Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 12 - Georgias Judicial Branch
Uploaded by
api-261440325Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 12 - Georgias Judicial Branch
Uploaded by
api-261440325Copyright:
Available Formats
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Georgia s
Judicial
Branch
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4a):
The three basic functions of government are separated into:
1. The Legislative Branch the General Assembly (Senate and
House of Representatives) makes the law
2. The Executive Branch the Governor, Lieutenant Governor,
Secretary of State, Attorney General, and State Treasurer
enforces the law
3. The Judicial Branch the State Supreme Court, Court of
Appeals, Circuit Courts, and Municipal Courts interprets the law
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4a):
Georgias Court System is divided into two levels, appellate
courts and trial courts:
Appellate Courts handle appeals from lower courts
1. Supreme Court of Georgia highest court in the state; has
seven members, six Justices and a Chief Justice; no jury
2. Court of Appeals twelve judges working in three man
panels to hear appeals; no jury
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4a):
Georgias Court System is divided into two levels, appellate
courts and trial courts:
Trial Courts lower courts with the original right, power, or
authority to intepret and apply the law
1. Superior Courts can hear almost any civil or criminal case;
consists of a judge and a jury
2. State Courts hold jurisdiction over misdemeanor violations
and civil cases; consists of judge and jury
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4a):
Georgias Court System is divided into two levels, appellate
courts and trial courts:
Trial Courts lower courts with the original right, power, or
authority to intepret and apply the law
3. Juvenile Courts jurisdiction over delinquent children under
17 years and deprived children under 18; no jury
(see SS8CG6)
4. Probate Courts handle administrative matters such as
wills; may have a jury
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4a):
Georgias Court System is divided into two levels, appellate
courts and trial courts:
Trial Courts lower courts with the original right, power, or
authority to intepret and apply the law
5. Magistrate Courts handles small civil claims, bad checks,
arrest warrants, etc.; no jury
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4a):
How are Judges selected in Georgia?
Most judges in Georgia are elected
Magistrate court judges may be elected or appointed by local
legislatures; juvenile court judges are appointed by superior
court judges
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
What do you remember about
Georgias Judicial System???
___ 1. The highest court in Georgia A. Superior Court
___ 2. May hear almost any civil or B. Supreme Court
criminal case C. Probate Court
___ 3. Handles wills and other admin- D. Court of Appeals
istrative matters E. Juvenile Court
___ 4. Handles small civil claims (e.g., F. State Courts
bad checks, arrest warrants, etc.) G. Magistrate Court
___ 5. Jurisdiction over misdemeanor
violations and civil cases
___ 6. Jurisdiction over delinquent
children under 17 years old
___ 7. Three-men teams hear appeals
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4b,c):
Civil vs. Criminal Law
Criminal law deals with actions that harm people or society
(e.g., DUI, murder, armed robbery, etc.)
Civil law deals with private disputes (e.g., divorce, property
ownership, contracts, personal injuries, etc.)
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4b,c):
Civil vs. Criminal Law
Civil cases are introduced by private
parties seeking monetary damages
Criminal cases are introduced by the
government seeking punishment (fine,
imprisonment, or death)
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4b,c):
Civil vs. Criminal Law
Civil cases are introduced by private
parties seeking monetary damages
Criminal cases are introduced by the
government seeking punishment (fine,
imprisonment, or death)
In civil cases, the defendant may be
forced to testify
In criminal cases, the defendant has the
right to defend himself or not to testify
under the 5
th
Amendment.
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4b,c):
Civil vs. Criminal Law
Civil cases are introduced by private
parties seeking monetary damages
Criminal cases are introduced by the
government seeking punishment (fine,
imprisonment, or death)
In civil cases, the defendant may be
forced to testify
In criminal cases, the defendant has the
right to defend himself or not to testify
under the 5
th
Amendment
In a civil case, the plaintiff only needs to
show guilt of the other party by a
preponderance of the evidence
In a criminal case, the prosecutor must
prove the defendant guilty beyond a
reasonable doubt
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4c & SS8CG6a,b,c):
Adult vs. Juvenile Justice
There are important differences between the way the justice
system is applied to adults and that way it is applied to youth:
1. Purpose The emphasis of adult court is on punishment,
while the emphasis in juvenile court is on rehabilitation.
