Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kertas 1 SPM Matematik Tambahan 2004-2010
Uploaded by
Cikgu Mohamad Esmandi HapniOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kertas 1 SPM Matematik Tambahan 2004-2010
Uploaded by
Cikgu Mohamad Esmandi HapniCopyright:
Available Formats
P a g e | 1
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
FUNCTIONS
1 Diagram shows the relation between set P and set Q.
State
a) the range of the relation,
b) the type of relation [2 marks]P1,2004
2 Given the function m x x h + 4 : and
8
5
2 :
1
+
kx x h , where m and k are constants, find the value of
m and of k. [3 marks]P1,2004
3 Given the function 0 ,
6
) ( = = x
x
x h and the composite function hg(x) = 3x, find
a) g(x)
b) the value of x when gh(x) = 5 [4 marks]P1,2004
4 In Diagram, the function h maps x to y and the function g maps y to z
Determine
a. h
-1
(5)
b. gh(2) [2 mark]P1,2005
5 The function w is define as 2 ,
2
5
) ( =
= x
x
x w
a) w
-1
(x)
b) w
-1
(4) [3 marks]P1,2005
6 The following information refers to the functions h and g
Find gh
-1
(x) [3 marks]P1,2005
7 In diagram, Set B shows the images of certain elements of set A
a) State the type of relation between set A and set B.
b) Using the function notation, write a relation between set A and set B
[2 marks]P1,2006
d
e
f
w
x
y
z
Set P Set Q
x
h
y
g
z
2
5
8
1 4 :
3 2 :
x x g
x x h
5
4
-4
-5
25
16
Set A Set B
P a g e | 2
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
8 Diagram show the function 0 , : =
x
x
x m
x h , where m is a constant.
Find the value of m
[2 marks]P1,2006
9 Diagram shows the linear functions h
a) State the value of m
b) Using the function notation, express h in terms of x.
[2 marks]P1,2007
10 Given the function 3 : x x f , find the values of x such that f(x) = 5 [2 marks]P1,2007
11 The following information is about the function h and the composite function h
2
.
Find the value of a and of b [3 marks]P1,2007
12 Diagram show the graph of the function 1 2 ) ( = x x f , for the domain 5 0 s s x
State
a) the value of t
b) the range of f(x) corresponding to the given domain
[3 marks]P1,2008
13 Given the functions 2 5 : + x x g and 3 4 :
2
+ x x x h , find
a) g
-1
(6)
b) hg(x) [4 marks]P1,2008
14 Given the functions f(x) = x 1 and g(x) = kx + 2, find
a) f(5)
b) the value of k such that gf(5) = 14 [3 marks]P1,2008
15 Diagram shows the relation between set X and set Y in the graph form.
State
a) the objects of q
b) the codomain of the relation
[2 marks]P1,2009
8
2
1
x
x
x m
h
0
1
m
5
1
2
4
6
x h(x)
b ax x h + : , where a and b are constants, and a > 0
35 36 :
2
x x h
O t
5
x
y
1
y = f(x)
2 4 6
Set X
p
q
r
s
Set Y
P a g e | 3
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
16 Given the function 3 2 : x x g and x x h 4 : , find
a) hg(x)
b) the value of x if ) (
2
1
) ( x g x hg = [4 marks]P1,2009
17 Given the function 1 3 : x x g , find
a) g(2)
b) the value of p when 11 ) (
1
=
p g [3 marks]P1,2009
18 Diagram shows the relation between set X and set Y in the graph form.
[3 marks]P1,2010
19 Given the function 1 2 : + x x g and 6 3 : + x x h , find
(a) g
-1
(x)
(b) hg
-1
(9)
[3 marks]P1,2010
20 Given the functions 8 : x x g and
3
2
,
2 3
: =
x
x
x
x g , find the value of hg(10)
[3 marks]P1,2010
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
1 Form the quadratic equation which has the roots -3 and
2
1
. Give your answer in the form
ax
2
+ bx + c = 0, where a, b and c are constants [2 marks]P1,2004
2 Solve the quadratic equation x(2x 5) = 2x -1.
Give your answer correct to three decimal places. [3 marks]P1,2005
3 A quadratic equation x
2
+ px + 9 = 2x has two equal roots. Find the possible value of p.
