Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exercise 1 Language of Anatomy
Uploaded by
maniz442Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exercise 1 Language of Anatomy
Uploaded by
maniz442Copyright:
Available Formats
3
Surface Anatomy
1. Match each of the following descriptions with a key equivalent, and record the key letter or term in front of the description.
Key: a. buccal c. cephalic e. patellar
b. calcaneal d. digital f. scapular
1. cheek 4. anterior aspect of knee
2. pertaining to the fingers 5. heel of foot
3. shoulder blade region 6. pertaining to the head
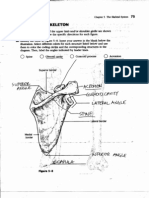
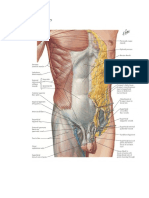
2. Indicate the following body areas on the accompanying diagram by placing the correct key letter at the end of each line.
Key:
a. abdominal
b. antecubital
c. axillary
d. brachial
e. cervical
f. crural
g. femoral
h. fibular
i. gluteal
j. inguinal
k. lumbar
l. occipital
m. oral
n. popliteal
o. pubic
p. sural
q. thoracic
r. umbilical
3. Classify each of the terms in the key of question 2 above into one of the large body regions indicated below. Insert the
appropriate key letters on the answer blanks.
1. appendicular 2. axial
Body Orientation, Direction, Planes, and Sections
4. Describe completely the standard human anatomical position. _________________________________________________
a; buccal
d; digital
f; scapular
e; patellar
b; calcaneal
c; cephalic
m
q
a
b
r
j
o
g
h
f
b, c, d, f, g, h, n, p a, e, i, j, k, l, m, o, q, r
Standing erect, feet together, head and toes pointed
forward, arms hanging at sides with palms forward.
e
l
c
d
k
i
n
p
NAME ____________________________________
LAB TIME/DATE _______________________
The Language of Anatomy
E X E R C I S E
R E V I E W S H E E T
1
4 Review Sheet 1
5. Define section. ______________________________________________________________________________________
6. Several incomplete statements are listed below. Correctly complete each statement by choosing the appropriate anatomical
term from the key. Record the key letters and/or terms on the correspondingly numbered blanks below.
Key: a. anterior d. inferior g. posterior j. superior
b. distal e. lateral h. proximal k. transverse
c. frontal f. medial i. sagittal
In the anatomical position, the face and palms are on the _1_ body surface; the buttocks and shoulder blades are on
the __2_ body surface; and the top of the head is the most _3_ part of the body. The ears are _4_ and _5_ to the shoulders
and _6_ to the nose. The heart is _7_ to the vertebral column (spine) and _8_ to the lungs. The elbow is _9_ to the fingers
but _10_ to the shoulder. The abdominopelvic cavity is _11_ to the thoracic cavity and _12_ to the spinal cavity. In humans,
the dorsal surface can also be called the _13_ surface; however, in quadruped animals, the dorsal surface is the _14_
surface.
If an incision cuts the heart into right and left parts, the section is a _15_ section; but if the heart is cut so that superior
and inferior portions result, the section is a _16_ section. You are told to cut a dissection animal along two planes so that both
kidneys are observable in each section. The two sections that will always meet this requirement are the _17_ and _18_ sec-
tions. Asection that demonstrates the continuity between the spinal and cranial cavities is a _19_ section.
1. 8. 14.
2. 9. 15.
3. 10. 16.
4. 11. 17.
5. 12. 18.
6. 13. 19.
7.
7. Correctly identify each of the body planes by inserting the appropriate term for each on the answer line below the drawing.
(a) (b) (c)
A cut along an imaginary plane through the body wall or organ.
a; anterior
g; posterior
j; superior
f; medial
j; superior
e; lateral
a; anterior
f; medial
h; proximal
b; distal
d; inferior
a; anterior
g; posterior
j; superior
i; sagittal
k; transverse
c; frontal
k; transverse
i; sagittal
median (mid-sagittal) plane frontal plane transverse plane
5 Review Sheet 1
8. Draw a kidney as it appears when sectioned in each of the three different planes.
9. Correctly identify each of the nine areas
of the abdominal surface by inserting the
appropriate term for each of the letters indi-
cated in the drawing.
a.
b.
c.
d.
e.
f.
g.
h.
i.
