Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solutions ch09
Uploaded by
api-239280915Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solutions ch09
Uploaded by
api-239280915Copyright:
Available Formats
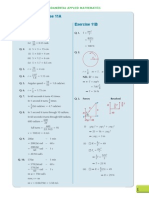
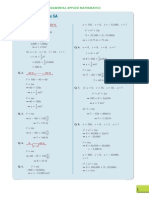
Chapter 9 Exercise 9A
Q. 1.
Q. 2.
Q. 3.
0.83 1,000 = 830 kg/m3
375
______
1,000
Q
Q. 9.
Weight = Vrg = (0.024)(1,000 g) = 24g N
= 0.375
(i) 1 m3 has mass 13.6 1,000,000
= 13,600,000 grammes
Q. 10.
Density = 13,600 kg/m3
(ii)
Q. 4.
Q. 5.
1,000
Q. 11.
= 13.6
Volume = 0.1 0.06 0.02
= 0.00012 m3
Mass
Density = _______
Volume
1.08
= ________ = 9,000 kg/m3
0.00012
9,000
Relative density = ______ = 9
1,000
980
1
___
14
1
(ii) V = __ ph(R2 + Rr + r2)
3
1
= __ p (6)(49 + 42 + 36)
3
= 254p cm3 = 0.000254p m3
Weight = Vrg = (0.000254p )(950)(g)
= 0.2413pg N
Mass
_______
(iii) Density =
Volume
1.026p + 0.2413p
__________________
=
0.001026p + 0.000254p
1.2673
= ________ = 990
0.00128
990
Specific gravity = ______ = 0.99
1,000
m3
Mass = Volume Density
1
= ___ 2,450 = 175 kg
14
Q. 6.
Q. 7.
Q. 8.
sv
60
60
0.95
40
38
100
98
sv
10
70
11
79
98
s = ____ = 0.98
100
79
s = ___ = 7.182
11
sv
100
100
0.9
0.9x
100 + x
100 + 0.9x
= 0.9625
100 + x
100 + 0.9x = 96.25 + 0.9625x
x = 60 ml
(i) Pressure = hrg = (2)(1,000)g
= 2,000g N/m2
(ii) Thrust = Pressure Area
= 2,000g (2)2 = 8,000g N
100 + 0.9x
__________
Exercise 9B
E
Q
Q. 1.
1
(i) V = __ ph(R2 + Rr + r2)
3
1
= __ p(18)(81 + 54 + 36)
3
= 1,026p cm3 = 0.001026p m3
Weight = Vrg = (0.001026p )(1,000)g
= 1.026pg N
Mass
Volume = _______
Density
70
____
Volume = p r2h = p (0.03)2 (0.1)
= 0.00009p m3
Weight = Vrg = (0.00009p )(800)g
= 0.072p g N
= 13,600 kg
13,600
_______
Volume = 0.4 0.3 0.2 = 0.024 m3
Weight = Vrg = (2)3(1,000)g
= 8,000g N
Q
Q. 2.
(i) Pressure = hrg = (0.11)(850)g
= 93.5g N/m2
(ii) Thrust = Pressure Area
= (93.5g)p (0.05)2
= 0.23375pg N
(iii) Weight = Vrg = p r2hrg
= p(0.05)2(0.11)(850)g
= 0.23375p g N
Q. 3.
Thrust = Pressure Area = (hrg)(pr2)
(b)
= (0.1)rg(p(0.2)2) = 0.00004prg
x
17
Weight = Vrg
1
= __ ph(R2 + Rr + r2)rg
3
1
__
= p(0.1){(0.05)2 + (0.05)(0.02)
