Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PP1
Uploaded by
AnkurBajaj27Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PP1
Uploaded by
AnkurBajaj27Copyright:
Available Formats
EXPERIMENT
AIMTo find the refractive indexes of (a) water (b) oil (transparent) using a plane mirror, a equiconvex lens, (made from a glass of known refractive index) and an adjustable object needle.
MATERIAL
A convex lens, a plane mirror, water, kerosene oil, clamp, stand, an optical needle, plumb line, knitting needle, half meter scale, glass slab a spherometer.
REQUIRED-
THEORYDEFINATION- Two or more thin lenses, placed in contact together to
have a common principal axis, form a lens combination. Focal Length- If f1,f2.............fn be the focal length of individual lens and F be the focal length of the combination. Then 1/f= 1/f1 + 1/f2 + . + 1/fn The lenses forming the combination must be thin to have their optical centres coinciding at one point to represent optical centre of the combination. (i) If f1 and f2 be the focal length of the glass convex lens and liquid lens and f be the focal length of their combination then 1/f = 1/f1 + 1/f2
(ii) Liquid lens formed a planoconcave lens with R1-R and R2=------then by using lens makers formula 1/f2 = (n-1) (1/R1 1/R2) = (n-1) (1/R 1/) = (n-1) (1/R 0) 1/f2 = (n-1) / R n = R/f2 +1 where n = Refractive index of the liquid and R is the radius of curvature of the lower surface of the convex lens. (iii) The radius of the lower surface of the convex lens is given by R = l2/6h + h/2
Here, l is the average distance between the legs of spherometer and h is the difference in the reading of the spherometer when placed first on convex lens and then on plane mirror.
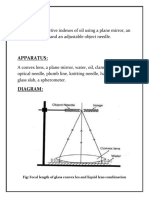
DIAGRAM-
PROCEDURE(a)
For focal length of convex lens. 1. Find rough focal length of convex lens. 2. Place a plane mirror on the horizontal base of the iron stand then a convex lens on the plane mirror. 3. Hold the needle in the clamp stand and adjust its position on the stand such that there is no parallax between tip of the needle and its image. [ the tip of needle appears touching the tip of its image] 4. Measure distance between tip and upper surface of the lens
by using a plumb line and half meter scale. Also measure the distance between tip of needle and upper surface of the mirror. Take the mean of these two reading. This mean distance will be equal to the focal length of the convex lens (f1). (b) For focal length of the combination. 5. Put a few drops of the water on the plane mirror and put the convex lens over it with its same face above as before. The water spreads in a form of layer and acts like a plano-concave lens as shown in Fig1. 6. Repeat the steps 3 and 4 to determine the equivalents focal length of combination. 7. Record the observation as given below in table 1.
8.
Repeat the steps 5, 6, 7 for other transparent liquid (kerosene oil).
(c)
For radius of curvature of convex lens surface. 9. Determine the pitch and the least count of the spherometer. 10. Remove the convex lens and dry it completely. Put the spherometer on this lens surface. 11. All the three legs of spherometer should placed symmetrically on the lens and adjust the central screw tip just to touch the surface of the lens. 12. Remove the spherometer from surface of lens and place on the plane mirror and turn the central screw so that its tip touch the plane mirror surface and record the readings as shown in table 2.
13. Repeat the steps 10 and 11 three time. 14. Obtain the impressions of three legs of spherometer on paper and marks them and their average distance l= (l1+l2+l3)/3
OBSERVATION1. Rough focal length of convex lens=cm. 2. Table 1, for the focal length of lens and combination.
Arrangement Distance of needle tip From lens From plane Mean surface x1 mirror x2 x=(x1 + (cm) (cm) x2)/2 Focal length x(cm) f1 = ..
Without liquid
With water With other Transparent Liquid (kerosene)
fw = .. f1 = ..