Body Cavities
10. Which body cavity would have to be opened for the following types of surgery or procedures? (Insert letter of key choice in
same-numbered blank. More than one choice may apply.)
Key: a. abdominopelvic c. dorsal e. thoracic
b. cranial d. spinal f. ventral
1. surgery to remove a cancerous lung lobe 4. appendectomy
2. removal of the uterus, or womb 5. stomach ulcer operation
3. removal of a brain tumor 6. delivery of pre-operative saddle anesthesia
frontal section sagittal section transverse section
(a)
(b)
(e)
(h)
(c)
(d)
(f)
(g)
(i)
epigastric region
right hypochondriac region
left hypochondriac region
umbilical region
right lumbar region
left lumbar region
hypogastric (pubic) region
right iliac reigon
left iliac region
e, f
a, f
b, c
a, f
a, f
d, c
6 Review Sheet 1
11. Name the muscle that subdivides the ventral body cavity. ____________________________________________________
12. Which organ system would not be represented in any of the body cavities? _______________________________________
13. What are the bony landmarks of the abdominopelvic cavity? __________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________________________________
14. Which body cavity affords the least protection to its internal structures? _________________________________________
15. What is the function of the serous membranes of the body? ___________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
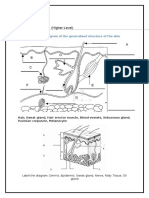
16. Using the key choices, identify the small body cavities described below.
Key: a. middle ear cavity c. oral cavity e. synovial cavity
b. nasal cavity d. orbital cavity
_________________ 1. holds the eyes in an anterior-facing position ________________ 4. contains the tongue
_________________ 2. houses three tiny bones involved in hearing ________________ 5. lines a joint cavity
_________________ 3. contained within the nose
17. On the incomplete flowchart provided below:
Fill in the cavity names as appropriate to boxes 38.
Then, using either the name of the cavity or the box numbers, identify the descriptions in the list that follows.
a. contained within the skull and vertebral column e. contains the heart
b. houses female reproductive organs f. contains the small intestine
c. the most protective body cavity g. bounded by the ribs
d. its name means belly h. its walls are muscular
cavity
1 Dorsal body cavity
3 cavity
(superior)
2 Ventral body cavity
Body ca vities
4
(inferior)
5 cavity
(superior)
6 cavity
(inferior)
7 cavity
(superior)
8 cavity
(inferior)
Skeletal, muscular, integumentary
the pelvis
Abdominal
The serous membranes produce a lubricating fluid (serous
Dorsally, the vertebral column; laterally and anteriorly,
fluid) that reduces friction as organs slide across one another or against the cavity walls during their functioning.
c; oral cavity
e; synovial cavity
d; orbital cavity
a; middle ear cavity
b; nasal cavity
1
8
1, 3, 4
2
5
6 or 7
5
6 or 7
cranial thoracic
abdominal pelvic
abdominopelvic vertebral/spinal
diaphragm
You might also like
- PERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 1.4-Learning TaskDocument9 pagesPERIDA EMMALYN T. - BSci103-Lesson 1.4-Learning TaskEmmalyn Perida100% (1)
- Exam Content Guide Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument28 pagesExam Content Guide Anatomy and PhysiologyWYATT C67% (3)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition CH - 01 - Test - BankDocument32 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition CH - 01 - Test - BankSiren-Relentless Schmidt75% (4)
- Chapter 11 - The Appendicular Skeletal SystemDocument6 pagesChapter 11 - The Appendicular Skeletal Systemmedianoche191% (11)
- CH 5 AnswersDocument22 pagesCH 5 AnswersYhormmie Harjeinifujah100% (2)
- WorksheetDocument1 pageWorksheetNiki CheeruNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 11 Practice TestDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 11 Practice Testmalenya150% (2)
- Integumentary System WorksheetDocument6 pagesIntegumentary System WorksheetKaye CorNo ratings yet
