Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
johnsonOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
johnsonCopyright:
Available Formats
7
CHAPTER II
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter presents the foreign and local related literature and studies,
conceptual framework and definition of term.
Review of Related Literature and Studies
The research included the following related literature and studies which
also tackled regional approach, curriculum and instrumental development which
reiterate the researchers study.
Related Literature. According to Cabrera (2012) education has been
regarded as a means toward economic stability and progress. The increase
productivity of the workforce is due mainly to the increase in the education and
training of the people. The success and development of the country would greatly
depend in the productivity of its human resources- which is considered as one of
the vital asset of the nation. And to have a good and competent manpower
resource; quality education and intensive training are necessary for the students
to become skilled and productive workers when they become part of the labor
force.
According to Dominguez and Romero (2009) employers believed that
applicants who have undergone job training are assumed to be more
knowledgeable and production. Also, they are competent enough in connection
to the job for there are respondents who had a problem with their co-workers in
terms of their differences in terms of principles and ideas which are expected in
an agency.
According to GOPINOY.com provide a list of good work habit to develop
such as: 1.) Set up a goal or a mission and apply a strong work ethic to provide
you that sense of direction needed to accomplish quality tasks in the shortest
time possible. 2.) Think positive. Do not think of the complexities of your job
instead, consider these difficulties as a challenge. Deal with the problem, do not
avoid them. Youre going to have to face the same problem eventually. 3.) It is a
good work habit to give importance to good attendance and punctuality. Doing so
can get you off to agood start and it can be a positive asset on your part. 4.)
Apply neatness, orderliness and speed by cleaning up and getting organized. It
allows you to work faster since it's easy to find things when the workplace is
clean and sorted out properly. 5.) Plan your day ahead of time. This is one of the
most important among the good work habits you should develop. List things that
you should prioritize to work the next day. This could guide you whenever you get
side tracked and forget what your original purpose was.
6.) Work smarter, not harder. Manage your time well; segregate activities into
time wasters or maximum use of time. Time wasters such as telephone calls and
dealing emails can just be kept short and on topic as well as keeping email
accounts separate for personal and work use. Focus on the list of priorities you
make and set limits for each task. 7.) Become self-employed psychologically.
Think of yourself as your own boss. You would want to make things happen in
the business, do good quality output and receive bigger income from it. Putting
yourself on the situation can motivate you to do great results. 8.) Play the inner
game of work. Know your purpose at work and do it with your own best innate
desires and abilities. These will help you to acquire all the ideas, successful
habits and best practices you will need in accomplishing tasks. 9.) Reduce
procrastination by motivating yourself with rewards or punishments. Postponing
or delaying one's work can cause career sabotage so be aware of its
consequences and try to be more positive.
Mendoza as cited by Bahian (2008) asserted that the students level of
achievement in significantly related to the on the job training what the students
learn from the classroom is what the students apply during OJT. The school
provided related instruction ad related skills; the role of industries is to sharpen
the students competencies ad activities. Thus, cooperating industries should
provide the student trainees the necessary reserves needed to improve their
performance level of proficiency and specific skills and field of specialization.
According to Koontz (2007) many opportunities for development can be
found on-the-job. Trainees can learn as they contribute to the aims of the
enterprise. However, because this approach requires competent higher level
managers who can teach and coach trainees, there are limitations to do on-thejob training. Planned progression is a technique that gives managers a clear idea
of their path of development. It may be perceived by trainees as a smooth path to
the top, but it really is a step-by-step approach which requires that task to be
done well at each level. Trainees learn about different enterprise functions by job
10
rotations. They may rotate through: non-supervisory work, observation
assignments (observing what managers do, rather than managing themselves)
and therefore has positive aspects and should benefits the trainees. Assistant to positions are frequently created to broaden the viewpoint of trainees by
allowing them to work closely with experienced managers who can give special
attention to the developmental needs of the trainees.
