Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Brazil Confronts An Interdependent World
Uploaded by
Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Brazil Confronts An Interdependent World
Uploaded by
Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanCopyright:
Available Formats
Brazil Confronts an Interdependent World
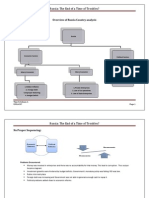
Timeline: Year 1807 1889 1930 1945-46 1947-62 1963 1964-84 1985 Event Kingdom of Brazil Republic Military Coup Varagas overthrown Economic progress Economic slowdown Military regime Democracy returned Impact Due to Napoleon defeating Portugal Due to coup and Pedro II being ousted Getulio Varagas was appointed as president Paved the way for democracy GDP growth averaged at 11% Led to military Regime Economy grew at 11.3% per year Foreign debt was $100 billion, a challenge for the new government
Sector wise Problems: Sector Education Problems faced School teachers were not fully qualified Quality of education was poor Countrys Educational system hampered productivity Productivity levels were low The productivity gap could be closed with improvements in labor organization and capital investments Severe drought 40 % homes did not have running water, 88% had no sewage systems Urban centers were plagued by air, water and solid waste pollution richest 20% held 60% of nations wealth Poorest 20% held 2 % of nations wealth 1 in 4 lived on less than $1 per day Severe drought Rise in Crime Policies adopted 20% federal budget spent on education Minimum expenditure per student raised from $208 to $260 per year Agriculture, Services and manufacturing were the key industries
Industry
Environment
One tenth of Amazon forest razed Population in Amazon basin grew from 6 million to 17 million
Poverty
$400 million provided to build dams and water facilities $450 million provided as credit to farmers
Vijay Krishnan A DM14257
Page 1
Brazil Confronts an Interdependent World
Industrial Development: 1964-83 (Military Regime) Problem Inflation grew annually at 88% Policy adopted Indexation of wages, rents, debts, savings, government bonds and credit Government borrowed from US banks Borrowed petrodollars from US Japanese style high tech targeting Impact It increased inflation
Insufficient tax revenues Oil price increase SOEs
Foreign debt increased Increased inflation Domestic market expanded, annual deficit halved
Economic Reform Plans: Economic Plan Cruzado plan Actions taken Froze prices for goods and services, introduced a new monetary unit called cruzado Wages and prices frozen Froze prices All financial assets were frozen De-indexation of economy Impact PCI fell by more than 6%, cumulative inflation reached 39,043,765% Devalued Cruzado by 65%, fiscal deficit soared Fiscal deficit worsened, inflation was out of control Filled government coffers by more than $1 billion Bankruptcies, Recession
Bresser Plan Summer Plan Collor Plan I Collor Plan II Cardosos Real Plan: Action Plan Combating Inflation
Attracting Investors
Privatization In-house Restructuring
Impact on Economy Cruzados translated in to URVs. 1 URV = $1 (US) checked price rise, inflation dropped down from 2600% to 50% Reduced Trade barriers and import taxes Northeast brazil had corporate income tax exemption which attracted investors Government subsidies increased, so it was cut back Telebras was auctiones and government earned $19 billion Repealed constitutional law that prohibited firing of Government employees Implemented retirement ages Pension system was reorganized
Vijay Krishnan A DM14257
Page 2
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Extrajudicial Settlement of Estate With Special Power of Attorney To Sell or To Enter Into Develpoment Agreement-1Document5 pagesExtrajudicial Settlement of Estate With Special Power of Attorney To Sell or To Enter Into Develpoment Agreement-1Lucille Teves78% (23)
- Barclays Capital - The - W - Ides of MarchDocument59 pagesBarclays Capital - The - W - Ides of MarchjonnathannNo ratings yet
- Vietnam - Market Entry DecisionsDocument1 pageVietnam - Market Entry DecisionsVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Sharma Industries (SI) : Structural Dilemma: Group No - 2Document5 pagesSharma Industries (SI) : Structural Dilemma: Group No - 2PRATIK RUNGTANo ratings yet
- (Nielsen) Macroeconomy - FMCG Q2 2021 For UNZADocument37 pages(Nielsen) Macroeconomy - FMCG Q2 2021 For UNZAalibasukiNo ratings yet
- Cadbury-Design of Product and ServiceDocument5 pagesCadbury-Design of Product and ServiceVijay Krishnan Anantharaman100% (12)
