Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.5
Uploaded by
Rais RahimiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.5
Uploaded by
Rais RahimiCopyright:
Available Formats
LESSON 5 Applying Archimedes
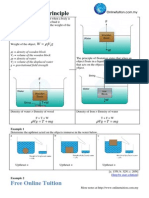
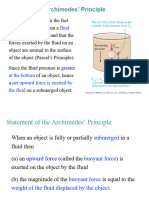
(a) Introduction The figure shows a load of mass 40 N suspended in air whereas the others show the same load immersed in water at four different depth.
(3) The .weight is caused by an upward force exerted by the fluid on the object and the force is known as . Or
(4) Sketch the following graph:
Estimate the spring balance readings for each figure and make the conclusion: (1) When an object is immersed partially or completely in a fluid, the weight of the object and it is called as ..weight. (2) The .. weight depends on the weight of water
(b) Archimedes Principle Archimedes Principle state that When an object is immersed in a fluid (a liquid or a gas) ,the buoyant force ( upthrust force) on the object is equal in size to the weight of fluid displaced by the object.
Density and Buoyancy
27
From Archimedess Principle : Buoyant Force = Weight of fluid displace = mg (note : F = ma) = Vg (note : = m ) Thus V FB = Vg
m-3 . Determine the volume of the object. Solution
Buoyant Force and Flotation
Where FB = Buoyant Force or Upthrust = Density of fluid V = Volume of fluid displaced or the volume of the object that immersed in the fluid.
Example 1 A metal sphere has a volume 5 x 10-4 m3 is immersed in water of density 1 x 103 kg m-3. Determine the upthrust experienced by the sphere? Solution
If Buoyant force = weight the object floats and stationary Buoyant force > weight the object moves up Buoyant force = weight the object moves dow n The Law of Flotation
Example 2 A wooden block with a density 4 x 10 3 kg m-3 and a mass of 5 kg is immersed in a liquid of density 1 x 103 kg m - 3. Calculate the buoyant force acting on the wooden block? Solution
A floating object displaces its own weight of fluid in which it floats. Example 4 An object of mass 5 kg floats on the surface water. What is the upthrust experienced by the object. Solution
Example 3 An object has a weight of 40 N in air and 36 N in a liquid of density 800 kg Example 5
28
Based on Figure (a), (b) ,(c) and (d) write the equations in words to relate the forces acting on the objects when the objects float and stationary.
Solution
Application of Archimedes Principle (1) Ship
Solution
Example 5 The figure shows a glass tube of mass 0.012 kg with uniform diameter and cross-sectional area 4 x 10-4 m2 , and it is filled with sand so that it is made vertical in a beaker containing water. [ Density of water is 1000 kg m-3 ]
A ship , though very heavy , floats on the surface of the sea. This is because the buoyant force = the weight of the ship. The buoyant force acting on the ship is large enough because the ship is hollow and the volume of water displaced by the ship is sufficiently large. ( FB = V g) The density of sea water varies with location and season. To ensure that a ship is loaded within safe limits , the Plimsoll line marked on the body of the ship acts as a guide. (2) Submarine
Determine (a) The upthrust (b) The mass of sand in the glass tube.
A submarine can sail on the surface or underneath it. Its outer hull is entirely watertight. Inside the hull are a number of tanks called ballast tanks which is used to
29
control its position and depth from the surface of the sea. If ballast tanks empty Upthrust = weight submarine floats If ballast tanks full Upthrust < weight submarine sinks
(3) Hydrogen filled balloon.