On-the-job training is a never-ending process. Patience and wisdom are
required of superiors, who must be able to delegate authority and give
recognition and praise for jobs well done. Effective coaches will develop the
strength and potentials of subordinates and help them overcome their
weaknesses. As mentioned by on-the-job training is one of the oldest and most
used types of informal training. It is considered informal because it does not
necessarily occur as part of a training program and because managers or peers
can serve as trainers. He further stated that if on-the-job training is too informal,
learning will not occur. On-the-job training has several advantages over other
training methods. It can be customized to the experiences and abilities of
trainees. Training is immediately applicable to the job because OJT occurs on the
job using actual tools and equipment. As a result, trainees are highly motivated to
learn. There are several disadvantages in the OJT approach. Managers and
peers may not use the same process to complete the task. They may pass on
bad habits as well as useful skills. Also, they may not understand that
demonstration, practice and feedback are important conditions for effective onthe-job training.
11
Effective OJT program include: 1. A policy statement that describes the
purpose of OJT and emphasizes the companys support for it. 2. A clear
specification of who is accountable for conducting OJT. 3. A thorough review of
OJT practices at other companies in similar industries. 4. Training of managers
and peers in the principles of structured OJT. 5. Availability of lesson plans,
checklists, procedure manuals, learning contracts and progress report forms for
use by employees who conduct OJT. 6. Evaluation of employees level of basic
skills before OJT.
Principles of On-the-Job Training Preparing for Instruction 1. Break down
the job into important steps. 2. Prepare the necessary equipment, materials and
supplies. 3. Decide how much time you will devote to OJT and when you expect
the employees to be competent in skill areas. Actual instruction 1. Tell the
trainees the objective of the task and ask them to watch you demonstrate it. 2.
Show the trainees how to do it without saying anything. 3. Explain the key points
or behaviors. (Write out the key points for the trainees, if possible.) 4. How the
trainees how to do it again. 5. Have the trainees do one more single parts of the
task and praise them for correct reproduction (optional). 6. Have the trainees do
the entire task and praise them for correct production. 7. If mistakes are made,
have the trainees practice until accurate reproduction is achieved. 8. Praise the
trainees for their success in learning the task.
Related Studies. Cristobal (2008), conducted a study entitled The Onthe-Job Training Program of Urdaneta City University. The research respondents
were the students enrolled in the Bachelor of Science in Commerce, Major in
12
Management, Management accounting, Banking in finance, Bachelor of Science
in accountancy and computer secretarial and who are currently enrolled in their
practicum course S.Y 2007-2008. The respondents overall perception toward
relevance and suitability along OJT are: 1.) The students practices weighted
mean of 2.94; 2.) The problems encountered by the students in the OJT program
were slightly serious as shown by the weighted mean 2.14; 3.) The problem
encountered by the supervisor in the OJT program was slightly serious as
evidenced by weighted mean of 1.78; 4.) The problems encountered by the
instructor in OJT program were slightly serious as shown by the weighted mean
of 2.11.
According to Cristobal the OJT program is a good program for augmenting
the knowledge skills and competencies of the task and activities included in the
OJT are routine that do not really require the application of the higher knowledge,
skills and competencies learned in the classroom. Initially the respondents are
not familiar and have difficulties in using the modern devices and equipment
used in their OJT.
Jaso (2007), proposed on the training for automotive technology at
Sorsogon State College. In his study he include the problems not by students
along the in the job training. It was disclosed that non-congruence between the
acquired level of competence is an automotive technology of their in job work
experience. The following are the problem encountered: 1.) Lack of congruency
between competencies learned in automotive. 2.) Lack of coordination between
ILDO and the partner industry. 3.) No work plan clearly presented to the OJT
13
along training requirements, expected behavior and placement. 4.) Lack of
supervision on the OJTs work performance. 5.) Lack of identified local shops
and industries where OJTs area of competencies in the areas AT-51, AT-52 and
AT-53 are needed. 6.) Work assignments of OJTs include menial and unrelated
jobs. 7.) Lack of options for OJTs to choose their work assignments in the
partner industry. 8.) Financial difficulties among OJTs. 9.) Lack of administrative
support to OJTs.
