Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 3 PMT
Uploaded by
Dewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 3 PMT
Uploaded by
Dewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungCopyright:
Available Formats
Dewi Lestari Natalia (1006704530) Teknik Metalurgi dan Material
Assignment 3
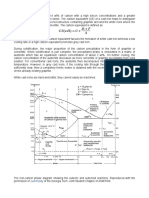
Question 1 A. Explain how Carbon content affects the strength of steels. Carbon content affects the strength of steel : the more cabon, so makes the steel stronger and make lower ductility. B. Microstructures of low carbon steels mainly consist of ferrite and pearlite. Describe about ferrite and pearlite. Ferrite : Body-centered cubic iron; also iron and steel alloys that have the BCC crystal structure. Pearlite : A two-phase microstructure found in some steels and cast irons; it results from the transformation of austenite of eutectoid composition and consists of alternating layers (or lamellae) of -ferrite and cementite. C. What is the function of alloying elements in steels? The function of alloying elements in steel are increase hardenability, improve strength, improve mechanical properties (at operating temperature), improve toughness for a given strength or hardness, increase wear resitance, improve magnetic properties. D. On the basis of microstructure, briefly explain why gray cast iron is brittle? Also describe typical applications of gray cast iron. The gray cast iron is brittle as a consequence of its microstructure; the tips of the graphite flakes are sharp and pointed. Typical applications of gray cast iron are engine blocks brake drums machine castings E. Compare white and nodular cast iron with respect to (a) composition and heat treatment, (b) microstructure and (c) mechanical characteristics. White Cast Iron Nodular Cast Iron a) 3,4% C, heat treatable at 3,4% C; 0,03-0,05% Mg; heat900C treatable to increase hardness b) Pearlite in cementite Graphite speroid in a matrix of ferrite, pearlite, or both c) Very hard but very brittle, Tough, ductile, almost like a
wear-resistant
steel
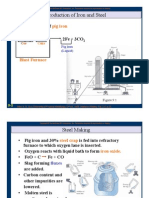
Question 2 A. Explain the stages of steel making conducted at PT. Krakatau Steel. You have to explain the process from iron ore to semi-finished products. Please be concise and focus on the concept and principle of each stage. Fe in terms of Fe2O3 is taking from the earth crust. % Fe in hematit devided into 2 (< 60% and >60%), Fe2O3 which % Fe < 60% is being pured, which the process are : 1. crushing and grinding iron ore 2. iron ore is cleaned in order to execute their impurities 3. separated between iron mineral and non iron mineral by magnetic separator the final result is consentrat (% Fe has been more than 60%). Consentrat can be processed in blast furnace because of its small size. Consentrat must be clotted first by agglomeration process, resulting pellet/sinter. After that, the process is reduction process, PT. Krakatau Steel uses direct reduction reduction process. direct reduction raw material : pellet process : pellet is reducted direcly by CO from CH4 , in the hylsa or midrex the result : sponge iron (small size) or hot briket iron (big size) electrical arc furnace (EAF) sponge iron is raw material for steel making process in EAF. The process is happened in solid phase, so energy used is less than energy used in blast furnace. When it is used in EAF, it can be used 100% sponge iron as bait material, because of the existance of non metallic inclusion. Sponge iron is entered to the furnace continually after the bait material previously melt (scrap) consumption of sponge iron in EAF, 70-90%, the remainder is return or scrap commercial. The greater sponge iron using better steel quality will be produced. B. Mention 3 (three) examples of engineering products made of steel. Automotive component Railways Gears
You might also like