3
+ (0.02)2}rg
17 x
p
Pressure at p = Pressure at q
x (850)g + (17 x)(13,600)g
= 17(1,000)g
= 0.00013ppg
The ratio is, therefore, 4 : 13
Q. 4.
x = 16.8 cm
(a)
Q
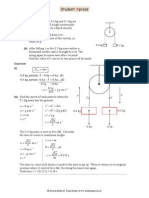
Q. 6. Pressure = hrg = (3)(1,000)g = 3,000g N/m2
Thrust = Pressure Area
8
p
= (3,000g)(2 2) = 12,000g N
1
(i) 2 2 h = 1 1 1 h = __ m
4
1
__
(1,000)(g) 250g N/m2
(ii) P = hrg =
4
(iii) T = P A = (250g)(4) = 1,000g N
()
Pressure at p = Pressure at q
Q
Q. 7.
h(1,000)g = 8(850)g
h = 6.8 cm
Difference = 8 6.8 = 1.2 cm
(b) Pressure under mercury = Pressure
under oil
(ii) P = hrg = (0.0225)(1,000)g
= 22.5g N/m2
h(950)g = 8(850)g
(iii) Thrust = P A = (22.5g)(p (16))
= 360p N
h = 7.16 cm
Q. 5.
Q
Q. 8.
(a)
17
q
4
(i) p R2h = __ pr3
3
4
p (16)h = __ p (27)
3
1
h = 2 __ cm = 0.0225 m
4
4
(i) pR2h = __ p r3
3
4
p(36)h = __ p (27)
3
h = 1 cm = 0.01 m
(ii) P = hrg = (0.01)(900)g = 9g N/m2
(iii) T = P A = (9g)(p (0.06)2)
= 0.0324p g N
Pressure at p = Pressure at q
h(13,600)g = 17(1,000)g
h = 1.25 cm
Difference = 17 1.25
= 15.75 cm
dyne _____________
105 Newtons
Q
Q. 9. 1 _____
=
= 0.1 N/m2
cm2
104 m2
Q. 10.
Q
(i)
Thrust = Pressure Area = (hrg)(pr2)
( )
22
= (2)(1,250)(9.8) ___ (1.4)2
7
= 150,920 N = 150.92 kN
M ______
750
3
(ii) Volume = __
r = 2,500 = 0.3 m
at x = Increase in depth
0.3
p r2x = 0.3 x = ___2
pr
Increase in pressure = hrg =
WI
50
= ___ 5 = ___ S = 10
S
S
WI
(50)
(ii) BL = SL ___ 4 = SL____ SL = 0.8
S
S
0.3
___
(1,250)g
pr2
(i) BH
Increase in thrust = P A
0.3
= ___2 (1,250)g(pr2)
pr
= 3,675 N = 3.675 kN
2O
(iii) In liquid, SL = 0.75
BL
Exercise 9C
Q. 1.
Apparent Wt.
Bouyancy = 12 8 = 4
W
12
B = __ 4 = __ S = 3
S
S
Q. 2.
50
Apparent Wt. = 50 BL
W
Apparent Wt. = 50 SL___I
S
35%
65%
(50)
Apparent Wt. = 50 0.75 ____
S
= 46.25 N
W = Vrg
( )
Q. 8.
Q
65
B = ____ V (1,000)g = 650Vg
100
Bouyancy in oil, BL = 80 64 = 16
But B = W r = 650 S = 0.65
Q. 3.
0.9, as in the last question
Q. 4.
B = 18 15 = 3
18
W
B = __ 3 = ___ S = 6
S
S
BL = 18 16 = 2
BL = SL Bw
2
2 = SL(3) SL = __
3
Q. 5.
BL = SLBW 16 = SL(20) SL = 0.8
Q. 9.
Q
(ii) W = rVg
BH
2O
( )
= Bouyancy in water
BL = Bouyancy in liquid
WI = Immersed weight
S = Specific gravity of object
SL = Specific gravity of liquid
5 = BH
50
4 = BL
2O
46
45
AIR
50
OIL
H2O
50
m3
( )
(iii) App. Wt. = Weight Bouyancy,
WI
B = ___
S
90pg
= 90pg _____
2.5
200
W
BL = SLBW = SL __ = 13.6 ____ = 160
17
S
Apparent weight = 200 160 = 40 N
Note:
250
= 90pg N
Apparent weight = 30 4.5 = 25.5 N
Q. 7.
9p
____
9p
= 2,500 ____ g
250
W 30
(i) B = __ = ___ = 5
6
S
Apparent weight = 30 5 = 25 N
( )
4
(i) V = __ pr3
3
4
= __ p(0.3)3
3
= 0.036p m3 OR
(ii) BL = SLBW = (0.9)(5) = 4.5
Q. 6.
Bouyancy in water, BW = 80 60 = 20
= 54pg N
Q
Q. 10.
pr2h
V = ____
3
r = 0.3, h = 0.7
22 (0.3)2
(i) V = ___ _____ (0.7)
7 3
33 3
____
V=
m OR V = 0.066 m3
500
(ii) W = rVg
( )
33
= 8,000 ____ 9.8
500
= 5,174.4 N
50
(iii)
BH
2O
WI 5174.4
= ___ = _______ = 646.6
8
S
Q
Q. 3.
(i)
0.1W
App. Wt. = Weight Bouyancy
= 5174.4 646.6
BL
= 4527.6 N
Q. 11.
0.9W
Let W = the weight of the body.
Let B = Bouyancy in water.
W1 = W B
( )
W where W = weight
BL = SLBW = SL __
S
of the immersed part.
BL = SLBW Bouyancy in liquid 1 = (0.8)B
W2 = W 0.8B
5W2 4W3 = 5(W 0.8B) 4(W 0.75B)
= W B = W1 QED
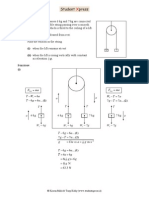
Exercise 9D
Q. 1.
3
__
3
of volume under water S = __
4
3
__
r = 1,000
4
= 750
0.9W
0.99W
BL = (1.1) _____ = ______
S
S
Since it is in equilibrium
0.1W + 0.9W = BL
0.99W
W = ______
S
S = 0.99
Similarily, W3 = W 0.75B
(ii) 0.99 of its mass will be below, as in
question 2.
Q.
Q 4.
3
Its specific gravity is __, as in question 1.
4
W = Vrg
Mg
= (0.1)(750)g
= 75g
75g
B=
= 100g
= ____
3
_
S
W
__
W = 20g
B=W+T
100g = 75g + T
T = 25g
Q. 2.
Let M = the mass of the glass
BL = SLBW
Its specific gravity is 0.8, as in question 1
( )
Let V = its volume, xV = volume under
the liquid
W
= sL __
S
W = Vrg
20g
= (0.8) ____
0.75
= V(800)g
( )
xV
1
= 21__ g
3
= 800Vg
B = Mg + 20g
1
21__g = Mg + 20g
3
1
M = 1__ kg
3
B = xV(1,200)g
= 1,200xVg
Since it is in equilibrium, W = B
800Vg = 1,200xVg
2
x = __
3
1
1
__ of its mass, or 33__%, is above the
3
3
surface.
Q
Q. 5.
B = 360 330 = 30
360
W
B = __ 30 = ____
S
S
S = 12. It is lead
Q. 6.
(iii) W = 12.5g, B = 4g
W=T+B
xV
T = 12.5 4 = 8.5g
= 83.3 N
Let V = its volume,
xV = volume under the sea.
Q. 9.
(i) V = (0.1)(0.2)(0.08)
= 0.0016 m3
B = weight of liquid displaced
= (xV)(1,030)g
(ii)
W = weight of the object
= V(900)g
a
w
Since B = W,
xV(1,030)g = V(900g)
