Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earth Moon Notes
Uploaded by
api-205903992Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Earth Moon Notes
Uploaded by
api-205903992Copyright:
Available Formats
Earth & Moon Notes
Chapter 19
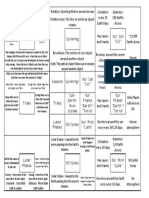
The Earth moves
in 2 ways
oRotation
oRevolution
The effects of the
movements
oDays/Nights
oSeasons
Rotation is spinning of
the earth on its axis
Axis- imaginary line
that passes through
the center of the earth
and the North and
South poles
The Axis
The axis is tilted at
an angle
23.5
o
The axis is responsible for the
difference in the length of sun
light hours
Sun light hours are NOT
constant (the same)
Rotation
Responsible for day and
night
It takes 24 hours to
rotate once
There are 24 hours in
one day
Revolution
Revolution the movement of one
object around another
The earth revolves around the
sun
One complete revolution is a
year
Revolution
Orbit: the Earths path around
the sun.
Orbits Shape = Elliptical
The Seasons
Due to the tilt
of the earths
axis
NOT due to
the distance
from the sun.
Direct/Indirect Rays
Sun has direct and indirect rays
Direct rays strike area around
equator
Warmer near equator
Direct/Indirect Rays
Indirect rays (slanted rays)
strike the north and south
poles
Cooler near poles
Direct Rays
Indirect Rays
Solstice
Solstice: the sun reaches its
greatest distance North or
South of the equator
Summer in N. Hemisphere =
Winter in S. Hemisphere
Summer Solstice
When are the solstices?
Summer Solstice: June 21
Longest day of the year
(Northern Hemisphere)
Winter Solstice: December 21
Shortest Day of the year
Winter Solstice
Equinox
Equinox: equal night (12 hour
day, 12 hour night)
The sun is directly over the
Equator
Day = Night
Equinox
When are the equinoxes?
Vernal Equinox: March 21
(First day of Spring)
Autumnal Equinox: September
21 (First day of Fall)
Gravity
Gravity: force that attracts all
objects to each other
Force: push or pull
Law of Universal Gravity
Its everywhere
Strength of Gravity
Strength depends on 2 factors
Mass: amount of matter in an
object
The bigger it is the stronger the gravity is
The smaller it is the weaker the gravity is
Distance: decrease gravity with
increase distance
The closer it is the stronger the gravity is
The farther it is the weaker the gravity is
The effects of Gravity
Tides
Weight
Inertia
Inertia: The tendency of an
object to resist a change in
motion
Newtons First Law of Motion: an
object at rest will stay at rest,
and an object in motion will stay
in motion until another force acts
on it.
Orbital Motion
Inertia and Gravity combine to
keep the Earth in orbit around
Sun
Inertia and Gravity combine to
keep the Moon in orbit around
Earth.
The Moon
The moon rotates once on its axis
in the same amount of time it
takes to revolve around the
earth.
Moon day = Moon Year
The same side of the moon
always faces the earth
A day or year on the moon =
29 days
Is the Moon Close or Far?
Perigee: point of the moons
orbit closest to the earth
Apogee: point of the moons
orbit farthest from the earth
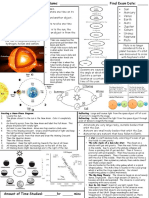
Phases of the Moon
Phases: the shapes of the moon
as seen from the earth
Depends on how much of the
moon that is reflecting sun
light faces the earth
Waxing Crescent First Quarter Waxing Gibbous
Waning Gibbous Waning Crescent Third Quarter
Full Moon
New Moon
Eclipses
Eclipse: partial or total blocking
of an object in space
Two types of eclipses
Solar- Sun
Lunar- Moon
Solar Eclipse
Moon directly between Earth &
sun, blocking sunlight
occurs with at New Moon
Types of Solar Eclipses
Total Solar Eclipse
Partial Solar Eclipse
Lunar Eclipse
Occurs when the earth is
between the sun and the moon
Occurs with a full moon
Types of Lunar Eclipses
Total Lunar Eclipse
Partial Lunar Eclipse
Lunar Eclipse
Moon Phase Video
Tides
Tides: the rise and fall of the
oceans
Due to the moons gravity
There are 2 high tides and 2 low
tides at any one time on earth.
