Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anti Arrhythmia Drugs
Uploaded by
Farid ZainuddinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti Arrhythmia Drugs
Uploaded by
Farid ZainuddinCopyright:
Available Formats
Anti-Arrhythmia Drugs
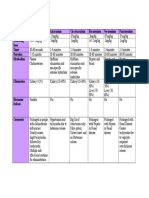
Classes Class 1A Slower Categories Names Na blockers Phase 0 blockers Actions Uses Mainly ventricular arrhythmias SVT (Supraventricular Tachycardia) Side effect Can aggravate / precipitate (new) arrhythmias Quinidine : headache, tinnitus, dizziness, blurred vision Procainamide : Lupus like effect (arthralgia/arthritis) Disopyramide : atropine (antimuscarinic) like effects, may cause CHF Lidocaine: Mainly neurologic side effects Mexiletine: Tremor, blurred vision, lethargy, nausea Quinidine Prolong APD Procainamide Prolong repolarization Disopyramide Depress conduction & prolong refractory period Negative inotropic Prolong QRS (ECG)
Class 1B Faster
Na blockers
Lidocaine Mexiletine Phenytoin
Effects only on depolarized / rapidly firing tissue Decrease APD and ERP (HisPurkinje; ventricles) Increase ventricular fibrillation threshold digitalis induced afterdepolarizations (Phenytoin) Suppresses abnormal automaticity (Flecainide) Slows conduction (AV node, Ventricles) atrial/ventricular refractoriness (Propafenone)
Class 1C Slower
Na blockers
Flecainide Propafenone Ethmozine
Ventricular arrhythmias ( esp. post MI) Lidocaine: IV (rapid action, not proarrhythmic) Mexiletine: Oral Phenytoin: digitalis induced arrhythmias Ventricular arrhythmias ( esp. post MI) Flecainide: PVCs Propafenone: Supravenricular arrhythmias
Both: Exacerbation of ventricular arrhythmias (sp. Flec) Flecainide: Negative inotropic effect Propafenone: Metallic taste, constipation
Class 2 Slower
blocker Phase 2 and 4 blockers
Propranolol Metoprolol Atenolol Sotalol* Nadolol
sympathetic stimulation + membrane stabilization - Reduce automaticity in SAN and Purkinje fibres - Slow conduction and ERP in SA node - APD and ERP in atria & ventricles Block outward K+ current during repolarization Prolong repolarization Prolong APD and ERP Sotalol (class II + Class III
Ventricular arrhythmias (post MI) Supraventricular tachycardia Tachycardia associated with thyrotoxicosis Atrial Fibrillation Recurrent ventricular tachyarrhythmias
Bronchospasm (avoid in asthmatics) Hypotension / fatigue / exercise intolerance CNS effects : sleep disturbances (sp. Propranolol)
Class 3 Slower
K blocker Phase 3 blockers First line drugs
Amiodarone Sotalol* Ibutilide
Amiodarone many adverse effects not recommended as first line drug Heart: Symptomatic bradycardia and heart block Lung: Pulmonary fibrosis Liver: hepatitis Thyroid: blocks peripheral conversion of T4 to T3 Skin: photosensitivity, dermatitis, discolouration Eye: corneal microdeposits Constipation Beware: combination with blockers / digoxin
Class 4 Slower
Ca blocker Verapamil, Diltiazem
Block L-type voltage gated Ca++ channels - both activated and inactivated states blocked - affect conduction in SA and AV nodes - prolong APD and ERP (AV nodal) - suppress early & delayed after-depolarizations
Mainly supraventricular tachycardia (preferred drug) Atrial fibrillation & flutter (to slow ventricular rate)
Adenosine Others Slower
Digoxin Slower
Others
Acts through adenosine receptors Directly inhibits AV nodal conduction & ERP (less effect on SA node) Inhibits Na-K ATPase Increases force of contraction Vagotonic Blocks AV conduction Slows ventricular rate in AF
Prompt conversion of PSVT (IV bolus) (drug of choice)
Flushing, Shortness of breath (? Bronchospasm) Dizziness, headache (less common)
USE: Atrial fibrillation (to slow the ventricular rate) (Also used in heart failure inotropic action)