- A-P - Ch01 - Organ Systems Overview HandoutDocument3 pagesA-P - Ch01 - Organ Systems Overview HandoutMaggie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- FAP All ChaptersDocument814 pagesFAP All ChaptersDenise Tully Vernier100% (26)
- Anatomy and Physiology Final Exam MsuDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Final Exam MsuAlibasher Macalnas100% (1)
- Anatomy Physiology Midterm Review Sheet 105 Questions Organ Systems Exam PrepDocument2 pagesAnatomy Physiology Midterm Review Sheet 105 Questions Organ Systems Exam PrepMarckenson Mondelus0% (1)
- Nervous System WorksheetDocument6 pagesNervous System WorksheetSteve MacarioNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes 1 &2Document3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes 1 &2Ivy100% (1)
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- 8Document11 pages8caripe22No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology NotesDocument28 pagesAnatomy and Physiology NotesBetty Wang85% (13)
- Examination Questions and Answers in Basic Anatomy and Physiology: 2000 Multiple Choice Questions PDFDocument508 pagesExamination Questions and Answers in Basic Anatomy and Physiology: 2000 Multiple Choice Questions PDFShyam100% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology LectrueDocument76 pagesAnatomy and Physiology LectrueButch Dumdum73% (15)
- Answers Chapter 10 and 11 ExamDocument7 pagesAnswers Chapter 10 and 11 ExamMara Romanoff75% (4)
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- N O I A N: AME Rigin Nsertion Ction ErveDocument16 pagesN O I A N: AME Rigin Nsertion Ction ErveJulie Brookelle Jacquinot100% (7)
- Chapter 15 Study QuestionsDocument18 pagesChapter 15 Study Questionsashok_solanki_23100% (1)
- Endocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDocument5 pagesEndocrine System Review Flashcards - QuizletDani Anyika100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument17 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyPamela Spam100% (1)
- Skeletal QuizDocument12 pagesSkeletal QuizMaria Robustelli100% (2)
- Muscular System WebquestDocument7 pagesMuscular System WebquestJxcari50% (2)
- Chapter-1 Anatomy & Physiology: RestrictedDocument36 pagesChapter-1 Anatomy & Physiology: RestrictedGoogle Bd86% (7)
- Anatomy and Physiology Module 1Document13 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Module 1JayR Mendones100% (2)
- Final Exam in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesFinal Exam in Anatomy and PhysiologyKeanu Ribs100% (2)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument7 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyFreeNursingNotes0% (1)
- HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: A GUIDE TO THE HUMAN BODYDocument51 pagesHUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY: A GUIDE TO THE HUMAN BODYMa Ruth Parel86% (7)
- Urinary System Test BankDocument30 pagesUrinary System Test BankVinz TombocNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Respiratory SystemDocument30 pagesANAPHY Respiratory SystemAshley Franceska CansanayNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Mid-Semster Study Notes PDFDocument32 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Mid-Semster Study Notes PDFsimone dumbrell100% (10)
- Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Matching QuestionsDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Matching QuestionsYi Pan Chen100% (10)
- Anatomy and Physiology OverviewDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OverviewBing58No ratings yet
- Bicol College Nursing Anatomy ExamDocument5 pagesBicol College Nursing Anatomy ExamPao ParelNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Exams and AnswersDocument27 pagesNervous System Exams and AnswersMaria Simionescu100% (7)
- Chapter 3-4 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument27 pagesChapter 3-4 Anatomy and PhysiologyOregon190100% (6)
- Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesSkeletal Systemwiredpsyche100% (7)
- Reproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIDocument33 pagesReproduction Test For Anatomy & Physiology IIlhayes1234100% (5)
- Skeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument29 pagesSkeletal System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD100% (1)
