Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cmos Inverter Layout Tutorial: Prepared By: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Uploaded by
krsrajesh1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cmos Inverter Layout Tutorial: Prepared By: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Uploaded by
krsrajesh1Copyright:
Available Formats
PRINCESS SUMAYA UNIVERSITY FOR TECHNOLOGY
CMOS INVERTER LAYOUT TUTORIAL
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
We will start the inverter by drawing a PMOS. The first step is to draw a poly layer. Click on draw a rectangle and choose the poly layer PO from the right side pane. Use the ruler to get a poly rectangle of width= 0.1 um, and a length about 1 um as shown in the figure below.
The second step is to draw a diffusion region. Draw a diffusion rectangle (DIFF) with a width of 0.48 um and a length of 0.9 um. Place the diffusion rectangle in the center of the diffusion area, that is, the diffusion area should be placed 0.4 um to the left and 0.4 um to the right of the POLY. The figure below shows the diffusion area placed. Place the diffusion area about in the middle of the poly as seen.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
The next step will be placing a PIMP area. Place the area over the diffusion area having a margin area of 0.14 um taken from every corner as below.
Each PMOS transistor should have an N-WELL base layer. Add a new N-WELL layer on your design. Take a 0.1 um margin from the bottom line. Stretch the N-WELL layer as seen below using the stretch tool found in the left toolbar. We will use this area in a couple of steps ahead.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Now add a metal area by choosing M1 from the right panel. The metal contact should be placed at 0.05 um from the right side of the diffusion and have a width of 0.23 um as seen below. Stretch the metal area down.
Until now, your design should look like this
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
In the same manner add a new metal area on the left side and stretch it up as follow.
Now place four contacts in the diffusion area as seen below. The contact should be at least 0.45 um away from the metal borders.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Now add a square NIMP area at the edge of the metal that you stretched upwards. Align the NIMP area to the PIMP rectangle as seen below.
Add a diffusion area inside the NIMP square. And as before, take a 0.14 um margin from all the corners to place a diffusion area like this.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Now place a contact in the diffusion area as seen below. The contact should be placed as before, that is at least 0.45 um from the metal borders. This contact represents the source of the PMOS.
You are almost done of designing the layout of your first PMOS. The design until now should look familiar as this one.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Now add a metal pin M1PIN on the source contact. Then press q on your keyboard and change the pins name to the same name you used for your supply, for example AVDD. The pin should be placed over the contact as seen below.
Now back to the original CMOS inverter circuit. As seen from the circuit, both gates of the NMOS and PMOS transistors Are connected together to form the input of the inverter. The gate of the MOS transistor is the POLY rectangle that we placed first. Thus the POLY of the PMOS will be stretched to meet the POLY of the NMOS and the PMOS drain which is represented by the metal rectangle that we stretched down should be in touch with the NMOS drain as seen from the circuit.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Stretch the POLY rectangle and add a place for a contact the will later represent the input pin as seen in the figure below.
Now add a metal rectangle with the same size (0.21 um x 0.3 um) and this will represent the base of the input contact. After that add a contact using the same dimensions rules that we used earlier. Add an M1PIN over the contact and rename it to IN. This is the inverters input signal.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
After this, create the NMOS using the same steps that we used for the PMOS but with the following differences: 1- The Diffusion areas width is half that for the PMOS, that is 0.24 um. 2- Replacing the PIMP area with a NIMP area using the same margin rules. 3- No N-WELL layer surrounds the NMOS. The design should look like the one below.
After that, start designing the source of the NMOS which will eventually be the contact at which the ground 0 volts is connected. This is achieved by drawing a 0.6 um x 0.6 um PIMP rectangle in which we place a 0.33 um x 0.33 um diffusion area. A contact along with an M1PIN called AVSS are placed using the same previous scheme. The design should look similar to this.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Now you have your complete design of your first inverter. But there is still one step to go. We need to define the output of out inverter. To do that, add an M1PIN on the common metal area between the two transistors. The M1PIN need not to be placed over a contact. Name the pin as the name you used in your schematic, for example OUT.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
Here it is. Your complete layout design for your CMOS inverter.
Verify your connections using the DRC test and then proceed with your simulations.
