Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment Name-Study of Phase Shift Oscillator
Uploaded by
mrana_56Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment Name-Study of Phase Shift Oscillator
Uploaded by
mrana_56Copyright:
Available Formats
American International University Bangladesh (AIUB) Faculty of Engineering
Analog Electronics 2 (LAB)
Experiment # 08 Experiment name: Study of Phase Shift Oscillator
Objective: A typical R-C phase shift oscillator will be constructed and studied in this experiment. The theoretical frequencies of the oscillation are: 6 For R-C Oscillator 2RC
1 2RC
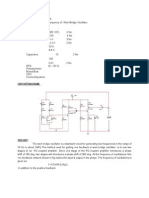
Circuit Diagram:
1 6 4( RC R)
For C-R Oscillator
6V
RC POT 100 K
2.7 K
10 uf + 1K R 1K R 1K R
C828
Vin, Channel 1
R2
3K
RE 2.7 K 100 uf
C 0.01 uf
C 0.01 uf
C 0.01 uf
Equipment required: 1. 2. 3. 4. Transistor (C828) DC Power Supply Oscilloscope Resistors a. 1 K 3 b. 2.7 K 2 c. 3 K 1 d. 33 K 1 e. 100 K (POT)1 f. 100 1
Vout, Channel 2
5. Capacitors a. 0.01 F b. 10 F
3 3
Procedure: 1. Connect the circuit as shown in the figure for R-C phase shift oscillator. 2. Vary the 100K POT to have the undistorted sine wave at the output terminal. 3. Determine the frequency of output and verify it with the theoretical frequency. 4. Determine the phase shift of the input and output signal. To so this, connect both the channels and operate the oscilloscope in XY mode. 5. Reconnect the circuit for C-R oscillator by interchanging the R and C elements. 6. Repeat steps 2, 3 and 4. Report: 1. Why R-C oscillator is called phase shift oscillator? 2. Why there is discrepancy between the observed and theoretical frequency? 3. How the amplitude and the frequency of oscillator ca be changed? 4. What type of feedback is used in the oscillator circuit? 5. What is frequency range of R-C oscillator? 6. Derive the above two equations.
You might also like
- Wien Bridge Oscillator Using OpampDocument4 pagesWien Bridge Oscillator Using OpampVishesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Experiment Name-Study of Wein Bridge OscillatorDocument2 pagesExperiment Name-Study of Wein Bridge Oscillatormrana_56No ratings yet
- LIC Manual NewDocument84 pagesLIC Manual NewVandhana PramodhanNo ratings yet
- Diode ApplicationsDocument46 pagesDiode ApplicationsLarry June EscalaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 04 Experiment Name-QPSK Modulation & Demodulation Aim Equipments NeededDocument10 pagesExperiment No. 04 Experiment Name-QPSK Modulation & Demodulation Aim Equipments NeededmuskanNo ratings yet
- Voltage-Series Feedback Amplifier Frequency ResponseDocument41 pagesVoltage-Series Feedback Amplifier Frequency ResponsevineethaNo ratings yet
- EE309 Notes 07 PDFDocument4 pagesEE309 Notes 07 PDFbals123456100% (1)
- Inverting Amplifiers Lab ReportDocument9 pagesInverting Amplifiers Lab ReportRaihan JannatiNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3-2marks-FET PDFDocument9 pagesUNIT 3-2marks-FET PDFpriyanka236No ratings yet
- RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument3 pagesRC Phase Shift Oscillatoreseses100% (1)
- Expt # 6 Two Port Network - Z ParametersDocument10 pagesExpt # 6 Two Port Network - Z ParametersRohanNo ratings yet
- Transient Response of RC CircuitDocument5 pagesTransient Response of RC CircuitJayesh Ruikar100% (1)
- Design and Simulate Sample and Hold CircuitDocument8 pagesDesign and Simulate Sample and Hold CircuitRen BurnettNo ratings yet
- 47-Wavelet Based Power Quality Disturbances Analysis of BLDC Motor Drive PDFDocument10 pages47-Wavelet Based Power Quality Disturbances Analysis of BLDC Motor Drive PDFveerannaNo ratings yet
- Triangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsDocument6 pagesTriangular Wave Generator Using Op Amp - WaveformsNagendrababu VasaNo ratings yet