Spring Tides
Occur at the New Moon and
Full Moon
When the sun and moon both
pull in the same direction
Very high tide
Spring Tide = Straight Line
Neap Tides
Occurs at the 1
st
quarter and
3
rd
quarter moon
When sun, earth and moon
form a 90
o
Angle
The high tide is not very
high
Moons Surface
Galileo is the first scientist
who looked at the moon with
a telescope
Features of the Moon
Maria: dark, flat surface
Thought they were seas
(oceans)
Really hardened rock
Craters: large pits on the surface
of the moon
Highlands: mountains on the moon
light colored
Characteristics of the Moon
Size & Density
of the earths diameter
Density is about the same
as the earths outer layers
Characteristics of the Moon
Temperature & Atmosphere
light side: 130
o
C = 266
o
F
Dark Side: -180
o
C = -292
o
F
There is no atmosphere so the
temperature always changes
Characteristics of the Moon
Water
No Liquid Water
Gravity
Gravity on the moon is about
1/6
th
as strong as on the earth
You might also like
- Astronomy Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesAstronomy Cheat SheetShahid Yousaf100% (2)
- Earth Moon and Sun PowerpointDocument33 pagesEarth Moon and Sun PowerpointemailtotesttestNo ratings yet
- How Did We Become Souls of DistortionDocument28 pagesHow Did We Become Souls of DistortionDustin ThomasNo ratings yet
- The River of Night: EridanusDocument16 pagesThe River of Night: EridanusRosa Maria Calazans100% (1)
- What Is AstronomyDocument34 pagesWhat Is AstronomyShahrul Razi100% (1)
- Mythological Story of Planets 2Document15 pagesMythological Story of Planets 2Ankit Singhal100% (3)
- Motion of The EarthDocument21 pagesMotion of The EarthNargis ShamimNo ratings yet
- Movement of The EarthDocument21 pagesMovement of The EarthAqilah Taufik100% (1)
- AccelerandoDocument34 pagesAccelerandoManuel Alejandro Crespo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 22.origin of Modern AstronomyDocument44 pages22.origin of Modern AstronomyChristine Valerio100% (1)
- Speed of LightDocument21 pagesSpeed of LightOleg VrabieNo ratings yet
- Earth and The Solar SystemDocument14 pagesEarth and The Solar SystemWilber TuryasiimaNo ratings yet
- Place&TimeDocument35 pagesPlace&TimeRenata AlvesNo ratings yet
- Motions in The SkyDocument47 pagesMotions in The SkyBrasa Y. de AlmiraNo ratings yet
- Space PhysicsNotesDocument44 pagesSpace PhysicsNotesthethmusan.2007No ratings yet
- Earth TiltDocument39 pagesEarth TilteurizirueNo ratings yet
- SCR NumericalDocument34 pagesSCR NumericalDevashishGuptaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: S11/12Ps-Iiib-11Document8 pagesLesson 1: S11/12Ps-Iiib-11Maurice LanceNo ratings yet
- HistoricalRoots of EcologicalCrisisDocument6 pagesHistoricalRoots of EcologicalCrisisJabłkowyBałwanek100% (1)
- Q4 Science 5 Summative TestDocument5 pagesQ4 Science 5 Summative TestRichard Protasio100% (4)
- Earth and Sun Relationships PDFDocument9 pagesEarth and Sun Relationships PDFAparajita MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Section 2: Phases, Eclipses, and TidesDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Section 2: Phases, Eclipses, and TidesPrasad ShahNo ratings yet
- Sci6 April8Document59 pagesSci6 April8Janmari FajardoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Moon?: THE MOON - A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!Document4 pagesWhat Is The Moon?: THE MOON - A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!Krystelle Joy ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Section 2: Phases, Eclipses, and TidesDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Section 2: Phases, Eclipses, and TidesSuhaimie CameronNo ratings yet
- Earth in Space-7th Grade Earth ScienceDocument22 pagesEarth in Space-7th Grade Earth Scienceleojohn2No ratings yet
- Earth in The UniverseDocument28 pagesEarth in The UniverseJemarjo SalandananNo ratings yet
- How Are These Objects Similar?: To What Direction That The Top Move?Document11 pagesHow Are These Objects Similar?: To What Direction That The Top Move?Louise BagapuroNo ratings yet