Density of hot air <<< density of cold air The balloons height can be controlled by turning the gas burner which heats the air on and off as needed. The hot air balloon floats and rises upwards when Upthrust > Weight of hot air (helium gas) + weight of airship fabric + weight of gondola + weight of passengers. The balloon descends when Upthrust < Weight of hot air (helium gas) + weight of airship fabric + weight of gondola + weight of passengers The balloon remains stationary when Upthrust = Weight of hot air (helium gas) + weight of airship fabric + weight of gondola + weight of passengers
A hydrogen-filled balloon will float up into the air if it is released. Air is a fluid and produces an upthrust. Density of air >>> density of hydrogen gas The balloon floats and rises upwards because Uptrust > Weight of hydrogen + weight of balloon + weight of string The balloon remains stationary in air when Uptrust = Weight of hydrogen + weight of balloon + weight of string
(4) Hydrometer
4) Hot air balloon
30
An hydrometer is an instrument used to measure the density of a liquid. It has a glass bulb which contains some lead to make it float upright , and long narrow neck with a scale marked on it caused the hydrometer more sensitive. The large air-filled glass bulb is used to displace more liquid and it caused the upthrust increases hence the hydrometer floats. In a liquid of lesser density , the hydrometer is more submerged. The hydrometer floats higher in a liquid of higher density.
TUTORIA L5
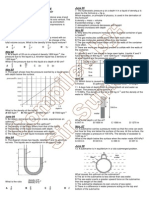
1 The figure shows a load hung from a spring balance is slowly submerged in water until it is immersed completely.
What will happen to the spring balance reading? A zero B decreases until zero C remains unchanged D decreases until reaches a constant value 2 Which of the following figure is true?
31
is the buoyant force experienced by the metal block? A C E 5 40N 20N 5N B D 30N 10N
An object of mass 2 kg with a density of 8 x 103kgm-3 is immersed in the sea water .If the density of the sea water is 1.03 x 103 kg m-3, what is the upthrust? A C 1.2 N 3.0 N E B D 4.0 N 2.6 N 3.4 N
An object has a volume 5 x 10- 4 m3 is hung from a spring balance. The reading of the spring balance is 8N.If the object is immersed fully in a liquid with a density 600 kg m-3, determine the reading of the spring balance now? A C E 1N 3N 8N B D 2N 5N
The figure shows four spheres , P, Q, R and S floating on water. 7
A body has a weight of 20N in air and 15 N in a liquid. If the volume is 5x 10-4 m3 , what is the density of the liquid? 400 kgm-3 1000 kgm-3 1200 kgm-3 D B 800
Which comparison is correct about the density of spheres P,Q,R and S? A P>Q>R>S B S>Q >R>PC P>R>Q>S D Q > R > P >S 4 A metal block has a volume 0.002 m3 is immersed in water. If the density of water is 1000 kgm-3,what
A kgm-3 C E 8
1200 kgm-3
Which of the following about a ship floating on the surface of sea is true? A The weight of the ship equals to mass of the sea water displaced
32
B C D
The weight of the ship equals to the weight of the sea water displaced The weight of ship is less than the weight of the sea water displaced The weight of the ship is more than the weight of the sea water displaced
11 The figure shows a cube of sides 0.1 m floats in water with of its height above the water level. [ The density of water = 1000 kgm3 ]
The figure shows a sphere object floating on the surface of a liquid. What is the weight of the cube? A C E Which of the following is true? A The volume of the liquid displaced by the sphere object equals to the volume of the sphere object The weight of the liquid displaced by the sphere object equals to the weight of the sphere object The mass of the sphere object equals to the mass of liquid in the container The density of sphere object equals to the density of the object 2.5N 7.5N 12.5N B D 5.0 N 10.0N
12 The figure shows a boy on a float.
C D
Which of the relationship between the physical quantities in the above situation is correct? A B C D Weight of water displaced = weight of the boy + weight of the float Weight of water displaced > weight of the boy + weight of the float Volume of water displaced = volume of the boy + volume of the float Volume of water displaced > volume of the boy + volume of the float
