Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Domperidone Motilium
Uploaded by
Alexis Paola Poblete MontejoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Domperidone Motilium
Uploaded by
Alexis Paola Poblete MontejoCopyright:
Available Formats
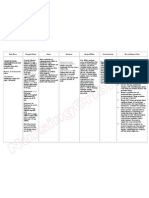
PHARMACOLOGIC SHEET
DRUG
Domperidone (Motillium) 1 tab TID
ACTION
Antidopaminergic Antiemetic
INDICATION/S
Symptomatic management of upper gastrointestinal motility disorders associated with chronic and subacute gastritis and diabetic gastroparesis. May also be used to prevent gastrointestinal symptoms associated with the use of dopamine agonist antiparkinsonian agents.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Contraindicated in patients with known sensitivity or intolerance to the drug. Domperidone should not be used whenever gastrointestinal stimulation might be dangerous, i.e., gastrointestinal hemorrhage, mechanical obstruction or perforation. Also contraindicated in patients with a prolactinreleasing pituitary tumor (prolactinoma).
ADVERSE EFECTS
Serum prolactin level may increase resulting in galactorrhoea in females (increasing of milk production, probably by increasing prolactin production by the pituitary gland) & less frequently gynaecomastia in males. CNS: dry mouth (1.9%), headache/migraine (1.2%), insomnia, nervousness, dizziness, thirst, lethargy, irritability (all<1%). Gastrointestinal (2.4%): abdominal cramps, diarrhea, regurgitation, changes in appetite, nausea, heartburn, constipation (all<1%). Endocrinological (1.3%): hot flushes, mastalgia, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, menstrual irregularities. Mucocutaneous (1.1%): rash, pruritus, urticaria, stomatitis, conjunctivitis. Urinary (0.8%): urinary frequency, dysuria. Cardiovascular (0.5%):
NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
Teaching points: Proper dosing: Missed dose: Take as soon as possible; not taking if almost time for next scheduled dose; not doubling doses. Obtaining medical attention if fainting, dizziness, irregular heartbeat or pulse, or other unusual symptoms occur.
edema, palpitations. Musculoskeletal (0.1%): leg cramps, asthenia. Miscellaneous (0.1%): drug intolerance. Laboratory parameters: elevated serum prolactin, elevation of AST, ALT and cholesterol (all<1%). Extrapyramidal phenomena are rare in adults; they reverse spontaneously as soon as treatment is stopped. When the blood-brain barrier is immature (as in infants) or impaired, the possible occurrence of neurological side effects cannot be excluded.
You might also like
- Drug Study DomperidoneDocument1 pageDrug Study DomperidoneGrace Iloreta RN100% (2)
- Drug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsCelline Isabelle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument7 pagesDrug Study CaseKevin Sam AguirreNo ratings yet
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- How Allopurinol Works to Treat Gout and Reduce Uric AcidDocument1 pageHow Allopurinol Works to Treat Gout and Reduce Uric AcidRachel SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Ceftazidime (Zeptrigen)Document4 pagesCeftazidime (Zeptrigen)105990No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJan DeeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MethotrexateDocument1 pageDrug Study MethotrexatekyawNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: - Ceftazidime Brand Name: - Tazidime ClassificationRadicalRayNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone indications contraindicationsDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY Ceftriaxone indications contraindicationsJ-lie GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Acetaminophen Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Study: Acetaminophen Nursing ResponsibilitiesAyeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Drug Study Potassium ChlorideDocument5 pagesDrug Study Potassium ChlorideKenneth Mark B. TevesNo ratings yet
- Kremil S CsDocument2 pagesKremil S Csunkown userNo ratings yet
- Dose, route, mechanism of action, indications, and nursing responsibilities for keto-analogues + EAADocument2 pagesDose, route, mechanism of action, indications, and nursing responsibilities for keto-analogues + EAAKrizha Angela NicolasNo ratings yet
