Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quest - Potential Energy and Energy Conservation
Uploaded by
Eric HuangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quest - Potential Energy and Energy Conservation
Uploaded by
Eric HuangCopyright:
Available Formats
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 1 This print-out should have 41 questions.
ns. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page nd all choices before answering. 001 10.0 points Suppose you want to ride your mountain bike up a steep hill. Two paths lead from the base to the top, one twice as long as the other. Compared to the average force you would exert if you took the short path, the average force you exert along the longer path is 1. one half as much. 2. Unable to determine; it depends on the time taken. 3. one fourth as much. 4. one third as much. 5. the same. 002 10.0 points A synthetic rubber band resists being stretched a distance x from equilibrium with a force Fb (x) = b x2 , where b is a constant. What is the potential energy Ub (x) associated with this elastic band? 1. zero 2. b x2 2 b x3 3. + 3 b x3 4. 3 b x2 5. + 2 6. 2 b x 7. +2 b x 003 10.0 points A ball of mass m is hung from the end of a vertical, unstretched spring of negligible mass and force constant k, then released from rest. After it has fallen a vertical distance it is momentarily at rest again. What is in terms of m, g, and k? 1. There is no point where v = 0 but = 0 mg 2k mg 3. = k 2mg 4. = k 2. = 5. Energy is not conserved in this case so the answer can be dierent each time you try it 004 (part 1 of 6) 10.0 points A heavy ball swings on a string in a circular arc of radius 2 m.
2m
Q P The two highest points of the balls trajectory are Q and Q ; at these points the string is 23 from the vertical. Point P is the lowest point of the balls trajectory where the string hangs vertically down. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . What is the balls speed at the point P ? Neglect air resistance and other frictional forces. Answer in units of m/s Q
005 (part 2 of 6) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the balls acceleration at the point P ? Answer in units of m/s2
23
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 2 izontal initial velocity. 006 (part 3 of 6) 10.0 points What is the balls speed at the point Q? 1. vQ = 0 m/s 2. vQ < 0 m/s 3. 0 m/s < vQ < vp 4. vQ > vp 5. vQ = vp 007 (part 4 of 6) 10.0 points What is the magnitude of the balls acceleration at the point Q? Answer in units of m/s2 008 (part 5 of 6) 10.0 points After several swings, the string breaks. The mass of the string and air resistance are negligible. If the break occurs when the ball is at point P , describe the motion of the ball after the break. 1. It moves horizontally with a constant speed. 2. It undergoes projectile motion with an initial velocity that points upward and to the right. 3. It moves horizontally with a constant acceleration. 4. It stays still. 7. IV only 5. It undergoes projectile motion with a horizontal initial velocity. 6. The ball falls vertically straight down. 009 (part 6 of 6) 10.0 points If the break occurs when the ball is at point Q, describe the motion of ball after the break. 1. It undergoes projectile motion with a hor011 10.0 points In a certain region of space, a force F(r) has an associated potential energy of the form U (r) = a r 2 b r = c , where a , b , and c are positive constants. What are the points, if any, where the force F(r) goes to zero? 1. The force goes to zero only at r = 0 . 4. It moves horizontally with a constant acceleration. 5. It stays still. 6. The ball falls vertically down. 010 10.0 points From a rooftop, one ball is dropped from rest while another identical ball is thrown downward. What will be the same for both balls? I) change of KE in the rst second of fall; II) change of PE in the rst second of fall; III) change of KE in the rst meter of fall; IV) change of PE in the rst meter of fall. 1. II only 2. I only 3. I and II only 4. None of these 5. III only 6. III and IV only 3. It undergoes projectile motion with an initial velocity that points upward and to the right. 2. It moves horizontally with a constant speed.
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 3 2. The force is zero only at r = c b.