x = 0.87
M = Vr
Answer: 87%
Q. 7.
1 = 0.0016r
r = 625
625
5
S = ______ = __
1,000 8
5
__
th of its length is submerged
8
5
Depth = __ 20 = 12.5 cm
8
V = (0.8)(0.6)(0.4) = 0.192 m3
B
W
Q. 10.
Q
B = 40 35 = 5
40
W
B = __ 5 = ___ S = 8
S
S
Q. 11.
Q
Total area = (80 60) + 2(80 40)
+ 2(60 40)
W = Vrg
= (0.192)(2,500)g = 480g
B = (0.192)(1,000)g = 192g
= 16,000 cm2
B+R=W
= 1.6 m2
192g + R = 480g
40
R = 288g = 2,822.4 N
60
Q. 8.
80
T
B
W
M
(i) V = __
r
12.5
= ______
2,500
= 0.005 m3
(ii) M = Vr
= 0.005(800)
= 4 kg
Volume = 1.6 0.0015
= 0.0024 m3
Weight = Vrg
= (0.0024)(8,000)g = 19.2g
Let X = the depth of the tank in the lake.
B = weight of liquid displaced
= (0.6 0.8 X)(1,000)g = 480Xg
B=W
480Xg = 19.2g
X = 0.04 m
= 4 cm
Q. 12.
Pressure at 5 cm = hpg
= (0.05)(900)g
= 45g
Pressure at 9.5 cm = (0.05)(900)g + (0.045)(1,000)g
= 90g
Pressure at 9.5 cm = Twice pressure at 5 cm
Pressure at 3 cm = (0.03)(900)g
= 27g
5 times pressure at 3 cm = 135g
Let x = the depth (in metres)
0.05
Pressure = (0.05)(900)g + (x 0.05)(1,000)g = 135g
45g + 1,000g 50g = 135g
x = 0.14 m
= 14 cm
Q. 13.
Let A = Atmospheric pressure
Q. 15.
Q
(i)
Pressure at 14 m = 2 Pressure at 2 m
A = 10,000g
= 7,200 p g N
= 98,000 N/m2
(i)
(ii)
Thrust = P A
( 3 p(1) )(1,000)g
= (6,300g)(p(2)2)
= 25,200 p g N
2,000
= ______pg N
3
(ii)
Pressure = hrg
= (7)(900)g = 6,300g N
Bouyancy = weight of liquid
displaced
2
__
1
= __ p(2)2(6) (900)g
3
A + 14(1,000)g = 2(A + 2(1,000)g)
Q. 14.
Bouyancy = weight of displaced
liquid
(iii)
Pressure = hrg
B = Fu Fd
7,200 p g = 25,200 p g Fd
= (2)(1,000)g
Fd = 18,000 p g N
= 2,000g
Thrust = P A
Q.
Q 16.
= (2,000g)(p(1)2)
h
= 2,000pg N
(iii)
B = Fu Fd
2,000
______p g = 2,000pg Fd
3
4,000
Fd = ______ pg N
3
1
Since pr2 = __(pR2), R = 2r
4
1
Volume = __ ph{(2r)2 + (2r)r + r2}
3
7
= __ phr2
3
7
Weight = Vrg = __ phr2rg
3
(ii)
Pressure at base = hrg
Thrust = P A = (hrg)(p(2r)2)
= 4 p hr2rg
Ratio, Thrust : Weight
7
= 4phr2rg : __phr2rg
3
= 12 : 7
Q. 17.
40.01 Oil
Water 40.64
0.63 Mercury
p
()
Pressure at p = Pressure at q
1
(i) P = hrg = __ (1,000)g = 500g N/m2
2
(40.64)(1,000)g = (40.01)rg
(ii) T = P A
+ (0.63)(13,600)g
( (8 ) )
12
__
= (500g) p
r = 801.6 kg/m3
(iii)