Another problem is the absence of work plan where training requirements,
expected behavior and replacement are identified the OJTs trainees are not
always supervised in their work performance. They also disclosed that local
shops are not identified where they could apply their competencies in AT-51-52
and AT-53. Some of the on the job trainees are asked to do menial jobs unrelated
to their training. They do not have options wherein to choose their work
assignments. Most of the OJT trainees felt the lack of administrative support in
the outside school training and many experienced financial problems. From the
disclosed problems among on the job training could be deduced that the
objective of this training program for students in automotive technology is
defeated. It means that there is a need to look into these problems for the benefit
of these students. The revealed problems imply that the success of the on the job
training programs depends on the collaborative efforts of the college and the
partner industry where students are assigned. The solutions to these problems
rest on the persons concerned for the welfare of the students.
14
Mamadra (2005), also conducted a study to find out the impact of the onthe-job training programs on the skills and values development of students in the
four areas of specialization such as automotive, electronics technology, computer
technology and electrical technology as well as the students values development
in terms of work attitude, self-reliance, self-discipline, resourcefulness, honesty
and patience among selected vocational-technical tertiary institutions in
Mindanao. In her study it was found out that the impact of the on-the-job training
program on skills and values development of the students depend on the
approaches of the skilled mentors to supplement the student trainees
competence in the classroom as well as the concepts that both the school and
the industries work together in the training of technological students as future
industrial workers.
The study of Decena (2005), entitled On the job training program of the
two year trade Technological University in Iba,Zambales give emphasis to some
items in the assessment instruments where the response of cooperating trainees
ad student trainees are not different such as: a. For objectives (to enable the
students to work a sophisticated equipment ad to prepare students for social ad
personal). b. For the assessment instrument on linkage (Inform the head of
educational institution of developments in the establishments whether positive or
negative). c. For the assessment instruments on industrial policies (Help student
trainees for advancement opportunities in the cooperating establishments); and
(Observe general rules and regulations of the company such as filing of leave,
working hours, use of uniform, good grooming, safety housekeeping). d. On
15
monitoring of trainees (OJT coordinators meet with industrial trainer and student
trainees during work site visitation); (Keeps records of all activities related to
industrial training); and (Participates in the evaluation of student trainees). e. On
problems encountered (tools are just enough for regular workers). f. On remedies
of problems (Requested some regular workers to bring extra hand tools)
Sony and Kim (2005) conducted study entitled Changes in attitude toward
work and workers identity in Korea. They summarize the conceptualization of
work ethic to the fact that the concept of work ethic has multiple meanings and
implication, pertaining to a variety of aspects related to work, including work
commitment, work value, attitude toward work, occupational value, organizational
commitment, perception of career development, ad work achievement.
According to the General Accounting Office (GAO) conducted a nationwide survey of Title III JTPA programs between 1982 and 1985. The survey
indicated that 80 percent of program participants received job search assistance,
compared with only 26 percent who received classroom training and 16 percent
who received on-the-job training. The low proportion of participants actually
receiving training resulted from the fact that trainers were largely funded on the
basis of job placement, not long-term labor market preparedness or earnings
improvement. Based on the General Accounting Office survey and an additional
year of study, the U.S. Department of Labor recommended greater emphasis on
job training to meet the needs of specific employers and particularly on on-thejob rather than classroom training.
16
In the statistical analysis in the study of Sirota et. al (2005) showed that a
level of achievement has six primary sources : 1. Challenge of the work itself
the extent to which the job uses an employees intelligence, abilities and skills. 2.
Acquiring of new skills; 3. Ability to perform having the training, direction,
resources authority, information and cooperation needed to perform well. 4.