AE : Can cause arrhythmias Nausea / vomiting Visual disturbances
You might also like
- Local Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel BlockersDocument4 pagesLocal Anesthetics - Blockers K+ Channel Blockers Ca2+ Channel Blockersmed testNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation Cheat SheetDocument14 pagesECG Interpretation Cheat Sheetrenet_alexandre75% (4)
- Emergency MedsDocument24 pagesEmergency MedsNursyNurse100% (1)
- Cardiovascular Drug IntroductionDocument3 pagesCardiovascular Drug IntroductionSamah Khan100% (1)
- Arrhythmia & Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsDocument49 pagesArrhythmia & Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsNitesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocument12 pagesCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNo ratings yet
- Cardiology HFDocument11 pagesCardiology HFdhayemaruNo ratings yet
- ECG Master Class-2Document138 pagesECG Master Class-2Shohag ID Center100% (1)
- Approach To Ventricular ArrhythmiasDocument18 pagesApproach To Ventricular ArrhythmiasDavid CruzNo ratings yet
- ACCSAP 10 Qs & As ReviewDocument470 pagesACCSAP 10 Qs & As ReviewAdeel Lakhiar100% (8)
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs Mechanisms Effects Uses Side Effects /TITLEDocument3 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs Mechanisms Effects Uses Side Effects /TITLEdoktorcoopNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drug Mechanisms and ClassificationDocument3 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drug Mechanisms and ClassificationPatrick Tan100% (1)
- Ninja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFDocument7 pagesNinja - Antiarrhythmic Drugs PDFErica Hyeyeon Lee100% (1)
- Managing Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsDocument29 pagesManaging Cardiac Dysrhythmias and Conduction ProblemsYlanni Coritana100% (1)
- ECG InterpretationDocument52 pagesECG InterpretationMarcus, RN98% (44)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome: Dr. H.M. Saifullah Napu, SPJP, FihaDocument47 pagesAcute Coronary Syndrome: Dr. H.M. Saifullah Napu, SPJP, FihaJual Beli Promosi100% (1)
- Pathology of the Heart: Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac DeathDocument11 pagesPathology of the Heart: Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease and Sudden Cardiac DeathIsabel CastilloNo ratings yet
- ACLS Simplify AlgorithmDocument6 pagesACLS Simplify AlgorithmKristine Monforte Coma UritaNo ratings yet
- DIT High Yield Questions PDFDocument13 pagesDIT High Yield Questions PDFjoshNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010 Revised May 31 2011Document12 pagesACLS Algorithms Adult 2010 Revised May 31 2011arturschander3614No ratings yet
- Poster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFDocument1 pagePoster 10 PALS 01 01 ENG V20100927 PDFAndy XiaoNo ratings yet
- Induction Agents MOA Onset, Duration Special Uses / Notes PropofolDocument3 pagesInduction Agents MOA Onset, Duration Special Uses / Notes PropofolpaveethrahNo ratings yet
- Ch-13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureDocument49 pagesCh-13 Drugs Used in Heart FailureShabrin SadikhNo ratings yet
- CH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaDocument29 pagesCH 46 Complications of AnaesthesiaChristian LeepoNo ratings yet
- INOTROPESDocument8 pagesINOTROPESessevyNo ratings yet
- Anti Arrhythmic DrugsDocument91 pagesAnti Arrhythmic DrugsAlex beharuNo ratings yet
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument86 pagesCongestive Heart FailureNabeel ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Sally Aburumman Bushra SaleemDocument75 pagesSally Aburumman Bushra SaleemAbdulrahman AlsayyedNo ratings yet