[3 marks]P1,2006
4 (a) Solve the following quadratic equation :
3x
2
+ 5x 2 = 0
(b) The quadratic equation hx
2
+ kx + 3 = 0, where h and k are constants, has two equal roots. Express h
in terms of k
[4 marks]P1,2007
5 It is given that -1 is one of the roots of the quadratic equation x
2
4x p = 0.
Find the value of p.
[2 marks]P1,2008
Set X
Set Y
p
q
r
s
1 2 3 4
State
(a) the relation in the form of ordered pairs.
(b) the type of the relation.
(c) the range of the relation.
P a g e | 4
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
6 The quadratic equation
2 2
2 p px x x = + , where p is a constant, has two different root. Find the range
of values of p. [3 marks]P1,2009
7 The quadratic equation (1 p)x
2
6x + 10 = 0, where p is a constant, has two different roots.
Find the range of values of p.
[3 marks]P1,10
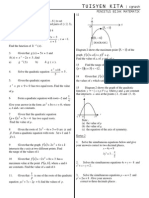
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
1 Find the range of values of x for which 12 ) 4 ( s x x . [3 marks]P1,04
2 Diagram shows the graph of the function 2 ) (
2
= k x y , where k is a constant.
Find
(a) the value of k
(b) the equation of the axis of symmetry
(c) the coordinates of the maximum point.
[3 marks]P1,04
3 The straight line y = 5x 1 does not intersect the curve y = 2x
2
+ x + p. Find the range of values of p.
[3 marks]P1,05
4 Diagram shows the graph of a quadratic functions f(x) = 3(x + p)
2
+ 2, where p is a constant.
The curve y = f(x) has the minimum point (1,q), where q is a
constant. State
a) the value of p,
b) the value of q,
c) the equation of the axis of symmetry.
[3 marks]P1,05
5 Diagram shows the graph of a quadratic function y = f(x). The straight line y = -4 is a tangent to the
curve y = f(x)
a) Write the equation of the axis of symmetry of the curve.
b) Express f(x) in the form (x + b)
2
+ c, where b and c are
constants.
[3 marks]P1,06
6 Find the range of the values of x for (2x 1)(x + 4) > 4 + x [2 marks]P1,06
7 Find the range of values of x for which x x + s1 2
2
[3 marks]P1,07
8 The quadratic function f(x) = x
2
+ 2x 4 can be expressed in the form f(x) = (x + m)
2
n, where m and n
are constant. Find the value of m and of n. [3 marks]P1,07
(2,-3) -3
O
y
x
(1,q)
x
y
y = f(x)
O
y = -4
x
y
y = f(x)
O 1 5
P a g e | 5
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
9 The quadratic function f(x) = p(x + q)
2
+ r, where p, q and r are constants, has a minimum value of -4.
The equation of the axis of symmetry is x = 3. State
a) the range of values of p
b) the value of q
c) the value of r [3 marks]P1,08
10 Find the range of the values of x for (x 3)
2
< 5 x [3 marks]P1,08
11 Diagram shows the graph of quadratic function ( ) q p x x f + + =
2
) ( , where p and q are constant.
State
a) the value of p
b) the equation of the axis of symmetry
[2 marks]P1,09
12 The quadratic function
2 2
4 ) ( a x x x f + + = , has maximum value 8. Find the value of a.
[3 marks]P1,09
13 Diagram shows the graph of a quadratic function y = f(x).
[3 marks]P1,10
14 The quadratic function f(x) = -x
2
+ 4x 3 can be expressed in the form of f(x) = -(x 2)
2
+ k, where k is
a constant.
(a) Find the value of k.
(b) Sketch the graph of the function f(x).
[4 marks]P1,10
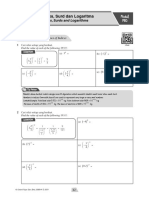
INDICES AND LOGARITHM
1 Solve the equation 32
4x
= 4
8x + 6
[3 marks]P1,2004
2 Given that m = 2 log
5
and p = 7 log
5
, express 9 . 4 log
5
in terms of m and p. [4 marks] P1,2004
(0, -9)
(-3, 0)
y
x
y
= f(x)
O
y
x
y = f(x)
- 1 3
5
State
(a) the roots of the equation y = f(x)
(b) the equation of axis of symmetry of the
curve.
