Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ass 2014
Uploaded by
api-252561013Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ass 2014
Uploaded by
api-252561013Copyright:
Available Formats
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014 Final page 1 of 6
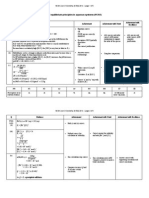
Assessment Schedule 2014
Chemistry: Demonstrate understanding of the properties of selected organic compounds (91165)
Evidence Statement
Q
Evidence
Achievement
ONE
(a)
Draws TWO alcohols correctly.
(b)(i)
Draws the primary alcohol that
is oxidised.
(ii)
Draws the product of the
reaction.
Achievement with Merit
Achievement with Excellence
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014 Final page 2 of 6
(c)
All three reactions are substitution reactions. In all three
reactions an atom or group of atoms is being replaced with
another atom or group of atoms.
In Reaction One; a Br atom replaces an H atom. UV light
is necessary.
In Reaction Two; a Cl atom replaces the OH group. No
conditions are required.
In Reaction Three; the Cl atom is replaced by NH2. No
conditions are required.
Two layers form in Reaction One as hexane is non-polar
and the product (bromohexane) is effectively also nonpolar. The water from the bromine water is polar and
therefore the non-polar organic reactant and product will
not dissolve in the water; because of this, two layers form
as this polar and non-polar layer do not mix.
States that all reactions are
substitution reactions.
States the condition required for
Reaction One.
Explains substitution reactions in
terms of atoms or groups of
atoms being replaced.
Compares and contrasts the
reactions by fully explaining
why all three reactions are
substitution reactions with
reasons involving the atoms or
groups of atoms.
States that water or Br2 (aq) is
polar
OR
Some organic compounds are
non-polar.
Explains why two layers form by
linking the following:
- water is polar and the
bromohexane / hexane is nonpolar
OR
- Polar and non-polar
compounds do not dissolve in
each other.
Explains fully why two layers
form by linking the following:
- water is polar and the
bromohexane / hexane is nonpolar
AND
- Polar and non-polar
compounds do not dissolve in
each other.
N1
N2
A3
A4
M5
M6
E7
E8
No response or no
relevant evidence
1a
2a
3a
5a
1m
2m
1e
2e
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014 Final page 3 of 6
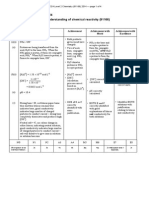
Question
Two
Evidence
(a)
Achievement
Merit
Excellence
Explains that a double bond is
required to prevent free rotation
and therefore it cannot be
molecule C as it has no carboncarbon double bond.
OR
In compound B, one of the
carbon atoms in the double bond
has two hydrogen atoms attached
to it.
Compares and contrasts the
structures by
Explaining that a carbon
carbon double bond is required
to prevent free rotation, and
therefore it cannot be molecule
C as it has no carbon-carbon
double bond.
AND
In compound B one of the
carbon atoms in the double bond
has two hydrogen atoms
attached to it.
ONE structure .
AND
TWO names correct.
Pentanamine or pentylamine or 1-aminopentane
3-methylhexanoic acid
2,4-dichlorohex-3-ene
(b)
Draws the cis and trans
molecules correctly.
For cis and trans isomers to occur a carbon-carbon double
bond must be present as this prevents any rotation about this
bond, and the atoms or groups of atoms attached to the two
carbon atoms are therefore fixed in position. This means that
molecule C cannot have cis and trans isomers as it does not
have a double bond.
For compound B one of the carbon atoms in the double bond
has two of the same atom attached to it (two Hs). Therefore
it cannot have cis and trans isomers because if these two H
atoms swapped position it would still be the same molecule.
Therefore only compound A can have cis and trans isomers
as it does have a double bond preventing free rotation, and it
does not have one of the carbons in the double bond with
two of the same atom or groups of atoms attached to it.
States a double bond required for
cis and trans isomerism.
OR
cannot be C as it has no double
bond.
States it cannot be B as one of
the carbons in the double bond
has 2 of the same atoms attached
to it.
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014 Final page 4 of 6
Na
(c)(i)
Has one product correct for
either reaction (i) or (ii).
(ii)
When propanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate, an acidbase reaction occurs in which sodium propanoate, water and
carbon dioxide are formed. It is acid-base because the
propanoic acid donates a proton, forming the propanoate ion.
When propanamine reacts with HCl or H2SO4, acid-base
reactions occur. Amines are bases and as a result amines
accept protons from acids. In these two reactions both
sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid donate protons to the
amine to form organic salts.
