Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Wttr宰: hottht.″ us…
Uploaded by
Klorin Min0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views6 pagesBernoulli Principle
Original Title
Bernoulli
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentBernoulli Principle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
96 views6 pagesWttr宰: hottht.″ us…
Uploaded by
Klorin MinBernoulli Principle
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
wie sd by.a moving fu
11. Wheh the water in the fube is not moving, the water level in
the vertical tubes aro th
Bernoull r
regular horizontal
tube
‘This shows that
2, When the stopper atthe énd X is opened for water to low,
the water levels ofthe vertical tubes decreases in height.
‘Thus ‘Water flows from
region of . to region of
3, A Bemoulli tube has a narrow passage along the horizontal
tube, At B, water flows with a ;
and exerts The water ate
level above B is the .. 7
narrow
en water out
‘4, Bernoulli principle states that as the velocity of a fluid increases , the pressure it exerts decreases.
5. Inthe diagram shown, when air is blown through the horizontal
tube, the air pressure in the horizontal tube decreases.
. force the water level in the
vertical tubes to rise. As air moves from a region of |
pressure to a region of ......+-+n10 pressure, therefore
‘The water level in the vertical tube
below Cis the as. eee
6. Ifair is purtped through a Bernoulli tube as shown, air will flow
at the narrow seetion creating a region of
stesussegerstesceesess Atmosphefie pressure will
force water to the highest level below B.
1's Hold @ sheet of paper horizontally in front of the mouth.
* Blow air acréss the upper surface of the paper.
* Observation; The free end ofthe paper is seen to rise.
2. * Hold two sheets of paper vertically and separated by a few em near the mouth
* Blow air through the space between the two sheets of papers.
the two sheets of paper are pressed together.
3 * A filter funnel is inverted and a ping pong ball is held under it.
* Airis blown at high speed through the funnel and the bal is released.
* Observati
blow hava
the ping porig ball floats under the filter funnel.
* Explanation
vnc
va
3 hm iy par wey Bh horizontal stow
* Hold a rnking sr heron otha oni endisnerthe opened endothe ES
vertical straw, —2verbical stras
* Blow air through the horizontal straw.
* Observation : Water level in the vertical steaw ris
** Explanatio
Bunsen burner
2.
3
4
s.
‘When the gas supply is connected, the gas flows through a narrow passage (Jet) tareed
near the air hole with .
‘The region near the jet experienced... a
“gas,
‘The outside air which is at a higher pressure is drawn in and mixed with the gas.
‘The mixture of air and yas flow up the barrel and is burnt completely.
When the air hole is closed, there isnot enough air resulting in incomplete
Acrofoil '
1
2.
3.
4
5
6
‘An aerofoi has top surface which is arched
anda relatively at bottom surface.
Air lows with higher velocity over the top
creating a region Of vrernsninesneneneee
Air flows with lower velocity below the aerofoit Qerofoil
creating a region of so
“There is a net upward pressure producing
anet upward force known as lift acting on
the aerofotl.
‘Aeroplane and its wings take the shape of aerofoil. When the velocity
ofthe aeroplane exceeds the stalling speed, the lit is
than its weight, the aeroplane takes off.
Flaps and slates on the wings can be extended to increase the
of the wings. It can help to produce
}
Flap
.-» during take off. (* Ifthe flaps are up, S/ate
- Raising of lowering the flaps will also Ce
increase the air resistance known as drag )
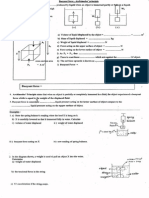
Questions :
2.
8) Draw a diagram to show four forces acting on an aircraft when itis flying with uniform velocity at a constant latitude,
b) State the relationship between the forces.
©) Explain briefly the pris
‘Acrofoil is used in racing cars as stabilizer, Explain how it works.
ples of the forces acting
. Ifa pilot puts up the flaps of one wing and the laps down on the other wing, what happens to the aircraft?