125
= ____ p g N
16
Water 40.64
(iii) W = Vrg
h Oil
( ){( 21 ) + ( 21 )( 18 ) + ( 18 ) } (1,000)g
1 1
= __p __
3 2
__ 2
__ __
__ 2
875
= ____pg
16
Weight 7
_______ = __
T
1
Q. 18.
3
Relative density of the wood = __ = 0.75
4
50
M ____
1 3
__
___
=
Volume = r =
m
750 15
(0.64)(1,000g) = h(801.6)g
h = 50.7 cm
= 507 mm
Q. 20.
Q
3r
10g
(i)
50g
Thrust = P A = rrg(pr2) = pr3rg N
(ii)
B = 50g + 10g = 60g = Weight of liquid
1
60g = ___ rg
15
r = 60 15 = 900
Q. 19.
(i) M = rV
= 13,600
B = Vrg = (_13 pr2(3r))rg = pr3rg
B = Fu Fd
pr3rg = Fu pr3rg
( )
s = 0.9
Pressure = hrg = rrg
Fu = 2pr3rg N
Q. 21.
Q
B1
( 2 ) = 6,800 kg
1
__
= 6.8 tonnes
B2
Water
Mercury
W = Vrg = (v1 + v2)(7,800)g
= 7,800(v1 + v2)g
B1 = v1(1,000)g = 1,000v1g
B2 = v2(13,600)g = 13,600v2g
Since the body is in equilibrium
B1 + B2 = W
Q. 3.
Q
B2
1,000v1g + 13,600v2g = 7,800(v1 + v2)g
T1
3S
7W
T1 + T2 = ____
30
2 (Taking moments about the lower end)
3
9W
W
W
__
(1) + ____ (5) = __(1) + __W(5) + T2(8)
4
4
3
10
5W
T2 = ____
48
7W 5W
T1 = ____ ____
30
48
31W
= _____
240
3
1
W 9W
W 3
1 __ + ____ = T1 + __ + __W + T2
4
4
3
10
2W
()
( )
2 Taking moments about p:
2W
2
____
(3) = F(5) F = __W
5
3
W
2
__
__
=W
(ii) 1 W +
5
3S
W 3
__ = __W
3S 5
5
S = __
9
(i)
3
_
4W
9W
W
BL = SLBW = SL __ B2 = (0.9) ___
= ____
3
_
10
S
W
1 F + ___ = W
3s
Q. 2.
Water
4
1
__
W
(i)
Oil
4
W
W
BW = __ B1 = __
= __
3
_
3
S
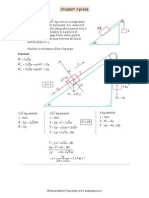
Exercise 9E
Q. 1.
3
W
4
B1
5,800v2 = 6,800v1
v1 ___
58 ___
29
__
v2 = 68 = 34
T2
Q. 4.
Q
F
x
1
2
1
2
B
2 p
(1 x) W
2
xW
Let W = the weight of the rod.
W
2S
t
Water
2
1
_W
(ii) 1 T + _ = W
2S
2 (Taking moments about t)
3
1
(2) = T(4) T = __W B = __W
4
4
1
W
__
__
(iii) 1 W +
=W
4
2S
W 3
__ = __W
2S 4
2
S = __
3
W
__
2
Let x = the length of the submerged part.
25xW
W
xW
BW = __ B = ____ = _____
9
0.36
S
25xW
1 _____ + F = W
9
2 (Taking moments about p).
x
1x
x
(1 x)W __ + _____ = F __ + 1 x
2
2
2
1
x
(1 x)W __ = F 1 __
2
2
(1 x)W
F = ________
2x
) (
() (
Putting this result into equation 1 gives:
(1 x)W
25xW ________
_____
+
=W
9
(2 x)
9(2 x)
... Multiply by _______
W
25x(2 x) + 9(1 x) = 9(2 x)
25x2 50x + 9 = 0
(5x 1)(5x 9) = 0
9
1
x = __ m (x = __ m is too long)
5
5
Answer: 20 cm is submerged.
Q. 5.
B2
B1
T1
1
BW =
W
__
S
B1 =
Oil
Water
_
1
2W
___
W
= ___
12
6
( )
_
1
2W
W
V = 0.8 ____
BL = SLBW = SL __
= ___
s
6
15
W
W
T1 + ___ + ___ + T2 = W
12 15
51
T1 + T2 = ___ W
60
( )
(Taking moments about the lower end).
