Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Addition To Musculoskeletal
Uploaded by
DrSingh1699Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Addition To Musculoskeletal
Uploaded by
DrSingh1699Copyright:
Available Formats
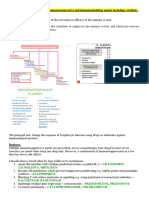
Immunosuppressive agents: sites of action
2 Proliferation
Agent Prednisone Cyclosporine Azathioprine Methotrexate Dactinomycin Cyclophosphamide Antilymphocytic globulin and monoclonal antiT-cell antibodies Rh3(D) immune globulin Tacrolimus
Site 2, 5 2, 3 2 2 2, 3 2 1, 2, 3
4 Cytokine secretion
3 Differentiation synthesis T cells or antibody Complement Interaction Antigen
1 Antigen recognition (B and T cells)
H IG H-YI E LD SYSTE MS
5 Tissue injury
(Adapted, with permission, from Katzung BG. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology, 7th ed. Stamford, CT: Appleton & Lange, 1997:924.)
Cyclosporine
Mechanism Clinical use Toxicity
Binds to cyclophilins. Complex blocks the differentiation and activation of T cells by inhibiting calcineurin, thus preventing the production of IL-2 and its receptor. Suppresses organ rejection after transplantation; selected autoimmune disorders. Predisposes patients to viral infections and lymphoma; nephrotoxic (preventable with mannitol diuresis).
Tacrolimus (FK506)
Mechanism Clinical use Toxicity
Similar to cyclosporine; binds to FK-binding protein, inhibiting secretion of IL-2 and other cytokines. Potent immunosuppressive used in organ transplant recipients. Signicantnephrotoxicity, peripheral neuropathy, hypertension, pleural effusion, hyperglycemia.
M USC U LOSKE LETAL
Azathioprine
Mechanism Clinical use Toxicity
Antimetabolite derivative of 6-mercaptopurine that interferes with the metabolism and synthesis of nucleic acids. Toxic to proliferating lymphocytes. Kidney transplantation, autoimmune disorders (including glomerulonephritis and hemolytic anemia). Bone marrow suppression. Active metabolite mercaptopurine is metabolized by xanthine oxidase; thus, toxic effects may be by allopurinol.
337
M U S C U LO S K E LE TAL AN D CO N N E C T I V E T I S S U EP HAR MACO LO G Y ( continue d) Recombinant cytokines and clinical uses
M USC U LOSKE LETAL
H IG H-YI E LD SYSTE MS
Agent Aldesleukin (interleukin-2) Erythropoietin (epoetin) Filgrastim (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor) Sargramostim (granulocytemacrophage colonystimulating factor) -interferon -interferon -interferon Oprelvekin (interleukin-11) Thrombopoietin
Clinical uses Renal cell carcinoma, metastatic melanoma Anemias (especially in renal failure) Recovery of bone marrow Recovery of bone marrow
Hepatitis B and C, Kaposis sarcoma, leukemias, malignant melanoma Multiple sclerosis Chronic granulomatous disease Thrombocytopenia Thrombocytopenia
338
You might also like
- Cherokee Herbal RemediesDocument292 pagesCherokee Herbal RemediesAlek Phabiovsky100% (2)
- Birth Plan + Hospital Bag Checklist: The Best EverDocument32 pagesBirth Plan + Hospital Bag Checklist: The Best Everelly fadhliahNo ratings yet
- Rope NegotiationDocument4 pagesRope NegotiationTH x TH100% (1)
- MedSurg Medications & TablesDocument71 pagesMedSurg Medications & TablesSarah PlunkettNo ratings yet
- Scrotal HerniaDocument9 pagesScrotal HerniaReymart BolagaoNo ratings yet
- Immunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrDocument31 pagesImmunomodulators: Dr. Kaushik Mukhopadhyay Assistant Professor, Dept. of Pharmacology Esi-PgimsrsyarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Speech in ActionDocument160 pagesSpeech in ActionSplashXNo ratings yet
- Immuno Modulator SDocument62 pagesImmuno Modulator SAntony Prakash RajNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive AgentsDocument36 pagesImmunosuppressive AgentsFlorensa Teolina NdruruNo ratings yet