10 The figure shows a balloon of mass 200 kg is floating in a stationary position in the air.
What is the upthrust of the balloon? A C E 10 N 100 N 2 000 N D B 20 N 200 N
13 The figure shows a boat has a safety limit line L. The volume of
33
the boat under the line L is 4 m3. The mass of the boat is 200 kg. [ The density of water = 1000 kgm3 ]
What is the maximum load can be carried by the boat to ensure the boat does not overload? A 2.0 X 103 Kg 10 Kg C 4.0 X 103 Kg 3 10 Kg E 5.0 X 103 Kg
3
What is the tension, T of the string? A C E 3.0 x 104 N 4.0 x 104 N 5.0 x 104N B D 3.5 x 104N 4.5 x 104N
B D
3.8 X 4.2 X
14 The figure shows The figure shows a test tube with uniform diameter and cross-sectional area 2 x 10-4 m2 , and it is filled with sand of mass 0.012 kg so that it is made vertical in a beaker containing water at a height 0.01 cm [ Density of water is 1000 kg m-3 ]
16 Which of the following is not the application of Archimedes Principle? A Submarine B C Hot air balloon plane Ship D Aero
17 Figure(a), Figure(b) and Figure(c) show a spring balance supporting a metal block K in three situations.
What is the mass of the test tube? A kg C kg E 0.040 Kg 15 The figure shows a metal block has a volume 0.5 m3 is tied to a string. The block is immersed in water. [ Density of the metal block = 8 x 103 kg m-3, Density of water = 1 x 103 kg m-3] 0.016 kg D 0.020 0.008 kg B 0.012 (c)
(a)
(b)
(a) Compare the readings of the spring balance in Figure(a) and Figure(b)
34
(b) Name three forces that act on K when it partially or totally in water. .. .. (c) State and explain the relationship between the forces in (b). (d) Name the principle involved in (c) ..
18 Figure (a) shows a wooden block with load, fully immersed in water. When the load is removed, the wooden block floats as shown in Figure (b).
Figure (c) shows a submarine, immersed in water with the ballast tanks filled with water. When the ballast tanks are emptied, the submarine floats as shown in Figure (4).
EMBED PBrush
(e) (i) What will happen to the reading of the spring balance in Figure (c) if the water is replaced with salt solution? .. .. (ii) Give one reason for your answer. .. ..
(a) (i) Based on Figure (a), Figure (b), Figure and Figure (d), state one observation common to both the wooden block and the submarine. .. .. .. (ii) List the forces which act on the wooden block and the submarine in Figure (b) and Figure (d). ...
35
The wooden block is immersed partially as shown in Figure (a) and it floats in a stationary position.
(iii) State the relationship between the forces listed in (a)(ii). (iv) Give one reason for your answer. . .. (b) Name the principle involved in the observations in Figure(a), Figure (b), Figure (c) and Figure(d). ..... (c) (i) What happens to the block in Figure (b) when a salt solution is added to the water?
. .
Figure(a) What is (c) The buoyant force of the block ? (d) The volume of the water displaced by the block. [ Density of water = 1000 kg m3 ] The wooden block is later pushed by a force until the upper surface of the wooden level is same as the water surface level as shown in Figure(b) .
(ii) Give answer.
one
reason
for
your
.. 19 A wooden block has a volume 2 x 10-3m3 and a density of 900 kg m3 . Determine (a) The mass of the wooden block (b) The weight of the wooden block
What is (e) The volume of the water displaced by the block at the new position? (f) The new buoyant force of the block ?
36
(g) The acceleration of the wooden block if the force is removed?
20 A large balloon is made by nylon bag is filled with 8 m 3 helium gas. (a) If the density of helium gas is 0.18 kg m-3, determine (i) the mass of the helium gas in the balloon. (ii) the weight of the helium gas in the balloon. (i) What is he resultant force acting on the balloon? (ii) Calculate the buoyant force acting on the balloon.
(iii) Determine the mass of the nylon bag. (b) The figure shows the balloon later is tied by a nylon string and a load of mass 3.65 kg hung at the other end of the string. The balloon floats in a fix height. [ The density of air =1.25 kg m-3]
(c) When the string attached to the load snaps, (i) What is the acceleration of the balloon.
(ii) What will happen to the motion of balloon when the height of the balloon increases?
37
. .. .. 21 (a) A fisherman finds that his boat is at different levels in the sea and in the river, although the boat carries the same load. The density of sea water 1 025 kg m-3 and of river water is 1 000 kg m-3. Figure(a) and Figure(b) illustrate the situation of the boat in the sea and in the river.