W
W
W
1 + ___(3) + T2(4) = __(1) + __(3)
2
2
15
103
T2 = ____W
240
51
103
T1 = ___W ____W
240
60
101
____
W
=
240
(i)
50
B
15
35
p
7
W
10
20
x
15
q
3W
10
Let x and y be the horizontal and
vertical components of the reaction at p,
x = 0 since no other forces act along
the vertical. Therefore, the reaction at p
is vertical. We shall henceforth call it R.
W
(ii) BW = __
S
T2
21
Q. 6.
B=
__
3
W
10
____
3W
= ____
10s
3W
1 ___ + R = W
10S
2 (Taking moments about q)
7
___
W(50) = R(65)
10
7
R = ___W
13
Putting this into equation 1 gives:
3W ___
7
___
+
W=W
10S 13
3W 6W
___ = ____
13
10S
39
___
S=
60
13
= ___
20
You might also like
- Newton 2008Document3 pagesNewton 2008api-239280915No ratings yet
- 22 April 2013 09:33: 3. Projectiles Page 1Document3 pages22 April 2013 09:33: 3. Projectiles Page 1api-239280915No ratings yet
- 26 March 2014 13:41: 3. Projectiles Page 1Document4 pages26 March 2014 13:41: 3. Projectiles Page 1api-239280915No ratings yet
- 4 Collisions Page 1Document5 pages4 Collisions Page 1api-239280915No ratings yet
- 27 April 2015 12:58: 3. Projectiles Page 1Document4 pages27 April 2015 12:58: 3. Projectiles Page 1api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2010Document3 pagesNewton 2010api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2007Document3 pagesNewton 2007api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2006Document3 pagesNewton 2006api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2009Document3 pagesNewton 2009api-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch11Document10 pagesSolutions ch11api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2012Document3 pagesNewton 2012api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2011Document3 pagesNewton 2011api-239280915No ratings yet
- Newton 2013Document3 pagesNewton 2013api-239280915100% (1)
- Solutions ch08Document34 pagesSolutions ch08api-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch14Document17 pagesSolutions ch14api-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch05Document28 pagesSolutions ch05api-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch13Document15 pagesSolutions ch13api-239280915No ratings yet
- 2011 Ms Lc020alp000evDocument28 pages2011 Ms Lc020alp000evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch10Document14 pagesSolutions ch10api-239280915No ratings yet
- 2007 LC 020 Alpo 00 EvDocument30 pages2007 LC 020 Alpo 00 Evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- 2006 LC 020 Alpo 00 EvDocument25 pages2006 LC 020 Alpo 00 Evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch01Document5 pagesSolutions ch01api-239280915No ratings yet
- 2010 LC 020 Alp 000 EvDocument28 pages2010 LC 020 Alp 000 Evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- 2008 LC 020 Alp 000 EvDocument30 pages2008 LC 020 Alp 000 Evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- 2012 Ms Lc020alp000evDocument28 pages2012 Ms Lc020alp000evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- 2009 LC 020 Alp 000 EvDocument28 pages2009 LC 020 Alp 000 Evapi-239280915No ratings yet
- 2013 Ms AppmDocument28 pages2013 Ms Appmapi-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch07Document22 pagesSolutions ch07api-239280915No ratings yet
- Solutions ch06Document10 pagesSolutions ch06api-239280915No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- CA Ashish Dewani - Resume-1Document2 pagesCA Ashish Dewani - Resume-1Payal JainNo ratings yet
- LTE Interview QuestionsDocument10 pagesLTE Interview QuestionsMahesh Pratap100% (1)