- Name Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsDocument12 pagesName Types Disease Mechanism AE Other C. Cycle Resistance (CP Pg. 326) Alkylating AgentsM PatelNo ratings yet
- Amyotrophic Lateral SclerosisDocument70 pagesAmyotrophic Lateral SclerosisLorenz Hernandez100% (1)
- Calcaneum Fractures: Jensen Joseph GMC KannurDocument104 pagesCalcaneum Fractures: Jensen Joseph GMC KannurAmel VnairNo ratings yet
- Viral Exanthems: Sahara Tuazan AbonawasDocument75 pagesViral Exanthems: Sahara Tuazan AbonawasMarlon Cenabre Turaja100% (1)
- IMMUNOMODULATORS (EDocFind - Com)Document67 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORS (EDocFind - Com)sac00772006No ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument87 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsNagu KopparapuNo ratings yet
- Administering Corticosteroids in Neurologic Diseases3724Document12 pagesAdministering Corticosteroids in Neurologic Diseases3724Carmen BritoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseFrom EverandCellular Endocrinology in Health and DiseaseAlfredo Ulloa-AguirreNo ratings yet
- Portfolio Template for Diploma in Occupational MedicineDocument11 pagesPortfolio Template for Diploma in Occupational MedicineChengyuan ZhangNo ratings yet
- 1 ImmunopharmDocument63 pages1 ImmunopharmDr.TamilvelanNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiDocument8 pagesImmunopharmacology: Dr. Hamad AlshabiHamad Alshabi100% (1)
- ExplanationDocument5 pagesExplanationAubrey GadorNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppresantmbbs 190608061036Document115 pagesImmunosuppresantmbbs 190608061036syarintaadeninaNo ratings yet
- Question 21c. Classification of Immunosuppressive and Imunomodulating Agents Including Cytokines and Clinical Uses.Document4 pagesQuestion 21c. Classification of Immunosuppressive and Imunomodulating Agents Including Cytokines and Clinical Uses.wanichysonlyNo ratings yet
- 2010 FDA Approved DrugsDocument4 pages2010 FDA Approved DrugsShruthi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Acute-Phase ProteinDocument17 pagesAcute-Phase ProteinAbhijith S. PNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressants Prof. Alhaider, 1431 HDocument45 pagesImmunosuppressants Prof. Alhaider, 1431 HMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive DrugsDocument40 pagesImmunosuppressive DrugsTamjid HossainNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOMODULATORSDocument44 pagesIMMUNOMODULATORSMaria khurshidNo ratings yet
- Cytoskeleton 2012Document4 pagesCytoskeleton 2012Dimitar DaskalovNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology CancerDocument21 pagesPharmacology CancerDương Hà Trúc TâmNo ratings yet
- Transplantation ImmunologyDocument3 pagesTransplantation ImmunologyKrizza UrmazaNo ratings yet
- FCPS Part1 Q BANK Physiology Flash Cards Very Important For Part 1Document49 pagesFCPS Part1 Q BANK Physiology Flash Cards Very Important For Part 1Sehar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Meyer 2010Document24 pagesMeyer 2010deltanueveNo ratings yet
- S 25 Staud ImmunomodulatorsDocument41 pagesS 25 Staud ImmunomodulatorsCarlo MaxiaNo ratings yet
- Effet Glucane Reishi 19 Janv 2023Document8 pagesEffet Glucane Reishi 19 Janv 2023ilyNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressant DrugsDocument6 pagesImmunosuppressant DrugsShoaib MohiuddinNo ratings yet
- Immunopharmacology ImmunosupressantsDocument15 pagesImmunopharmacology ImmunosupressantsPraज्ञा GharpankarNo ratings yet
- Sem4a Insulin1995 JBCDocument4 pagesSem4a Insulin1995 JBCAntonella Farabelli SuarezNo ratings yet
- Mycophenolate Mofetil and Its Mechanisms of Action: ReviewDocument34 pagesMycophenolate Mofetil and Its Mechanisms of Action: ReviewAnna GozaliNo ratings yet
