Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Extraction
Uploaded by
api-257471763Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Extraction
Uploaded by
api-257471763Copyright:
Available Formats
Paparwarin S.
11-4
Introduction
Since medicinal plants from jungle contain many active compounds such as
alkaloids, steroids, and tannins contained in bark or other parts of Amazon Jungle plants,
the company has used bark from a particular plant found in Amazon Jungle to produce a
new active drug. Alkaloid extraction is the first step of the process. Efficient method of
extraction will be benefit for companys drug.
To isolate or purify alkaloid, we concern about alkaloids chemical property, acidbase chemistry, and aqueous solutions in a medicinal plant extraction. Alkaloids are
chemical substance primarily found in plants and flowering plants. They compose of
carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. Alkaloids mostly are weak bases and dissolve
poorly in water but dissolve in organic solvent such as diethyl ether. Alkaloids, organic
compounds, contains an amino group is called amine which consisted of a nitrogen atom
by bonding with hydrogen atoms, alkyl groups, or combination of these three.
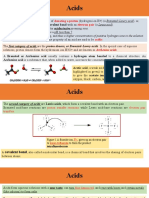
Acids are defined as substance that dissolve or ionize in water to produce H+ions.
Bases are defined as substance that dissolve or ionize in water to produce OH-ions.
Mention their properties, acids and bases are different in properties. Acids have sour
taste, cause color changes in plant dyes, react with metals to produce hydrogen gas, and
react with carbonates and bicarbonates to produce carbon dioxide gas. Bases have a
bitter taste, feeling of slippery, and cause color changes in plant dyes. When we defined
Bronsted-Lowry definition of acids and based, a Bronsted acid is a proton donor (donates
H+), and Bronsted base is a proton acceptor (accept H+).
Solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. The solute is the
substance present in the smaller amount, and the solvent is the substance present in the
larger amount. In this research we mostly mention on aqueous solutions, in which the
solute is a liquid or a solid and the solvent is water.
Body (Reasoning)
According to the companys medicinal plant extraction, bark they ordered from
South America and started to extract step by step. First, they broke the bark up into
smaller pieces to increase more surface areas of chemical interaction. Then the bark was
added into a reaction vessel with water (polar molecule) and acetic acid (weak acid)
because this step was to bring acidity of the bark up (the bark initially insoluble and less
polar). Before that, acids were added into water, acids dissolved in water and produced or
gave up proton (H+ or H3O+).
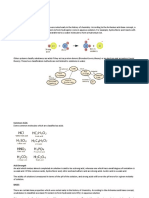
H2O + CH3COOH H3O+ + CH3COOWhen pieces of the bark, which have alkaloid substance (contained amine group - R3N),
were added into water and acetic acids. Acids gave its proton (H3O+) to anime group and
the molecule became (R3NH3O+) by attached of lone pairs of oxygen and nitrogen. The
dilute acid would protonate the alkaloids, making more polar and water soluble. Next step,
the mixture was boiled overnight (24 hrs.) to yield target substance from the bark and
increase rate of reaction by stimulation of heat and this extraction will be used in next
step. They filtered undissolved material and plant residue out of the mixture to have pure
Paparwarin S. 11-4
acid extraction of alkaloids. After the mixture was filtered, they added a base into the
filtrate continuing until it reaching up pH of 9-10. Assumed that base they used was
sodium hydroxide (NaOH). Raising pH allowed extraction of alkaloids solution less
soluble and they came out as precipitate formed (NaR3N). Adding base, the acid would
be neutralize, the extraction of alkaloids solution deprotonated.
R3NH3O+ + NaOH R3N+ + Na+ + OH- NaR3N(s) + 2(H2O)(l)
After this chemical reaction, NaR3N(s)was no longer water soluble but was still in water.
Lastly, pure alkaloid was filtered out as the precipitate and the company would bring this
precipitate on test.