- Chemistry Paper 1 2009Document7 pagesChemistry Paper 1 2009Robert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- QuenchingDocument24 pagesQuenchingHakan Yamanoğlu100% (4)
- Heat Treatment Definition and ObjectivesDocument56 pagesHeat Treatment Definition and ObjectivesAakarsh RastogiNo ratings yet
- Ferrous Material Structure and Binary Alloy SystemDocument68 pagesFerrous Material Structure and Binary Alloy SystemUsman FarooqNo ratings yet
- Microstructure of Metal MaterialsDocument70 pagesMicrostructure of Metal MaterialsEddyWang100% (14)
- Corrosion in Crude Distillation Overhead System A ReviewDocument10 pagesCorrosion in Crude Distillation Overhead System A ReviewSalem GarrabNo ratings yet
- Metallurgy Assignment - Rev - 3Document21 pagesMetallurgy Assignment - Rev - 3Maria CutajarNo ratings yet
- Maleable Cast IronsDocument0 pagesMaleable Cast IronsGilang Miky Pratama AlwianNo ratings yet
- Effect of heat treatment on spring steel microstructures and propertiesDocument7 pagesEffect of heat treatment on spring steel microstructures and propertiesMahmood KhanNo ratings yet
- Cast iron microstructures and propertiesDocument8 pagesCast iron microstructures and propertiesAlberto LunaNo ratings yet
- Iron and Steel Production-Class LetureDocument30 pagesIron and Steel Production-Class LetureAustin Okoth Omondi100% (1)
- Activated Carbon From BambooDocument19 pagesActivated Carbon From BambooErik WeeksNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron: A Widely Used MaterialDocument19 pagesCast Iron: A Widely Used MaterialHarshaDesuNo ratings yet
- Metallographic Study of Steel and Cast IronDocument7 pagesMetallographic Study of Steel and Cast IronNader MohammedNo ratings yet
- Lecture n.9 Cast IronDocument25 pagesLecture n.9 Cast IronMOHAMMAD JAWAD QASIMNo ratings yet
- Heat TreatmentDocument179 pagesHeat TreatmentDebye101100% (1)
- Chapter Two Week 5Document4 pagesChapter Two Week 5Fildanis FikriNo ratings yet
- Chemical Compositions, Microstructure and Mechanical  Properties of Roll Core Used Ductile Iron in Centrifugal Casting Composite Rolls PDFDocument6 pagesChemical Compositions, Microstructure and Mechanical  Properties of Roll Core Used Ductile Iron in Centrifugal Casting Composite Rolls PDFShankey JAlanNo ratings yet
- BG2802 Heat Treatment and Mechanical Properties of SteelsDocument11 pagesBG2802 Heat Treatment and Mechanical Properties of SteelsVenus LimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Ferrous AlloysDocument31 pagesLecture 9 - Ferrous Alloysmahmoud foudaNo ratings yet
- Write The Various Classification of Engineering MaterialsDocument7 pagesWrite The Various Classification of Engineering Materialsashok pradhanNo ratings yet
- Closed-Book Practice-Ch 11 (2015!03!16)Document17 pagesClosed-Book Practice-Ch 11 (2015!03!16)Juan100% (1)
- Castiron Its StructureDocument71 pagesCastiron Its Structuresk.bashaNo ratings yet
- MMSE Journal Vol.7 2016Document114 pagesMMSE Journal Vol.7 2016Leonardo MonteiroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Materials 27-29Document40 pagesEngineering Materials 27-29Sanu SouravNo ratings yet
- Ductile Iron Documents 1Document277 pagesDuctile Iron Documents 1emir_osman5940No ratings yet
- Chapter Five Iron and Steel Making 5.1 IronDocument7 pagesChapter Five Iron and Steel Making 5.1 IronsaedNo ratings yet
- Cast IronDocument64 pagesCast IronEr Vishal Divya JagadaleNo ratings yet
- Wrought IronDocument32 pagesWrought IronHicham KorichiNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Part: Chapter-1Document10 pagesTheoretical Part: Chapter-1hayder1920No ratings yet
- Ijesrt: Effect of Bismuth in Trace Level On The Properties of Gray Cast IronDocument4 pagesIjesrt: Effect of Bismuth in Trace Level On The Properties of Gray Cast IronN. Arda EyyüboğluNo ratings yet
- EAS107 Lab 1Document14 pagesEAS107 Lab 1Mohd Ashraf Mohd Ismail100% (1)
- Cast IronDocument79 pagesCast IronMaroof FaheemNo ratings yet
