Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Equation Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
Kuber BakthanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Equation Sheet PDF
Uploaded by
Kuber BakthanCopyright:
Available Formats
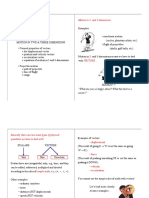
Vectors
Addingvectors
Vectorcomponents
! ! !
If C = A + B then C x = Ax + Bx and
C y = Ay + By
!
A = A i + A j + A k
x
Motionin1D
Displacement
Averagevelocity
Instantaneousvelocity
Averagespeed
Instantaneousspeed
Averageacceleration
Instantaneous
acceleration
Accelerationdueto
gravity
Kinematicequationsfor
constantacceleration
Instantaneous
acceleration
Relativevelocity
!x = x2 " x1
!x
vav x =
!t
!x dx
vx (t) = lim
=
!t "0 !t
dt
total distance s
average speed =
=
total time
t
speed = vx
!v
aav x = x
!t
!vx dvx d 2 x
ax (t) = lim
=
= 2
!t "0 !t
dt
dt
2
g = 9.81 m/s towardthecenterofthe
R=vo2sin2/g
ax = 0 and ay
Centripetal
acceleration
ac =
Thirdlaw
( v0 x + vx )
!x = x " x0 = vav x t =
!x = 12 ax t 2 + v0 x t
vx2 = v02x + 2ax !x
1
2
= !g
v2
r
Tangentialacceleration
dv
,wherevisthespeed
at =
dt
Period
2! r
v=
T
vx = v0 x + ax t
1
2
!
dr
dt
!
!
dv d 2 r
= 2
dt dt
Ifaparticlepmoveswithvelocity v pA
Rangeequation
Projectilemotion
earth
vav x =
!
!r
!
v(t) = lim
=
!t "0 !t
!
!v
!
a(t) = lim
=
!t "0 !t
relativetoreferenceframeA,whichisinturn
!
movingwithvelocity vAB relativeto
referenceframeB,thevelocityprelativetoB
!
!
!
is v pB = v pA + vAB
NewtonsLaws
Secondlaw
Motionin2Dand3D
Instantaneousvelocity
!
!
Fnet = ma
( v0 x + vx ) t
force FAB exertedbyobjectAonB.
!
!
FBA = ! FAB
Whentwobodiesinteract,theforce FBA
exertedbyobjectBonAisequalin
magnitudeandoppositeindirectiontothe
You might also like
- Kinematics: Linear Motion in One Dimension: Class 1Document16 pagesKinematics: Linear Motion in One Dimension: Class 1Able RyderNo ratings yet
- Physics I Fall 2013-2014 First Midterm ExaminationDocument8 pagesPhysics I Fall 2013-2014 First Midterm ExaminationHassan FadenNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 P1Document25 pagesLecture01 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet
- Physics 1:: MechanicsDocument25 pagesPhysics 1:: MechanicsCao Gia BảoNo ratings yet
- Quantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Document5 pagesQuantity: (Uniform Acceleration)Anoni AnonNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument11 pagesPhysicsEthylNo ratings yet
- List of EquationsDocument4 pagesList of EquationsAnonymous y8WGaZOINo ratings yet
- MECHANICS Kinematics: Chapter 2 - Motion Along A Straight LineDocument11 pagesMECHANICS Kinematics: Chapter 2 - Motion Along A Straight LineDan AltmanNo ratings yet
- Solution For Chapter 4 Differential FlowDocument24 pagesSolution For Chapter 4 Differential Flowkombat13_708353334100% (3)
- MET 304 Engineering AnalysisDocument31 pagesMET 304 Engineering AnalysisOscar WangNo ratings yet
- Physics I NotesDocument23 pagesPhysics I NotesZacharyNo ratings yet
- Modul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Document64 pagesModul Xi Sem 1 2009-2010Herman_MLNo ratings yet
- Section1 2Document22 pagesSection1 2James WrightNo ratings yet
- Lecture02 P1Document29 pagesLecture02 P1Vy BuiNo ratings yet
- King Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsDocument22 pagesKing Fahd University of Petroleum & MineralsTommyVercettiNo ratings yet
- CURVILINEAR MOTION COMPONENTSDocument17 pagesCURVILINEAR MOTION COMPONENTSSekut TawarNo ratings yet
- Exam01 EqDocument2 pagesExam01 Eqashish2199No ratings yet
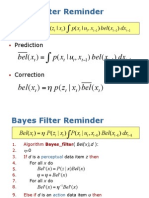