Efficient extraction process refers to high yield of alkaloids extraction. However,
less toxic waste, less solvent used, shorter time and other green factors should be also
concerned. To improve the extraction method, I suggest to follow some steps:
(1) Break the bark up into smaller pieces The company should make the bark powder
to be the initial substance to increase interaction surface (Step 1).
(2) Add the bark into a reaction vessel with water and acetic acid The amount of water
and acetic acid must be at optimum level derived by companys experiment. However, it
depends on type of extracted alkaloid (Step 2).
Summary
In this extraction process, alkaloids were isolated from the bark of medicinal
plant found in Amazon Jungle. Polarity of molecule and the polarity of solvent must match
if the molecule is to be extracted into the solvent. Acid-base chemistry played a crucial
role in this extraction method both in extracting and neutralizing process. Acids acted as
proton donor while bases acted as proton receiver. However, the green laboratory
approach should be concerned for our sustainable world.
Paparwarin S. 11-4
Part 2 short answer
1.
Explain one common use of acid/base chemistry in everyday life. ( /5)
Acid-base chemistry are used in industrial process, biological system, and our daily life.
Acid has sour taste and base has bitter taste. Acid we can found around; for example,
acetic acid in vinegar, citric acid in citrus fruits, lactic acid in sour milk, and ascorbic acid
in vitamin C, and important acid in our stomach to help digestion of proteins is called
hydrochloric acid (HCl). For base we can found in everyday; for example, soaps made
from sodium hydroxide and baking soda consists of sodium bicarbonate.
2.
Give an example and reason of a precipitation reaction (not the one used above). ( /5)
When an aqueous solution of silver nitrate (AgNO3) is added to an aqueous
solution of Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a brown solid is precipitated out of solution called
silver hydroxide (AgOH).
AgNO3 (aq)+ NaOH(aq) Ag+ + NO3- + Na+ + OH- AgOH(s) + NaNO3 (aq)
Ag+ + OH- AgOH(s)
The reaction involves with the exchange of two compounds. Both silver (Ag+) and
hydroxide (OH- ) are insoluble compounds, so they form a brown solid as precipitate.
While nitrate (Na3-) and sodium (Na+) are soluble compounds, they remain aqueous
solution.
Paparwarin S. 11-4
Reference
1. Hanson, B. A. (2005). Chemical Behavior and Its Application to Medical Molecules.
Understanding Medicinal Plants: Their Chemistry and Therapeutic Action (119-127).
Retrieved
https://books.google.co.th/books?id=2JbToYS46SMC&pg=PA4&lpg=PA4&dq=understandin
g+medicinal+plant&source=bl&ots=U8auZ0fck&sig=OizAkG8YPSeNhxH8JJXxZBEC9fY&hl=en&sa=X&ei=acHDVOCdFISO8QWWgYKQCw&v
ed=0CDAQ6AEwAw#v=onepage&q=understanding%20medicinal%20plant&f=false
2. Halpern, J. (n.d.). Retrieved January 25, 2015 from the Chem Wiki:
http://chemwiki.ucdavis.edu/Wikitexts/Prince_George's_Community_College/General_
Chemistry_for_Engineering/Unit_3%3A_Nomenclature_and_Stoichiometry/Chapter_8%3A
_Aqueous_Solutions/Chapter_8.6%3A_Acid_Base_Reactions
3. Columbia University Press. (n.d.). In Encyclopdia Britannica online. Retrieved from
amino group http://www.infoplease.com/encyclopedia/science/aminogroup.html#ixzz3PKvHjyzk
4. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. (December 24, 2014). Retrieved January 25, 2015 from
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alkaloid#Properties
5. The Editors of Encyclopdia Britannica. (January 14, 2014). In Encyclopdia Britannica
online. Retrieved from
http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/15672/alkaloid
6. SciencePhotoLibrary. (n.d.). Retrieved January 25, 2015 from
http://www.sciencephoto.com/media/4351/view
7. Gupta, A., Naraniwal, M., & Kothari, V. (n.d.). Modern Extraction Methods for Preparation of
Bioactive Plants Extracts.