Explain how a submarine on the surface submerges. (c) Figure(c) and Figure (d) illustrate the working principle of a hydrometer. The depth to which the test tube sinks depends on its surrounding liquid.
Figure(c) Figure(d) Explain how you would design a hydrometer that can determine a wide range of densities of liquid, using the idea of the working principle of a hydrometer shown above. Draw a diagram that shows the design of your hydrometer and in your explanation, emphasise the following aspects:
(i) What is meant by density? (ii) Using Figure(a) and Figure(b) , compare the levels of the boat and the volumes of water displaced by the boat. Relating the mass of the boat with its load, the volume of water displaced and the density of the water , deduce a relevant physics concept. Name the physics principle that explains the above situations. (b) A submarine can sail on the sea surface and under the sea.
38
(i) the stability of the hydrometer (ii) the sensitivity of the hydrometer (iii) the ability to measure a wide range of densities of liquids (iv) the calibration of the hydrometer
22
Easy to pull the fishing net Figure (a)
Difficult pull the fishing net Figure(b)
More difficult to pull the net Figure(c) Figure (a), Figure (b) and Figure (c) show three different situations when a fisherman is pulling a fishing net from the sea. In Figure (a), the fisherman finds it easy to pull a fishing net while most of the net is in the water. However, the fisherman finds it difficult as the fishing net is emerging from the water surface as shown in Figure (b) and Figure (c). Based on the observations: State one suitable inference that can be made. (b) State one appropriate hypothesis for an investigation.
(a)
With the use of apparatus such wooden rod, spring balance, beaker and other apparatus , describe an experimental framework to test your hypothesis. In your description , state clearly the following: (i) Aim of the experiment (ii) Variables in the experiment (iii) List of apparatus and materials (iv) Arrangement of the apparatus (v) The procedure of the experiment which include the method of controlling the manipulated variable and the method of measuring the responding variable. (vi) Way you would tabulate the data (vii) Way you would analysis the data
(c)
39
You might also like
- Lesson 3 5 Application Des PrincipalDocument11 pagesLesson 3 5 Application Des PrincipalShobby ShobanaNo ratings yet
- Physics SS1 EquilibriumDocument28 pagesPhysics SS1 EquilibriumOlusolaNo ratings yet
- Ch13 SSMDocument18 pagesCh13 SSMJuanca AbadNo ratings yet
- Exercises ArchimedesDocument4 pagesExercises ArchimedesAnonymous UypCttW100% (2)
- Archimedes' PrincipleDocument11 pagesArchimedes' Principle1818dave100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Bouyancy: Archimedes Continued To Do More Experiments and Came UpDocument19 pagesChapter 3: Bouyancy: Archimedes Continued To Do More Experiments and Came Up翁绍棠100% (1)
- FluidsDocument5 pagesFluidsdil19860209No ratings yet
- Archimedes' Principle and Buoyant ForcesDocument20 pagesArchimedes' Principle and Buoyant ForcesAnonymous yfkitRbSvZNo ratings yet
- HW-1 2Document4 pagesHW-1 2Ozan YakarNo ratings yet
- CHP 36Document17 pagesCHP 36Abhiram Reddy100% (1)
- Buoyancy and Archimedes Principle - 2023-3Document29 pagesBuoyancy and Archimedes Principle - 2023-3Jenny ZhangNo ratings yet
- Pascal, Des & BernoulliDocument15 pagesPascal, Des & BernoulliNor Hidaya Md SaidNo ratings yet
- 10 FluidDynamicsDocument39 pages10 FluidDynamicsSyed Raheel AdeelNo ratings yet
- FloatationDocument11 pagesFloatationhoney1002No ratings yet
- Buoyancy Problem SolutionsDocument3 pagesBuoyancy Problem SolutionsKeiole86% (7)