P a g e | 6
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
3 Solve the equation 2
x + 4
- 2
x + 3
= 1 [3 marks] P1,2005
4 Solve the equation 1 ) 1 2 ( log 4 log
3 3
= x x [3 marks] P1,2005
5 Given that p
m
= 2 log and r
m
= 3 log , express
|
.
|
\
|
4
27
log
m
m
in terms of p and r. [4 marks] P1,2005
6 Solve the equation
2
3 2
4
1
8
+
=
x
x
. [3 marks] P1,2006
7 Given that y x xy
2 2 2
log log 3 2 log + = , express y in terms of x. [3 marks] P1,2006
8 Solve the equation x x
3 3
log ) 1 ( log 2 = + [3 marks] P1,2006
9 Given that x b =
2
log and y c =
2
log , express
|
.
|
\
|
c
b 8
log
4
, in terms of x and y. [4 marks] P1,2007
10 Given that 9(3
n 1
) = 27
n
, find the value of n. [3 marks] P1,2007
11 Solve the equation, 16
2x 3
= 8
4x
[3 marks] P1,2008
12 Given that 3 log log
2 4
= x , find the value of x. [3 marks] P1,2008
13 Given 243 27 3
3
=
n n
, find the value of n. [3 marks]P1,2009
14 Given that 0 log log
2 8
= q p , express p in terms of q. [3 marks]P1,2009
15 Solve the equation :
9
8
3 3
2
=
+ x x
[3 marks]P1,2010
16 Given a = 3 log
2
and b = 5 log
2
, express 45 log
8
in terms of a and b. [3 marks]P1,2010
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
1 Diagram shows a straight line PQ with the equation 1
3 2
= +
y x
. The point P lies on the x-axis and the
point Q lies on the y-axis.
Find the equation of the straight line perpendicular to PQ and passing
through the point Q.
[3 marks] P1,2004
2 The point A is (-1, 3) and the point B is (4, 6). The point P moves such that PA : PB = 2 : 3. Find the
equation of the locus of P. [3 marks] P1,2004
x
y
Q
P
O
P a g e | 7
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
3 The following information refers to the equations of two straight lines, JK and RT, which are
perpendicular to each other.
Express p in terms of k.
[2 marks] P1,2005
4 Diagram shows the straight line AB which is perpendicular to the straight line CB at the point B.
The equation of the straight line CB is y = 2x -1
Find the coordinates of B.
[3 marks] P1,2006
5 The straight line 1
6
= +
h
y x
has a y-intercept of 2 and is parallel to the straight line y + kx = 0. Determine
the value of h and of k. [3 marks] P1,2007
6 The vertices of a triangle are A(5, 2), B(4, 6) and C(p, -2). Given that the area of the triangle is 30 unit
2
,
find the values of p. [3 marks] P1,2007
7 Diagram shows a straight line passing through S(3, 0) and T(0, 4)
a) Write down the equation of the straight line ST in form
1 = +
b
y
a
x
.
b) A point P(x, y) moves such that PS = PT. Find the equation of
the locus of P.
[4 marks] P1,2008
8 The point (0, 3), (2, t) and (-2, -1) are the vertices of a triangle. Given that the area of the triangle is 4
unit
2
, find the values of t.
[3 marks] P1,2008
9 Diagram shows a straight line AC
The point B lies on AC such that AB : BC = 3 : 1
Find the coordinates of B
[3 marks]P1,2009
JK : y = px + k
RT : y = (k 2)x + p
Where p and k are constants.
C
B
A(0, 4)
O
x
y
y
x
T(0, 4)
S(3, 0)
O
O
C(4, 0)
x
B(h, k)
A(-2, 3)
y
P a g e | 8
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
10 A straight line passes through A(-2, -5) and B(6, 7).
(a) Given C(h, 10) lies on the straight line AB, find the value of h.
(b) Point D divides the line segment AB in the ratio 1 : 3. Find the coordinates of D.
