Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ir 2101
Uploaded by
Rachel RowlandOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ir 2101
Uploaded by
Rachel RowlandCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Sheet No.
PD60043-N
Typical Connection
Features
Floating channel designed for bootstrap operation
Fully operational to +600V
Tolerant to negative transient voltage
dV/dt immune
Gate drive supply range from 10 to 20V
Undervoltage lockout
3.3V, 5V, and 15V logic input compatible
Matched propagation delay for both channels
Outputs in phase with inputs (IR2101) or out of
phase with inputs (IR2102)
Description
The IR2101(S)/IR2102(S) are high voltage, high
speed power MOSFET and IGBT drivers with inde-
pendent high and low side referenced output chan-
nels. Proprietary HVIC and latch immune CMOS
technologies enable ruggedized monolithic con-
struction. The logic input is compatible with stan-
dard CMOS or LSTTL output, down to 3.3V logic. The
output drivers feature a high pulse current buffer
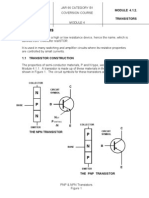
HIGH AND LOW SIDE DRIVER
Packages
Product Summary
V
OFFSET
600V max.
I
O
+/- 130 mA / 270 mA
V
OUT
10 - 20V
t
on/off
(typ.) 160 & 150 ns
Delay Matching 50 ns
IR2101
IR2102
IR2101
(
S
)
IR2102
(
S
)
8 Lead SOIC
8 Lead PDIP
stage designed for minimum driver cross-conduction. The floating channel can be used to drive an N-channel
power MOSFET or IGBT in the high side configuration which operates up to 600 volts.
www.irf.com 1
V
CC
V
B
V
S
HO
LO COM
HIN
LIN LIN
HIN
up to 600V
TO
LOAD
V
CC
V
CC
V
B
V
S
HO
LO COM
HIN
LIN LIN
HIN
up to 600V
TO
LOAD
V
CC
(Refer to Lead Assignments for correct pin
configuration). This/These diagram(s) show
electrical connections only. Please refer to
our Application Notes and DesignTips for
proper circuit board layout.
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
2 www.irf.com
Symbol Definition Min. Max. Units
V
B
High side floating supply voltage -0.3 625
V
S
High side floating supply offset voltage V
B
- 25 V
B
+ 0.3
V
HO
High side floating output voltage V
S
- 0.3 V
B
+ 0.3
V
CC
Low side and logic fixed supply voltage -0.3 25
V
LO
Low side output voltage -0.3 V
CC
+ 0.3
V
IN
Logic input voltage (HIN & LIN) -0.3 V
CC
+ 0.3
dV
S
/dt Allowable offset supply voltage transient 50 V/ns
P
D
Package power dissipation @ T
A
+25C (8 lead PDIP) 1.0
(8 lead SOIC) 0.625
Rth
JA
Thermal resistance, junction to ambient (8 lead PDIP) 125
(8 lead SOIC) 200
T
J
Junction temperature 150
T
S
Storage temperature -55 150
T
L
Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds) 300
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings indicate sustained limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. All voltage param-
eters are absolute voltages referenced to COM. The thermal resistance and power dissipation ratings are measured
under board mounted and still air conditions.
W
C/W
V
C
Symbol Definition Min. Max. Units
V
B
High side floating supply absolute voltage V
S
+ 10 V
S
+ 20
V
S
High side floating supply offset voltage Note 1 600
V
HO
High side floating output voltage V
S
V
B
V
CC
Low side and logic fixed supply voltage 10 20
V
LO
Low side output voltage 0 V
CC
V
IN
Logic input voltage (HIN & LIN) (IR2101) & (HIN & LIN) (IR2102) 0 V
CC
T
A
Ambient temperature -40 125
Note 1: Logic operational for V
S
of -5 to +600V. Logic state held for V
S
of -5V to -V
BS
. (Please refer to the Design Tip
DT97-3 for more details).
Recommended Operating Conditions
The input/output logic timing diagram is shown in figure 1. For proper operation the device should be used within the
recommended conditions. The V
S
offset rating is tested with all supplies biased at 15V differential.