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PonceNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities for Metronidazole AdministrationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities for Metronidazole AdministrationKristine AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Oral Rehydration Solution: A Drug Study OnDocument7 pagesOral Rehydration Solution: A Drug Study OnRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Aspirin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAspirin Drug StudyEdelweiss Marie CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateMikko EnocNo ratings yet
- CalciumadeDocument1 pageCalciumadeHsintan Hsu100% (1)
- Clarithromycin Drug SummDocument1 pageClarithromycin Drug SummWarrenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Vitamin B ComplexDocument1 pageDrug Study - Vitamin B ComplexmikErlh0% (1)
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Potassium Drug StudyDocument2 pagesPotassium Drug StudyNasrah N. Musa100% (2)
- Drug Study - LactuloseDocument1 pageDrug Study - LactuloseCarla Tongson MaravillaNo ratings yet
- RanitidineDocument2 pagesRanitidinecen janber cabrillosNo ratings yet
- Stugeron® TabletsDocument3 pagesStugeron® TabletsmahgadNo ratings yet
- Colchicine Drug Study For Gouty ArthritisDocument3 pagesColchicine Drug Study For Gouty ArthritisLeslie PaguioNo ratings yet
- ONDANSETRONDocument1 pageONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- Drug Study ParacetamolDocument1 pageDrug Study ParacetamolIris BalinoNo ratings yet
- Piperacillin-Tazobactam Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesPiperacillin-Tazobactam Nursing ResponsibilitiesAnalyn SarmientoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY SpironolactoneDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY SpironolactoneJerremy LuqueNo ratings yet
- West Visayas Nursing Drug StudyDocument1 pageWest Visayas Nursing Drug StudyKhryss Paula BaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DulcolaxDocument1 pageDrug Study DulcolaxLuige Avila100% (1)
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDocument1 pageTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- Tolvaptan-Drug StudyDocument1 pageTolvaptan-Drug Studykaycelyn jimenez100% (2)
- DibencozideDocument1 pageDibencozideJoana Limco Gil AbayanNo ratings yet
- Potassium Chloride (K-LYTE)Document2 pagesPotassium Chloride (K-LYTE)Kristine Young100% (1)
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- DRUG CeftazidimeDocument1 pageDRUG Ceftazidimerholiboi0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument12 pagesDrug StudyAnne Marie Angelica BilonoNo ratings yet
- ETHAMBUTOLDocument2 pagesETHAMBUTOLXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studykrizzia raymundoNo ratings yet
- Clonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyDocument3 pagesClonidine & Furosemide Drugs StudyGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- 11 Drug StudyDocument11 pages11 Drug Studygreench08No ratings yet
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJan Lianne BernalesNo ratings yet
- Fluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 pageFluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiescen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- OxacillinDocument1 pageOxacillinSergi Lee OrateNo ratings yet
- Fe SO4Document3 pagesFe SO4CarmellaDawnNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism, Indications, Side Effects & Nursing CareDocument16 pagesDrug Mechanism, Indications, Side Effects & Nursing Careclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- TelmisartanDocument2 pagesTelmisartanRea LynNo ratings yet
- Metoclopramide DSDocument1 pageMetoclopramide DSAngelica Idio0% (1)
- DS - ColchicineDocument2 pagesDS - ColchicineMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of ChloramphenicolDocument3 pagesDrug Study of Chloramphenicolcasimir1128No ratings yet
- GI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDocument3 pagesGI: Diarrhea/loose: Stools, Fulminant Hepatitis, Hepatic Dysfunction, JaundiceDaniela Claire FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Paracetamol (Calpol)Document1 pageDrug Study - Paracetamol (Calpol)Bianca Watanabe - RatillaNo ratings yet
- AMLODIPINEDocument2 pagesAMLODIPINERye AnchNo ratings yet
- Calcium Carbonate for Bone HealthDocument14 pagesCalcium Carbonate for Bone HealthBianca Freya Porral85% (13)