- ACLS Study GuideDocument28 pagesACLS Study GuideNicole Berry100% (1)
- Ecg Post TestDocument9 pagesEcg Post TestLala SantiNo ratings yet
- DeathCertificate PDFDocument3 pagesDeathCertificate PDFUrischarNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medical Procedures GuideDocument57 pagesEmergency Medical Procedures GuideDuane Liloc100% (1)
- Secondary Arterial HypertensionDocument32 pagesSecondary Arterial HypertensionAndi SusiloNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Circulatory Shock, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Cardio TransDocument7 pagesCardio TransweissNo ratings yet
- ACLS Drugs: Primary Medications Used in Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesACLS Drugs: Primary Medications Used in Cardiac Arrest AlgorithmsChintami Octavia100% (1)
- ArrhythmiaDocument31 pagesArrhythmiaAbdallah Essam Al-ZireeniNo ratings yet
- ACUTE DECOMPENSATED HEART FAILUREDocument71 pagesACUTE DECOMPENSATED HEART FAILUREVivek Anandan100% (1)
- Arrhythmia 2Document31 pagesArrhythmia 2rittvedNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs 1Document32 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs 1AliImadAlKhasakiNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test Purpose Normal Result Nursing ResponsibilityDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test Purpose Normal Result Nursing Responsibilitykennethfe agron100% (1)
- HW InotropesDocument3 pagesHW InotropesNatalie YeohNo ratings yet
- American Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoDocument50 pagesAmerican Heart Association Guidelines For CPR 2015: Christopher RyalinoLightNo ratings yet
- Seminar on Hemorrhage and ShockDocument239 pagesSeminar on Hemorrhage and Shockparmeshori100% (1)
- Cardiac RehabilitationDocument87 pagesCardiac RehabilitationMaya Vil100% (2)
- ICE DrugsDocument2 pagesICE DrugsRichelle FrondaNo ratings yet
- Electrophysiological Maneuvers For Arrhythmia Analysis-Cardiotext Publishing (2014)Document211 pagesElectrophysiological Maneuvers For Arrhythmia Analysis-Cardiotext Publishing (2014)Ali Uğur Soysal100% (1)
- Bradycardia and TachycardiaDocument66 pagesBradycardia and TachycardiaKarissaNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromeDocument5 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromeLuis OportoNo ratings yet
- The Ehra Book of Intervntional Electrophysiology - OxfordDocument321 pagesThe Ehra Book of Intervntional Electrophysiology - Oxfordmorris njageNo ratings yet
- Dead On ArrivalDocument35 pagesDead On ArrivalFitria Diah Suharjo100% (1)
- Cardiac Drugs Questions OptimizedDocument110 pagesCardiac Drugs Questions OptimizedSanaz Niksefat100% (2)
- Conduction System: Rhythm Identification and TreatmentDocument12 pagesConduction System: Rhythm Identification and Treatmenthops23No ratings yet
- Anti Arrhythmic DrugsDocument4 pagesAnti Arrhythmic DrugsJane IjeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology RevisedDocument59 pagesPharmacology Revisedjohnstockton12100% (1)
- Cardiogenic Shock NclexDocument81 pagesCardiogenic Shock NclexKrishna SapkotaNo ratings yet
- ECG Basics: NG Jit BengDocument38 pagesECG Basics: NG Jit BengNur Atiqah ZainalNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine, Atracurium, Cis-Atracurium, Rocuronium, VDocument1 pageComparison of Neuromuscular Blocking Drugs: Succinylcholine, Atracurium, Cis-Atracurium, Rocuronium, VMarshallMcGoughNo ratings yet