Perceived importance of the employees job the importance to the organization,
to the customer and to the society; 5. Recognition received from performance
non financial (such a simple thank you from the boss or a customer) and
financial (compensation and advancement that are based on performance.); and
6. Working for a company of which the employee can be proud because of its
purpose, its products ( their quality and their impact on customers and society),
its business success, its business ethics (treatment of customers, employees,
investors, and community), and the quality of its leadership.
You might also like
- Final For Influence of OJTDocument39 pagesFinal For Influence of OJTAnthony B. AnocheNo ratings yet
- Ako Ang Finale Joane NarrativeDocument40 pagesAko Ang Finale Joane NarrativeJames WilliamNo ratings yet
- Adamson University Student Secures InternshipDocument5 pagesAdamson University Student Secures InternshipJim Bryan RazNo ratings yet
- Key Concerns and Steps for Staffing International Operations with ExpatriatesDocument1 pageKey Concerns and Steps for Staffing International Operations with ExpatriatesMaureen LeonidaNo ratings yet
- Dalawinon Farmers Cooperative: A Community of Growth and EmpowermentDocument7 pagesDalawinon Farmers Cooperative: A Community of Growth and EmpowermentShany Mae PlaydaNo ratings yet
- I. Significant LearningDocument3 pagesI. Significant LearningLaizel RodulfoNo ratings yet
- O o o o o o O: Economic SustainabilityDocument4 pagesO o o o o o O: Economic SustainabilityFirst LastNo ratings yet
- My OJT Journal Week 1 (WCPD) : Monday 7:00am - 5:00pmDocument6 pagesMy OJT Journal Week 1 (WCPD) : Monday 7:00am - 5:00pmRose Ann Mae PescasioNo ratings yet
- A Narrative Report On Government Agency and Other Agency Related Establishments On-The-Job Training ProgramDocument18 pagesA Narrative Report On Government Agency and Other Agency Related Establishments On-The-Job Training ProgramBenj Jamieson Jocson DuagNo ratings yet
- Ayala CorporationDocument3 pagesAyala CorporationEuniceChungNo ratings yet
- Challenges customs brokers faced during the pandemicDocument2 pagesChallenges customs brokers faced during the pandemickatlicNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report OJT First SemDocument8 pagesNarrative Report OJT First SemAnjello De Los ReyesNo ratings yet
- Criminology Internship Report 11Document16 pagesCriminology Internship Report 11Karlz LimNo ratings yet
- Reaction PaperDocument1 pageReaction PaperMerari ValenciaNo ratings yet
- The Premier University in Zamboanga Del Norte: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityDocument1 pageThe Premier University in Zamboanga Del Norte: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityCHARLEES BRAVONo ratings yet
- On The-Job-Training Experience at PersonivDocument3 pagesOn The-Job-Training Experience at PersonivCharle TsaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document13 pagesChapter 5Alna JaeNo ratings yet
- Abstract BSCA 2010 2015Document46 pagesAbstract BSCA 2010 2015Rea TapiaNo ratings yet
- EMPENO - MYCAJANE - F-NARRATIVE-REPORT ExampleDocument38 pagesEMPENO - MYCAJANE - F-NARRATIVE-REPORT ExampleIan Mateo VelascoNo ratings yet
- Narrative ReportDocument1 pageNarrative ReportL.J. IlaganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 NEWDocument6 pagesChapter 3 NEWAlexandria SamaritaNo ratings yet
- Chinese TycoonDocument1 pageChinese TycoonCenon Aquino100% (1)