- Characterization of A Conserved Structural Determinant Controlling Protein Kinase Sensitivity To Selective InhibitorsDocument11 pagesCharacterization of A Conserved Structural Determinant Controlling Protein Kinase Sensitivity To Selective InhibitorsJohn HolmanNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of Pharmacology and GeneticsDocument39 pagesMolecular Biology of Pharmacology and GeneticsSusi RutmalemNo ratings yet
- Jak Stat InhibitorsDocument64 pagesJak Stat InhibitorsSupratim KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Immunosuppressive Drug TherapyDocument25 pagesImmunosuppressive Drug Therapyapi-3741769100% (2)
- نشر بيادرDocument10 pagesنشر بيادر9mw75p5b5nNo ratings yet
- Acute Phase ReactantsDocument6 pagesAcute Phase ReactantsRahul Teja G100% (1)
- Gout DrugsDocument1 pageGout DrugsMichael BrownNo ratings yet
- CD28-dependent Rac1 Activation Is The Molecular Target of Azathioprine in Primary Human CD4 T LymphocytesDocument14 pagesCD28-dependent Rac1 Activation Is The Molecular Target of Azathioprine in Primary Human CD4 T LymphocytesasmanNo ratings yet
- Hematopoietic Growth Factors and Treatments for Leukocyte DisordersDocument11 pagesHematopoietic Growth Factors and Treatments for Leukocyte DisordersKimberlyRobelinNo ratings yet
- IMMUNOSUPPRESANTSDocument13 pagesIMMUNOSUPPRESANTSasriNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Antithymocyte Globulin (Thymoglobulin®) Impairs The Thymic Out-Put of Both Conventional and Regulatory CD4 T Cells After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Adult PatientsDocument8 pagesRabbit Antithymocyte Globulin (Thymoglobulin®) Impairs The Thymic Out-Put of Both Conventional and Regulatory CD4 T Cells After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation in Adult PatientsGhanta Ranjith KumarNo ratings yet
- ImmunoDocument11 pagesImmunoJoshua BlumbergNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy in Gynecology by DR Kiran AshokDocument48 pagesChemotherapy in Gynecology by DR Kiran Ashokkiranadr100% (3)
- A Global Increase in 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels Marks Osteoarthritic ChondrocytesDocument11 pagesA Global Increase in 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Levels Marks Osteoarthritic Chondrocytescriters007No ratings yet
- Ajpendo 00125 2020Document7 pagesAjpendo 00125 2020EMANUEL CAMILO MARTINEZ VILLAMIZARNo ratings yet
- BMC Clinical Pathology: Protection of Early Phase Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Cholinergic AgonistsDocument13 pagesBMC Clinical Pathology: Protection of Early Phase Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Cholinergic AgonistsPrachi KariaNo ratings yet
- AMPK Promove Expressão Gênica de GLUT 4 em Humanos. MCGGE (2008)Document8 pagesAMPK Promove Expressão Gênica de GLUT 4 em Humanos. MCGGE (2008)Anderson Ranieri MassahudNo ratings yet
- 5 PBDocument17 pages5 PBAisha MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Neddylation and MTOR Inhibition in Acute My 2019 Translational OnDocument12 pagesEffects of Neddylation and MTOR Inhibition in Acute My 2019 Translational OnFrankenstein MelancholyNo ratings yet
- tmp35D4 TMPDocument3 pagestmp35D4 TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Role of Progesterone in Tlr4-Myd88-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Pre-EclampsiaDocument5 pagesRole of Progesterone in Tlr4-Myd88-Dependent Signaling Pathway in Pre-EclampsiaCarl Enrique PSNo ratings yet
- Disease Genes: Peter BesmerDocument47 pagesDisease Genes: Peter BesmerBrad PamnaniNo ratings yet
- Ferrara 2003Document8 pagesFerrara 2003Chaima DjabouNo ratings yet
- Irinotecan: Mechanisms of Tumor Resistance and Novel Strategies For Modulating Its ActivityDocument11 pagesIrinotecan: Mechanisms of Tumor Resistance and Novel Strategies For Modulating Its ActivityCindyGaniNo ratings yet
- tmp90FE TMPDocument10 pagestmp90FE TMPFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Growth Factors and Growth Factor Receptors in Cancer: T. RajkumarDocument7 pagesGrowth Factors and Growth Factor Receptors in Cancer: T. RajkumarMohammed AladhraeiNo ratings yet