- Equipment List: Equipment and Supplies Quantity Needed Learning/Testing Station Equipment NeededDocument3 pagesEquipment List: Equipment and Supplies Quantity Needed Learning/Testing Station Equipment NeededVictoriano MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4: Hypovolemic ShockDocument20 pagesLecture 4: Hypovolemic Shockj.doe.hex_87No ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Volume and Vascular Tone RegulationDocument2 pagesPharmacology of Volume and Vascular Tone RegulationgraycorypNo ratings yet
- (Advanced Cardiac Life Support) : ACLS Algorithms 2018Document18 pages(Advanced Cardiac Life Support) : ACLS Algorithms 2018cristina100% (1)
- ECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07Document60 pagesECG Interpretation and Dysrhythmias: Karen L. O'Brien MSN, RN JAN 07ampogison08No ratings yet
- Chest TubesDocument12 pagesChest TubesMark Hammerschmidt100% (4)
- Nursing Responsibilities in Handling AntibioticsDocument4 pagesNursing Responsibilities in Handling Antibioticsrichardmd20% (1)
- ACLS ChartDocument1 pageACLS ChartJev DespiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Airway and Ventilatory ManagementDocument5 pages2 - Airway and Ventilatory ManagementJessie E. GeeNo ratings yet
- Emergency DrugsDocument9 pagesEmergency DrugsaldwinngNo ratings yet
- Adult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateDocument1 pageAdult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateRyggie Comelon0% (1)
- Thyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanDocument27 pagesThyroid Gland: Sheena Mae SangutanMarrah Avila Acuin100% (1)
- Post-anesthesia hypotension and hypertension treatmentDocument4 pagesPost-anesthesia hypotension and hypertension treatmentDianne GalangNo ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- Arrhythmias!Document49 pagesArrhythmias!mospala285No ratings yet
- Case 02 Arrhythmias 2Document23 pagesCase 02 Arrhythmias 2pqp7mpk7v6No ratings yet
- Holter Monitoring Report 2018Document27 pagesHolter Monitoring Report 2018win100% (1)
- Ecg Charts - PDF Final - Doc 2016Document6 pagesEcg Charts - PDF Final - Doc 2016ZweNo ratings yet
- AF Guide: Mechanisms, Management, and Treatment Options for Atrial FibrillationDocument55 pagesAF Guide: Mechanisms, Management, and Treatment Options for Atrial FibrillationNikhil Kumar100% (1)
- DysrythmiasDocument4 pagesDysrythmiasmgmjlm01_881676250100% (1)
- ABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Atrial ArrhythmiasDocument6 pagesABC of Clinical Electrocardiography Atrial ArrhythmiasIgnacio Aguilar ValdiviesoNo ratings yet
- ECG Made Easy by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar Associate Professor Medicine Chinkipora Sopore KashmirDocument320 pagesECG Made Easy by DR Bashir Ahmed Dar Associate Professor Medicine Chinkipora Sopore KashmirProf Dr Bashir Ahmed Dar Chinki Pora Sopore Kashmir100% (2)
- Patho Week 3Document4 pagesPatho Week 3Lin LanNo ratings yet
- ACC/AHA/ESC Practice GuidelineDocument39 pagesACC/AHA/ESC Practice GuidelineSomnath Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Moartea Subita CardiacaDocument63 pagesMoartea Subita CardiacaAlexa whyNo ratings yet
- SP M8 User ManualDocument282 pagesSP M8 User ManualRoger100% (1)
- Unipulse 400Document6 pagesUnipulse 400Eliel VelasquezNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma Pulmonary Oedema (Cardiac Asthma) : Avoid .AvoidDocument1 pageBronchial Asthma Pulmonary Oedema (Cardiac Asthma) : Avoid .AvoidjincymariyamNo ratings yet
- ECG Interpretation SkillsDocument46 pagesECG Interpretation SkillsSumeet TripathiNo ratings yet
- Main Applications of ECG DiagnosisDocument19 pagesMain Applications of ECG DiagnosisMaria Rowena O. SalvoNo ratings yet
- Article - ECG Vs MCGDocument7 pagesArticle - ECG Vs MCGpaul_calburean7899No ratings yet
- Laporan Kasus 6 Cvs - Kelompok J - 2013Document47 pagesLaporan Kasus 6 Cvs - Kelompok J - 2013Nadiya Afifah AgusNo ratings yet