- Archemids PrincipleDocument10 pagesArchemids PrincipleMUHAMMAD AKRAMNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Basic PhysicsDocument36 pagesPressure: Basic Physicsmontu97No ratings yet
- Exp 3Document8 pagesExp 3ValentinoDullSatinNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Unit 2Document14 pagesPressure: Unit 2Sumit ShahNo ratings yet
- CH-5 UpthrustDocument23 pagesCH-5 UpthrustSuman DubeyNo ratings yet
- HidrostaticDocument42 pagesHidrostaticasdfgbugmenotNo ratings yet
- CPP FiitjeeDocument18 pagesCPP FiitjeeAmey Kale0% (1)
- Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.2Document7 pagesChapter Pressure:Lesson 3.2Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Pressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsDocument14 pagesPressure Questions For IGCSE PhysicsLai Kee Kong100% (1)
- CL-9_Phy_Solution-WS-5_23-24Document5 pagesCL-9_Phy_Solution-WS-5_23-24ashishgambhir1986No ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Unit 4 - Justine T. SaldivarDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics - Unit 4 - Justine T. SaldivarJustine Tizon SaldivarNo ratings yet
- Cape 2003 Unit 1 Paper 1Document10 pagesCape 2003 Unit 1 Paper 1petey78No ratings yet
- Test Class 9Document2 pagesTest Class 9aasthaagarwal1729No ratings yet
- 3.5 ArchimedesDocument16 pages3.5 ArchimedessheyzulkifliNo ratings yet
- 3.5 ArchimedesDocument16 pages3.5 ArchimedessheyzulkifliNo ratings yet
- Exercise 5A 5B & 5CDocument6 pagesExercise 5A 5B & 5CSrijita SinhaNo ratings yet
- NA2 Chapter 3Document26 pagesNA2 Chapter 3thugsdei100% (1)
- ch5 Phy PDFDocument39 pagesch5 Phy PDFStar Packs Print SolutionNo ratings yet
- Fluids PDFDocument6 pagesFluids PDFccbcorcoles0% (2)
- 8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsDocument8 pages8a-Fluids MC Practice ProblemsUpeka WeerasinghaNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 1 QuestionsDocument6 pagesPhysics Form 1 Questionspartmore enterprises100% (3)
- Experiment 3 (Archimedes Principle)Document3 pagesExperiment 3 (Archimedes Principle)shark eyeNo ratings yet
- Pressure AnsDocument2 pagesPressure AnsHansraj RahulNo ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument15 pagesBuoyancyToader Ionut Octavian100% (1)
- Calculate Mass of Air, Pressure at Pool Bottom, Breathing UnderwaterDocument2 pagesCalculate Mass of Air, Pressure at Pool Bottom, Breathing UnderwaterHaffiz AtingNo ratings yet
- BuoyancyDocument9 pagesBuoyancyChristineNo ratings yet
- Yaba College of Technology: Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics (Cec107) Lecturer: Olayinka Ojewunmi (Wk3)Document6 pagesYaba College of Technology: Civil Engineering Department Fluid Mechanics (Cec107) Lecturer: Olayinka Ojewunmi (Wk3)Abdulsabur AdenijiNo ratings yet
- Understanding Liquid Pressure and Its ApplicationsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Liquid Pressure and Its ApplicationsJoseph TingNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 1Document20 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 1haikukkkNo ratings yet
- Archimedes PrincipleDocument7 pagesArchimedes PrincipleRoselle Tura75% (8)
- Exp206 Des Principle-1Document7 pagesExp206 Des Principle-1Tiea Maryze VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- ProblemsDocument3 pagesProblemsimPERFECTme09No ratings yet
- Density Buoyant Force and PressureDocument9 pagesDensity Buoyant Force and PressureEduard Benjamin LauronNo ratings yet
- Ch. 5 Upthrust in FluidsDocument10 pagesCh. 5 Upthrust in Fluidsrudranilm2008No ratings yet
- Fluids Practice Problems and SolutionsDocument10 pagesFluids Practice Problems and SolutionsLiam James Payne100% (1)
- Archimedes Principle Q & ADocument4 pagesArchimedes Principle Q & Asimonckt100% (1)
- Fluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesFluids Practice Problems: Multiple Choice QuestionsHey Zac100% (1)