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
2. Jurisdiction Juvenile Courts have jurisdiction (the right to
rule) over cases involving children under 17 years old, or
children under 18 who do not have a parent or guardian.
3. Terminology Juveniles are taken into custody and adults
are arrested; adults are found guilty and juveniles are
found delinquent; etc.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4c & SS8CG6a,b,c):
Adult vs. Juvenile Justice
There are important differences between the way the justice
system is applied to adults and that way it is applied to youth:
4. Procedure The adult and juvenile justice processes are different.
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG4c & SS8CG6a,b,c):
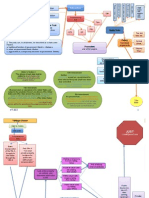
Juvenile vs. Adult Justice Procedures
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Minor is taken into custody
Minor is taken to a juvenile
detention center
Minor is released or sent to a
formal or informal hearing
Minor is warned or given
a small punishment
at an informal hearing
Minor is charged
at a formal
hearing
Minor enters plea agreement or faces trial
If found delinquent (guilty), judge gives a
disposition (sentence)
Adult is arrested if probable
cause exists
Adult is committed to jail
or released on bail
Adult is given an arraignment
where probable cause is
reviewed, an attorney is
appointed, and a plea is entered
A court date is set and a
trial is conducted
If convicted (found guilty), the
person is sentenced and the guilty
verdict may be appealed.
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG6b):
Juvenile Justice
If charged with a crime and taken into custody, juveniles
have rights similar to adults:
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
1. The right to remain silent when
questioned about an alleged crime
2. The right to have an attorney present
when questioned by the police
3. The right to be represented by an
attorney at trial
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG6b):
Juvenile Justice
Not all juvenile misconduct is considered delinquent:
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
1. Unruly behavior is behavior that is
disorderly or disobedient, but not
necessarily criminal (e.g., truancy,
underage drinking, curfew violations,
running away from home, etc.).
2. Delinquent behavior is behavior in
which a criminal act has been
committed (e.g., theft or damage
of property; illegal weapon
possession; sale of illegal drugs, etc.).
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG6b):
Juvenile Justice
Unruly behavior and delinquent behavior carry different
penalties:
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
1. Unruly behavior may result in
commitment to juvenile detention centers
for up to two years (but may be extended
by another two years if the court deems
necessary).
2. Delinquent behavior may result in
commitment to juvenile detention
centers for periods of 12 to 60 months
(but not to extend past the 21
st
birthday).
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG6b):
The Seven Deadly Sins Act of 1994
There are seven crimes which, if committed by a juvenile
between 13-17 years old, may result in trial as an adult:
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
1. Murder
2. Voluntary Manslaughter
3. Aggravated Sodomy
4. Aggravated Child Molestation
5. Aggravated Sexual Battery
6. Rape
7. Armed robbery if committed
with a firearm
The term aggravated refers to crimes
committed under the threat of serious or
deadly force
Like the U.S. Constitution, the GA Constitution provides
for a separation of powers (SS8CG6b):
The Seven Deadly Sins Act of 1994
There are seven crimes which, if committed by a juvenile
between 13-17 years old, may result in trial as an adult:
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
If found guilty of one of the seven
deadly sins, they will face
imprisonment for a minimum of 10
years.
If found guilty, the delinquent will
remain in juvenile detention until
the age of 17 and then be
transferred to prison or face the
death penalty.
What do you remember about
Juvenile Justice???
___ 1. Crime committed under the threat of A. Unruly
extreme or deadly force.
B. Aggravated
___ 2. Disorderly or disobedient conduct.
C. Seven Deadly
___ 3. Juvenile conduct considered to be Sins
criminal.