- List of SDAsDocument4 pagesList of SDAsAthouba SagolsemNo ratings yet
- Caring Seedlings TLE Weekly PlanDocument3 pagesCaring Seedlings TLE Weekly PlanMarjorie RaymundoNo ratings yet
- ZXJ 10 SPCDocument7 pagesZXJ 10 SPCMuhammad Yaseen100% (1)
- DVOR Principle 코이카 양식Document71 pagesDVOR Principle 코이카 양식Undral Batbayar100% (1)
- Finimpianti Power EngDocument2 pagesFinimpianti Power EngJosip GrlicaNo ratings yet
- Cropprotectionequipment-Rocker Sprayer - Specification (: Indian StandardDocument9 pagesCropprotectionequipment-Rocker Sprayer - Specification (: Indian Standardgini associatesNo ratings yet
- Mini-Com Cat6E - ®TX6 ™ PLUS UTP Coupler ModulesDocument2 pagesMini-Com Cat6E - ®TX6 ™ PLUS UTP Coupler Moduleslejlas77No ratings yet
- Chlor Rid SlidesDocument47 pagesChlor Rid Slidesmohammed goudaNo ratings yet
- The Arcane Formulas or Mental AlchemyDocument121 pagesThe Arcane Formulas or Mental AlchemyTim Boire100% (1)
- Formulating and Solving LPs Using Excel SolverDocument8 pagesFormulating and Solving LPs Using Excel SolverAaron MartinNo ratings yet
- Adiabatic Production of Acetic AnhydrideDocument7 pagesAdiabatic Production of Acetic AnhydrideSunilParjapatiNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: High-Speed DiodesDocument7 pagesData Sheet: High-Speed DiodesZoltán ÁgostonNo ratings yet
- CA 1 - Đề thi AV5 - CLC - Made - efDocument5 pagesCA 1 - Đề thi AV5 - CLC - Made - efQuang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Explosive Ordnance DisposalDocument13 pagesExplosive Ordnance DisposalZelwisNo ratings yet
- Hardware Devices Used in Virtual Reality TechnologiesDocument6 pagesHardware Devices Used in Virtual Reality TechnologiesTheMoon LightNo ratings yet
- TM-1870 AVEVA Everything3D - (2.1) Draw Administration (CN)Document124 pagesTM-1870 AVEVA Everything3D - (2.1) Draw Administration (CN)yuehui niuNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Document5 pagesAn Introduction To Pascal Programming MOD 2010Johnas DalusongNo ratings yet
- Grupo Stoncor Description - Stonhard Carboline Fibergrate PDFDocument22 pagesGrupo Stoncor Description - Stonhard Carboline Fibergrate PDFAndres OsorioNo ratings yet
- Marginal Field Development Concepts (Compatibility Mode)Document17 pagesMarginal Field Development Concepts (Compatibility Mode)nallay1705100% (1)
- Ethics in ResearchDocument21 pagesEthics in Researchmukku_raviNo ratings yet
- PC 4 Product List 2019 - Pc4Document28 pagesPC 4 Product List 2019 - Pc4ShNo ratings yet
- Texas Final LeadsDocument36 pagesTexas Final Leadsabdullahmohammed4460No ratings yet
- Methanol Technical Data Sheet FactsDocument1 pageMethanol Technical Data Sheet FactsmkgmotleyNo ratings yet
- Schippers and Bendrup - Ethnomusicology Ecology and SustainabilityDocument12 pagesSchippers and Bendrup - Ethnomusicology Ecology and SustainabilityLuca GambirasioNo ratings yet
- Configure NTP, OSPF, logging and SSH on routers R1, R2 and R3Document2 pagesConfigure NTP, OSPF, logging and SSH on routers R1, R2 and R3Lars Rembrandt50% (2)
- Techniques-Of-Attitude-Scale-Construction FullDocument344 pagesTechniques-Of-Attitude-Scale-Construction FullLuthfi fharuq Al Fairuz67% (3)
- Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin On Socket Healing After Mandibular Third Molar ExtractionsDocument10 pagesEfficacy of Platelet-Rich Fibrin On Socket Healing After Mandibular Third Molar Extractionsxiaoxin zhangNo ratings yet
- Dayal Bagh: Spircon 2013: Book of AbstractsDocument202 pagesDayal Bagh: Spircon 2013: Book of AbstractsSant Mat100% (2)