3. The force is zero at the two values of r that satisfy a r 2 b r + c = 0 . 4. There is no point where the force is zero. 5. The force goes to zero as r . 6. The force is zero only at r = b 2a. 9.9 kg 2.8 m
3.2 kg Use conservation of energy to determine the nal speed of the rst mass after it has fallen (starting from rest) 2.8 m .The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . Answer in units of m/s 015 10.0 points
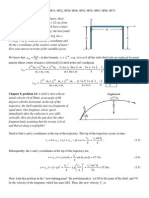
012 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A frictionless roller coaster is given an initial velocity of v0 at height h = 26 m . The radius of curvature of the track at point A is R = 36 m. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . B v0 A h 2 h 3 h
R
A block of mass m slides on a horizontal frictionless table with an initial speed v0 . It then compresses a spring of force constant k and is brought to rest. v k m m =0 How much is the spring compressed x from its natural length?
2 v0 2g 2 v0 2. x = 2m mk 3. x = v0 g m 4. x = v0 k k 5. x = v0 gm
Find the maximum value of v0 so that the roller coaster stays on the track at A solely because of gravity. Answer in units of m/s 013 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points Using the value of v0 calculated in question 1, determine the value of h that is necessary if the roller coaster just makes it to point B. Answer in units of m 014 10.0 points A 9.9 kg mass is attached to a light cord that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The other end of the cord is attached to a 3.2 kg mass.
1. x =
k m mg 7. x = v0 k 6. x = v0
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 4 k mg mg 9. x = v0 k m 10. x = v0 kg 8. x = v0 016 10.0 points A block starts at rest and slides down a frictionless track except for a small rough area on a horizontal section of the track (as shown in the gure below). It leaves the track horizontally, ies through the air, and subsequently strikes the ground. The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s2 . v h 2m 9.81 m/s2 479 g Calculate the balls height above the waters surface at this lowest point of its trajectory. Answer in units of m 018 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points What is the tension of the bungee cord when the ball is at its lowest point? Answer in units of N 019 10.0 points A 119 g mass is attached to the end of an unstressed vertical spring (of constant 52.5 N/m) and then dropped. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . What is its maximum speed? Answer in units of m/s 020 10.0 points A mass m is released from a height h above the ground. It is given an initial horizontal velocity of magnitude v0 . What is the speed of the mass when it hits the ground? 1. v = gh
1.2 m =0.2
3.53 m At what height h above the ground is the block released? Answer in units of m 017 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points Note: A bungee cord can stretch, but it is never compressed. When the distance between the two ends of the cord is less than its unstretched length L0 , the cord folds and its tension is zero. For simplicity, neglect the cords own weight and inertia as well as the air drag on the ball and the cord. A bungee cord has length L0 = 21 m when unstretched; when its stretched to L > L0 , the cords tension obeys Hookes law with spring constant 81 N/m. To test the cords reliability, one end is tied to a high bridge of height 60 m above the surface of a river) and the other end is tied to a steel ball of mass 96 kg. The ball is dropped o the bridge with zero initial speed. Fortunately, the cord works and the ball stops in the air a few meters before it hits the water and then the cord pulls it back up. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 .
2. Undetermined, since we dont know the angle at which the mass hits the ground. 3. v = 4. v = 5. v = 6. v = 7. v = 8. v = 9. v =
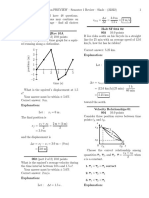
2 v0 +
gh 2
gh 2 2gh
2 v0 + g h 2 v0 + 2 g h 2 v0 gh + 2 2 2 v0 +gh 2
021 10.0 points A(n) 63.5 g ball is dropped from a height of
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 5 50.4 cm above a spring of negligible mass. The ball compresses the spring to a maximum displacement of 4.37158 cm. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . of the block at the bottom of the track is 16 m/s, and the block experiences an average frictional force of 5 N while sliding up the track. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . T
vT
x
R vB
Calculate the spring force constant k. Answer in units of N/m 022 10.0 points Suppose a cannon is propped against a massive tree to reduce recoil when it res.