C
V
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
www.irf.com 3
Symbol Definition Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
V
IH
Logic 1 input voltage (IR2101)
Logic 0 input voltage (IR2102)
V
IL
Logic 0 input voltage (IR2101)
Logic 1input voltage (IR2102)
V
OH
High level output voltage, V
BIAS
- V
O
100 I
O
= 0A
V
OL
Low level output voltage, V
O
100 I
O
= 0A
I
LK
Offset supply leakage current 50 V
B
= V
S
= 600V
I
QBS
Quiescent V
BS
supply current 30 55 V
IN
= 0V or 5V
I
QCC
Quiescent V
CC
supply current 150 270 V
IN
= 0V or 5V
I
IN+
Logic 1 input bias current
I
IN-
Logic 0 input bias current
V
CCUV+
V
CC
supply undervoltage positive going 8 8.9 9.8
threshold
V
CCUV-
V
CC
supply undervoltage negative going 7.4 8.2 9
threshold
I
O+
Output high short circuit pulsed current 130 210 V
O
= 0V
V
IN
= Logic 1
PW 10 s
I
O-
Output low short circuit pulsed current 270 360 V
O
= 15V
V
IN
= Logic 0
PW 10 s
Symbol Definition Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
t
on
Turn-on propagation delay 160 220 V
S
= 0V
t
off
Turn-off propagation delay 150 220 V
S
= 600V
t
r
Turn-on rise time 100 170
t
f
Turn-off fall time 50 90
MT Delay matching, HS & LS turn-on/off 50
Static Electrical Characteristics
V
BIAS
(V
CC
, V
BS
) = 15V and T
A
= 25C unless otherwise specified. The V
IN
, V
TH
and I
IN
parameters are referenced to
COM. The V
O
and I
O
parameters are referenced to COM and are applicable to the respective output leads: HO or LO.
Dynamic Electrical Characteristics
V
BIAS
(V
CC
, V
BS
) = 15V, C
L
= 1000 pF and T
A
= 25C unless otherwise specified.
V
mA
3 V
CC
= 10V to 20V
V
0.8 V
CC
= 10V to 20V
mV
A
3 10
1
V
IN
= 5V (IR2101)
V
IN
= 5V (IR2102)
V
IN
= 0V (IR2101)
V
IN
= 0V (IR2102)
ns
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
4 www.irf.com
Functional Block Diagram
PULSE
GEN
HIN
UV
DETECT
LIN
COM
HO
V
S
V
CC
LO
V
B
R
Q
S
PULSE
FILTER
HV
LEVEL
SHIFT
IR2101
IR2102
PULSE
GEN
HIN
UV
DETECT
LIN
COM
HO
V
S
V
CC
LO
V
B
R
Q
S
PULSE
FILTER
HV
LEVEL
SHIFT
Vcc
Vcc
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
www.irf.com 5
Lead Definitions
Symbol Description
HIN Logic input for high side gate driver output (HO), in phase (IR2101)
HIN Logic input for high side gate driver output (HO), out of phase (IR2102)
LIN Logic input for low side gate driver output (LO), in phase (IR2101)
LIN Logic input for low side gate driver output (LO), out of phase (IR2102)
V
B
High side floating supply
HO High side gate drive output
V
S
High side floating supply return
V
CC
Low side and logic fixed supply
LO Low side gate drive output
COM Low side return
Lead Assignments
8 Lead PDIP 8 Lead SOIC
IR2101 IR2101S
8 Lead PDIP 8 Lead SOIC
IR2102 IR2102S
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
6 www.irf.com
Figure 2. Switching Time Waveform Definitions
HIN
LIN
t
r
t
on
t
f
t
off
HO
LO
50% 50%
90% 90%
10% 10%
HIN
LIN
50% 50%
Figure 1. Input/Output Timing Diagram
HIN
LIN
HO
LO
HIN
LIN
Figure 3. Delay Matching Waveform Definitions
HIN
LIN
HO
50% 50%
10%
LO
90%
MT
HO LO
MT
HIN
LIN
50% 50%
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
www.irf.com 7
Figure 6A. Turn-On Time vs Temperature Figure 6B. Turn-On Time vs Supply Voltage
Figure 7A. Turn-Off Time vs Temperature
Figure 7B. Turn-Off Time vs Supply Voltage
Temperature (C)
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Temperature (C)
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
0
100
200
300
400
500
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
T
u
r
n
-
O
n
D
e
l
a
y
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
Max.