- EDC 2 Marks Q ADocument16 pagesEDC 2 Marks Q Akunaraj100% (3)
- Diode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabDocument4 pagesDiode Valve Effect: Electrical and Electronics LabLare ONo ratings yet
- Pulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFDocument15 pagesPulse and Digital Circuits (PDC) QB PDFlakshmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Duality Concept and Circuit DualityDocument16 pagesIntroduction to Duality Concept and Circuit DualityRohanNo ratings yet
- Finally Power DiodeDocument8 pagesFinally Power DiodeAndrei50% (2)
- Oscillator PDFDocument4 pagesOscillator PDFJoshua DuffyNo ratings yet
- ADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFDocument21 pagesADE Lab Manual - Analog Part PDFJk RinkuNo ratings yet
- EXPT - 02 - Study of Single Stage BJT AmplifierxDocument5 pagesEXPT - 02 - Study of Single Stage BJT AmplifierxPrakash Narkhede100% (1)
- Ee 435 2Document43 pagesEe 435 2EdamEdamNo ratings yet
- Multivibrator Circuit AnalysisDocument41 pagesMultivibrator Circuit AnalysisSanjana PulapaNo ratings yet
- Scheme Eee Unit3 QBDocument35 pagesScheme Eee Unit3 QBMaaz S100% (2)
- LIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsDocument4 pagesLIC Lecture 3-Current Sources As Active Loads and Voltage Sources MaterialsMadhavan SamNo ratings yet
- 08-Com101 AMDocument11 pages08-Com101 AMHồng HoanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices Experiment 4Document13 pagesElectronic Devices Experiment 4ArvinALNo ratings yet
- PE Lecture Notes KTU 2022 1-8-22Document99 pagesPE Lecture Notes KTU 2022 1-8-22meenujataj469481100% (1)
- Linear Wave Shaping-Integrator and DifferentiatorDocument5 pagesLinear Wave Shaping-Integrator and DifferentiatorManjot Kaur0% (1)
- Chapter 2 - OscillatorDocument60 pagesChapter 2 - OscillatorNURUL NADHIRAH ROSDINo ratings yet
- Electrical Circuit Lab ManualDocument38 pagesElectrical Circuit Lab Manualecessec67% (3)
- Unit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveDocument12 pagesUnit-3::Half Wave Rectifier, Ripple Factor, Full WaveHemant TulsaniNo ratings yet
- Ec8361-Adc Lab ManualDocument118 pagesEc8361-Adc Lab ManualmuminthajNo ratings yet
- EDC Question BankDocument13 pagesEDC Question BankvenzkrishNo ratings yet
- Energy MeterDocument11 pagesEnergy MeterRushab SirsatNo ratings yet
- 8051 CH2Document89 pages8051 CH2Amardeep PotdarNo ratings yet
- AC DC Analysis BJT Diffrential Amp PDFDocument8 pagesAC DC Analysis BJT Diffrential Amp PDFtanishk jainNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication PracticalDocument35 pagesOptical Communication PracticalShahid Farooqi0% (1)
- To Make A DC Switching Circuit Using SCR'sDocument2 pagesTo Make A DC Switching Circuit Using SCR'sH Aries OñaNo ratings yet
- MINIPROJECTHARTLEYOSCILLATORDocument15 pagesMINIPROJECTHARTLEYOSCILLATORPramod SultaneNo ratings yet
- Signal Conditioning CircuitsDocument115 pagesSignal Conditioning CircuitsAmmad Ilyas100% (1)
- IC 741 Op-Amp Tutorial and CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesIC 741 Op-Amp Tutorial and CharacteristicsBenNo ratings yet
- Twin T NetworkDocument2 pagesTwin T NetworkVijayalakshmi PrakashNo ratings yet
- EC8351-Electronic Circuits-I PDFDocument21 pagesEC8351-Electronic Circuits-I PDFVish NUNo ratings yet
- DC - Ac Inv.Document82 pagesDC - Ac Inv.Jegadeeswari GNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits SyllabusDocument5 pagesAnalog Circuits SyllabusVilayil jestinNo ratings yet
- 15ecl48 VTU Raghudathesh RC Wein Bridge OscillatorsDocument7 pages15ecl48 VTU Raghudathesh RC Wein Bridge OscillatorsraghudatheshgpNo ratings yet
- BS Lab ManualDocument76 pagesBS Lab ManualWasim100% (1)
- CMOS Amplifiers - Problems PDFDocument20 pagesCMOS Amplifiers - Problems PDFAnurag AnandNo ratings yet