- The Indian Telecom Industry and The Role of Indian Government AgenciesDocument30 pagesThe Indian Telecom Industry and The Role of Indian Government AgenciesVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Joint Ventures in China - How To Deal With ThemDocument4 pagesJoint Ventures in China - How To Deal With ThemVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- The Glastonbury FestivalDocument2 pagesThe Glastonbury FestivalVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- British AirwaysDocument3 pagesBritish AirwaysVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Russia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 2Document2 pagesRussia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 2Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Transforming Korea - Finanical Crisis and Institutional ReformDocument2 pagesTransforming Korea - Finanical Crisis and Institutional ReformVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Russia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 1Document2 pagesRussia - The End of A Time of Troubles - 1Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- China - To Get Rich Is GloriousDocument2 pagesChina - To Get Rich Is GloriousVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Russia 1994Document2 pagesRussia 1994Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Remaking The Rainbow Nation - South Africa 2002Document2 pagesRemaking The Rainbow Nation - South Africa 2002Vijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Mexico - Crisis and CompetetivenessDocument2 pagesMexico - Crisis and CompetetivenessVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Brazil 2003 - Inflation Targeting and Debt DynamicsDocument2 pagesBrazil 2003 - Inflation Targeting and Debt DynamicsVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- Argentina - Anatomy of A Financial CrisisDocument2 pagesArgentina - Anatomy of A Financial CrisisVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- V Jayadevan MethodDocument10 pagesV Jayadevan MethodVijay Krishnan AnantharamanNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument8 pagesAssignmentnaabbasiNo ratings yet
- Coal Bottom Ash As Sand Replacement in ConcreteDocument9 pagesCoal Bottom Ash As Sand Replacement in ConcretexxqNo ratings yet
- The Welcome Magazine FLORENCEDocument52 pagesThe Welcome Magazine FLORENCEJohn D.No ratings yet
- How To Reach Staff Training CentreDocument4 pagesHow To Reach Staff Training CentreRituparna MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Commercial BanksDocument9 pagesCommercial BanksPrathyusha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Global Market Segmentation TechniquesDocument84 pagesGlobal Market Segmentation TechniquesRica de los SantosNo ratings yet
- BCG MatrixDocument5 pagesBCG MatrixAliza AliNo ratings yet
- CRM ProcessDocument9 pagesCRM ProcesssamridhdhawanNo ratings yet
- List of Companies: Group - 1 (1-22)Document7 pagesList of Companies: Group - 1 (1-22)Mohammad ShuaibNo ratings yet
- Fiscal Policy of IndiaDocument16 pagesFiscal Policy of IndiaAbhishek Sunnak0% (1)
- Science and Technology and Nation BuildingDocument3 pagesScience and Technology and Nation BuildingJasmine CarpioNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2019 Final TCM 83-498650 PDFDocument153 pagesAnnual Report 2019 Final TCM 83-498650 PDFzain ansariNo ratings yet
- Cbo Score of The Aca - FinalDocument364 pagesCbo Score of The Aca - FinalruttegurNo ratings yet
- Oxylane Supplier Information FormDocument4 pagesOxylane Supplier Information Formkiss_naaNo ratings yet
- 25-07-2023 DSRDocument4 pages25-07-2023 DSRRishavNo ratings yet
- Social Science Class Viii WORKSHEET-1-Map WorkDocument2 pagesSocial Science Class Viii WORKSHEET-1-Map WorkChahal JainNo ratings yet
- Determination of Income, Consumption, SavingsDocument24 pagesDetermination of Income, Consumption, SavingsAmit PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- Bank Chalan PDFDocument2 pagesBank Chalan PDFIshita SharmaNo ratings yet
- CI Principles of MacroeconomicsDocument454 pagesCI Principles of MacroeconomicsHoury GostanianNo ratings yet
- Balance StatementDocument5 pagesBalance Statementmichael anthonyNo ratings yet
- Liquidity RatioDocument3 pagesLiquidity RatioJodette Karyl NuyadNo ratings yet
- The End of Japanese-Style ManagementDocument24 pagesThe End of Japanese-Style ManagementThanh Tung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chapt 12Document50 pagesChapt 12KamauWafulaWanyamaNo ratings yet
- Finance Process & Terms & ConditionsDocument3 pagesFinance Process & Terms & ConditionsPalash PatankarNo ratings yet
- Strama Ch1 Hexa ArchDocument5 pagesStrama Ch1 Hexa ArchKrizNo ratings yet
- Difference Between EPF GPF & PPFDocument3 pagesDifference Between EPF GPF & PPFSrikanth VsrNo ratings yet