8. Chang, R., & Goldsby, K.A., (2010). Reactions in Aqueous Solutions (118-171). Chemistry.
You might also like
- 2.acids, Bases and SaltsDocument9 pages2.acids, Bases and SaltsayanNo ratings yet
- 25 May Acids Bases and Salts PPTDocument72 pages25 May Acids Bases and Salts PPTShubham Sharma100% (1)
- Investigatory Project Chemistry PH in Everyday LifeDocument23 pagesInvestigatory Project Chemistry PH in Everyday LifeHarshita Jain67% (3)
- General Chemistry Week 6 8Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry Week 6 8marjorie branzuelaNo ratings yet
- Here You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostDocument22 pagesHere You Will Get Following Materials:-: All Study Materials in Free of CostHimanshi YadavNo ratings yet
- Acids & Bases: Neha Kapil Scientific Officer NitraDocument33 pagesAcids & Bases: Neha Kapil Scientific Officer NitraNeha KapilNo ratings yet
- Acids, Base and SaltsDocument20 pagesAcids, Base and SaltsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- How Acids & Bases Impact Our Daily LivesDocument16 pagesHow Acids & Bases Impact Our Daily LivesAhmed fatahNo ratings yet
- Organic Derivatives of WaterDocument7 pagesOrganic Derivatives of WaterIra Candice GumafelixNo ratings yet
- Acid, Base and Salt NoteDocument40 pagesAcid, Base and Salt NoteSamuel WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases, & SaltsDocument55 pagesAcids, Bases, & SaltsShelley Chopra ChughNo ratings yet
- Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument21 pagesAcids, Bases and Saltsdarth92vaderNo ratings yet
- Acids: Donating A Proton Electron PairDocument7 pagesAcids: Donating A Proton Electron PairNomi SattiNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Chemistry NotesDocument8 pagesPharmaceutical Chemistry NotesZaheer Uddin100% (1)
- Tiếng anh 6Document78 pagesTiếng anh 6Đạo LêNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry Chapter 7Document39 pagesBasic Chemistry Chapter 7adwinanilNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument11 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsCollins Obari AdiyeNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases SaltsDocument13 pagesAcids Bases SaltsChito JarciaNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument7 pagesAcids and BasesM.zuhair asifNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts NotesDocument22 pagesAcids Bases and Salts NotesHaneefah AhmedNo ratings yet
- 7th Ans 30.08.2020Document3 pages7th Ans 30.08.2020rufusanto2016No ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Notes PDFDocument13 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Notes PDFRajkumari MishraNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases ExplainedDocument92 pagesAcids and Bases ExplainedHo Hsiao JiunNo ratings yet
- Chem Module Acid BaseDocument12 pagesChem Module Acid BaseRANJEET SHARMANo ratings yet
- Bicol University College of Agriculture and Forestry: Acids and BasesDocument23 pagesBicol University College of Agriculture and Forestry: Acids and BasesAngelo Bon BalmesNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases IGCSE NotesDocument15 pagesAcids and Bases IGCSE NotesMisbah KamranNo ratings yet
- Natural Indicators: A Self-Made pH ScaleDocument5 pagesNatural Indicators: A Self-Made pH ScaleJuni FranciaNo ratings yet
- Non-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationDocument35 pagesNon-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationApurba Sarker Apu100% (9)
- Year 7 Chemistry WK 4 L2, 3Document3 pagesYear 7 Chemistry WK 4 L2, 3JennieNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base TheoryDocument7 pagesAcid-Base Theoryariza baylosisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Poster ExperimentDocument8 pagesChemistry Poster ExperimentPutri SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Arrhenius Definition of An AcidDocument27 pagesArrhenius Definition of An AcidnelsonNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases IGCSE NotesDocument15 pagesAcids and Bases IGCSE Notessaowanee toonchueNo ratings yet