x m
B
What is x? Answer in units of m 024 (part 2 of 3) 10.0 points What is the speed of the block at the top of the track? Answer in units of m/s 025 (part 3 of 3) 10.0 points What is the centripetal acceleration of the block at the top of the track? Answer in units of m/s2 026 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points Suppose the incline is frictionless for the system shown. The angle of inclination is 28 , the spring constant is 208 N/m and the mass of the block is 5.05 kg. The block is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . 208 N/m
The range of the cannonball will be 1. decreased. 2. unchanged. 3. increased. 023 (part 1 of 3) 10.0 points A block of mass 0.5 kg is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass, compressing the spring a distance of x as shown in the gure. The spring constant is 197 N/m. When released, the block travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point B, the bottom of a vertical circular track of radius 0.5 m, and continues to move up the track. The speed
x kg =0
28
5 5. 0
How far x does it move down the incline before coming to rest?
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 6 Answer in units of m 027 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points Choosing down the incline as the positive direction, what is its acceleration at its lowest point? Answer in units of m/s2 028 10.0 points A pendulum made of a string and a sphere is able to swing in a vertical plane. The pendulum is released from a position of 71 from vertical as shown in the gure below. The string hits a peg located a distance d below the point of suspension and rotates about the peg. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . at A, where A is at the same level as the center of the loop. Answer in units of N 030 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points Consider a dierent situation when the initial height at C has not yet been specied. What is the minimum kinetic energy of the block at B, which is located at the top of the loop, so that the block can pass by this point without falling o from the track? Answer in units of J 031 10.0 points A(n) 766 kg elevator starts from rest. It moves upward for 4 s with a constant acceleration until it reaches its cruising speed of 1.8 m/s. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . Find the average power delivered by the elevator motor during the period of this acceleration. Answer in units of kW 032 10.0 points A 9.22 kg block is released from A at height 4.72 m on a frictionless track shown. The radius of the track is 2.37 m. The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . A
7.5 kg 11 m
d
71
9.8 m/s2 Find the smallest value of d (highest peg position) in order for the sphere to swing in a full circle centered on the peg. Answer in units of m 029 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A 2.2 g mass is released from rest at C which has a height of 1.4 m above the base of a loop-the-loop and a radius of 0.17 m . The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 . C 2.2 g B 0.17 m 1.4 m A
h R
Determine the magnitude of the acceleration for the block at P. Answer in units of m/s2 033 10.0 points A massive ball bearing of mass m, is rolling with negligible friction around the inside of a circular vertical track of radius R. The force the track exerts on the rolling ball at the bottom of the circle is found to be 5 m g in magnitude.
D Find the normal force pressing on the track
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 7 R agram above correspond to equilibrium position(s)? 1. Points V and Z only. Using conservation of energy and Newtons second law, nd the magnitude of the force the track exerts on the ball when it is halfway up the loop. Answer in units of m g 034 10.0 points The potential energy of a two-particle system A separated by a distance r is U (r) = , where r A = 120 J m is a constant. Find the radial force Fr if r = 65.7 m. Answer in units of N 035 10.0 points Two atoms of equal mass interact with a potential energy U (r) = A B 4 8 r r A > 0, B > 0 2. Points T , V and Z. 3. Point V only. 4. Points T and Z only. 5. Point T only. 6. Point Z only. 7. Points T and V only. 037 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points Which of the points represented in the diagram above correspond to stable equilibrium position(s)? 1. Points T , V and Z. 2. Points T and Z only. 3. Points V and Z only. 4. Point T only. 5. Point Z only. 6. Points T and V only. 7. Point V only. 038 10.0 points The graph is a potential energy diagram for a particle in some system as a function of position x.
At what separation is the force zero? 1. r = 2. r = 3. r = 4. r =
4
B A 2A B B 2A A B
036 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points Use the potential energy vs. position plot shown below to answer the following two questions. U (x) V x T Z Which of the points represented in the di-
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 8 Potential Energy vs Position B Potential Energy (J) U(x)
A x0 0 x0 2x0 3x0 4x0 5x0 x
What is the force F on the particle at x = 3 x0 ? B 5 x0 B A 2. F = 4 x0 A 3. F = 5 x0 A 4. F = 4 x0 1. F = 5. F = 0 6. F = 7. F 8. F 9. F 10. F A 4 x0 BA = 4 x0 B = 4 x0 B = 5 x0 B = 4 x0
x2 x3 Position Which of the following is a correct statement about the motion of the particle? 1. It comes to rest at either x0 or x2 and remains at rest. 2. It oscillates with maximum position x2 and minimum position x0 . 3. It moves to the left of x0 and does not return. 4. It cannot reach either x0 or x2 . 5. It moves to the right of x3 and does not return. 040 (part 1 of 2) 10.0 points A particle moving along the x-axis has a potential energy U (x), as shown in the accompanying graph. Scale factors: a = 4.4 m, b = 25 J.