3. Table 2, for finding h.
S.No. Initial C.S.R. on convex lens (a) No. of complete rotations (n) Final C.S.R. on plane mirror surface (b) m= (a-b) h=n if a>b pitch = +m (100+aL.C. b) If a<b
1. 2. 3. Mean value of h = ..cm
CALCULATION(i) l=(l1+l2+l3)/3 = cm (ii) R= l2/6h + h2/2 = cm (iii) f2 = ff1/(f-f1) = cm (iv) n = 1 + R/f2 = .
RESULTS(i) The refractive index of water nw = ..
(ii) The refractive index of other liquid (kerosene oil) nl = ..
PRECAUTIONS1. The plane mirror should be clean and fully shining surface. 2. The liquid taken should be transparent. 3. The parallax should be removed tip to tip. 4. The eye should be at a distance about 30 cm from the needle while removing the parallax.
You might also like
- Refractive Indexes of Water and OilDocument12 pagesRefractive Indexes of Water and OilKajal Varshney78% (148)
- Physics (Anisha)Document7 pagesPhysics (Anisha)GauravMittal100% (1)
- Optics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionFrom EverandOptics and Optical Instruments: An IntroductionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- IndexDocument11 pagesIndexAnkit RajNo ratings yet
- Contact Lens Design Tables: Tables for the Determination of Surface Radii of Curvature of Hard Contact Lenses to Give a Required Axial Edge LiftFrom EverandContact Lens Design Tables: Tables for the Determination of Surface Radii of Curvature of Hard Contact Lenses to Give a Required Axial Edge LiftNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 2Document15 pagesPhysics Project 2Hitesh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Physic 2 - DeletedDocument17 pagesPhysic 2 - DeletedVedant SinghNo ratings yet
- Refractive Indexes of Water and OilDocument12 pagesRefractive Indexes of Water and OilsumitsingwtfNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project KENDRIYA VDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project KENDRIYA VOm Kushwaha50% (2)
- Physics Investorygatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investorygatory Projectjay danenjeyanNo ratings yet
- Investigatory ProjectDocument16 pagesInvestigatory ProjectSayan BhowmickNo ratings yet
- UjjjjqqqqqDocument12 pagesUjjjjqqqqqRanjeet Kumar100% (2)
- To Find The Refractive Indexes of A WateDocument12 pagesTo Find The Refractive Indexes of A WateAnirudh VakheelNo ratings yet
- Last in FianalDocument19 pagesLast in FianalAbhijit MuneshwarNo ratings yet
- Refractive Index 4Document17 pagesRefractive Index 4Surianandhan0% (1)
- Yhyhnu 6 Kmvfgu 7 NgeDocument11 pagesYhyhnu 6 Kmvfgu 7 NgejhgsfajgNo ratings yet
- Samrat PhysicsDocument11 pagesSamrat PhysicsSamratNo ratings yet
- Refractve Index in Water and Oil Phy Project Class 12Document12 pagesRefractve Index in Water and Oil Phy Project Class 12hsepidNo ratings yet
- Physics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensDocument16 pagesPhysics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensHemnathpalaniNo ratings yet
- 12 Phy Pro 1Document39 pages12 Phy Pro 1poorni sakthiNo ratings yet
- OBJECTIVEDocument13 pagesOBJECTIVESaish ParkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 17 PDF FreeDocument15 pagesPhysics Project 17 PDF Freefreefirelegend27No ratings yet
- Last Incomplete 333Document16 pagesLast Incomplete 333Abhijit MuneshwarNo ratings yet
- Physics IPDocument11 pagesPhysics IPkarthick KNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics Projectgerich32177% (13)
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectBarsha DasNo ratings yet
- To Find The Refractive Index of WaterDocument13 pagesTo Find The Refractive Index of WaterUtkarshNo ratings yet
- Physics-Investigatory JD (Repaired)Document14 pagesPhysics-Investigatory JD (Repaired)ABHISHEK TIWARINo ratings yet
- 2Document10 pages2jashwanth kumar58No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectAll about GamingNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 5Document15 pagesPhysics Project 5ankitNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics ProjectsherineNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics Projectiqq ewNo ratings yet