- Code of Ethics of Customs BrokersDocument6 pagesCode of Ethics of Customs BrokersElla Mae Mahinay VillarinNo ratings yet
- Total Quality Management Strategies of Multi-Pack CorporationDocument31 pagesTotal Quality Management Strategies of Multi-Pack CorporationGwen BrossardNo ratings yet
- Interview Procedures Telecom Sector BangladeshDocument3 pagesInterview Procedures Telecom Sector BangladeshJamir ShakhawatNo ratings yet
- Customs warehouses and bonded facilitiesDocument2 pagesCustoms warehouses and bonded facilitiesAce ParkerNo ratings yet
- Internship Week ReportsDocument12 pagesInternship Week ReportsDrei Gardiola AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Ra 9280Document7 pagesRa 9280Jay-arr ValdezNo ratings yet
- Standard With Styling-2018Document6 pagesStandard With Styling-2018Ramoncito C. PascuaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Ojt Buo Chapter 1 4Document53 pagesThesis Ojt Buo Chapter 1 4reyansranocoNo ratings yet
- B. Narrative Report About PdeaDocument3 pagesB. Narrative Report About PdeaSophia JoppaNo ratings yet
- Chapter II Template Review of Related Literature 1Document4 pagesChapter II Template Review of Related Literature 1Geojanni PangibitanNo ratings yet
- 6 Chapter-1Document60 pages6 Chapter-1maria evangelistaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Tariff Reform Program GuideDocument4 pagesPhilippine Tariff Reform Program GuideLuis GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Sample Request InterviewDocument3 pagesSample Request InterviewMira AmirrudinNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Unit 1 Expectation Technical English 2Document2 pagesActivity 1 Unit 1 Expectation Technical English 2Carmen De La CruzNo ratings yet
- Prohibited Acts and Penalties under Philippine Clean Water and Air ActsDocument4 pagesProhibited Acts and Penalties under Philippine Clean Water and Air ActsMonaliza LiztsNo ratings yet
- New Format Letter HeadDocument3 pagesNew Format Letter HeadJC Salvador GaiteNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent - ME OJTDocument13 pagesLetter of Intent - ME OJTcresjohnNo ratings yet
- 1st Day of OJT3Document47 pages1st Day of OJT3mobile legend practiceNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Case Studies Hotel Management LawDocument2 pagesFormative Assessment Case Studies Hotel Management LawKimberly Gabatan0% (1)
- Documentation (Ojt)Document9 pagesDocumentation (Ojt)Kristin Gysel Pascua100% (1)
- On-the-Job Training at the Bureau of Customs Port of IliganDocument14 pagesOn-the-Job Training at the Bureau of Customs Port of IliganMusa Batugan Jr.No ratings yet
- Narrative SoemcoDocument32 pagesNarrative SoemcoLyn Ambray67% (3)
- Related Literature (Joan)Document6 pagesRelated Literature (Joan)Santa Dela Cruz NaluzNo ratings yet
- BSOA Program OutcomesDocument1 pageBSOA Program OutcomesNorilyn VispoNo ratings yet
- Perceived Advantage of Social Networking Sites in Selected Restaurants in Lucena City Chapter 3Document5 pagesPerceived Advantage of Social Networking Sites in Selected Restaurants in Lucena City Chapter 3hannapott0% (1)
- Profile LamcorDocument26 pagesProfile LamcorRaquel Aragon Mien100% (2)
- SLU-BWD Agreement for BSBA Internship ProgramDocument3 pagesSLU-BWD Agreement for BSBA Internship ProgramAnonymous H2L7lwBs3No ratings yet
- Dee D. Silva, Dpa, Ceso VDocument1 pageDee D. Silva, Dpa, Ceso VIvy Ann AlmerolNo ratings yet