x0 x1
039 10.0 points A conservative force has the potential energy function U (x), shown by the graph. A particle moving in one dimension under the inuence of this force has kinetic energy 1.0 Joule when it is at position x1 .
huang (th23745) Chapter 7: Potential Energy and Energy Conservation thompson (9009) 9 5b 4b [J] 3b 2b 1b 0 a 2a C A 3a 4a x [m] 5a 6a B
What is the force exerted on the particle when x = 3 a (point A, the lowest point on the curve)? Answer in units of N 041 (part 2 of 2) 10.0 points If the particle has a mass of 9.9 kg and is released from rest at x = 5 a, what is the particles velocity when it reaches x = a? Answer in units of m/s
You might also like
- AssignDocument10 pagesAssignkakaNo ratings yet
- Momentum Review QuestionsDocument5 pagesMomentum Review Questionssomeguy01123No ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument17 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBaoduy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Revision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWDocument14 pagesRevision Midterm Exam Physics1 NEWBá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- Torque Dynamics ProblemsDocument3 pagesTorque Dynamics ProblemsJoshua JonesNo ratings yet
- Rolling cylinder and disk kinetic energyDocument5 pagesRolling cylinder and disk kinetic energyMichael Kevin YangNo ratings yet
- Momentum Practice SolutionsDocument15 pagesMomentum Practice SolutionsMax Derp NgNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Sample Physics 71Document11 pagesFinal Exam Sample Physics 71Jay VeeNo ratings yet
- 13 Moment of Inertia and Torque-ProblemsDocument6 pages13 Moment of Inertia and Torque-ProblemsMichael Kevin YangNo ratings yet
- Latihan UTSDocument13 pagesLatihan UTSAyu Patresia NababanNo ratings yet
- Phyc 2121 Week 11 20Document89 pagesPhyc 2121 Week 11 20Faith SocoNo ratings yet
- Quest Circular Motion 1 KeyDocument5 pagesQuest Circular Motion 1 KeyCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Shell Fragment Landing DistanceDocument9 pagesShell Fragment Landing DistanceAndrian Dean Handika CsTahtaNo ratings yet
- Cbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa1 2014 PDFDocument4 pagesCbse Class 11 Physics Sample Paper Sa1 2014 PDFbhag singhNo ratings yet
- Ap C4 MJDocument15 pagesAp C4 MJParewa Scorp0% (1)
- Practice Test FinalDocument23 pagesPractice Test FinalAllison TielkingNo ratings yet
- National University Physics Midterm ExamDocument4 pagesNational University Physics Midterm ExamBá Phong LêNo ratings yet
- PHYC 2121 Week 11-14 ReviewDocument89 pagesPHYC 2121 Week 11-14 ReviewAlbern BarbacNo ratings yet
- Practice Final ExamDocument7 pagesPractice Final ExamChetanya SinglaNo ratings yet
- Physics 40A Final Exam SolutionsDocument12 pagesPhysics 40A Final Exam SolutionsMt RushNo ratings yet
- Resistive Forces SolutionsDocument4 pagesResistive Forces SolutionsdicksquadNo ratings yet
- Newton's 2nd Law-ProblemsDocument3 pagesNewton's 2nd Law-Problems1996andreNo ratings yet
- AP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesAP Physics - Chapter 8 Practice Test: Multiple Choicedipankar65No ratings yet
- PHYSICS WEEK 11-20 BDocument89 pagesPHYSICS WEEK 11-20 BdawnoundeNo ratings yet
- Loop the Loop Physics ProblemDocument10 pagesLoop the Loop Physics ProblemShirsa Guha100% (1)
- Physics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Document6 pagesPhysics 1 2016-17 Quiz3Khoa TrầnNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3JeeveshNo ratings yet