Typ.
0
100
200
300
400
500
10 12 14 16 18 20
T
u
r
n
-
O
n
D
e
l
a
y
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
Max.
Typ.
0
100
200
300
400
500
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
Typ.
T
u
r
n
-
O
f
f
D
e
l
a
y
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
10 12 14 16 18 20
Max.
Typ.
T
u
r
n
-
O
f
f
D
e
l
a
y
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
T
u
r
n
-
O
n
D
e
l
a
y
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
Input Voltage (V)
Figure 6C. Turn-On Time vs Input Voltage
Figure 7C. Turn-Off Time vs Input Voltage
0
100
200
300
400
500
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20
T
u
r
n
-
O
f
f
D
e
l
a
y
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
Input Voltage (V)
Max.
Typ.
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
8 www.irf.com
Figure 10A. Turn-Off Fall Time vs Temperature
Temperature (C) VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 10B. Turn-Off Fall Time vs Voltage
Temperature (C)
Figure 12A. Logic "1" Input Voltage (IR2101)
Logic "0" Input Voltage (IR2102)
vs Temperature
Figure 12B. Logic "1" Input Voltage (IR2101)
Logic "0" Input Voltage (IR2102)
vs Voltage
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
I
n
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
M in.
T
u
r
n
-
O
f
f
F
a
l
l
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
0
50
100
150
200
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
Typ.
0
50
100
150
200
10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
Typ. T
u
r
n
-
O
f
f
F
a
l
l
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
10 12 14 16 18 20
I
n
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
M in.
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 9A. Turn-On Rise Time vs Temperature Figure 9B. Turn-On Rise Time vs Voltage
Temperature (C) VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
0
100
200
300
400
500
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
Typ.
T
u
r
n
-
O
n
R
i
s
e
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
Typ.
T
u
r
n
-
O
n
R
i
s
e
T
i
m
e
(
n
s
)
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
www.irf.com 9
Temperature (C) Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 14A. High Level Output
vs Temperature
Figure 14B. High Level Output vs Voltage
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
H
i
g
h
L
e
v
e
l
O
u
t
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
Figure 15A. Low Level Output
vs Temperature
Temperature (C) Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 15B. Low level Output vs Voltage
L
o
w
L
e
v
e
l
O
u
t
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
H
i
g
h
L
e
v
e
l
O
u
t
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
L
o
w
L
e
v
e
l
O
u
t
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
Figure 13A. Logic "0" Input Voltage (IR2101)
Logic "1" Input Voltage (IR2102)
vs Temperature
Temperature (C) Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 13B. Logic "0" Input Voltage (IR2101)
Logic "1" Input Voltage (IR2102)
vs Voltage
0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4
10 12 14 16 18 20
I
n
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
M ax.
0
0.8
1.6
2.4
3.2
4
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
I
n
p
u
t
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
M ax.
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
10 www.irf.com
Figure 17A. VBS Supply Current
vs Temperature
Figure 17B. VBS Supply Current
vs Voltage
VBS Floating Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 18A. Vcc Supply Current
vs Temperature
V
c
c
S
u
p
p
l
y
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Temperature (C)
Temperature (C)
V
c
c
S
u
p
p
l
y
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Figure 18B. Vcc Supply Current
vs Voltage
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
V
B
S
S
u
p
p
l
y
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
Typ.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
Typ.
0
30
60
90
120
150
10 12 14 16 18 20
Max.
Typ.
V
B
S
S
u
p
p
l
y
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
0
30
60
90
120
150
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
Typ.