- Anatomy Study GuideDocument181 pagesAnatomy Study GuideNirvanafly100% (1)
- Anatomy & Physiology Muscles Flashcards - QuizletDocument10 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Muscles Flashcards - Quizletmalenya1No ratings yet
- Test Bank Endocrine PDFDocument29 pagesTest Bank Endocrine PDFWenzy Cruz100% (3)
- List of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1Document6 pagesList of Mnemonics For Upper Limbs-1chitrojan142269% (13)
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument4 pagesAnatomy Mnemonicskiara91% (56)
- Medical Terminology Practice SheetsDocument7 pagesMedical Terminology Practice Sheetsmarcus colgrove100% (1)
- Introduction To AnatomyDocument9 pagesIntroduction To AnatomyFoo FuuNo ratings yet
- Histology Quiz 3Document10 pagesHistology Quiz 3Nick JacobNo ratings yet
- Muscle Groups and Actions MindmapDocument24 pagesMuscle Groups and Actions Mindmapdkavanagh_anatomy100% (1)
- Anatomy Final Exam Study GuideDocument15 pagesAnatomy Final Exam Study GuideAndy Tran100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology OrientationDocument9 pagesAnatomy and Physiology OrientationBeatriz Nidea83% (6)
- Anatomy and Physiology Terms: Brief Definitions, Roots & Morphology; An Abecedary; Vol 2-Planes & DirectionsFrom EverandAnatomy and Physiology Terms: Brief Definitions, Roots & Morphology; An Abecedary; Vol 2-Planes & DirectionsNo ratings yet
- The Language of AnatomyDocument7 pagesThe Language of AnatomyLinziJaeOnelNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology and PathophysiologyDocument23 pagesACTIVITY 1 Human Anatomy and Physiology and PathophysiologyShaila Joy Campano100% (1)
- Lebico Camille Sci 3a Act. 1Document3 pagesLebico Camille Sci 3a Act. 1wannieNo ratings yet
- WB CHPT 1 11 12 14 16 17Document2 pagesWB CHPT 1 11 12 14 16 17api-264668182No ratings yet
- Surface Anatomy: The Language of AnatomyDocument5 pagesSurface Anatomy: The Language of AnatomyHitagi CrabNo ratings yet
- NLN Medication Exam Study Guide QuizletDocument36 pagesNLN Medication Exam Study Guide Quizletmaniz442No ratings yet
- Study Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology ExamDocument64 pagesStudy Guide for NLN RN Pharmacology Exammaniz442No ratings yet
- Anaphylactic ReactionsDocument1 pageAnaphylactic Reactionsmaniz442No ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument1 pageCranial Nervesmaniz442No ratings yet
- Chapter18 Solutions - SmallDocument14 pagesChapter18 Solutions - Smallmaniz442No ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 pageMyocardial Infarctionmaniz442No ratings yet
- Heparin Lab TestDocument1 pageHeparin Lab Testmaniz442No ratings yet
- NURSING PHARMACOLOGY TIPSDocument19 pagesNURSING PHARMACOLOGY TIPSmaniz442100% (2)
- Cardiac ElectrophysiologyDocument1 pageCardiac Electrophysiologymaniz442No ratings yet
- QRS ComplexDocument1 pageQRS Complexmaniz442No ratings yet
- Mark Klimek Yellow BookDocument5 pagesMark Klimek Yellow Bookmaniz44295% (19)
- 6 Rights of Medication AdministrationDocument1 page6 Rights of Medication Administrationmaniz442100% (1)
- Hinkle PPT CH 21Document26 pagesHinkle PPT CH 21maniz442No ratings yet
- Chapter 19 review questions on nuclear reactions and radioactivityDocument2 pagesChapter 19 review questions on nuclear reactions and radioactivitymaniz442No ratings yet
- Chapter 19 review questions on nuclear reactions and radioactivityDocument2 pagesChapter 19 review questions on nuclear reactions and radioactivitymaniz442No ratings yet
- Hinkle PPT CH 10Document15 pagesHinkle PPT CH 10maniz442No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 11e FinalDocument26 pagesChapter 10 11e Finalmaniz442No ratings yet
- Chapter 24 - Organic ChemistryDocument13 pagesChapter 24 - Organic Chemistrymaniz442No ratings yet
- Hinkle PPT CH 17Document25 pagesHinkle PPT CH 17maniz442100% (2)
- Hinkle PPT CH 22Document21 pagesHinkle PPT CH 22maniz442No ratings yet
- Hinkle PPT CH 20Document34 pagesHinkle PPT CH 20maniz442100% (1)
- Chapter 25 - Synthetic and Natural Organic PolymersDocument14 pagesChapter 25 - Synthetic and Natural Organic Polymersmaniz442100% (1)