D. Delinquent
___ 4. The purpose of juvenile justice.
E. Punishment
___ 5. The purpose of adult criminal justice.
F. Rehabilitation
___ 6. May cause a juvenile to be tried as an adult.
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS:
In a democratic society, rule of law influences
the behavior of citizens, establishes
procedures for making policies, and limits the
power of government? Rule of law also
teaches that adults should be held to a higher
degree of accountability than children. How
does Georgias juvenile justice system differ
from the adult criminal justice system? Why
are the two different? Explain.
SS8CG4 The student will analyze the role of the judicial branch in Georgia state government.
SS8CG6 The student will explain how the Georgia court system treats juvenile offenders.
Acknowledgements
Hodge, Cathy M. Time Travel Through Georgia. Athens, GA: WesMar Incorporated
DBA/Voyager Publications, 2005.
Marsh, Carol. The Georgia Experience: 8
th
Grade Social Studies Teachers Edition
Student Workbook. Peachtree City, GA: Gallopade International, 2008.
You might also like
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of US Court System and StructureFrom EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of US Court System and StructureNo ratings yet
- CG Georgia Judicial and BranchDocument23 pagesCG Georgia Judicial and Branchapi-291938215No ratings yet
- Unit 11 - Georgia GovernmentDocument61 pagesUnit 11 - Georgia Governmentapi-261440325No ratings yet
- CH 4Document34 pagesCH 4Jeherul HoqueNo ratings yet
- The US Jury System ExplainedDocument14 pagesThe US Jury System ExplainedLăcrămioara BodnarescuNo ratings yet
- Hierarchy and Functions of Courts & Justice System in USA - OverviewDocument8 pagesHierarchy and Functions of Courts & Justice System in USA - OverviewStruat Christoper John BroadNo ratings yet
- JuvenileDocument5 pagesJuvenileJasneet BaidNo ratings yet
- India's judicial structure and highest courts outlinedDocument11 pagesIndia's judicial structure and highest courts outlinedRitika RitzNo ratings yet
- StaffEng Instruction JudicialDocument10 pagesStaffEng Instruction Judicialaplite54808No ratings yet
- Criminal Law Foundation EvaluationsDocument7 pagesCriminal Law Foundation Evaluationsrosa martinezNo ratings yet
- CourtComparisons Article 3 CourtDocument9 pagesCourtComparisons Article 3 CourtAnonymous puqCYDnQNo ratings yet
- What Is Judicial ReviewDocument3 pagesWhat Is Judicial ReviewashdajeeNo ratings yet
- State and Local GovernmentDocument7 pagesState and Local Governmentapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Court Role and StructureDocument22 pagesCourt Role and StructureМаксим ВласенкоNo ratings yet
- Judicial System ComparisonsDocument38 pagesJudicial System ComparisonsGauravChoudharyNo ratings yet
- DD - HH Foro D. Const.Document4 pagesDD - HH Foro D. Const.Gonzalo OjedaNo ratings yet
- Types of Law - IcivicsDocument2 pagesTypes of Law - Icivicsapi-2610094560% (1)
- Challenging Conditions of Prisons And: JailsDocument56 pagesChallenging Conditions of Prisons And: JailsKristalJaneMendozaNo ratings yet
- Judicial System in France, Uk PDFDocument38 pagesJudicial System in France, Uk PDFAdv Girish ManiyedathNo ratings yet
- American Government Chapter 13 2020Document54 pagesAmerican Government Chapter 13 2020Gikonyo MararoNo ratings yet
- Indian Federalism Project WorkDocument17 pagesIndian Federalism Project WorkAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Anzjle 10.211.1 - 7 MawdsleyDocument8 pagesAnzjle 10.211.1 - 7 Mawdsleyadhcuvhufjvufugi kbugucyduch5uvvNo ratings yet
- Fulltext PDFDocument15 pagesFulltext PDFAlisha StantonNo ratings yet