- G11 Phy Q3 FinalDocument5 pagesG11 Phy Q3 FinalWesen GebeyawNo ratings yet
- Homework #4Document28 pagesHomework #4mahrbhojia0% (1)
- Forces and Gravity QuestionsDocument4 pagesForces and Gravity QuestionsJan DefrNo ratings yet
- 102 Physics Answers-EK EditionDocument15 pages102 Physics Answers-EK Editionadom09No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Solids Important Questions 2022-23Document49 pagesCBSE Class 11 Physics Chapter 9 - Mechanical Properties of Solids Important Questions 2022-23Fennix AGNo ratings yet
- Unit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsDocument57 pagesUnit Term 2 Energy Review QuestionsLissa Hannah100% (1)
- Phyc 2121 Week 11 20Document89 pagesPhyc 2121 Week 11 20crz shrNo ratings yet
- Work-energy principle and impulse-momentum principle problems and solutionsDocument11 pagesWork-energy principle and impulse-momentum principle problems and solutionsKavitha KandulaNo ratings yet
- Oldmidterm 01Document7 pagesOldmidterm 01davidchoikekekekNo ratings yet
- Midterm 02 Review QuestionsDocument9 pagesMidterm 02 Review QuestionsJudith EllisNo ratings yet
- Physics ProblemsDocument19 pagesPhysics ProblemsArthur1966100% (1)
- Impulse and Collisions Print-Out QuestionsDocument4 pagesImpulse and Collisions Print-Out QuestionsrupaliroyNo ratings yet
- Online Review AnswersDocument15 pagesOnline Review AnswersdebshistoryfairNo ratings yet
- Phys 204 Final Exam MechanicsDocument5 pagesPhys 204 Final Exam MechanicsMalik ANo ratings yet
- Forces on masses connected by rope over pulleyDocument28 pagesForces on masses connected by rope over pulleydebasijNo ratings yet
- Physics Work and Energy ProblemsDocument12 pagesPhysics Work and Energy ProblemsAlyssa Fermin0% (1)
- HW06 - Linear MomentumDocument6 pagesHW06 - Linear MomentumBradley NartowtNo ratings yet
- Semester 1 Review QuestionsDocument7 pagesSemester 1 Review QuestionsCanjiNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 2016-2017-01Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016-2017-01Gia Hân EmiNo ratings yet
- Practice Midterm 02Document8 pagesPractice Midterm 02Ha ViNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Force and Uniform Circular Motion ProblemsDocument6 pagesCentripetal Force and Uniform Circular Motion Problemsnanio_7No ratings yet
- 2.2 ForceDocument16 pages2.2 ForcecetinNo ratings yet
- Recitation CH 4 1 CompressDocument6 pagesRecitation CH 4 1 Compressallan zenarosaNo ratings yet
- (Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Phyc-121 Week 1-10Document84 pages(Amaleaks - Blogspot.com) Phyc-121 Week 1-10Amanda Dinah RamilNo ratings yet
- Newton's 2nd Law of Motion ExplainedDocument14 pagesNewton's 2nd Law of Motion ExplainedGarrey BrionesNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum and Its Conservation in One and Two DimensionsDocument59 pagesLinear Momentum and Its Conservation in One and Two DimensionsruukiNo ratings yet
- Solution Assignment 1: (Fall 2013) : Question # 1Document72 pagesSolution Assignment 1: (Fall 2013) : Question # 1Ayaan JuttNo ratings yet
- Phyc2122 Sem1 W1 10 GR12Document85 pagesPhyc2122 Sem1 W1 10 GR12Diana Jane Lauzon LluragNo ratings yet
- Phyc 2121 Week 11 20Document89 pagesPhyc 2121 Week 11 20Renato JrNo ratings yet