Most commercial jet aircrafts fly at very high altitudes.
a) What isthe m:
) As the altitude increases, what will you expect to happen to the minimum speed at which the aircraft can remain
idvantage of this?
airborne? Explain.
40
coor sr
sonamane> 2 un 5 wonatr00a nt
sofue sm foo000 Swoqo; 2m
cantor V ar; J TMA “WHO Fe OU s20p
sons roroco Sumopoy aN ci ft ‘peeeoq pooerd eq Suod urd
amas @ pone aquebapdpongsyimomeg Z| JL ear orp oy spo oye
amy Joye snous 21 amg
songro ry ‘dou .
pe ung sung (P) sqmouog a1sonu ot é 3
mud : usuyndo we snoys otamiiy B11 afl ‘Smeone
; 5 an
hi a a syypy‘aépund sgmmoug,
-rsn 23 pt uo paseq zouopesiiommgry “fh
semen
oo
‘pent
Teg 2xpo pods xp
‘sen mn51 307 women
pao nen 2p a A
‘ag 29770 THAN ogy
ahi el dzi on gor Yb 98)
g'2aRsTp
229 96 Dh o¢ 92 a aq po arena eA 2
Ting Spun
‘eymapad iar
‘pans atp Jo suonroydde Ayep om} 2ureN] (Pp) Ld
rome
O mnonaee, = "
ap pasjouu agpuud esiyd 00 EN, (°) SSS sae samp inept ¥
r eS saxiQond smoung yen
‘e) up oasur om wed (a) pou nouea eH ‘ony Siga Bayonoj 20 30 RIN. “g
2 pus O soqna ayn UL se ‘aq ¥ xBeonp SemHoy
opeoy po sun uy voneazsge an as (@) jo mans w snows Tz aR 3
Tami quod
_— aS on Rieeea aa
= sroinansonm ell ¢ ‘urn.oxfiny cesar se steqnyeeuromyjouons
r= ar) a , sunmystnniiney q MAEMO MTROPEE Lh oo fname eon ¥
| game stood fe 20) 2 ae “yur sayy - ‘asmzaaq sma00
1“ rode woo st asad qamod
etre ommn yagRONeR EMU 0 me ee sonoma 0
\ STOEL ypuryvonmmarny q) Xmoeamendaa ou,
‘a
yma, ve amend ae amp Spo ma
al oll sopmowmnanaid Vy amed we anemad wo son rma 4
7 K $5 auaufishtod
-yomdyy DigeqmUAER;OREAD — ywodwhpoaLTspe2a!9 aa uanty
uj uaoys se uondonp apm smresedde atp Ynop apie X mod 7 Apopn Te aud
tao sate PUR O 4 saqra JeORIA DOIN B seecrnd
29 B ‘Dora aq 21 aod e Ayr eam sp3o19
— ese tama 51 “El unownn moy or pamome st Se) ‘X yod ye Aysuep ye ONL V
{C1 Win wo caste moving tama he sme vcard sitet side, the dives el ha ts iu to msn a close ; pe
N\A etter hm bestia em evig var xch ter Th phenomena canbe explained using 3. Fue hows © ping pong ball eld inside after
sie
oct ofthe airbetwen the car faster or slower if eomparedto the velocity of atthe outer side of the fos down ong tee
ve reso (2) () Mark the region inthe diagram where the
(© Using sven) an expavhy xs are moving twa ech lies () site the coon eo esr in
a caris moving i ona sigh si if
(aces cming uray setsmodhost ecxsensiobe ting. Expintow tis) () Maa te fet acing onthe pig
. ong ballin Figure 1.
(©) Suggest away to overcome the phenomena in (in arcing ca ©) Explain how the forces, 2 marked prevent
. the ball from fling tothe !