Figure 16A. Offset Supply Current
vs Temperature
O
f
f
s
e
t
S
u
p
p
l
y
L
e
a
k
a
g
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
0 100 200 300 400 500 600
Max.
Figure 16B. Offset Supply Current
vs Voltage
VB Boost Voltage (V)
O
f
f
s
e
t
S
u
p
p
l
y
L
e
a
k
a
g
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Temperature (C)
0
100
200
300
400
500
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
www.irf.com 11
L
o
g
i
c
I
n
p
u
t
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Figure 20A. Logic "0" Input Current
vs Temperature
Temperature (C) VCC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 20B. Logic "0" Input Current
vs Voltage
0
1
2
3
4
5
10 12 14 16 18 20
L
o
g
i
c
"
0
"
I
n
p
u
t
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
u
A
)
Max.
V
C
C
U
V
L
O
T
h
r
e
s
h
o
l
d
+
(
V
)
Figure 21A. Vcc Undervoltage Threshold(+)
vs Temperature
Temperature (C)
Figure 21B. Vcc Undervoltage Threshold(-)
vs Temperature
V
C
C
U
V
L
O
T
h
r
e
s
h
o
l
d
-
(
V
)
6
7
8
9
10
11
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Max.
Min.
Typ.
6
7
8
9
10
11
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
M in.
Typ.
Temperature (C)
0
1
2
3
4
5
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Max.
Figure 19A. Logic"1" Input Current
vs Temperature
Temperature (C)
L
o
g
i
c
1
I
n
p
u
t
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
L
o
g
i
c
1
I
n
p
u
t
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Figure 19B. Logic"1" Input Current
vs Voltage
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
M ax.
Typ.
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
10 12 14 16 18 20
M ax.
Typ.
Vcc Supply Voltage (V)
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
12 www.irf.com
O
u
t
p
u
t
S
i
n
k
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
m
A
)
Temperature (C)
Figure 23A. Output Sink Current
vs Temperature
Figure 23B. Output Sink Current
vs Voltage
O
u
t
p
u
t
S
i
n
k
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
m
A
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Typ.
M in.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
10 12 14 16 18 20
Typ.
M in.
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
O
u
t
p
u
t
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
m
A
)
Figure 22A. Output Source Current
vs Temperature
Temperature (C)
Figure 22B. Output Source Current
vs Voltage
O
u
t
p
u
t
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
m
A
)
0
100
200
300
400
500
10 12 14 16 18 20
Typ.
Min.
VBIAS Supply Voltage (V)
0
100
200
300
400
500
-50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Typ.
Min.
IR2101/IR2102
(
S
)
www.irf.com 13
IR WORLD HEADQUARTERS: 233 Kansas St., El Segundo, California 90245 Tel: (310) 252-7105
Data and specifications subject to change without notice. 4/18/2003
01-6014
01-3003 01 (MS-001AB) 8 Lead PDIP
Case outlines
01-6027
01-0021 11 (MS-012AA)
8 Lead SOIC
8 7
5
6 5
D B
E
A
e 6X
H
0.25 [.010] A
6
4 3 1 2
4. OUTLINE CONFORMS TO J EDEC OUTLINE MS-012AA.
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONING & TOLERANCING PER ASME Y14.5M-1994.
2. CONTROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIMETER
3. DIMENSIONS ARE SHOWN IN MILLIMETERS [INCHES].
7
K x 45
8X L
8X c
y
FOOTPRINT
8X 0.72 [.028]
6.46 [.255]
3X 1.27 [.050]
8X 1.78 [.070]
5 DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSIONS.
6 DIMENSION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROTRUSIONS.
MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT TO EXCEED 0.25 [.010].
7 DIMENSION IS THE LENGTH OF LEAD FOR SOLDERING TO
A SUBSTRATE.
MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT TO EXCEED 0.15 [.006].