- Bayes Filter Reminder: Bel (X P (X Bel (XDocument26 pagesBayes Filter Reminder: Bel (X P (X Bel (XTaimoor ShakeelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Motion Along A Straight LineDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Motion Along A Straight LineAfnan Azizi100% (2)
- Chapter 11, Solution 71.: COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization SystemDocument1 pageChapter 11, Solution 71.: COSMOS: Complete Online Solutions Manual Organization SystemLUIS ALEXANDER RODRIGUEZ ZAPATANo ratings yet
- Kinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsDocument23 pagesKinematics: Motion of A Particle in One and Two DimensionsJimmy LauNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS 71 - REVIEWERDocument33 pagesPHYSICS 71 - REVIEWERMarc Justin VergaraNo ratings yet
- Lecture01 P1Document30 pagesLecture01 P1thanhgold1105No ratings yet
- Week 1 - KinematicsDocument15 pagesWeek 1 - Kinematicsデーナ(ヤギ)No ratings yet
- All Integral FormulasDocument2 pagesAll Integral FormulasArslanZafarNo ratings yet
- phy201_lect8Document25 pagesphy201_lect8meidinania0No ratings yet
- Particle Kinematics: Part I. Rectilinear MotionDocument18 pagesParticle Kinematics: Part I. Rectilinear MotionbmyertekinNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Kinematics in One Dimension PDFDocument42 pagesModule 2 - Kinematics in One Dimension PDFshadowosNo ratings yet
- POE Formula Sheet Rev 3 - 24 - 12 PDFDocument6 pagesPOE Formula Sheet Rev 3 - 24 - 12 PDFstuart ashrafNo ratings yet
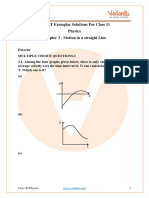
- NCERT Exemplar For Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 - Motion in A Straight Line (Book Solutions)Document40 pagesNCERT Exemplar For Class 11 Physics Chapter 3 - Motion in A Straight Line (Book Solutions)Sanjana MehtaNo ratings yet
- Kinematics of Curved MotionDocument43 pagesKinematics of Curved MotionBEYZA ÇAVUŞOĞLUNo ratings yet
- IntegrationDocument2 pagesIntegrationTeju AshuNo ratings yet
- Integral EulerDocument2 pagesIntegral EulermasrukinmasNo ratings yet
- Equation SheetDocument2 pagesEquation SheetKao LimNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Midterm#1 - Fall2023Document2 pagesFormula Sheet - Midterm#1 - Fall2023M.SNo ratings yet
- Section1 3Document21 pagesSection1 3sonti11No ratings yet
- PROJECTILE MOTION NOTESDocument28 pagesPROJECTILE MOTION NOTESAngelia SombreaNo ratings yet
- HWK Chapter2Document5 pagesHWK Chapter2Carlos Serrano100% (3)
- Power of XDocument2 pagesPower of XmgrfanNo ratings yet
- 2 - 3D MotionDocument14 pages2 - 3D MotionFatah Imdul Umasugi100% (2)
- Solution For Chapter 4 Differential Flow PDFDocument24 pagesSolution For Chapter 4 Differential Flow PDFBowo Yuli PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Kinematics CurveDocument30 pagesTopic 3 - Kinematics CurveBoodjieh So ImbaNo ratings yet
- Calculo Integral 2Document3 pagesCalculo Integral 2tina castilloNo ratings yet
- MCG4308 Lec4Document25 pagesMCG4308 Lec4Christian PaultreNo ratings yet
- CFD NotesDocument68 pagesCFD NotesPraveen P JoseNo ratings yet
- CFD Course Notes OverviewDocument68 pagesCFD Course Notes OverviewPankaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12Document37 pagesLecture 12Sarah Rachel100% (1)
- p1200 Lecture2 PDFDocument32 pagesp1200 Lecture2 PDFTakudzwa MiltonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2. Kinematics in One DimensionDocument74 pagesChapter 2. Kinematics in One DimensionMaggie WestbrookNo ratings yet
- Kinematics in Two Dimensions Projectile MotionDocument17 pagesKinematics in Two Dimensions Projectile MotioneviroyerNo ratings yet
- TIA MLC Formula SheetDocument13 pagesTIA MLC Formula SheetAlex100% (1)