[4 marks]P1,2010
11 Point P moves such that its distance is always 5 units from Q(-3 , 4). Find the equation of the locus
of P.
[3 marks]P1,2010
STATISTICS
1 The mean of four numbers is m . The sum of the squares of the numbers of the numbers is 100 and the
standard deviation is 3k. Express m in term of k.
[3 marks]P1,2005
2 A set of positive integers consists of 2, 5 and m. The variance for this set of integers is 14. Find the
value of m. [3 marks]P1,2006
3 A set of data consists of five numbers. The sum of the numbers is 60 and the sum of the squares of the
numbers is 800.
Find, for the five numbers
a) the mean
b) the standard deviation. [3 marks]P1,2007
4 A set of seven numbers has a mean of 9.
a) Find Ex
b) When a number k is added to this set, the new mean is 8.5. Find the value of k.
[3 marks]P1,2008
5 A set of 12 numbers x
1
, x
2
, , x
12
, has a variance of 40 and it is given that Ex2 = 1080
Find
a) the mean, x
b) the value of Ex [3 marks]P1,2009
6 A set of data consists of 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 7 and 9. Determine the interquartile range of the data.
[3 marks]P1,2010
CIRCULAR MEASURE
1 Diagram shows a circle with centre O.
Given that the length of the major arc AB is 45.51 cm, find the length, in
cm of the radius.
(use t = 3.142)
[3 marks]P1,2004
A
B
O
0.354 rad
P a g e | 9
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
2 Diagram shows a circle with centre O
The length of the minor arc AB is 16 cm and the angle of the major sector
AOB is 290
o
. Using t = 3.142 find
a) the value of u, in radians.
(Give your answer correct to four significant figures.)
b) the length in cm of the radius of the circle.
[3 marks]P1,2005
3 Diagram show sector OAB with centre O and sector AXY with centre A.
Given that OB = 10 cm, AY = 4 cm, ZXAY = 1.1 radians and the length of arc AB
= 7 cm, calculate
a) the value of u, in radian,
b) the area in cm
2
, of the shaded region.
[4 marks]P1,2006
4 Diagram shows a sector BOC of a circle with centre O.
It is given that AD = 8 cm and
BA = AO = OD = DC = 5 cm, Find
a) the length in cm of the arc BC
b) the area in cm
2
of the shaded region.
[4 marks]P1,2007
5 Diagram shows a circle with centre O and radius 10 cm.
Given that P, Q, and R are points such that OP = PQ and ZOPQ = 90
o
,
find
(Use t = 3.142)
a) ZQOR, in radians,
b) The area in cm
2
of the shaded region.
[4 marks]P1,2008
A
B
O
u
u
O
Y
A
B
X
C
B
D
A
O
1.85 rad
Q
P
O
R
10 cm
P a g e | 10
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
6 Diagram shows a sector BOC of a circle with centre O.
It is given that ZBOC = 1.42 radians, AD = 8 cm and OA = AB = OD = DC = 5 cm
Find
a) the length in cm of arc BC
b) the area in cm
2
of the shaded region
[4 marks]P1,2009
7 Diagram shows sector OPQ of a circle with centre O, and sector NRS of a circle with centre N.
[3 marks]P1,2010
DIFFERENTIATION
1 Differentiate ( )
4 2
5 2 3 x x with respect to x.
[3 marks]P1,2004
2 Two variables, x and y, are related by the equation
x
x y
2
3 + = . Given that y increases at a constants rate
of 4 units per second, find the rate of change of x when x = 2
[3 marks]P1,2004
3 Given that
( )
2
5 3
1
) (
=
x
x h , evaluate ) 1 ( h ' ' .
[4 marks]P1,2005
O
A D
B C
8 cm
10 cm
O
R Q
N
P
S
Given ZPOQ = 1.5 radians and
ZRNS = 0.5 radian, find the area, in cm
2
of the shaded region.
P a g e | 11
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
4 The volume of water, V cm
3
in a container is given by h h V 8
3
1
3
+ = , where h cm is the height of the
water in the container. Water is poured into the container at the rate of 10 cm
3
s
-1
. Find the rate of
change of the height of water, in cm s
-1
, at the instant when its height is 2 cm.