- Acid, Base, and SaltDocument12 pagesAcid, Base, and SaltTamoghna DeyNo ratings yet
- Leyte Normal University: Republic of The Philippines Tacloban CityDocument6 pagesLeyte Normal University: Republic of The Philippines Tacloban CityAdrian VerzosaNo ratings yet
- AAH - AR - Etapa 3 - FQEDocument8 pagesAAH - AR - Etapa 3 - FQEAmi ChanNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument26 pagesAcids and BasesAira DeomanoNo ratings yet
- Science Revision All ChaptersDocument9 pagesScience Revision All ChaptersBhavyaa JoshiNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument13 pagesAcids and BasesTahmed HasanNo ratings yet
- What Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterDocument11 pagesWhat Is An Acid and A Base?: Classification of MatterNishidh SinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument10 pagesIntroduction to Acids, Bases and SaltscharanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Acids, Bases and Salts: Classification of MatterSumit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Acid Bases and SaltsDocument26 pagesAcid Bases and SaltsTracy ChangNo ratings yet
- C5-Acid Base and SaltDocument14 pagesC5-Acid Base and SaltHarshaWakodkarNo ratings yet
- Project On ChemistryDocument13 pagesProject On ChemistryBadhal PaudelNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Reaction Report from Salahaddin University Biology StudentDocument6 pagesAcid-Base Reaction Report from Salahaddin University Biology StudentArtiest ArtNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Acid and Base Reactions NotesDocument43 pagesModule 6 - Acid and Base Reactions NotesKristy LamNo ratings yet
- Tests Capsaicin Alkaloid Siling LabuyoDocument5 pagesTests Capsaicin Alkaloid Siling LabuyoNandya Nandiia100% (1)
- CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Key PointsDocument8 pagesCBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Key PointsshanthaNo ratings yet
- Lesson-2 Class 10Document7 pagesLesson-2 Class 10Dishu SinghNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases SaltsDocument74 pagesAcids Bases SaltshaloNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and Salts Class10Document7 pagesAcids Bases and Salts Class10aanbalanNo ratings yet
- Analyzing An Acid SpillDocument10 pagesAnalyzing An Acid SpillMolly Zhang100% (1)
- Acids and BasesDocument11 pagesAcids and BasesDarla GreyNo ratings yet
- Acids & Bases: Properties, Reactions & pHDocument9 pagesAcids & Bases: Properties, Reactions & pHVenusCrazy 550No ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Acids, Bases and SaltsDocument24 pagesChapter 11 Acids, Bases and SaltsSook JeanNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Chapter - A4 - v1Document27 pagesAcids and Bases Chapter - A4 - v1markmchemNo ratings yet
- BASIC ChemistryDocument13 pagesBASIC ChemistryNurharis MunandarNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing For PortfolioDocument7 pagesCreative Writing For Portfolioapi-257471763No ratings yet
- IsisDocument4 pagesIsisapi-257471763No ratings yet
- Acid Baselab 2Document7 pagesAcid Baselab 2api-257471763No ratings yet
- Eradicate Hunger MoroccoDocument2 pagesEradicate Hunger Moroccoapi-257471763No ratings yet
- Religious Tension in LaosDocument2 pagesReligious Tension in Laosapi-257471763No ratings yet
- Ceo's StatementDocument1 pageCeo's Statementapi-257471763No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument15 pagesUntitled Presentationapi-257471763No ratings yet
- Company AnalysissDocument14 pagesCompany Analysissapi-257471763No ratings yet
- William Shakespeare's: The Comedy of ErrorsDocument19 pagesWilliam Shakespeare's: The Comedy of ErrorsAsjsjsjsNo ratings yet