- Kinematics in One Dimension: Giancoli, PHYSICS, 6/E © 2004. ElectronicallyDocument39 pagesKinematics in One Dimension: Giancoli, PHYSICS, 6/E © 2004. ElectronicallySN JohnNo ratings yet
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin OthmanDocument24 pagesUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia: Mechanical Engineering Dynamics DDE2063 BY En. Khairulnizam Bin OthmanSuhayl AzminNo ratings yet
- Tajuk 2Document70 pagesTajuk 2gsharkzNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 NotesDocument12 pagesLecture 9 NotesKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Commentary IOC FinalDocument3 pagesCommentary IOC FinalKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- ItineraryDocument2 pagesItineraryKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Calculus Limits Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesCalculus Limits Cheat SheetKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Physics 121 Spring 2015: Week Day Date Lecture Topic Smartphysics Text Reading HW Tutorial LabDocument1 pagePhysics 121 Spring 2015: Week Day Date Lecture Topic Smartphysics Text Reading HW Tutorial LabKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Jakarta: Important InformationDocument3 pagesJakarta: Important InformationKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- PE 09-28-1 Short Answer ExampleDocument8 pagesPE 09-28-1 Short Answer ExampleKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- BduvudkDocument11 pagesBduvudkKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Campus and VicinityDocument1 pageCampus and VicinityKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Office Hours Today: 2-3+pm in My Office (Padelford C-326) : HW12 (3.4) Closes Today, HW13 (10.2) Closes Monday NightDocument7 pagesOffice Hours Today: 2-3+pm in My Office (Padelford C-326) : HW12 (3.4) Closes Today, HW13 (10.2) Closes Monday NightKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Arch150syllabus Sp15Document5 pagesArch150syllabus Sp15Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- MbaDocument2 pagesMbaKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument3 pagesGRADE 11 Holiday HomeworkKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Intl StatementFinResp 2014Document1 pageIntl StatementFinResp 2014Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document9 pagesLec 2Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Cs Project Report - Sample1Document55 pagesCs Project Report - Sample1Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Intl PaymentForm 2014Document1 pageIntl PaymentForm 2014Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Penny Electroplating LabDocument4 pagesPenny Electroplating LabKuber Bakthan0% (1)
- Facts and Formulas SAT Math 2Document11 pagesFacts and Formulas SAT Math 2Arshad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- GRADE 11 Holiday HomeworkDocument3 pagesGRADE 11 Holiday HomeworkKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 (Option G) Further Organic ChemistryDocument0 pagesChapter 18 (Option G) Further Organic ChemistryKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Writing An Extended Essay in EconomicsDocument3 pagesWriting An Extended Essay in EconomicsKuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- CHS Extended Essay Deadlines Class of 2013Document2 pagesCHS Extended Essay Deadlines Class of 2013Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- Cs Project Report - Sample1Document55 pagesCs Project Report - Sample1Kuber BakthanNo ratings yet
- History PracticeDocument4 pagesHistory PracticeKuber BakthanNo ratings yet