Prepared by: Eng. Hazem W. Marar
You might also like
- Vintage New U47 Build GuideDocument16 pagesVintage New U47 Build Guidepiretto77No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document21 pagesTutorial 2Suren D. SalvatoreNo ratings yet
- Layout of An InverterDocument14 pagesLayout of An Inverter3nadhsNo ratings yet
- Basic InverterDocument54 pagesBasic InverterNireekshan SodavaramNo ratings yet
- Design of A Microstrip Patch Antenna Using CST MicroWave StudioDocument12 pagesDesign of A Microstrip Patch Antenna Using CST MicroWave Studioaishuvc1822100% (1)
- MOS as a Switch Simulation in MicrowindDocument6 pagesMOS as a Switch Simulation in MicrowindAttique Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Animatronics Workshop ManualDocument44 pagesAnimatronics Workshop ManualMithun P S100% (1)
- ECE 240 - Project1-CMOS InverterDocument7 pagesECE 240 - Project1-CMOS InverterAbhishek Sthanik GubbiNo ratings yet
- CADSOFT EAGLE TUTORIAL GUIDEDocument14 pagesCADSOFT EAGLE TUTORIAL GUIDEJuan C. Guarnizo BNo ratings yet
- Build a 2M Moxon Antenna for ARES UseDocument14 pagesBuild a 2M Moxon Antenna for ARES UseKenburNo ratings yet
- Cadence Layout Tutorial With Post Layout SimulationDocument27 pagesCadence Layout Tutorial With Post Layout SimulationobaejNo ratings yet
- Plate Results and Design ForcesDocument10 pagesPlate Results and Design Forcesthirumalaichettiar100% (1)
- Fractal Magic DIY HDTV Antenna PDFDocument56 pagesFractal Magic DIY HDTV Antenna PDFDarin ArmsteadNo ratings yet
- Tangent GalvanometerDocument4 pagesTangent GalvanometerMatin Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Fractal Magic DIY HDTV AntennaDocument56 pagesFractal Magic DIY HDTV Antennadetroit_me2553100% (3)
- Firefly PCB Assembly Guide - Build Your Own Tube AmplifierDocument16 pagesFirefly PCB Assembly Guide - Build Your Own Tube AmplifierRenier Orlando BlancoNo ratings yet
- The Electronic Diagram of The Monophonic FM Receiver Made With TDA7088T Is Shown On PicDocument5 pagesThe Electronic Diagram of The Monophonic FM Receiver Made With TDA7088T Is Shown On PicBhatiaEktaNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3: Layout Design of A CMOS Inverter: ECE 4101 Computer and Information Lab III (ECE 4141 VLSI Design Part)Document11 pagesExperiment No. 3: Layout Design of A CMOS Inverter: ECE 4101 Computer and Information Lab III (ECE 4141 VLSI Design Part)Ghanshyam V RaoNo ratings yet
- ATrulyPortableMoxonRectangleForNearlyNo toolFieldAssemblyDocument12 pagesATrulyPortableMoxonRectangleForNearlyNo toolFieldAssemblyJeff BeardenNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document10 pagesLab 2IrfanKhanNo ratings yet
- FRB 15 Watt Instruction PacketDocument8 pagesFRB 15 Watt Instruction PacketStephen Dunifer100% (1)
- Piezo ResistiveDocument25 pagesPiezo ResistiveAbcd PqrsNo ratings yet
- Artwork Generation for PCB DesignDocument25 pagesArtwork Generation for PCB DesignNileshMagareNo ratings yet
- Complementary MetalDocument5 pagesComplementary MetalesaidanNo ratings yet
- PSAS Lab ManualDocument79 pagesPSAS Lab Manualmukesh80125No ratings yet
- 15 Watt FET FM Amp Rev 2 Assembly InstructionsDocument7 pages15 Watt FET FM Amp Rev 2 Assembly InstructionsStephen Dunifer100% (4)
- MT5081 FEM Simulation Instructions for Hole Diameter Parameter StudyDocument4 pagesMT5081 FEM Simulation Instructions for Hole Diameter Parameter StudyIrina AveraldoNo ratings yet
- BuzzerDocument7 pagesBuzzerNaresh CherukuriNo ratings yet
- Lab Title:: Introduction To Microwind and Analysis of CMOS 0.25 MicronDocument7 pagesLab Title:: Introduction To Microwind and Analysis of CMOS 0.25 MicronWilliam GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Introduction To Mos TechnologyDocument57 pagesUnit 2 Introduction To Mos Technologykshitiz vNo ratings yet
- Summing AmplifierDocument13 pagesSumming AmplifierMaheen KhalilNo ratings yet
- Lec 20Document20 pagesLec 20NivethaNo ratings yet
- Snap Fits Pager ReportDocument8 pagesSnap Fits Pager Reportapi-524551643No ratings yet
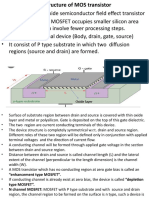
- MOS Logic Family: Understanding the Basics of MOSFET Operation and MOS Logic GatesDocument35 pagesMOS Logic Family: Understanding the Basics of MOSFET Operation and MOS Logic Gatesvinayak mastaNo ratings yet