- Santa Maria Bulacan CampusDocument9 pagesSanta Maria Bulacan CampusJessie J.No ratings yet
- EMCORDocument13 pagesEMCORDy Ju Arug AL100% (1)
- Asynchronous Activity No. 3 Indonesia Literatures AbeDocument3 pagesAsynchronous Activity No. 3 Indonesia Literatures AbeMCLEAN JOSHUA BERANANo ratings yet
- Tantuico JR V RepublicDocument10 pagesTantuico JR V RepublicMhaliNo ratings yet
- Marvin Villamer General Manager Mitsubishi MotorsDocument3 pagesMarvin Villamer General Manager Mitsubishi Motorschristian agustinNo ratings yet
- MOA-OJT Endorsement LetterDocument2 pagesMOA-OJT Endorsement LetterRegine TillamanNo ratings yet
- Thesis SoftengDocument17 pagesThesis SoftengAllyssa Jozel NitafanNo ratings yet
- IV. Assessment of The OJT A. New Knowledge, Attitudes, and Skills AcquiredDocument2 pagesIV. Assessment of The OJT A. New Knowledge, Attitudes, and Skills AcquiredBanana QNo ratings yet
- HRM Exercises: 1. IntroductionDocument6 pagesHRM Exercises: 1. IntroductionHtar Thiri MonNo ratings yet
- OJT Effects on Student Academic PerformanceDocument34 pagesOJT Effects on Student Academic PerformanceJosette PlazaNo ratings yet
- TESDADocument2 pagesTESDAjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Raise Organic Chicken: N0. Name Project BaranggayDocument3 pagesRaise Organic Chicken: N0. Name Project BaranggayjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Pejay 15 ReyDocument12 pagesPejay 15 ReyjohnsonNo ratings yet
- JojornDocument12 pagesJojornjohnsonNo ratings yet
- OJT Report Summary at Dwinar Computer CenterDocument7 pagesOJT Report Summary at Dwinar Computer CenterjohnsonNo ratings yet
- LJ OjtDocument1 pageLJ OjtjohnsonNo ratings yet
- JojornDocument12 pagesJojornjohnsonNo ratings yet
- JojornDocument12 pagesJojornjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Pejay 15 ReyDocument12 pagesPejay 15 ReyjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Its MeDocument7 pagesIts MejohnsonNo ratings yet
- AhhhhhhhhhhhhhhDocument8 pagesAhhhhhhhhhhhhhhjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report OJTDocument11 pagesNarrative Report OJTxian_rockz1167% (3)
- CharrrDocument11 pagesCharrrjohnsonNo ratings yet
- AhhhhhhhhhhhhhhDocument8 pagesAhhhhhhhhhhhhhhjohnsonNo ratings yet
- CharrrDocument11 pagesCharrrjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Narrative Report OJTDocument11 pagesNarrative Report OJTxian_rockz1167% (3)
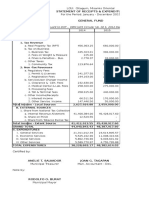
- Summary Receipts & Expenditure 2015Document3 pagesSummary Receipts & Expenditure 2015johnsonNo ratings yet
- Mayor's Office and departments salaries and benefits supplemental budgetDocument6 pagesMayor's Office and departments salaries and benefits supplemental budgetjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Summary Receipts & Expenditure 2015Document3 pagesSummary Receipts & Expenditure 2015johnsonNo ratings yet
- Water System of GitagumDocument1 pageWater System of GitagumjohnsonNo ratings yet
- Transmital T. Minyang-Summary & Receipts & ExpenditureDocument1 pageTransmital T. Minyang-Summary & Receipts & ExpenditurejohnsonNo ratings yet
- OriginalDocument3 pagesOriginalMagdi MohsenNo ratings yet
- Manual - Slide Warmer - XH-2001Document4 pagesManual - Slide Warmer - XH-2001Luis Eduardo Grados MolinaNo ratings yet
- HP Color Laserjet Managed MFP E77825Dn: DatasheetDocument4 pagesHP Color Laserjet Managed MFP E77825Dn: Datasheetmolik1No ratings yet