- Rotation Revolution NotesDocument2 pagesRotation Revolution NotesRabia SabirNo ratings yet
- The Movements of The Earth and Its EffectsDocument20 pagesThe Movements of The Earth and Its EffectseverNo ratings yet
- Lunar SlidesDocument6 pagesLunar SlidesAaron MccallNo ratings yet
- 08 MoontidesplanetsDocument15 pages08 Moontidesplanetsapi-242405009No ratings yet
- Study Guide 2014 Sol 3 8 Earth Patternscycles ChangeDocument2 pagesStudy Guide 2014 Sol 3 8 Earth Patternscycles Changeapi-324793261No ratings yet
- The Earth (New Version)Document29 pagesThe Earth (New Version)pepesitoNo ratings yet
- Earth's Rotation and RevolutionDocument48 pagesEarth's Rotation and RevolutionArenas JenNo ratings yet
- Moon Phases PPT Notes 1Document16 pagesMoon Phases PPT Notes 1api-294483847No ratings yet
- Ability To Use Celestial Bodies To Determine The Ships PositionDocument40 pagesAbility To Use Celestial Bodies To Determine The Ships PositionSandunMigaraNo ratings yet
- Earth's MotionDocument7 pagesEarth's Motionapi-526073862No ratings yet
- Earth's Revolution: Seasons and Retrograde Motion of PlanetsDocument18 pagesEarth's Revolution: Seasons and Retrograde Motion of PlanetsSameer WaliaNo ratings yet
- Motions of EarthDocument9 pagesMotions of EarthChris MarceloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 24 'Earth and The Solar System'Document6 pagesChapter 24 'Earth and The Solar System'Nayeem Hakim100% (1)
- ABEN55a - Lecture 02Document4 pagesABEN55a - Lecture 02Karylle Anne MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Law of Universal GravitationDocument5 pagesLaw of Universal GravitationJonnabelle Rose Torrefranca LinasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document5 pagesLesson 3Huda MadiNo ratings yet
- The Motion of Earth, Lunar Motion and The ConstellationDocument21 pagesThe Motion of Earth, Lunar Motion and The ConstellationRoda ES JimbertNo ratings yet
- 2 Space Systems (FINAL PART) Earth, Sun, MoonDocument44 pages2 Space Systems (FINAL PART) Earth, Sun, MoonKiki JoNo ratings yet
- Earth's Motion - ALVAREZDocument30 pagesEarth's Motion - ALVAREZSirTeeNo ratings yet
- Cel. Nav TheoryDocument27 pagesCel. Nav TheoryRahul DevnathNo ratings yet
- How Does Earth Move (Autosaved)Document23 pagesHow Does Earth Move (Autosaved)Dede MohamedNo ratings yet
- The Moon: A Look at Our Nearest NeighborDocument24 pagesThe Moon: A Look at Our Nearest NeighborSetyo NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Keplers LawsDocument23 pagesKeplers LawsJhulia IlogonNo ratings yet
- Relative Motion of Earth, Moon, SunDocument23 pagesRelative Motion of Earth, Moon, SunShahbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Lse 3069 - Rotation of The Earth and Its Effects - 2021Document12 pagesLse 3069 - Rotation of The Earth and Its Effects - 2021mark shikaazeNo ratings yet
- Earth in SpaceDocument16 pagesEarth in SpaceDefensor Pison GringgoNo ratings yet
- Earth's RevolutionDocument2 pagesEarth's RevolutionHannahNo ratings yet
- Sems LotusDocument1 pageSems Lotusapi-315554878No ratings yet
- and Interactions: EarthDocument47 pagesand Interactions: EarthNagarajNo ratings yet
- Rotation and Revolution: What Causes Night and Day? What Causes The Seasons To Change?Document5 pagesRotation and Revolution: What Causes Night and Day? What Causes The Seasons To Change?ajay_competitionNo ratings yet
- Earth Movements. MonicaDocument4 pagesEarth Movements. MonicaBencel May Diaz Paez100% (1)
- The Moon: A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!Document36 pagesThe Moon: A Look at Our Nearest Neighbor in Space!RamNo ratings yet
- Lecture # 1 GSADocument26 pagesLecture # 1 GSAMalaham Pari KhanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Space: By:Kennidi WatsonDocument4 pagesEarth and Space: By:Kennidi Watsonapi-356714607No ratings yet
- Motion of The EarthDocument1 pageMotion of The EarthBasco Martin Jr100% (1)
- Astronomy MidtermDocument5 pagesAstronomy MidtermAhmet Saim YılmazNo ratings yet