- Understanding About CMOS Fabrication TechnologyDocument8 pagesUnderstanding About CMOS Fabrication TechnologyAjay Kumar MattupalliNo ratings yet
- (EE476) (Lab 1) 09ece - Group8Document20 pages(EE476) (Lab 1) 09ece - Group8Trung LyamNo ratings yet
- Solns 4Document14 pagesSolns 4ramprakash_rampelliNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Dipole AntennaDocument3 pagesHow To Make A Dipole AntennarzmNo ratings yet
- Gate 2019 NotesDocument20 pagesGate 2019 NotesIndian IndianNo ratings yet
- Planar Device TutorialDocument33 pagesPlanar Device TutorialSI ButtNo ratings yet
- DIY Fractal HDTV AntennaDocument33 pagesDIY Fractal HDTV AntennaLeonel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Breadboards and Resistors in Series LabDocument15 pagesBreadboards and Resistors in Series LabAdeena SaifullahNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of TransistorsDocument10 pagesFabrication of TransistorsDurga PrasathNo ratings yet
- Minimum Baffle Method for RefractorsDocument5 pagesMinimum Baffle Method for RefractorsLuizNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS of CMOS VLSI 5th SEM ECE PDFDocument190 pagesFUNDAMENTALS of CMOS VLSI 5th SEM ECE PDFVarunKaradesaiNo ratings yet
- Lab HFSS MonopoleDocument6 pagesLab HFSS MonopoleKuro Shiro100% (1)
- Eznec PrimerDocument11 pagesEznec PrimerOttis WillebenNo ratings yet
- Plane Stress Bracket: Problem DescriptionDocument28 pagesPlane Stress Bracket: Problem DescriptionChong JongNo ratings yet
- Creating An Inverter Layout Using L-EditDocument9 pagesCreating An Inverter Layout Using L-Editrakheep123No ratings yet
- STAAD - Plate ElementDocument21 pagesSTAAD - Plate Elementkanakanay100% (5)
- Analyzing Carbon Nanotubes with AFM and SEMDocument13 pagesAnalyzing Carbon Nanotubes with AFM and SEMSaransh RajNo ratings yet
- Assignment 197,163,164,198Document14 pagesAssignment 197,163,164,198Shubham GuptaNo ratings yet
- Digital Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors For Curved SurfaceDocument11 pagesDigital Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors For Curved Surfaceiprao0% (1)
- Analog Digital Bicmos RealizationDocument63 pagesAnalog Digital Bicmos RealizationSravana JyothiNo ratings yet
- AutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing a Floor PlanFrom EverandAutoCAD 2010 Tutorial Series: Drawing a Floor PlanRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Handbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringFrom EverandHandbook of Mechanical and Materials EngineeringRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- MOS Integrated Circuit DesignFrom EverandMOS Integrated Circuit DesignE. WolfendaleNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Actuators: Theory and Computational MethodsFrom EverandSolenoid Actuators: Theory and Computational MethodsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- CeDocument5 pagesCekrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- ArticleDocument1 pageArticlekrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Mobile Communications 2012Document214 pagesMobile Communications 2012krsrajesh1No ratings yet
- H 261Document15 pagesH 261krsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Mba ProjectDocument37 pagesMba ProjectAjesh ReddyNo ratings yet
- Embedded - Frank VahidDocument174 pagesEmbedded - Frank VahidTottem RamanaNo ratings yet
- Unix TrainingDocument365 pagesUnix Trainingkrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- 01 ch01Document0 pages01 ch01krsrajesh1No ratings yet
- UnixfaqDocument7 pagesUnixfaqkrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Bulk Density TableDocument6 pagesBulk Density Tabletinz_3No ratings yet
- Introduction To VLSI Circuits and Systems Solution Manual by John P Uyemura PDFDocument77 pagesIntroduction To VLSI Circuits and Systems Solution Manual by John P Uyemura PDFSatish Bollam88% (8)
- Manuals Supplier NameDocument10 pagesManuals Supplier Namekrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Boiler Energy Audit ManualDocument29 pagesBoiler Energy Audit ManualAnubhav100% (11)