- Iso 128-34-2001 PDFDocument18 pagesIso 128-34-2001 PDFAhmed MaaloulNo ratings yet
- (Inorganic Chemistry Concepts 10) Prof. Dr. Kozo Sone, Prof. Dr. Yutaka Fukuda (Auth.) - Inorganic Thermochromism (1987, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg)Document143 pages(Inorganic Chemistry Concepts 10) Prof. Dr. Kozo Sone, Prof. Dr. Yutaka Fukuda (Auth.) - Inorganic Thermochromism (1987, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg)darkangel9000100% (1)
- Prosedur Penggajian: Payroll ProcedureDocument5 pagesProsedur Penggajian: Payroll ProcedureVira TrianaNo ratings yet
- Test General Product Support Assessment (MOSL1)Document21 pagesTest General Product Support Assessment (MOSL1)Romeo67% (3)
- Students Perceptions of Their Engagement Using GIS Story MapsDocument16 pagesStudents Perceptions of Their Engagement Using GIS Story Mapsjj romeroNo ratings yet
- Polymer Solar Cells PDFDocument19 pagesPolymer Solar Cells PDFJulio Andrés Casal RamosNo ratings yet
- Philippine Duplicators 13th Month Pay ComputationDocument2 pagesPhilippine Duplicators 13th Month Pay ComputationDennis Jay Dencio ParasNo ratings yet
- Utility TheoryDocument43 pagesUtility TheoryMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- ARNU15GL2G4Document2 pagesARNU15GL2G4julioNo ratings yet
- Technical Report: Design of Metal Anchors For Use in Concrete Under Seismic ActionsDocument16 pagesTechnical Report: Design of Metal Anchors For Use in Concrete Under Seismic ActionsJulioGoesNo ratings yet
- Brevini Helical Bevel Helical Gearboxes Posired 2 PB PLB Series - 2022Document76 pagesBrevini Helical Bevel Helical Gearboxes Posired 2 PB PLB Series - 2022Jacob RamseyNo ratings yet
- Sample Integration Test PlanDocument16 pagesSample Integration Test PlanAnkita WalkeNo ratings yet
- Customer No.: 22855256 IFSC Code: DBSS0IN0811 MICR Code: Branch AddressDocument9 pagesCustomer No.: 22855256 IFSC Code: DBSS0IN0811 MICR Code: Branch AddressBalakrishna SNo ratings yet
- MELC 3 Employ The Appropriate Communicative Styles For Various Situations (Intimate, Casual, Conversational, Consultative, Frozen)Document2 pagesMELC 3 Employ The Appropriate Communicative Styles For Various Situations (Intimate, Casual, Conversational, Consultative, Frozen)Mar Sebastian82% (11)
- Earthquake Engineering Predicts Structural Response From Ground MotionDocument21 pagesEarthquake Engineering Predicts Structural Response From Ground MotionSamsul 10101997No ratings yet
- Manual For Renewal of Dog LicenseDocument12 pagesManual For Renewal of Dog Licensescibs123456No ratings yet
- Study Material for Promotion ExamsDocument197 pagesStudy Material for Promotion ExamsamarNo ratings yet
- Annex A C of RMC No. 57 2015Document5 pagesAnnex A C of RMC No. 57 2015Sergy DictadoNo ratings yet
- Linux InstallationDocument4 pagesLinux InstallationRayapudi LakshmaiahNo ratings yet
- Water Pollution in The PhilippinesDocument11 pagesWater Pollution in The PhilippinesJuliane MayorgaNo ratings yet
- In c1 20 Ex CteDocument7 pagesIn c1 20 Ex CteAlejandro HernándezNo ratings yet
- A Sample Demonstration Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesA Sample Demonstration Lesson PlanMarie Patrize Punzalan100% (1)
- Radioactivity PhenomenonDocument20 pagesRadioactivity PhenomenonNeetesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument14 pagesEndocrine System NotesSteven100% (1)
- ASC EVOIPneo Mitel enDocument2 pagesASC EVOIPneo Mitel enService Level ManagementNo ratings yet
- HypertextDocument3 pagesHypertextivyjoyNo ratings yet
- Oath of Authenticity Research DocumentsDocument1 pageOath of Authenticity Research DocumentsPrincess Lynn PaduaNo ratings yet
- Total Chrom TutorialDocument94 pagesTotal Chrom TutorialRachelHechanovaNo ratings yet
- Users Manual of Rdlc320 Control SystemDocument36 pagesUsers Manual of Rdlc320 Control SystemriderbeeNo ratings yet