- United States v. Jarrillo-Luna, 10th Cir. (2007)Document10 pagesUnited States v. Jarrillo-Luna, 10th Cir. (2007)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Assigment LawDocument10 pagesAssigment LawnoamiNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitDocument13 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Eleventh CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Untitleddocument 1Document2 pagesUntitleddocument 1api-323098706No ratings yet
- Criminal procedure adjudication processDocument7 pagesCriminal procedure adjudication processValeriu27No ratings yet
- SCOTUS JurisdictionDocument8 pagesSCOTUS JurisdictionMarianna NajaryanNo ratings yet
- Substantive Vs ProceduralDocument2 pagesSubstantive Vs ProceduralZainne Sarip BandingNo ratings yet
- Q. Discuss The Features of US Constitution. Ans-Introduction: - The United States Constitution Stands As The Cornerstone ofDocument9 pagesQ. Discuss The Features of US Constitution. Ans-Introduction: - The United States Constitution Stands As The Cornerstone ofdasrajpratim24No ratings yet
- Juvenile Justice Reform - Jarrett SipesDocument14 pagesJuvenile Justice Reform - Jarrett Sipesapi-429802400No ratings yet
- Juvenile VS Adult Justice SystemDocument4 pagesJuvenile VS Adult Justice SystemDon NelsonNo ratings yet
- Supreme Court upholds constitutionality of Act No. 2886 in homicide caseDocument3 pagesSupreme Court upholds constitutionality of Act No. 2886 in homicide casebenipayo. lawNo ratings yet
- Judicial Role & Prevented Law: Week 16-18: The Legal Foundation For Public Education: An OverviewDocument18 pagesJudicial Role & Prevented Law: Week 16-18: The Legal Foundation For Public Education: An OverviewJoshua Ico AsisNo ratings yet
- Basic Legal CitationDocument7 pagesBasic Legal CitationJM TrammellNo ratings yet
- Due Process of LawDocument8 pagesDue Process of LawStanley Green100% (1)
- 6500 Motion DataDocument34 pages6500 Motion DataHarold RobertsNo ratings yet
- Criminal Justice SystemDocument4 pagesCriminal Justice SystemaileenairaNo ratings yet
- File 0893Document8 pagesFile 0893Herridge100% (2)
- Assignment: Submitted By-Pooja Yadav LLB 4 SEM Section - C ROLL NO - 861Document8 pagesAssignment: Submitted By-Pooja Yadav LLB 4 SEM Section - C ROLL NO - 861Pooja YadavNo ratings yet
- The Legal Profession in UK, US andDocument3 pagesThe Legal Profession in UK, US andHorvat AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Differences between procedural and substantive criminal lawDocument8 pagesDifferences between procedural and substantive criminal lawNaif OmarNo ratings yet
- Substantive and procedural law definedDocument5 pagesSubstantive and procedural law definedEarleen Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law and Procedure Chapter 2Document3 pagesCriminal Law and Procedure Chapter 2Daniel LyndsNo ratings yet
- Maryland Judicial Ethics Opinion On Questioning Defendants About Immigration StatusDocument3 pagesMaryland Judicial Ethics Opinion On Questioning Defendants About Immigration StatusJ CoxNo ratings yet
- EngLabInd 6 Pashchenko 3Document3 pagesEngLabInd 6 Pashchenko 3АндрійNo ratings yet
- Complete Judicial Branch Breakdown ReadingDocument3 pagesComplete Judicial Branch Breakdown Readingapi-265361711No ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Judicial Review in Usa and PakDocument3 pagesComparative Study of Judicial Review in Usa and PakkamranNo ratings yet
- DOJ Civil Rights Division Socioeconomic Bias Warning To State Judicial Branch, California Supreme Court - Judicial Council of CaliforniaDocument9 pagesDOJ Civil Rights Division Socioeconomic Bias Warning To State Judicial Branch, California Supreme Court - Judicial Council of CaliforniaCalifornia Judicial Branch News Service - Investigative Reporting Source Material & Story IdeasNo ratings yet
- Letter To Lexington Police DepartmentDocument4 pagesLetter To Lexington Police Departmentthe kingfishNo ratings yet
- Judicial Review in the US and IndiaDocument22 pagesJudicial Review in the US and Indiashivam mishraNo ratings yet