- Fluids Buoyancy Lecture 3Document30 pagesFluids Buoyancy Lecture 3riomjNo ratings yet
- Upthrust IX TestDocument2 pagesUpthrust IX TestM b sagarNo ratings yet
- ch. 5Document13 pagesch. 5Sandy ShohdyNo ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial 3Document4 pagesPhysics Tutorial 3Kimmola K SmallNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5: Pressure and States of MatterDocument18 pagesChapter-5: Pressure and States of MatterhasanNo ratings yet
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisFrom EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisNo ratings yet
- 5 Chemicals For ConsumersDocument14 pages5 Chemicals For ConsumerssweemoiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.6Document9 pagesLesson 3.6Maniyarasan VengadasalamNo ratings yet
- Science P2 Trial PMR 2011 KLDocument19 pagesScience P2 Trial PMR 2011 KLRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Sains N9 K1 K2 PMR 2011Document48 pagesSains N9 K1 K2 PMR 2011Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.2Document7 pagesChapter Pressure:Lesson 3.2Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Matematik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan PMR 2011 SARAWAKDocument16 pagesMatematik Kertas 2 Peperiksaan Percubaan PMR 2011 SARAWAKeddielawNo ratings yet
- LESON 3.4 Forces & PressureDocument5 pagesLESON 3.4 Forces & PressureRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Pressure:Lesson 3.3Document15 pagesChapter Pressure:Lesson 3.3Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.1 Forces & PressureDocument5 pagesLesson 3.1 Forces & PressureRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Science P1 Trial PMR 2011 KLDocument18 pagesScience P1 Trial PMR 2011 KLRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Percubaan PMR 2011 Sabah Math 1 AnswerDocument1 pagePercubaan PMR 2011 Sabah Math 1 AnswerRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Science P2 Trial PMR 2011 MRSMDocument22 pagesScience P2 Trial PMR 2011 MRSMNorafiza HashimNo ratings yet
- Module Science:Generation of ElectricityDocument15 pagesModule Science:Generation of ElectricityRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 RadioactivityDocument23 pagesNota Padat Fizik F5 Radioactivityslokkro97% (33)
- SOALAN P2 Mid YearDocument17 pagesSOALAN P2 Mid YearDalila100% (2)
- Trial SPM MRSM 2007 P1 MathematicsDocument35 pagesTrial SPM MRSM 2007 P1 MathematicsRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- SOALAN P1 Mid YearDocument14 pagesSOALAN P1 Mid YearDalila100% (1)
- Module Science: Land & Its ResourcesDocument18 pagesModule Science: Land & Its ResourcesRais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Perfect Score Add Maths 2011 Module 1 - Module 5Document48 pagesPerfect Score Add Maths 2011 Module 1 - Module 5Hayati Aini Ahmad100% (3)
- Perfect Score SBP Fizik SPM 2011 AnswerDocument30 pagesPerfect Score SBP Fizik SPM 2011 AnswersarahrozaimiNo ratings yet
- PMR Trial 2011 - Science (Pahang)Document55 pagesPMR Trial 2011 - Science (Pahang)Maxis JaisiNo ratings yet
- Perfect Score SBP Fizik SPM 2011 QuestionDocument53 pagesPerfect Score SBP Fizik SPM 2011 QuestionSamion AwaldinNo ratings yet
- Modul 13 IntegrationDocument16 pagesModul 13 Integrationhasnitajb0% (1)
- PMR Trial 2011 Sce Q&A TerengganuDocument44 pagesPMR Trial 2011 Sce Q&A TerengganuSimPorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion TEACHER's GUIDEDocument45 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion TEACHER's GUIDEMohd Khairul Anuar100% (7)
- Chapter 5 Light Teachers GuideDocument38 pagesChapter 5 Light Teachers GuideSyahrulNo ratings yet
- PMR Trial 2011 Sce Q&A (Melaka)Document58 pagesPMR Trial 2011 Sce Q&A (Melaka)SimPorNo ratings yet