- Hinkle PPT CH 61Document44 pagesHinkle PPT CH 61maniz442No ratings yet
- Hinkle PPT CH 13Document59 pagesHinkle PPT CH 13maniz442No ratings yet
- Hinkle PPT CH 19Document29 pagesHinkle PPT CH 19maniz442No ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document43 pagesChapter 3maniz442No ratings yet
- Hinkle PPT CH 18Document20 pagesHinkle PPT CH 18maniz442100% (1)
- Chapter 10 11e FinalDocument26 pagesChapter 10 11e Finalmaniz442No ratings yet
- A&p Lab Ex 36Document4 pagesA&p Lab Ex 36Blink182Tigger92% (13)
- Summary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument4 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 2 Organisation of The Organism - CIE Biology IGCSECarola Bogezi100% (1)
- Practice QuestionDocument6 pagesPractice QuestionPAVITHRAN PadmanabhanNo ratings yet
- Visceral RenalDocument120 pagesVisceral RenalShivik PatelNo ratings yet
- Super Short Notes of Anatomy and Physiology by Pooja????????????Document174 pagesSuper Short Notes of Anatomy and Physiology by Pooja????????????shankarmeti2004No ratings yet
- Sensory Systems OverviewDocument72 pagesSensory Systems OverviewcholoNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 4 Epithelial TissueDocument12 pagesEssentials of Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 4 Epithelial TissueCASSANDRA BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Musket 2.1 FixDocument7 pagesMusket 2.1 FixgirlsNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonography of Gastrointestinal Foreign Bodies: DVM, Dominique G. Penninck, DVMDocument10 pagesUltrasonography of Gastrointestinal Foreign Bodies: DVM, Dominique G. Penninck, DVMrai jaine DarmantaNo ratings yet
- 24 HR Chick ReviewerDocument4 pages24 HR Chick ReviewerClarebelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Understanding Bronchial AsthmaDocument25 pagesUnderstanding Bronchial AsthmaRio Jane AsimanNo ratings yet
- 6 Life ProcessesDocument39 pages6 Life ProcessesPrashant Sirohi50% (2)
- The Digestive System Notes - Grade 9Document3 pagesThe Digestive System Notes - Grade 9bd6cpynwmpNo ratings yet
- Immunohematology MCQsDocument21 pagesImmunohematology MCQsMeerva El-zein84% (19)
- 7 0 Student WorkbookDocument17 pages7 0 Student Workbookapi-343368893No ratings yet
- School Science Lesson on Body Systems Teaches Circulatory, Respiratory FunctionsDocument20 pagesSchool Science Lesson on Body Systems Teaches Circulatory, Respiratory FunctionsLoiweza AbagaNo ratings yet
- Elsevier LTD - MCQs For Netter's Head and Neck Anatomy For Dentistry (2015)Document279 pagesElsevier LTD - MCQs For Netter's Head and Neck Anatomy For Dentistry (2015)anasNo ratings yet
- Lecture - One: Anatomy of The Anterior Abdominal WallDocument25 pagesLecture - One: Anatomy of The Anterior Abdominal WallAhmed OudahNo ratings yet
- Biology Presentation Class 7Document11 pagesBiology Presentation Class 7binu biju100% (2)
- Anatomi Trias Mengisap, Menelan dan BernapasDocument74 pagesAnatomi Trias Mengisap, Menelan dan BernapasAnonymous KrEomRrNo ratings yet
- Oral Physiology and Occlusion ReviewerDocument100 pagesOral Physiology and Occlusion ReviewerNUELLAELYSSE DELCASTILLO100% (3)
- Cytoskeleton and Cell MotilityDocument31 pagesCytoskeleton and Cell MotilityHappy KhungaNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument6 pagesDigestive SystemCeleste Atienza BawagNo ratings yet
- WORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesWORKSHEET 2.1 Animal and Plant CellLim Wai Wai100% (1)
- CL1 HaemopoiesisDocument41 pagesCL1 HaemopoiesisSamuel George100% (1)
- DigestionDocument3 pagesDigestionmuneeza dueveshNo ratings yet
- EMT NotesDocument58 pagesEMT NotesJosue PasillasNo ratings yet
- Strategies for Passing a Multiple Choice ExamDocument86 pagesStrategies for Passing a Multiple Choice ExamRizwan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Guideline PDFDocument26 pagesBlood Transfusion Guideline PDFEmhemed Amer TabibNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology BreastDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology BreastJames Daniel CodamonNo ratings yet
- Lesson - Cell Division - DifferentiationDocument8 pagesLesson - Cell Division - DifferentiationramyaNo ratings yet