- Federal Rules of Civil ProcedureDocument25 pagesFederal Rules of Civil ProcedureDarien VarelaNo ratings yet
- In Re G.L.S., in The Matter of G.L.S., 745 F.2d 856, 4th Cir. (1984)Document6 pagesIn Re G.L.S., in The Matter of G.L.S., 745 F.2d 856, 4th Cir. (1984)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- 14th Amendment Flow ChartDocument6 pages14th Amendment Flow Chartdmsurveysspam100% (7)
- Bill of Rights Summary & ExplanationDocument2 pagesBill of Rights Summary & ExplanationAli ShawaizNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Criminal JusticeDocument4 pagesRunning Head: Criminal JusticeJoe WesshNo ratings yet
- Why Courts Matter for Dispute Resolution and Checks on PowerDocument5 pagesWhy Courts Matter for Dispute Resolution and Checks on PowerBeatrice andikaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Introduction To Law 6th EditionDocument38 pagesSolution Manual For Introduction To Law 6th Editionglaivefang2a8v67100% (9)
- GeographypdfDocument5 pagesGeographypdfapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Skeleton Notes Milestones Review NotesDocument107 pagesSkeleton Notes Milestones Review Notesapi-261440325No ratings yet
- NSV 4Document1 pageNSV 4api-261440325No ratings yet
- Midterm Study GuideDocument4 pagesMidterm Study Guideapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchor Cards 094-096Document1 pageAnchor Cards 094-096api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchor Cards 109-111Document1 pageAnchor Cards 109-111api-261440325No ratings yet
- NSV 2Document1 pageNSV 2api-261440325No ratings yet
- NSV 1Document1 pageNSV 1api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchor Cards 091-093Document1 pageAnchor Cards 091-093api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchor Cards 103-105Document1 pageAnchor Cards 103-105api-261440325No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Revolutionary War PeriodDocument10 pagesPowerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 2 The Revolutionary War Periodapi-261440325100% (1)
- Anchor Cards 106-108Document1 pageAnchor Cards 106-108api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchor Cards 100-102Document1 pageAnchor Cards 100-102api-261440325No ratings yet
- Historypart 2Document6 pagesHistorypart 2api-261440325No ratings yet
- Historypart 1Document7 pagesHistorypart 1api-261440325No ratings yet
- Unit 3 Study GuideDocument1 pageUnit 3 Study Guideapi-261440325No ratings yet
- State and Local GovernmentDocument7 pagesState and Local Governmentapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 2 Lesson 2 Georgia As A Trustee ColonyDocument10 pagesPowerpoint Notes Unit 2 Lesson 2 Georgia As A Trustee Colonyapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 2 Lesson 3 Georgia As A Royal ColonyDocument8 pagesPowerpoint Notes Unit 2 Lesson 3 Georgia As A Royal Colonyapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Unit 4 Study GuideDocument1 pageUnit 4 Study Guideapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 1 Causes of The American RevolutionDocument11 pagesPowerpoint Notes Unit 3 Lesson 1 Causes of The American Revolutionapi-261440325100% (1)
- Test Correction and Reflection Sheet PDFDocument2 pagesTest Correction and Reflection Sheet PDFAlbert Ng Wee PoNo ratings yet
- Powerpoint Notes Unit 2 Lesson 1 Exploration of The New WorldDocument8 pagesPowerpoint Notes Unit 2 Lesson 1 Exploration of The New Worldapi-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchorcards034 036Document1 pageAnchorcards034 036api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchorcards037 039Document1 pageAnchorcards037 039api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchorcards031 033Document1 pageAnchorcards031 033api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchorcards025 027Document1 pageAnchorcards025 027api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchorcards028 030Document1 pageAnchorcards028 030api-261440325No ratings yet