- Op-Amps As Ac Amplifers: Capacitor-Coupled Voltage FollowerDocument7 pagesOp-Amps As Ac Amplifers: Capacitor-Coupled Voltage FollowerNisha Kotyan G RNo ratings yet
- Measure and Design a RC Phase Shift OscillatorDocument4 pagesMeasure and Design a RC Phase Shift OscillatorNA NANo ratings yet
- 6 RC Phase ShiftDocument6 pages6 RC Phase ShiftengineerluvNo ratings yet
- Expt. 6 EEE 214: Oscillator C - R For RC 2 6 Oscillator R - C For R) / 4 (R 6 1 RC 2 1Document1 pageExpt. 6 EEE 214: Oscillator C - R For RC 2 6 Oscillator R - C For R) / 4 (R 6 1 RC 2 1sabitavabiNo ratings yet
- Wien Bridge OscillatorDocument12 pagesWien Bridge OscillatorARIFINNo ratings yet
- Wein Bridge Oscillator FrequencyDocument6 pagesWein Bridge Oscillator Frequencyinspectornaresh100% (1)
- Analog Communication Lab ManualDocument60 pagesAnalog Communication Lab Manualjsingh19No ratings yet
- Water PurificationDocument14 pagesWater Purificationmrana_56No ratings yet
- How The Train TurnsDocument4 pagesHow The Train Turnsmrana_56No ratings yet
- How Water Filters WorkDocument4 pagesHow Water Filters Workmrana_56No ratings yet
- Bullets Working PrincipleDocument4 pagesBullets Working Principlemrana_56No ratings yet
- Dynamics of FlightDocument3 pagesDynamics of Flightmrana_56No ratings yet
- Jet Engines: What Is A Jet Engine?Document4 pagesJet Engines: What Is A Jet Engine?mrana_56100% (1)
- How Helicopter Works How Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter WorksDocument11 pagesHow Helicopter Works How Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Workshow Helicopter Worksmrana_56No ratings yet
- Why Digital?Document16 pagesWhy Digital?mrana_56No ratings yet
- Communication Systems - Telephone SystemDocument15 pagesCommunication Systems - Telephone Systemmrana_56100% (1)
- Information Source and SignalDocument61 pagesInformation Source and Signalmrana_56No ratings yet
- 4plasma DisplayDocument8 pages4plasma Displaymrana_56No ratings yet
- Cordless TelephoneDocument5 pagesCordless Telephonemrana_56No ratings yet
- Airplanes Airplanes Airplanes Airplanes AirplanesDocument5 pagesAirplanes Airplanes Airplanes Airplanes Airplanesmrana_56No ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Duplex (Telecommunications)Document4 pagesDuplex (Telecommunications)mrana_56100% (1)
- TV CameraDocument9 pagesTV Cameramrana_56No ratings yet
- Dual Tone Multi Frequency SignalingDocument4 pagesDual Tone Multi Frequency Signalingmrana_56No ratings yet
- TelephonyDocument32 pagesTelephonyJoseph Velez CabiloganNo ratings yet
- Communications SatelliteDocument9 pagesCommunications Satellitemrana_56No ratings yet
- Telephone ExchangeDocument3 pagesTelephone Exchangemrana_56No ratings yet
- 1 1 Traditional TelephonyDocument13 pages1 1 Traditional TelephonyBeOne DwiNo ratings yet
- Gate+any Written+any Viva Syllabus For ECE and EEDocument10 pagesGate+any Written+any Viva Syllabus For ECE and EEmrana_56No ratings yet
- Wirless NetworksDocument44 pagesWirless Networksmrana_56No ratings yet
- How Telephones Work - An OverviewDocument3 pagesHow Telephones Work - An Overviewmrana_56No ratings yet
- PhotovoltaicsDocument30 pagesPhotovoltaicsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Multimedia CommunicationsDocument7 pagesMultimedia Communicationsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Optical Components for Communication SystemsDocument105 pagesOptical Components for Communication Systemsmrana_56No ratings yet
- Isometric and Orthographic ProjectionDocument13 pagesIsometric and Orthographic Projectionmrana_56No ratings yet
- Recommended Books For GATE ECEDocument2 pagesRecommended Books For GATE ECEmrana_56No ratings yet
- Polarization of DielectricsDocument9 pagesPolarization of Dielectricsmrana_56No ratings yet