0.25 [.010] C A B
e1
A
A1
8X b
C
0.10 [.004]
e1
D
E
y
b
A
A1
H
K
L
.189
.1497
0
.013
.050 BASIC
.0532
.0040
.2284
.0099
.016
.1968
.1574
8
.020
.0688
.0098
.2440
.0196
.050
4.80
3.80
0.33
1.35
0.10
5.80
0.25
0.40
0
1.27 BASIC
5.00
4.00
0.51
1.75
0.25
6.20
0.50
1.27
MIN MAX
MILLIMETERS INCHES
MIN MAX
DIM
8
e
c .0075 .0098 0.19 0.25
.025 BASIC 0.635 BASIC
This datasheet has been download from:
www.datasheetcatalog.com
Datasheets for electronics components.
You might also like
- 常用ic P系列 Pt Pt6312b sDocument4 pages常用ic P系列 Pt Pt6312b sRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- 2SK2837 Datasheet en 20090929Document6 pages2SK2837 Datasheet en 20090929mirelaNo ratings yet
- 1N4934 - 1N4937 Fast Rectifiers: FeaturesDocument5 pages1N4934 - 1N4937 Fast Rectifiers: FeaturesRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- 8 - Permanent Capacitor Single-Phase InductionDocument8 pages8 - Permanent Capacitor Single-Phase InductionRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Ups Nobreak Ts Shara Ts 42 PDFDocument1 pageUps Nobreak Ts Shara Ts 42 PDFRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Intel Smart Response Technology User Guide 3Document3 pagesIntel Smart Response Technology User Guide 3Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Ewf1070m Service ManualDocument28 pagesEwf1070m Service ManualRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- PROG05 Manualv C1Document14 pagesPROG05 Manualv C1Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- World's most energy efficient temperature sensor datasheetDocument7 pagesWorld's most energy efficient temperature sensor datasheetRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Uf - NF - PF Conversion Chart PDFDocument4 pagesCapacitor Uf - NF - PF Conversion Chart PDFRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- American Wire Gauge Conductor Size TableDocument3 pagesAmerican Wire Gauge Conductor Size TablevahrmNo ratings yet
- An 10896Document46 pagesAn 10896Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- World's most energy efficient temperature sensor datasheetDocument7 pagesWorld's most energy efficient temperature sensor datasheetRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- World's most energy efficient temperature sensor datasheetDocument7 pagesWorld's most energy efficient temperature sensor datasheetRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- LA4227SANDocument4 pagesLA4227SANRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- CD8227GPDocument8 pagesCD8227GPAlfredo Valencia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 常用ic P系列 Pt Pt6312b sDocument4 pages常用ic P系列 Pt Pt6312b sRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- 74HC HCT595 PDFDocument24 pages74HC HCT595 PDFseanz001No ratings yet
- Users Guide (Ac PG Usbasp Ug v2.0)Document24 pagesUsers Guide (Ac PG Usbasp Ug v2.0)mendimanoNo ratings yet
- Guide To Design of Flyback and Forward Transformers3 - YouSpice, SPICE Simulation CommunityDocument24 pagesGuide To Design of Flyback and Forward Transformers3 - YouSpice, SPICE Simulation CommunityRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Uf - NF - PF Conversion Chart PDFDocument4 pagesCapacitor Uf - NF - PF Conversion Chart PDFRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Fan4822 189181 PDFDocument11 pagesFan4822 189181 PDFRachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- FAN4800 Low Startup Current PFC/PWM Controller Combinations: Features DescriptionDocument19 pagesFAN4800 Low Startup Current PFC/PWM Controller Combinations: Features Descriptionseyyedali2006No ratings yet