- Course Prepared by M.Jayaprasad Materials, Manufacturing and Testing of EngineDocument63 pagesCourse Prepared by M.Jayaprasad Materials, Manufacturing and Testing of EngineGopi GopinathNo ratings yet
- 1931 6834 1 SMDocument12 pages1931 6834 1 SMchpinto10% (1)
- 1.iron-Carbon Phasse DiagramDocument21 pages1.iron-Carbon Phasse Diagramnickboon100% (1)
- Metallurgy Dual Phase Steel: November 29Document4 pagesMetallurgy Dual Phase Steel: November 29roseNo ratings yet
- Types of Cast IronsDocument11 pagesTypes of Cast IronsawesomeyogeshwarNo ratings yet
- 7 - Carbon Steel & Heat TreatmentDocument32 pages7 - Carbon Steel & Heat TreatmentAbdelrahmanNo ratings yet
- SteelDocument14 pagesSteelgodwinirabor4850% (2)
- 금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Document10 pages금속재료 중간고사 기출문제 (2006-2016)Li Ken LokNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment and Properties of Steels ExplainedDocument14 pagesHeat Treatment and Properties of Steels Explained035K Ayush ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment Study On Carbon SteelDocument6 pagesHeat Treatment Study On Carbon SteelramaNo ratings yet
- Microstructures Study of Ferrous and Non Ferrous AlloysDocument9 pagesMicrostructures Study of Ferrous and Non Ferrous AlloysIlman FaiqNo ratings yet
- Material Science 1 Assignment 2Document4 pagesMaterial Science 1 Assignment 2Mehul BansalNo ratings yet
- Types of Structural Steel Properties & FactorsDocument14 pagesTypes of Structural Steel Properties & FactorsSIDDIQUI HasmataliNo ratings yet
- 1 - Demir Ve Celik Uretimi - 2021 - 1Document99 pages1 - Demir Ve Celik Uretimi - 2021 - 1atilla kayangilNo ratings yet
- Alloy Steels and Cast IronDocument6 pagesAlloy Steels and Cast IronMurugan RajaNo ratings yet
- Cast Irons: MSE 206-Materials Characterization I Lecture-6Document21 pagesCast Irons: MSE 206-Materials Characterization I Lecture-6Jose Luis Valin RiveraNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Characterization of Deformed and Heat Treated Copper-Eutectoid Steel Powder Reinforced CompositesDocument14 pagesMechanical Characterization of Deformed and Heat Treated Copper-Eutectoid Steel Powder Reinforced CompositesTJPRC PublicationsNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron (C.I) : A-StructureDocument3 pagesCast Iron (C.I) : A-Structureحسين كاظم ياسينNo ratings yet
- Iron Carbon Diagram (ChE Handbook)Document21 pagesIron Carbon Diagram (ChE Handbook)Mohamed Ismail100% (1)
- Materials Science MetalsDocument35 pagesMaterials Science MetalsPelajar IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of SteelsDocument41 pagesHeat Treatment of Steelsyaswanth1992No ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Steel Making PRDocument38 pagesToaz - Info Steel Making PRtitiNo ratings yet
- Development of High-Strength Steel Wire With Superior WeldabilityDocument5 pagesDevelopment of High-Strength Steel Wire With Superior WeldabilitySmruti Ranjan PattanayakNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 - Heat Treatment of Steels - Quenching & TemperingDocument14 pagesLab 4 - Heat Treatment of Steels - Quenching & TemperingSarah AkuteyNo ratings yet
- 18-6 Theoretical PartsDocument11 pages18-6 Theoretical Partshayder1920No ratings yet
- Development of Bake-Hardenable Al-Killed Steel Sheet by Box Annealing ProcessDocument10 pagesDevelopment of Bake-Hardenable Al-Killed Steel Sheet by Box Annealing ProcessRamírez WillebaldoNo ratings yet
- Heat Treatment of SteelDocument51 pagesHeat Treatment of SteelRAMA BAGAS ADITYA TM 2DNo ratings yet
- Steel GRP 3Document5 pagesSteel GRP 3Maria Chrisma BanzonNo ratings yet
- Product and Industrial Designe MET 28-10-11Document31 pagesProduct and Industrial Designe MET 28-10-11Haider ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Processing of Automotive MaterialsDocument34 pagesLecture 5 - Processing of Automotive MaterialsKamal SurenNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0148296319307854 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0148296319307854 MainDewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungNo ratings yet
