDocument54 pagesAnatomi JantungsaifudinNo ratings yet
- Blood Circulation and TransportDocument23 pagesBlood Circulation and TransportcikzafirahNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyNikka Aubrey Tegui-inNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System +Document14 pagesCardiovascular System +Yasin AbassNo ratings yet
- Vascular or Circulatory System RemhilDocument9 pagesVascular or Circulatory System Remhilremhil malicdemNo ratings yet
- Circulatory_System_in_Humans_Document4 pagesCirculatory_System_in_Humans_petra.t.ayalNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Circulatory SystemDocument157 pagesUnit 4 Circulatory SystemChandan ShahNo ratings yet
- ANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument3 pagesANP Heart Anatomy & PhysiologySheana Tmpl100% (1)
- Austin CardiologyDocument15 pagesAustin CardiologyAustin Publishing GroupNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ActivityDocument5 pagesCirculatory System ActivityKeen Jude CaminosNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System ExplainedDocument2 pagesCirculatory System ExplainedCookies AndcreamNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System LectureDocument5 pagesCardiovascular System LectureMarci MunirNo ratings yet
- Ron Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Document4 pagesRon Seraph Anjello Javier - Q1 Sci. 9 FA No.1Mute GuerreroNo ratings yet
- The HeartDocument2 pagesThe Heartmaty.visintainerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology - Circulatory System - The HeartDocument14 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Circulatory System - The Heartxuxi dulNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary CirculationDocument12 pagesPulmonary CirculationAdrianPaul Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 5129 Combined Science - Biology SectionDocument11 pages5129 Combined Science - Biology SectionKhairunnisaaHAriffinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport: 2.1 The Transport System in HumansDocument7 pagesChapter 2: Blood Circulation and Transport: 2.1 The Transport System in HumansChloe LianNo ratings yet
- GastroschisisDocument2 pagesGastroschisisCarlos Caipo CardosoNo ratings yet
- BIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Document9 pagesBIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Jv Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument25 pages1 Anatomy and PhysiologyMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To BetweenDocument6 pagesChapter 20 - Introduction To The Cardiovascular System: Away From To Betweentomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesAnaphy Cardiovascular SystemFraiza BirowaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartDocument12 pagesGrade 7 CH 4.05 The HeartMunmun AfnanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartNina Anne ParacadNo ratings yet
- BMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartDocument7 pagesBMED 66 Chapter 14 HeartBSMT 1-1, TAN, NICOLE SELINA L.No ratings yet
- Syok Hipovolemik EnglishDocument25 pagesSyok Hipovolemik Englishatmarida 123No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Sys Part 1Document10 pagesCardiovascular Sys Part 1LawrenceNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System Check UpDocument7 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Check UpKolea 2003No ratings yet
- Grade 9 L 6 Circulatory SystemDocument5 pagesGrade 9 L 6 Circulatory SystemJAYDEN JANSZNo ratings yet
- Human HeartDocument2 pagesHuman HeartriNo ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Ten Step TemplateDocument1 pageTen Step TemplateTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Works Cited - MISDocument1 pageWorks Cited - MISTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- The Value of Gold Vs Stock MarketDocument37 pagesThe Value of Gold Vs Stock MarketTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Devry Vs Phoenix Financial ComparisonDocument12 pagesDevry Vs Phoenix Financial ComparisonTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Kuehne BADM622Document16 pagesKuehne BADM622Tim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Typing Diacritical Marks On Your PCDocument1 pageTyping Diacritical Marks On Your PCTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- FINAL Stats ProjectDocument19 pagesFINAL Stats ProjectTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- American AutoDocument1 pageAmerican AutoTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Lab 13 Urine AnalysisDocument5 pagesLab 13 Urine AnalysisTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Ten Step TemplateDocument1 pageTen Step TemplateTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Kidneys and Metals QuestionsDocument2 pagesKidneys and Metals QuestionsTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Thick and Quick Large Granny SquareDocument3 pagesThick and Quick Large Granny SquareTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- How To Genetics ProblemsDocument15 pagesHow To Genetics Problemskylev100% (3)
- Karma Kagyu NgondroDocument8 pagesKarma Kagyu NgondroTim Kuehne67% (3)
- Karma Kagyu NgondroDocument8 pagesKarma Kagyu NgondroTim Kuehne67% (3)
- Respieratory Overview PDFDocument1 pageRespieratory Overview PDFTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Exam 1Document2 pagesExam 1Tim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Ripple Knit AfghanDocument3 pagesRipple Knit AfghanTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Amazing ShrugDocument5 pagesAmazing ShrugTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Positions PDFDocument1 pageAnatomical Positions PDFTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Typing Diacritical Marks On Your PCDocument1 pageTyping Diacritical Marks On Your PCTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Thick and Quick Granny SquaresDocument4 pagesThick and Quick Granny SquaresTim Kuehne100% (1)
- Celtic Strip AfghanDocument5 pagesCeltic Strip AfghanTim Kuehne100% (1)
- Cardiac PDFDocument3 pagesCardiac PDFTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- 8 31 13 PalabrasDocument1 page8 31 13 PalabrasTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Pattons Lace Triangle ShawDocument4 pagesPattons Lace Triangle ShawTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Practice WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDiffusion Practice WorksheetsTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Diffusion Practice WorksheetsDocument4 pagesDiffusion Practice WorksheetsTim KuehneNo ratings yet
- Spanish Words for Hugging, Hurrying and CoatsDocument1 pageSpanish Words for Hugging, Hurrying and CoatsTim KuehneNo ratings yet