- Add Math IntegrationDocument12 pagesAdd Math Integrationkamil muhammad100% (1)
- Progression & Differentiation Feb 2012Document6 pagesProgression & Differentiation Feb 2012Rais RahimiNo ratings yet
- Synthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Iron OxideDocument8 pagesSynthesis and Characterization of Nanoparticles of Iron OxideDipteemaya BiswalNo ratings yet
- The Practice of TratakaDocument7 pagesThe Practice of TratakaNRV APPASAMY100% (2)
- Fox Hunting - The Art of Dating and SeductionDocument93 pagesFox Hunting - The Art of Dating and SeductionEdward Ashley Latimore100% (1)
- Read Me Slave 2.1Document7 pagesRead Me Slave 2.1Prasad VylaleNo ratings yet
- Installing OpenSceneGraphDocument9 pagesInstalling OpenSceneGraphfer89chopNo ratings yet
- Colortrac Cx40 Utilities Service Manual PDFDocument21 pagesColortrac Cx40 Utilities Service Manual PDFTintila StefanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementDocument24 pagesChapter 1 Measurements: 1.1 Units of MeasurementEsmira Melić ŠutkovićNo ratings yet
- Well Logging 1Document33 pagesWell Logging 1Spica FadliNo ratings yet
- Fractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideDocument84 pagesFractions, Decimals and Percent Conversion GuideSassie LadyNo ratings yet
- Lpi - 101-500Document6 pagesLpi - 101-500Jon0% (1)
- JCL RefresherDocument50 pagesJCL RefresherCosta48100% (1)
- U.S. Copyright Renewals, 1962 January - June by U.S. Copyright OfficeDocument471 pagesU.S. Copyright Renewals, 1962 January - June by U.S. Copyright OfficeGutenberg.orgNo ratings yet
- COM295r3 Communication Process WorksheetDocument2 pagesCOM295r3 Communication Process Worksheetfa1therrNo ratings yet
- RoboServer Users Guide PDFDocument25 pagesRoboServer Users Guide PDFdavid0young_2No ratings yet
- Vibration TransducerDocument2 pagesVibration TransducerSurendra Reddy0% (1)
- Digital Citizenship RubricDocument1 pageDigital Citizenship Rubricapi-300964436No ratings yet
- Friction Stir Welding: Principle of OperationDocument12 pagesFriction Stir Welding: Principle of OperationvarmaprasadNo ratings yet
- Reflexiones Sobre La Ciencia de La Administración PúblicaDocument19 pagesReflexiones Sobre La Ciencia de La Administración PúblicaPedro Olvera MartínezNo ratings yet
- SWR SRB Product SheetDocument2 pagesSWR SRB Product SheetCarlo AguiluzNo ratings yet
- ASTM C186 - 15a Standard Test Method For Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic CementDocument3 pagesASTM C186 - 15a Standard Test Method For Heat of Hydration of Hydraulic CementKalindaMadusankaDasanayakaNo ratings yet
- Varying ViewsDocument5 pagesVarying Viewsforevertay2000No ratings yet
- Vocabulary and grammar practice for future technologyDocument4 pagesVocabulary and grammar practice for future technologyRosa MartinezNo ratings yet
- Win10 Backup Checklist v3 PDFDocument1 pageWin10 Backup Checklist v3 PDFsubwoofer123No ratings yet
- "Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of TortsDocument4 pages"Difference Between Private and Public Nuisance": Law of Tortsaridaman raghuvanshiNo ratings yet
- Variable frequency drives for electric submersible pumpsDocument34 pagesVariable frequency drives for electric submersible pumpshermit44535No ratings yet
- Introduction To Literary TheoryDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Literary TheoryAnil Pinto100% (4)
- Vblock® Systems Password ManagementDocument22 pagesVblock® Systems Password ManagementVakul BhattNo ratings yet
- 55fbb8b0dd37d Productive SkillDocument6 pages55fbb8b0dd37d Productive SkilldewiNo ratings yet
- Professional Training Academy: Professional Level IV - Preparation & Final TestDocument2 pagesProfessional Training Academy: Professional Level IV - Preparation & Final TestJayant SinhaNo ratings yet