- EIS - Obat HerbalDocument62 pagesEIS - Obat HerbalDewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Assignment b3 MetfisDocument3 pagesAssignment b3 MetfisDewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Assignment B2Document3 pagesAssignment B2Dewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Paper Shoe Power GeneratorDocument6 pagesPaper Shoe Power GeneratorDewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungNo ratings yet
- PMT Ass 1Document3 pagesPMT Ass 1Dewi Lestari Natalia MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Eltra EncoderDocument2 pagesEltra EncoderVăn QuyềnNo ratings yet
- Petroleum and Petroleum Products - Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) - SpecificationDocument8 pagesPetroleum and Petroleum Products - Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) - SpecificationJon GoeltomNo ratings yet
- Screw Conveyor Specification for Industrial UseDocument5 pagesScrew Conveyor Specification for Industrial UseAbinashBeheraNo ratings yet
- Asme CCase N-432Document4 pagesAsme CCase N-432julianmorantesNo ratings yet
- Smart Cleat 0212Document12 pagesSmart Cleat 0212Ozan AtıcıNo ratings yet
- Sitren PSR 100 0209 en 2000 IfDocument2 pagesSitren PSR 100 0209 en 2000 IfSuryasai RednamNo ratings yet
- Eye C GasDocument3 pagesEye C GasLuis ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cooling: Operating Temperature Arrhenius Equation Radiation Transformer Oil Mineral Oil PaperDocument2 pagesCooling: Operating Temperature Arrhenius Equation Radiation Transformer Oil Mineral Oil PaperVishnu PillaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Me1203Document20 pagesUnit 2 Me1203Muthuvel MNo ratings yet
- Glitter Laser Machines CashDocument5 pagesGlitter Laser Machines CashAns JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Hitatchi ProfileDocument15 pagesHitatchi ProfileAbdul AleemNo ratings yet
- Eeto Handheld Laser WelderDocument6 pagesEeto Handheld Laser WelderalbertNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Lab Visit: Background EssayDocument1 pageNanotechnology Lab Visit: Background EssayLearningHoodNo ratings yet
- Cold Extrusion For Bearing Pin in Automotive Application by 5-Axis CNCDocument13 pagesCold Extrusion For Bearing Pin in Automotive Application by 5-Axis CNCAhmad SyafiqNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Sio Diffusion Coefficients Based On Kinetic Curves of Silica Grain DissolutionDocument3 pagesCalculation of Sio Diffusion Coefficients Based On Kinetic Curves of Silica Grain DissolutionNallely CasasNo ratings yet
- 350 MW Power Plant Technical SpecificationsDocument7 pages350 MW Power Plant Technical SpecificationsEricGaringanaoNo ratings yet
- BS 6166 Part 3Document32 pagesBS 6166 Part 3Michael JonesNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ethanol Content From Ginebra Gin by Fractional DistillationDocument4 pagesDetermination of Ethanol Content From Ginebra Gin by Fractional DistillationToni Sy EncinaresNo ratings yet
- EXPORT COUNCIL LISTDocument32 pagesEXPORT COUNCIL LISTHarjotNo ratings yet
- Report On Cascading TransformersDocument28 pagesReport On Cascading Transformerspalak yadavNo ratings yet
- O6 Tool Steel: Chemical AnalysisDocument3 pagesO6 Tool Steel: Chemical AnalysischandraNo ratings yet
- Cutting RoomDocument45 pagesCutting RoomSuchismitaShauryaNo ratings yet
- Einhell BT-TB 13 e Manual ENDocument20 pagesEinhell BT-TB 13 e Manual ENGustavs KrievkalnsNo ratings yet
- Haas Mill WIPS Probe Training ManualDocument44 pagesHaas Mill WIPS Probe Training ManualpocerilloNo ratings yet
- Whirlpool Awe 6616 W PDFDocument41 pagesWhirlpool Awe 6616 W PDFflorin071No ratings yet
- BM2312 004Document30 pagesBM2312 004julia.sacco.20No ratings yet