- Chap6 PhysicsDocument23 pagesChap6 PhysicsMadhavi SivanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics Ii: Technological University of The Philippines-Taguig Electrical Engineering DepartmentDocument34 pagesPhysics Ii: Technological University of The Philippines-Taguig Electrical Engineering DepartmentEsmeralda TapizNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics of A Human BodyDocument13 pagesThermodynamics of A Human BodyJuan Carlos Cahuasquí IntriagoNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 6 CDCDocument3 pagesScience Grade 6 CDCVlad VizcondeNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 06Document4 pagesWorksheet 06Vijay BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Presentations ISO 50001 BiH 2013 PDFDocument222 pagesPresentations ISO 50001 BiH 2013 PDFAnonymous LEVNDh4No ratings yet
- GravitationDocument45 pagesGravitationthinkiit100% (1)
- Solar Power Engineer-Ahmed KamalDocument2 pagesSolar Power Engineer-Ahmed KamalahmedNo ratings yet
- EerDocument5 pagesEerNedunuri.Madhav MurthyNo ratings yet
- Exp. 7 Gas DiffusionDocument2 pagesExp. 7 Gas DiffusionElaine PuiNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities IIDocument9 pagesBuilding Utilities IILeonard MalateNo ratings yet
- Tetryonic Theory - An OverviewDocument11 pagesTetryonic Theory - An OverviewjuliolpzNo ratings yet
- Navid Chowdhury IsArguments For Nuclear As Renewable EnergyDocument3 pagesNavid Chowdhury IsArguments For Nuclear As Renewable Energylram70No ratings yet
- English Solar Farm Proposal by TSF-Jan 2011Document38 pagesEnglish Solar Farm Proposal by TSF-Jan 2011saravoot_j100% (1)
- AAPinsky ProblemsInPhysicsDocument342 pagesAAPinsky ProblemsInPhysicshyoung65100% (1)
- Proposal For Solar Power in Rural AreasDocument3 pagesProposal For Solar Power in Rural Areasahmedzia143No ratings yet
- Renewable Electricity Action Program (REAP)Document77 pagesRenewable Electricity Action Program (REAP)SamsonNo ratings yet
- The Origin of Chemical Elements - 1948 - Gamow, Bethe, AlpherDocument2 pagesThe Origin of Chemical Elements - 1948 - Gamow, Bethe, Alpherstickygreenman100% (1)
- 2001 BESSY BorisenkoDocument2 pages2001 BESSY BorisenkoXan TolusNo ratings yet
- PANIPAT THERMAL POWER STATION BASICSDocument26 pagesPANIPAT THERMAL POWER STATION BASICSratrideviinhostelNo ratings yet
- Offshore Solar EnergyDocument3 pagesOffshore Solar EnergyIshwarya SrikanthNo ratings yet
- A Reviewof Studies On Central Receiver Solar Thermal Power PlantsDocument28 pagesA Reviewof Studies On Central Receiver Solar Thermal Power PlantsValeria Rueda100% (1)
- Uganda Power & EnergyDocument10 pagesUganda Power & EnergyEd ChikuniNo ratings yet
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument31 pagesNuclear ChemistryFatin IziantiNo ratings yet
- Baseline Study For Grid Emission Factor by PTM-DANIDADocument28 pagesBaseline Study For Grid Emission Factor by PTM-DANIDAyogaanandhNo ratings yet
- SolarDocument15 pagesSolarArnabNo ratings yet
- Power Generation and Supply Exam AbDocument11 pagesPower Generation and Supply Exam AbMichael Adu-boahen50% (2)
- Energy Can Neither Be Created Nor Destroyed, Only Altered in FormDocument2 pagesEnergy Can Neither Be Created Nor Destroyed, Only Altered in FormKalpNo ratings yet
- CH 27 Answers PDFDocument13 pagesCH 27 Answers PDFMuhammad SalmanNo ratings yet
- The God Particle PDFDocument8 pagesThe God Particle PDFSabrina PB100% (1)
- Handbook of Energy Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2016Document71 pagesHandbook of Energy Economic Statistics of Indonesia 2016Jeff LiewNo ratings yet