- 1 5ke6 8 (C) (A) - 1 5ke550 (C) (A) (Do-201ae)Document4 pages1 5ke6 8 (C) (A) - 1 5ke550 (C) (A) (Do-201ae)Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Phase Angle Control of SCR Using AT89C51Document11 pagesPhase Angle Control of SCR Using AT89C51Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- 1 5ke6 8 (C) (A) - 1 5ke550 (C) (A) (Do-201ae)Document4 pages1 5ke6 8 (C) (A) - 1 5ke550 (C) (A) (Do-201ae)Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- TLE49x5L Family V1 5 Data SheetDocument20 pagesTLE49x5L Family V1 5 Data SheetValerica DavidNo ratings yet
- MC 1458Document18 pagesMC 1458Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Instalar e Usar o Modo Windows XP No Windows 7Document4 pagesInstalar e Usar o Modo Windows XP No Windows 7Rachel RowlandNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Probe On-Wafer DiodesDocument3 pagesProbe On-Wafer DiodesAmador Garcia IIINo ratings yet
- RA30H3340M MitsubishiElectricDocument8 pagesRA30H3340M MitsubishiElectricashfaqNo ratings yet
- Analysis of BJT AmplrDocument3 pagesAnalysis of BJT AmplrMalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- TPA-1 v1.0.0 User ManualDocument10 pagesTPA-1 v1.0.0 User ManualagarramelagarompaNo ratings yet
- LM5116Document37 pagesLM5116Evanier Souza de AlencarNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument1 pageQuestion BankShailendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Applications of Diodes AnalysisDocument32 pagesApplications of Diodes AnalysisMister X100% (1)
- Experiment No: 1 Aim:: To Study Commands of PspiceDocument18 pagesExperiment No: 1 Aim:: To Study Commands of PspiceRudra Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- A 1.8 Self-Biased Complementary Folded Cascode AmplifierDocument3 pagesA 1.8 Self-Biased Complementary Folded Cascode Amplifiernaxter25No ratings yet
- ADC Lab ManualDocument46 pagesADC Lab ManualDinesh Kumar A RNo ratings yet
- Sync Separation CircuitDocument4 pagesSync Separation CircuitMoon SunNo ratings yet
- Lectures 8-14 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) and CircuitsDocument56 pagesLectures 8-14 Bipolar Junction Transistors (BJTS) and CircuitsChristian CalmaNo ratings yet
- Industrial EngineeringDocument84 pagesIndustrial EngineeringmuetanianNo ratings yet
- Course TitleDocument142 pagesCourse TitleMr.A.Sriram Asst. ProfNo ratings yet
- TIA+Differential Amplifier TexasDocument8 pagesTIA+Differential Amplifier TexasHrishikesh KunchepuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 BJT1Document13 pagesLecture 6 BJT1马铃淑No ratings yet
- EC8361 - Analog and Digital Circuits Laboratory Manual - by LearnEngineering - inDocument82 pagesEC8361 - Analog and Digital Circuits Laboratory Manual - by LearnEngineering - inPavithra PrakashNo ratings yet
- RCA Transistor Servicing GuideDocument196 pagesRCA Transistor Servicing GuideClaudioMarcelioNo ratings yet
- AD831Document16 pagesAD831Vicent Ortiz GonzalezNo ratings yet
- RF ChokeDocument8 pagesRF ChokeZohaib HassanNo ratings yet
- Experiment-291: Characterizing an OptocouplerDocument9 pagesExperiment-291: Characterizing an OptocouplerPadmo PadmundonoNo ratings yet
- Common Source JFET AmplifierDocument12 pagesCommon Source JFET AmplifierBharathReddyNo ratings yet
- ASCDocument5 pagesASCmintoissacNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Semiconductor MCQsDocument47 pagesCambridge Semiconductor MCQsSumanta BhattacharyyaNo ratings yet
- BasicElectronicsbyDebashisDe 1 PDFDocument836 pagesBasicElectronicsbyDebashisDe 1 PDFKhalid YahyaNo ratings yet
- XP1044 QL MACOM v2 PDFDocument10 pagesXP1044 QL MACOM v2 PDFxmenNo ratings yet
- An Inexpensive Easy To Build Diy Valve TesterDocument10 pagesAn Inexpensive Easy To Build Diy Valve TesterManuel SilveiraNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument23 pagesTransistorsKhalil AliNo ratings yet
- AD829AQ-High Speed Video OpampDocument13 pagesAD829AQ-High Speed Video OpamphariharanccetNo ratings yet
- LM1558/LM1458 Dual Operational Amplifier: General Description FeaturesDocument6 pagesLM1558/LM1458 Dual Operational Amplifier: General Description Featuresapisit02No ratings yet