- Anchorcards022 024Document1 pageAnchorcards022 024api-261440325No ratings yet
- Lagman Vs MedialdeaDocument3 pagesLagman Vs MedialdeaJustice PajarilloNo ratings yet
- LABREL-De Jesus Vs AquinoDocument3 pagesLABREL-De Jesus Vs AquinoArcee CruzNo ratings yet
- TRADEMARKDocument14 pagesTRADEMARKAshutosh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 3661Document3 pagesRepublic Act 3661Gilbert MalcolmNo ratings yet
- App LeaveDocument2 pagesApp Leavekhalid_faqeerNo ratings yet
- Summary (Libel Case)Document1 pageSummary (Libel Case)Jee JeeNo ratings yet
- Sports Connection Pte Ltd v Deuter Sports GmbH: Non-competition clause was not a condition and breach was not sufficiently serious to permit terminationDocument42 pagesSports Connection Pte Ltd v Deuter Sports GmbH: Non-competition clause was not a condition and breach was not sufficiently serious to permit terminationBoon LeeNo ratings yet
- Universal Robina v. Lim (2007)Document3 pagesUniversal Robina v. Lim (2007)mc.rockz14No ratings yet
- 1 Iloilo Jar Corp. v. Comglasco Corp Aguila GlassDocument7 pages1 Iloilo Jar Corp. v. Comglasco Corp Aguila GlassFrancis LeoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines) City of Makati) S.S. AffidavitDocument4 pagesRepublic of The Philippines) City of Makati) S.S. AffidavitmkbysNo ratings yet
- CVC India's Apex Vigilance Body for Curbing CorruptionDocument4 pagesCVC India's Apex Vigilance Body for Curbing CorruptionkumarNo ratings yet
- United States v. Dominic Rotolo, 950 F.2d 70, 1st Cir. (1991)Document4 pagesUnited States v. Dominic Rotolo, 950 F.2d 70, 1st Cir. (1991)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Wells Fargo Vs CIRDocument2 pagesWells Fargo Vs CIREmil BautistaNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Case Digests in Corporation Law 2015 18Document74 pagesCompilation of Case Digests in Corporation Law 2015 18Soc SaballaNo ratings yet
- Osorio Vs NaveraDocument9 pagesOsorio Vs NaverajeviloricoNo ratings yet
- ACLU v. FBI, NSADocument12 pagesACLU v. FBI, NSARachel KingNo ratings yet
- Computer Identics Corporation v. Southern Pacific Company, 756 F.2d 200, 1st Cir. (1985)Document9 pagesComputer Identics Corporation v. Southern Pacific Company, 756 F.2d 200, 1st Cir. (1985)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- British Airways Motion to DismissDocument1 pageBritish Airways Motion to DismissPJANo ratings yet
- Accenture Raising Legal and Ethical Concerns and Prohibiting RetaliationDocument5 pagesAccenture Raising Legal and Ethical Concerns and Prohibiting RetaliationAindrila BeraNo ratings yet
- Case. Allarde Vs COADocument3 pagesCase. Allarde Vs COAJan Aguilar EstefaniNo ratings yet
- Vicente Ong Lim Sing, JRDocument5 pagesVicente Ong Lim Sing, JRKristine GarciaNo ratings yet
- Food Panda 3Document4 pagesFood Panda 3André CobarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Cap 1201 PDFDocument54 pagesCap 1201 PDFDanita CatoNo ratings yet
- Feliciano v. PasicolanDocument3 pagesFeliciano v. PasicolanAndotNo ratings yet
- Vda. de Tan v. Veterans Backpay CommissionDocument6 pagesVda. de Tan v. Veterans Backpay CommissionPaolo Antonio EscalonaNo ratings yet
- United States v. Dennis Kirk Doty, 943 F.2d 50, 4th Cir. (1991)Document2 pagesUnited States v. Dennis Kirk Doty, 943 F.2d 50, 4th Cir. (1991)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Komisarjevsky Arrest 031102Document9 pagesKomisarjevsky Arrest 031102mbrackenburyNo ratings yet
- Liability ExplainedDocument34 pagesLiability ExplainedAnonymous qFWInco8cNo ratings yet
- MA Family Institute Amicus Brief - Mass DOMA CasesDocument33 pagesMA Family Institute Amicus Brief - Mass DOMA CasesKathleen PerrinNo ratings yet
- Rayos V Hernandez and Tansueco V de DumoDocument3 pagesRayos V Hernandez and Tansueco V de DumoZandrina RatertaNo ratings yet