- Latihan Soal IDocument6 pagesLatihan Soal IMas GigihNo ratings yet
- 798 - Section 00 - PrefaceDocument12 pages798 - Section 00 - PrefaceduongpndngNo ratings yet
- Template Printing OnlyDocument15 pagesTemplate Printing OnlyKelly LuluNo ratings yet
- GNED 500 Social AnalysisDocument2 pagesGNED 500 Social AnalysisEshita SinhaNo ratings yet
- 01-NAC-Introduction To Ship Stability (160419)Document40 pages01-NAC-Introduction To Ship Stability (160419)MuhammadIlhamNugroho100% (1)
- TERRAZO - Specifications and Design GuideDocument50 pagesTERRAZO - Specifications and Design GuidejuanNo ratings yet
- MIESDocument4 pagesMIESSumit YadavNo ratings yet
- Level 4Document7 pagesLevel 4Tudor PricopNo ratings yet
- Urn Uvci 01 Ro 1g267oxmr4ln080w3loz8vyekd095p#nDocument2 pagesUrn Uvci 01 Ro 1g267oxmr4ln080w3loz8vyekd095p#nionpopescuNo ratings yet
- GPF (General Provident Fund) Rules, 1960 and Contributory Provident FundDocument9 pagesGPF (General Provident Fund) Rules, 1960 and Contributory Provident FundFinance AdministrationNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Analysis of Business RisksDocument7 pagesTheoretical Analysis of Business RisksresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Product Service Bulletin: ACPSB24 TCI Analog Card Transistor Q7 Testing and RepairDocument13 pagesProduct Service Bulletin: ACPSB24 TCI Analog Card Transistor Q7 Testing and RepairEmilio Cortes T.No ratings yet
- Define and Optimize The Competitive Advantage Value Using DMADV Approach: A Case Study at PTDocument7 pagesDefine and Optimize The Competitive Advantage Value Using DMADV Approach: A Case Study at PTmuhtia luchfiNo ratings yet
- Private Company Issues and Opportunities 2020 - Family Business EditionDocument58 pagesPrivate Company Issues and Opportunities 2020 - Family Business EditionBusiness Families FoundationNo ratings yet
- Facility Location Selection Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument3 pagesFacility Location Selection Multiple Choice QuestionsSweta MorabiyaNo ratings yet
- JASD Servo Driver Manual UpdatedDocument71 pagesJASD Servo Driver Manual Updatedmecatronico87No ratings yet
- M0000561 sch100 v1.4 IngDocument20 pagesM0000561 sch100 v1.4 IngLenin Romero100% (1)
- PWC ProfilesDocument4 pagesPWC ProfilesAU TPCELLNo ratings yet
- KSA SASO QualityMarkRequirementsForSpecificProducts enDocument1 pageKSA SASO QualityMarkRequirementsForSpecificProducts ennavas1972No ratings yet
- Process Safety KPIsDocument2 pagesProcess Safety KPIssheerazali100% (1)
- Raspberry Pi: The Complete Beginner's GuideDocument26 pagesRaspberry Pi: The Complete Beginner's GuideAnadiKashyapNo ratings yet
- 2019-2020 CB500F维修手册Document9 pages2019-2020 CB500F维修手册zhouhongxuanzhxNo ratings yet
- Pas 10 - Events After The Reporting PeriodDocument11 pagesPas 10 - Events After The Reporting PeriodBritnys Nim100% (1)
- Privatizing of Fertilizer Sub SectorDocument50 pagesPrivatizing of Fertilizer Sub SectorTobiNo ratings yet
- ANAND MEDIPRODUCTS DENTAL EQUIPMENTDocument23 pagesANAND MEDIPRODUCTS DENTAL EQUIPMENTdrmallikarjun19No ratings yet
- Power Electronics: Ministart Softstarter BA 9010, BN 9011Document4 pagesPower Electronics: Ministart Softstarter BA 9010, BN 9011Manel EstebanNo ratings yet
- Direct Tax Reform in India: An Impact Analysis With Special Reference To Government RevenueDocument21 pagesDirect Tax Reform in India: An Impact Analysis With Special Reference To Government RevenueMayur WalunjNo ratings yet