- The Reasons For Seasons: Edward M. Murphy Space Science For Teachers 2005Document60 pagesThe Reasons For Seasons: Edward M. Murphy Space Science For Teachers 2005Tony CresicbeneNo ratings yet
- Earth-Sun Relationships: The Reasons For The SeasonsDocument25 pagesEarth-Sun Relationships: The Reasons For The SeasonsSyed MajeedNo ratings yet
- Positions of The Sun, Moon, Stars and Distant Galaxies, Nebulas and Quasars. Motion of ObjectsDocument38 pagesPositions of The Sun, Moon, Stars and Distant Galaxies, Nebulas and Quasars. Motion of Objectsjanice guen beydenNo ratings yet
- Space Physics Presentation 1Document11 pagesSpace Physics Presentation 1RayyanNo ratings yet
- 7th Grade Science March News LetterDocument2 pages7th Grade Science March News Letterapi-205903992No ratings yet
- 2015-16 Mms Student HandbookDocument34 pages2015-16 Mms Student Handbookapi-205903992No ratings yet
- 2015-16 Mhs Student Handbook Opening DayDocument37 pages2015-16 Mhs Student Handbook Opening Dayapi-205903992No ratings yet
- 6th and 7th Computer SyllabusDocument2 pages6th and 7th Computer Syllabusapi-205903992No ratings yet
- Web Design 1 Pacing GuideDocument9 pagesWeb Design 1 Pacing Guideapi-205903992No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Detailed Curr, 61 PagesDocument58 pages7th Grade Detailed Curr, 61 Pagesapi-205903992No ratings yet
- Ms Office ClassDocument7 pagesMs Office Classapi-205903992No ratings yet
- 7th SC Rules and Grading 15-16Document2 pages7th SC Rules and Grading 15-16api-205903992No ratings yet
- 7th Science Pacing Guide 15-16 DetailedDocument29 pages7th Science Pacing Guide 15-16 Detailedapi-205903992No ratings yet
- S L o TricountyDocument2 pagesS L o Tricountyapi-205903992No ratings yet
- Cang DocumentDocument14 pagesCang Documentapi-205903992No ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report 1Document7 pagesPhysics Lab Report 1Liana BelleNo ratings yet
- Mohit Chawla (Chandigarh) PDFDocument21 pagesMohit Chawla (Chandigarh) PDFnishink9No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics - Gravitation NotesDocument9 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics - Gravitation NotesAyush GoelNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Toefl Listening Part CDocument2 pagesGroup 3: Toefl Listening Part CRizka Saumi DalimuntheNo ratings yet
- Horoscope of KM705463: Download FontsDocument3 pagesHoroscope of KM705463: Download Fontschithiravel GryffindorNo ratings yet
- Astro Discourse CommunityDocument11 pagesAstro Discourse Communityapi-346409475No ratings yet
- Latitude and LongitudeDocument5 pagesLatitude and LongitudeTallia WhartonNo ratings yet
- Extra Assignment Astronomy - Telescope SimulationsDocument3 pagesExtra Assignment Astronomy - Telescope SimulationsgabriellarataNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 6 - Q4 - W7Document9 pagesDLL - Science 6 - Q4 - W7Arnel LopezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - AAS-2010Document59 pagesChapter 8 - AAS-2010AprizalNo ratings yet
- The Matallic Planets of AlchemyDocument17 pagesThe Matallic Planets of AlchemyramonjuarezNo ratings yet
- Dark Matter, Dark Energy and Rotation CurvesDocument9 pagesDark Matter, Dark Energy and Rotation CurvesopalNo ratings yet
- Amy Jade Winehouse - Teste Astrologia Nível 2Document1 pageAmy Jade Winehouse - Teste Astrologia Nível 2Marketing BrighidNo ratings yet
- STS Module 1 - Chapter 1Document11 pagesSTS Module 1 - Chapter 1manaoislaurenceNo ratings yet
- SpaceX Ex Parte Re G-7Document7 pagesSpaceX Ex Parte Re G-7文刀同学No ratings yet
- Arsalan SolarDocument11 pagesArsalan SolarHilal AhmadNo ratings yet
- COM 221 ARR DraftDocument17 pagesCOM 221 ARR DraftZack OverfieldNo ratings yet
- Intersetellar Trvael An EssayDocument2 pagesIntersetellar Trvael An Essay18th Attack SquadronNo ratings yet
- SpectroscopieBasseResolution enDocument43 pagesSpectroscopieBasseResolution enMarco Aurelio MinozzoNo ratings yet
- Gd3202 Hydrography Ii Module 05 Tidal Constituent: What Is It?Document20 pagesGd3202 Hydrography Ii Module 05 Tidal Constituent: What Is It?Ski SundaeNo ratings yet