2 2 © Explain what wil happen wher
1 bat ais replaced wih a nibber ball ofthe same
he 1, (0) arvenits Pipe stato at aninreaso fo epeed
A ‘oa foning Mid wl causa dcreaso in is postira
sila cnc ged tans
| (8 Tovoly fas reuse pce beeen
becarv ey sal
= et (©) Since the air between the two cars is moving so fast, R
eines germatea er presse ber compre Db er
gue above shows ht re fou fore acting onthe eoplane porn cl thc Tere, high ress a e
(a) Name the forces F,, F,,F, and F,. ini ig outer side of the car wil push the car inwards towards,
ober
Susterconedo fens bce
xo cowrcs preston ter bo
snot choses, ee pata cey
C= bocturocs heen scon be tu sae as
foalog phenomena. The asf designed 9 have
et high pressure at the op of te car and lower pressure
‘The Figure shove shows te seofol design ofthe wing ofan aeroplane. att atom co a cr wb pushed dowrards
(Marke area with highest velocity using an alphabet X and lowest velocity witha Yin the Figure above. ‘ote ground.
eS heaaer ee aeerennaaneante ‘evi 2) Fn tet F Ut oF Ares,
Gi) Why isthe aero shape used inthe design of an aerplace’s wing? nent
®
(iv) State2faetors which woald influence the resultant force acting onthe aro. x
=p towatectap
sites hose a pas
ser tert (Tra aero shape wil maketh vlotysbove to
“wing higher tan te vlc below th wing. This
‘Peer pong be rate wil create a high pressure at the bottom of re wing,
‘and he iting fore creatd wil it the aeroplane to.
caus oy.
Figure (09) Horzonta veloc ifthe aeroplane fat an
angle facing the movement ir
foe hone pad ce
Tsang
srz20N,
FISHY SLOMEN C_ajdyouna spsuPLY 9
2 ‘Soumey olpurs omy woomtod | dioua satinowed ajdioungsjeosed ¥
{Buons sao wopms e smoys 71 uesieig 'g juowamovayd axoge ap suredxo HOR
‘xo Jou s20p 3
umop 240m [I
un nay 1 aang
Jaded amp Jo ofpo amp ‘saded
3H 0 don vo waoyg st AOA HEI 38 se Uo o8.0 way
"AOU BU,
vaGong
aonpoud sty moy mejdg_ (0) ess pone pup Buons £q pouH
ae Pins OPM upg osnoy v Jo Joor ain saoys 1] wee Z
ed a wo sce win yo uonoanp Ea
pars amg wo x09
“wonisod —S
— a 2
fury 1 soded amp sosme> mp 2ax0j st (Q) ‘soy ary
i ons yor
C2 TE ANA PI& oy edu sd Jo sone snows eed
1S amd uy saded 2p yo uonisod ap amediuoy (8)
amssaad ysemoy 2tp ssouatiodya a v
“7S amajy ut umoys se vonssod sy sa8ueyo soded oxy ‘dean
{fue Jo a[zz0u om Wo SmoY se Uoyy Pus HOV 8 wy SuBuEy ded Jo aoxd © saoys 1 amnBiy “9
“20.9 ‘a ‘V ‘wonssod yoy LmoKp uoanieq HAO}
peal 81 ame woqie seq Buod-Bud 247 Jo uoprpu0s
2f9Q, Ip sous sweep Suvmoqjos om Jo TIA
9 uo ig
m
a b umhng
“ipBuoy aures aip Jo sBumns wo papuedsns
eq Suod-Juid sms om swoys 6 wes y
‘ost soppueo ay) Jo won0g amp 78 OH
sour
‘tpues am uod0uIq vox uNNoeA
souroseg sourey aypuo
seumey 2ipur>
‘Touum pura w ut poowyd adeys
noe ue MI oolGo we SmOYS EF MIEBEIC. “ge =r iS
syvak svd Was
4 Lesson 30: answers
1, same, Py=Py=Pe= Pion + Pye
2. Pa > Pp > Pc, high pressure , low pressure
3. higher speed, lower pressure , lowest, Py > Pe > Pa
=P regular horizontal
‘tube
water
ia?
5. atmospheric pressure , high, low, P, > Pp > Pc, highest. 6. faster, low pressure, Px > Po > Py
aie air alt
iy Sree ee SS
woe_ta if ot
1, Blowing causes the air to move faster ereating a region of low pressure. The atmospheric pressure acting from below, which is greater,
pushes the paper upwards.