- To Find The Refractive Indexes of A WateDocument12 pagesTo Find The Refractive Indexes of A Wateadityapandey955507No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectkuser6398No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument14 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectAbhishek Raja88% (16)
- Physics Project MDocument20 pagesPhysics Project Mvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- Physics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensDocument18 pagesPhysics-Investigatory To Find The Refractive Indices of (A) Water (B) Oil (Transparent) Using A Plane Mirror, An Equiconvex LensvnaraenNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- Sunbeam School, Sultanpur: Subject: PhysicsDocument11 pagesSunbeam School, Sultanpur: Subject: PhysicsmitaliNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument15 pagesPhysicsjhardik607No ratings yet
- Physics (Investigatory Project)Document21 pagesPhysics (Investigatory Project)shreyamohanty298No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectAvani GuptaNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectThalha SNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Physics Project PRDocument16 pagesToaz - Info Physics Project PRUtkarshNo ratings yet
- Physics - Investigatory - Project Optics FINALDocument18 pagesPhysics - Investigatory - Project Optics FINALdduma240106No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument9 pagesPhysics ProjectsamNo ratings yet
- New PDFDocument16 pagesNew PDFThalha SNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument20 pagesPhysics Projectvishaljinjala7No ratings yet
- Physics Investigative ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics Investigative ProjectAmie AbdulNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectLakshya BhatiNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics Projectadatta546No ratings yet
- Expt#6Document5 pagesExpt#6akhtar140No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument12 pagesPhysics Projectradhu1310No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project KENDRIYA VDocument17 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project KENDRIYA VNavneethan PillaiNo ratings yet
- Schlegel, Richard - Atemporal Processes in Physics (1948)Document12 pagesSchlegel, Richard - Atemporal Processes in Physics (1948)Lorenz49No ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Chapter 10 1 AtkinsDocument32 pagesPhysical Chemistry Chapter 10 1 AtkinswenNo ratings yet
- DFT Calculations of Molecular Magnetic Properties of Coordination CompoundsDocument23 pagesDFT Calculations of Molecular Magnetic Properties of Coordination CompoundslitespaklaNo ratings yet
- Heat Conduction Composite WallDocument22 pagesHeat Conduction Composite WallMoosa NaseerNo ratings yet
- Assignment-12 and SolutionDocument11 pagesAssignment-12 and SolutionadimeghaNo ratings yet
- Head Losses in Pipes: NomenclatureDocument2 pagesHead Losses in Pipes: NomenclatureAudrey Patrick KallaNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Distribution Transformers - Single Phase - EE25S3H PDFDocument4 pagesLow Voltage Distribution Transformers - Single Phase - EE25S3H PDFGalih TrisnanugrahaNo ratings yet
- Determining Independent Control of Dual-Frother Systems - Gas Holdup, Bubble Size and Water Overflow RateDocument11 pagesDetermining Independent Control of Dual-Frother Systems - Gas Holdup, Bubble Size and Water Overflow RateJose Luis Barrientos RiosNo ratings yet
- INDÍSE LosssssssssssssssDocument4 pagesINDÍSE LosssssssssssssssDarioNo ratings yet
- On The Rotational Dynamics of The Rattleback: 1 BackgroundDocument17 pagesOn The Rotational Dynamics of The Rattleback: 1 Backgroundulysse_d_ithaqu7083No ratings yet
- Navigat X Mk1 DatasheetDocument2 pagesNavigat X Mk1 DatasheetcristianocalheirosNo ratings yet