When propan-1-ol reacts with HCl, a substitution reaction
occurs; in this reaction the Cl from HCl replaces the OH
group from propan-1-ol, forming a haloalkane.
The reaction between conc. H2SO4 / heat, and propan-1-ol is
an elimination reaction because an OH group attached to
C1, and a hydrogen atom from C2 are both removed from
the organic molecule. A double bond forms between C1 &
C2, with the elimination of water, forming propene.
States THREE correct types of
reaction.
OR
States a correct type of reaction
with a supporting reason.
Full explains one of the acid-base
reactions.
OR
Identifies AND partially explains
TWO different types of reactions.
Compares and contrasts the
reactions by:
Fully explaining one of the acidbase reactions.
AND
Fully explaining the substitution
reaction.
AND
Fully explaining the elimination
reaction.
N1
N2
A3
A4
M5
M6
E7
E8
No response or no
relevant evidence
1a
2a
3a
5a
1m
2m
1e
2e
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014 Final page 5 of 6
Question
Three
(a)(i)
(ii)
(b)(i)
Evidence
Achievement
Merit
It is an addition reaction because the double bond is
breaking and an H and a Cl are being added to each of the
carbons that were in the double bond.
Recognises that atoms are
being added across the double
bond.
Because the double bond is
breaking and an H and a Cl are
being added to each of the
carbons that were in the double
bond.
It is the major product because the hydrogen atom from HCl
more often adds onto the carbon atom in the double bond
which already contains the most hydrogen atoms; in this
case, C1. Therefore the Cl atom from the HCl joins onto the
carbon atom in the double bond which had the least number
of hydrogen atoms; in this case, C2.
States Markovnikov's rule.
Explains why the major product
forms in Reaction 1.
It is an elimination reaction because two atoms are being
removed from the molecule and a double bond is being
formed between the carbon atoms from which the atoms
have been removed.
Recognises that atoms are
being removed in Reaction 2.
Explains that two atoms are being
removed from the molecule and a
double bond is being formed
between the carbon atoms from
which the atoms have been
removed.
(ii)
Correctly draws the product for
Reaction 4.
(c)(i)
Draws TWO repeating units for
the polymer formed in Reaction
5.
Excellence
NCEA Level 2 Chemistry (91165) 2014 Final page 6 of 6
(ii)
The molecular formulae of the two repeating units of both
polymers are the same, but the structural formulae are
different.
OR
States repeating units are structural isomers.
Addition polymerisation occurs when the C=C breaks and
the carbon atoms in this double bond join to each other from
adjacent molecules to form long chains.
In Reaction 3, the polymer formed will have a carbon with
one hydrogen and a methyl group, and a carbon with one
hydrogen and an ethyl group, as its repeating unit, due to the
double bond being on the C2 position.
In Reaction 5, since the double bond is in a different
position (the C1 position), the polymer formed will have as
its repeating unit a carbon atom with 2 hydrogen atoms
attached, and a carbon atom with one hydrogen attached and
a propyl group attached.
Recognises different positions
of double bonds within the
structures of Reactions 3 & 5.
OR
States that the monomers are
structural isomers or something
similar.
Explains that the double bond
located in different positions
results in two different polymers
Compares and contrasts the two
polymers.
N1
N2
A3
A4
M5
M6
E7
E8
No response or no
relevant evidence
1a
2a
3a
5a
3m
4m
1e
with minor error
/ omission.