2. The fast moving air between the two sheets of paper creates a region of low pressure. The atmospheric pressure, which is higher,
acting from outside, pushes the papers towards one another.
blow hard
3. The ar flowg faster between ping pong ball and wall of filter funnel
creating a region of low pressure. The atmospheric pressure
acting from below the ping pong ball is higher.
‘There is anct force upwards, pushing the atl agains the wall of iter funnel
4. The fast moving air lowing out of horizontal straw creates a region of
Jow pressure at the open end ofthe vertical straw.
“Atmospheric pressure foroes the water level to rise,
‘iy moves, faster,
high spent,
oe foo pressure mio!
Tow prescurt
Application of Bemoulli principle
‘Bunsen burner; 1, high speed 2. low pressure. 5. combustion
Acrofoil : 2. low pressure 3. high pressure
5. greater
6. surface area, lift
Questions Lift
1. ~ Engine thrusts produced when gas burt is ejected causing
‘change of momentum,
~ rag is pruced by ai esistance engine lag
~ Weight isthe force acting onthe mass by gravitational pul, thrust
~ Lifts caused by the net pressure upwards when the agplane
move against the air stream. nt
2. The aerofil is fited with the arched surface downwards on top "
‘of the back wheels. This produces a net force downwards to press
the wheels on the road making the ear more stable.
3. One wing goes up, the other wing comes down causing the airplane to bank.
4. a) Air is thinner, there wil be less air resistance.
b) The aircraft needs a higher speed to stay airborne. The density of air decreases, the ff produced also decreases.
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- 47 - Optical Devices 2Document7 pages47 - Optical Devices 2Klorin MinNo ratings yet
- ETasci 2013 SurfacePreparationHowToDocument14 pagesETasci 2013 SurfacePreparationHowToMASIZKANo ratings yet
- 1409 3880v1Document32 pages1409 3880v1Klorin MinNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature WorksheetDocument3 pagesNomenclature WorksheetKlorin Min100% (1)
- Review1Worksheet PDFDocument2 pagesReview1Worksheet PDFKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument36 pagesPDFKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Chemicalworksheet PDFDocument2 pagesChemicalworksheet PDFKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- See BreezeDocument1 pageSee BreezeKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Ading W2轟: Mass Ofliquid Displaced=.… C) Weint Ofliq遍Document6 pagesAding W2轟: Mass Ofliquid Displaced=.… C) Weint Ofliq遍Klorin Min100% (1)
- Peka ChemistryDocument2 pagesPeka ChemistryKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Exercise Form 1 Chapter 4 Variety of Resources On EarthDocument5 pagesExercise Form 1 Chapter 4 Variety of Resources On EarthSyahrul100% (1)
- Quadratic EqnDocument7 pagesQuadratic EqnSolehah Abdul RahimNo ratings yet
- 94605Document36 pages94605Klorin MinNo ratings yet
- ETasci 2013 SurfacePreparationHowToDocument14 pagesETasci 2013 SurfacePreparationHowToMASIZKANo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of GrapheneDocument3 pagesThermal Conductivity of GrapheneKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Straight LineDocument20 pagesStraight LineSolehah Abdul Rahim100% (3)
- Chapter 2 Questions BankDocument6 pagesChapter 2 Questions BankXuan Deng FamNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument6 pagesAnswerKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- 2 0 Forces and Motion1Document35 pages2 0 Forces and Motion1Klorin MinNo ratings yet
- March April 2015 Examination Timetable-AmendedDocument52 pagesMarch April 2015 Examination Timetable-AmendedKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- 1P01 EngDocument8 pages1P01 EngKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Qeq MethodDocument6 pagesQeq MethodKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Postulates of Atomic ModelDocument2 pagesPostulates of Atomic ModelKlorin MinNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Study of The Structure of Silver Clusters: Rene FournierDocument13 pagesTheoretical Study of The Structure of Silver Clusters: Rene FournierKlorin MinNo ratings yet