- Calprotectin Release From Human Neutrophils Is Induced by Porphyromonas Gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide Via The CD-14-Toll-like Receptor-Nuclear Factor JB PathwayDocument8 pagesCalprotectin Release From Human Neutrophils Is Induced by Porphyromonas Gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide Via The CD-14-Toll-like Receptor-Nuclear Factor JB PathwayCristianNo ratings yet
- Role of Reactive Oxygen Species in p53 Activation During Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis of Rat Mesangial CellsDocument7 pagesRole of Reactive Oxygen Species in p53 Activation During Cisplatin-Induced Apoptosis of Rat Mesangial CellsPandji 'Utuh'No ratings yet
- Up-Regulation of Luciferase Gene Expression With Antisense Oligonucleotides: Implications and Applications in Functional Assay DevelopmentDocument5 pagesUp-Regulation of Luciferase Gene Expression With Antisense Oligonucleotides: Implications and Applications in Functional Assay DevelopmentFilip IlievskiNo ratings yet
- Inhibitors of Immune Response (site of actionDocument39 pagesInhibitors of Immune Response (site of actionGd SuarantaNo ratings yet
- 3.pleural Effusion Imaging - Overview, Radiography, Computed TomographyDocument32 pages3.pleural Effusion Imaging - Overview, Radiography, Computed TomographyAchmadRizaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ErgonomicsDocument18 pagesChapter 8 ErgonomicsAsif Rahman RaktimNo ratings yet
- Giant Skin TagDocument2 pagesGiant Skin Tagshf.mxlikNo ratings yet
- Anvisa National Health Surveillance AgencyDocument52 pagesAnvisa National Health Surveillance AgencyVimarsha HSNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy Rehabilitation Paraplegic PatientDocument7 pagesOccupational Therapy Rehabilitation Paraplegic PatientAlina PasăreNo ratings yet
- IRB Definitions (Is It Research? and Definitions of Exempt, Expedited and Full)Document4 pagesIRB Definitions (Is It Research? and Definitions of Exempt, Expedited and Full)analyn123No ratings yet
- Gardens For Patients With Alzheimer's DiseaseDocument3 pagesGardens For Patients With Alzheimer's DiseaseKritikou1547No ratings yet
- Inserto CHOL - LIQ SPINREACTDocument2 pagesInserto CHOL - LIQ SPINREACTIng BiomédicoNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Hyrax Distalizer JO PDFDocument7 pagesHybrid Hyrax Distalizer JO PDFCaTy ZamNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document81 pagesScience 5Michael Joseph Santos100% (2)
- Pathology - List - 89.8.20Document25 pagesPathology - List - 89.8.20Mamula RiazNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine For Severe PIHDocument4 pagesHydralazine For Severe PIHYwagar YwagarNo ratings yet
- Spironolactone Class Indications: 25MG TAB, 50Mg Tab, 100Mg TabDocument2 pagesSpironolactone Class Indications: 25MG TAB, 50Mg Tab, 100Mg TabAhmad KusayiriNo ratings yet
- DR Koenig Redacted Expert Report Publicly FiledDocument14 pagesDR Koenig Redacted Expert Report Publicly FiledBrit StackNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Spelling WordsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 Spelling Wordsapi-3705891No ratings yet
- Physiotherapy in LeprosyDocument4 pagesPhysiotherapy in LeprosymichaelsophianNo ratings yet
- FISIOGRAFT ENG Set 17 PDFDocument28 pagesFISIOGRAFT ENG Set 17 PDFmaxNo ratings yet
- Implants Session I Revised 21 Sept 2012Document17 pagesImplants Session I Revised 21 Sept 2012Norman AjxNo ratings yet
- History of Medicine in India from Ancient Times to Ayurvedic Golden AgeDocument6 pagesHistory of Medicine in India from Ancient Times to Ayurvedic Golden AgeGhulam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Resume 2018Document2 pagesResume 2018api-396582921No ratings yet