- EE364 Maxwell Simulation Assignment 1Document37 pagesEE364 Maxwell Simulation Assignment 1jalilemadiNo ratings yet
- 2000 (LTPP) FHWA-RD-98-085 Temperature Predictions and Adjustment Factors For Asphalt Pavemen PDFDocument49 pages2000 (LTPP) FHWA-RD-98-085 Temperature Predictions and Adjustment Factors For Asphalt Pavemen PDFTim LinNo ratings yet
- Deleuze and The Genesis of Form PDFDocument6 pagesDeleuze and The Genesis of Form PDFRoman RuizNo ratings yet
- Petrographic Examination of Hardened Concrete: Standard Practice ForDocument14 pagesPetrographic Examination of Hardened Concrete: Standard Practice ForHéctor Armando Valderrama BaqueroNo ratings yet
- Continuous Beams DesignDocument8 pagesContinuous Beams DesignPanashe ChikomweNo ratings yet
- Void Content of Reinforced Plastics: Standard Test Methods ForDocument3 pagesVoid Content of Reinforced Plastics: Standard Test Methods ForStéfany Vier SteffenNo ratings yet
- Lucas, 1941 - Common Deffects Ice CreamDocument30 pagesLucas, 1941 - Common Deffects Ice CreamdavidNo ratings yet
- Is The Moon The Creation of IntelligenceDocument4 pagesIs The Moon The Creation of Intelligencedlazar_1100% (1)
- 01 GeoStrucAnal Cylinder Elastic PDFDocument12 pages01 GeoStrucAnal Cylinder Elastic PDFSiddhant KaushikNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy 1Document40 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy 1SOURAV BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- INTEGRATED NCM MEDICINE WITH S-NCM NEW KNOWLEDGE 2nd Edition PDFDocument153 pagesINTEGRATED NCM MEDICINE WITH S-NCM NEW KNOWLEDGE 2nd Edition PDFAzaNo ratings yet
- Marlin App CDocument12 pagesMarlin App Cedgardiaz5519No ratings yet
- Coordinate Reference SystemsDocument120 pagesCoordinate Reference SystemsBenciu Florin ValentinNo ratings yet
- The Importance of ConcreteDocument25 pagesThe Importance of ConcreteSuhaidi AliasNo ratings yet
- Multispace & Multistructure. Neutrosophic TransdisciplinarityDocument802 pagesMultispace & Multistructure. Neutrosophic TransdisciplinarityEugen SokolovNo ratings yet
- The Theory of InterestDocument13 pagesThe Theory of InterestdenireziNo ratings yet
- Composite Failure AnalysisDocument251 pagesComposite Failure AnalysisFernandoNo ratings yet
- Rippability of RocksDocument4 pagesRippability of RocksAnonymous pFXVbOS9TWNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Edward's Menagerie New Edition: Over 50 easy-to-make soft toy animal crochet patternsFrom EverandEdward's Menagerie New Edition: Over 50 easy-to-make soft toy animal crochet patternsNo ratings yet
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- House Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetFrom EverandHouse Rules: How to Decorate for Every Home, Style, and BudgetNo ratings yet
- 100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiFrom Everand100 Micro Amigurumi: Crochet patterns and charts for tiny amigurumiRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Crochet Creatures of Myth and Legend: 19 Designs Easy Cute Critters to Legendary BeastsFrom EverandCrochet Creatures of Myth and Legend: 19 Designs Easy Cute Critters to Legendary BeastsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Swatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersFrom EverandSwatch This, 3000+ Color Palettes for Success: Perfect for Artists, Designers, MakersRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (54)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Amigurumi Cats: Crochet Sweet Kitties the Japanese Way (24 Projects of Cats to Crochet)From EverandAmigurumi Cats: Crochet Sweet Kitties the Japanese Way (24 Projects of Cats to Crochet)No ratings yet
- Treasure Bookmaking: Crafting Handmade Sustainable JournalsFrom EverandTreasure Bookmaking: Crafting Handmade Sustainable JournalsNo ratings yet
- Crochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!From EverandCrochet Impkins: Over a million possible combinations! Yes, really!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (157)