- ArticleDocument1 pageArticlekrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Lab 5 v6Document9 pagesLab 5 v6krsrajesh1No ratings yet
- ContentsDocument2 pagesContentskrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Shift SheduleDocument1 pageShift Shedulekrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Excel 2007 WorkbookDocument1 pageNew Microsoft Office Excel 2007 WorkbookRahul BagraitNo ratings yet
- HC 900 Software SpecificationDocument16 pagesHC 900 Software Specificationkrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Varsity BrochureDocument4 pagesVarsity Brochurekrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Real Time Embedded SystemDocument2 pagesReal Time Embedded Systemkrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- EJX530ADocument10 pagesEJX530Akrsrajesh1No ratings yet
- Poster Weldingpositions enDocument1 pagePoster Weldingpositions endpit1No ratings yet
- Manual-V2Document44 pagesManual-V2Ray DavisNo ratings yet
- Optimize Coke Moisture with Quenching System UpgradeDocument96 pagesOptimize Coke Moisture with Quenching System UpgradeSushmit ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- MOOG MACHINING STANDARDSDocument5 pagesMOOG MACHINING STANDARDSmanimeczNo ratings yet
- Activated Sludge MathDocument21 pagesActivated Sludge MathJR Zuniga100% (1)
- Flow ChartDocument1 pageFlow ChartDishankSantwaniNo ratings yet
- CVD Vs PVD Advantages and Disadvantages 98752 r0Document1 pageCVD Vs PVD Advantages and Disadvantages 98752 r0Nuradityatama AditNo ratings yet
- Uj2 48 52Document5 pagesUj2 48 52AS BaizidiNo ratings yet
- SATA 3-2.5 Inch SSD (3-Year Warranty) : MAS0902 MAS0902 MAS0902Document1 pageSATA 3-2.5 Inch SSD (3-Year Warranty) : MAS0902 MAS0902 MAS0902Bladimir Rojas MamaniNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of Ferrous MetalsDocument8 pagesHeat Treatment of Ferrous Metalsarchangeluriel06No ratings yet
- DR Ahmed Heikal Lecture 4 PDFDocument47 pagesDR Ahmed Heikal Lecture 4 PDFArman KhanNo ratings yet
- Ujian Sekolah Bahasa Inggris Kelas 6 SDN 18 Ladang NAMEDocument2 pagesUjian Sekolah Bahasa Inggris Kelas 6 SDN 18 Ladang NAMEhasila silaNo ratings yet
- Steel Manufacturing ProcessDocument7 pagesSteel Manufacturing ProcessWinny Shiru MachiraNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: "MOS Technology" Redirects Here. For The Company, SeeDocument5 pagesMosfet: "MOS Technology" Redirects Here. For The Company, SeeshohobiNo ratings yet
- DurGrip SGCCDocument18 pagesDurGrip SGCCsuksesNo ratings yet
- The ISASMELT ProcessDocument3 pagesThe ISASMELT ProcesssatyaNo ratings yet
- Industrial Training (BHUSHAN STEEL)Document16 pagesIndustrial Training (BHUSHAN STEEL)Ankit Singh MalikNo ratings yet
- Cmosedu ModelsDocument5 pagesCmosedu Modelsraymar2kNo ratings yet
- GE - 5star TubesDocument20 pagesGE - 5star TubeskgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- Buderus 7225Document4 pagesBuderus 7225Ajeng GaleriNo ratings yet
- Raw Materials and Processes in Paper MakingDocument8 pagesRaw Materials and Processes in Paper MakingAkbar Ramadhan SyambasNo ratings yet
- DND 638Document2 pagesDND 638webmaster2649No ratings yet
- Lecture 01Document27 pagesLecture 01Tahminul IslamNo ratings yet
- Anil Special Steel Industries LimitedDocument17 pagesAnil Special Steel Industries LimitedDevendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 27 Advanced Machining Processes1Document37 pagesChapter 27 Advanced Machining Processes1vaniNo ratings yet
- WPQ Is 2062 Haresh Shah W1Document1 pageWPQ Is 2062 Haresh Shah W1Anand KesarkarNo ratings yet
- TEC ALT Process Descriptions and Flow DiagramsDocument45 pagesTEC ALT Process Descriptions and Flow DiagramsUli ArthaNo ratings yet
- Cimbclicks1pdf OriginalDocument25 pagesCimbclicks1pdf OriginalMOHDFADYSHAHNIZAM SAMSIRNo ratings yet
- Flip-Chip Packaging Using PES (Printing Encapsulation Systems) and Underfill Epoxy ResinDocument4 pagesFlip-Chip Packaging Using PES (Printing Encapsulation Systems) and Underfill Epoxy ResinnecromareNo ratings yet
- Protective Coating For Steel StructuresDocument21 pagesProtective Coating For Steel StructurescrazyrimzyNo ratings yet