1e
Cut Scores
Score range
Not Achieved
Achievement
Achievement with Merit
Achievement with Excellence
07
8 14
15 18
19 24
You might also like
- Learning Objectives As91392Document1 pageLearning Objectives As91392api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2014Document5 pagesAss 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2014Document12 pagesExm 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2012Document4 pagesAss 2012api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2013Document12 pagesExm 2013api-252561013No ratings yet
- As 91435Document3 pagesAs 91435api-271057641No ratings yet
- Exm 2014Document16 pagesExm 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- As 91389Document2 pagesAs 91389api-252561013No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives As91165Document2 pagesLearning Objectives As91165api-252561013No ratings yet
- As 91165Document3 pagesAs 91165api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2013Document6 pagesAss 2013api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2012Document12 pagesExm 2012api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2012Document12 pagesExm 2012api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2012Document6 pagesAss 2012api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2014Document4 pagesAss 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- As 91390Document3 pagesAs 91390api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2014Document12 pagesExm 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2012Document12 pagesExm 2012api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2014Document12 pagesExm 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2013Document12 pagesExm 2013api-252561013No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives As91167Document1 pageLearning Objectives As91167api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2013Document5 pagesAss 2013api-252561013No ratings yet
- As 91167Document2 pagesAs 91167api-252561013No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives As91390Document2 pagesLearning Objectives As91390api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2014Document5 pagesAss 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2014Document6 pagesAss 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Ass 2014Document4 pagesAss 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Exm 2014Document12 pagesExm 2014api-252561013No ratings yet
- Learning Objectives As91393Document1 pageLearning Objectives As91393api-252561013No ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Chemical Bonding Learning Task 2-1: Statement or Answers The QuestionDocument4 pagesChemical Bonding Learning Task 2-1: Statement or Answers The QuestionJerome Fresado100% (1)
- ASNT Supplement To Materials And Processes 2016 新版Document90 pagesASNT Supplement To Materials And Processes 2016 新版xia67% (3)
- Edexcel Chemistry A-level Topic 1 Atomic Structure FlashcardsDocument131 pagesEdexcel Chemistry A-level Topic 1 Atomic Structure FlashcardsHarriet StrattonNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument513 pagesUntitledLalit SharmaNo ratings yet
- 0620 Example Candidate Responses Paper 4Document43 pages0620 Example Candidate Responses Paper 4Hidayah TeacherNo ratings yet
- Kinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Document28 pagesKinetic Molecular Model of Liquids and Solids: Lesson 1Fern Baldonaza100% (1)
- Hints & Solutions: NSEJS - STAGE-I (2016-17) Paper Code: Js-530Document11 pagesHints & Solutions: NSEJS - STAGE-I (2016-17) Paper Code: Js-530Bhuvnesh MathurNo ratings yet
- General ObjectivesDocument20 pagesGeneral ObjectivesSamuel BlessNo ratings yet
- R K Sharma Coordination Chemistry 10-30Document23 pagesR K Sharma Coordination Chemistry 10-30Kamal KishoreNo ratings yet
- F2 End Term ExamsDocument78 pagesF2 End Term ExamsOchieng WilberforceNo ratings yet
- Isosterism and BioisosterismDocument7 pagesIsosterism and Bioisosterismmezuniga1100% (1)
- WAEC Chemistry Syllabus 2022 PDF Download AvailableDocument26 pagesWAEC Chemistry Syllabus 2022 PDF Download AvailableSamuel AikinsNo ratings yet
- CHM-2045 Exam 1 Sample QuestionsDocument7 pagesCHM-2045 Exam 1 Sample QuestionsFrankNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 7th Edition McMurry Solutions Manual DownloadDocument6 pagesChemistry 7th Edition McMurry Solutions Manual DownloadRoger Wright100% (21)
- Biological Science Canadian 2nd Edition Freeman Test BankDocument26 pagesBiological Science Canadian 2nd Edition Freeman Test BankPaulPowerscxjy100% (53)
- Chemistry 1152 Practice Final ExamDocument18 pagesChemistry 1152 Practice Final Examdeckbyte865No ratings yet
- Chem 373 - Lecture 26: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules-IDocument20 pagesChem 373 - Lecture 26: Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules-INuansak3No ratings yet
- Beginning Organic Chemistry 2Document2 pagesBeginning Organic Chemistry 2Daniel Alejandro Rojas ToroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Powerpoint Honors - Student VersionDocument131 pagesChapter 8 Powerpoint Honors - Student VersionMario PachecoNo ratings yet
- Bansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEDocument824 pagesBansal Classes Chemistry Study Material For IIT JEEHarshitShukla0% (1)
- PharmacologyDocument148 pagesPharmacologyJean Libay PekasNo ratings yet
- Molecular Shapes and VSEPR TheoryDocument24 pagesMolecular Shapes and VSEPR TheoryAly HashamNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates LabDocument15 pagesCarbohydrates LabFrancis Ryannel S. De CastroNo ratings yet
- Acid StrengthDocument6 pagesAcid StrengthRachel CauNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications 3rd EditionDocument12 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry With Biological Applications 3rd EditionJohnny Shields100% (35)
- Assignment - 1 Book 1Document8 pagesAssignment - 1 Book 1Game FactoNo ratings yet
- Full PDFDocument634 pagesFull PDFFATHIYA RIZQA SALSABILLANo ratings yet
- CH307 Inorganic Kinetics: Dr. Andrea Erxleben Room C150 Andrea - Erxleben@nuigalway - IeDocument50 pagesCH307 Inorganic Kinetics: Dr. Andrea Erxleben Room C150 Andrea - Erxleben@nuigalway - Ieneel721507No ratings yet
- Aromatic CompoundsDocument9 pagesAromatic CompoundsAmany100% (1)