[4 marks]P1,2005
5 The point P lies on the curve ( )
2
5 = x y . It is given that the gradient of the normal at P is
4
1
. Find the
coordinates of P.
[3 marks]P1,2006
6 It is given that
7
3
2
u y = , where u = 3x 5. Find
dx
dy
in terms of x.
[4 marks]P1,2006
7 Given that 4 3
2
+ = x x y
a) find the value of
dx
dy
when x = 1
b) express the approximate change in y, in terms of p, when x changes from 1 to 1 + p, where p is a
small value.
[4 marks]P1,2006
8 The curve y = f(x) is such that
dx
dy
= 3kx + 5, where k is a constant. The gradient of the curve at x = 2 is
9. Find the value of k.
[2 marks]P1,2007
9 The curve 64 32
2
+ = x x y has a minimum point at x = p, where p is a constant. Find the value of p.
[3 marks]P1,2007
10 Two variables, x and y are related by the equation
2
16
x
y = . Express in terms of h, the approximate
change in y, when x changes from 4 to 4 + h, where h is a small value.
[3 marks]P1,2008
11 The normal to the curve x x y 5
2
= at point P is parallel to straight line y = -x + 12. Find the equation
of the normal to the curve at point P.
[4 marks]P1,2008
12 A block of ice in the form of a cube with sides x cm, melts at a rate of 9.72 cm
3
per minute. Find the rate
of change of x at the instant when x = 12 cm.
[3 marks]P1,2009
13 The gradient function of a curve is 6 = kx
dx
dy
, where k is a constant. It is given that the curve has a
turning point at (2, 1). Find
a) the value of k
b) the equation of the curve.
[4 marks]P1,2009
P a g e | 12
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
14 Given y = 2x(x 6), find
(a)
dx
dy
(b) the value of x when y is minimum
(c) the minimum value of y. [3 marks]P1,2010
15 The volume of a sphere is increasing at a constant rate of 12.8 t cm
3
s
-1
. Find the radius of the sphere at
the instant when the radius is increasing at a rate of 0.2 cm s
-1
.
[Volume of sphere =
3
3
4
r V t = ] [3 marks]P1,2010
PROGRESSIONS
1 Given a geometric progression ..., ,
4
, 2 , p
y
y express p in terms of y.
[2 marks]P1,2004
2 Given an arithmetic progression -7, -3, 1,, state three consecutive terms in this progression which sum
up to 75.
[3 marks]P1,2004
3 The volume of water in a tank is 450 litres on the first day. Subsequently, 10 litres of water is added to
the tank everyday. Calculate the volume, in litres, of water in the tank at the end of the 7
th
day.
[2 marks]P1,2004
4 Express the recurring decimal 0.969696 as a fraction in its simplest form.
[4 marks]P1,2004
5 The first three terms of a sequence are 2, x, 8. Find the value of x so that the sequence is
i) an arithmetic progression,
ii) a geometric progression.
[2 marks]P1,2005
6 The first three terms of an arithmetic progression are 5, 9, 13. Find
i) The common difference of the progression,
ii) The sum of the first 20 terms after the 3rd term.
[4 marks]P1,2005
7 The sum of the first n terms of the geometric progression 8, 24, 72, is 8744. Find
a) the common ratio of the progression,
b) the value of n
[4 marks]P1,2005
8 The 9th term of an arithmetic progression is 4 + 5p and the sum of the first four terms of the progression
is 7p 10, where p is a constant. Given that the common difference of the progression is 5, find the
value of p.
[3 marks]P1,2006
9 The third term of a geometric progression is 16. The sum of the third term and the fourth term is 8. Find
a. the first term and the common ratio of the progression,
b. the sum to infinity of the progression.
[4 marks]P1,2006
P a g e | 13
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
10 a) Determine whether the following sequence is an arithmetic progression or a geometric
progression.
16x, 8x, 4x,
b) Give a reason for the answers in (a).
[2 marks]P1,2007
11 Three consecutive terms of an arithmetic progression are 5 x, 8, 2x. Find the common difference of the
progression.
[3 marks]P1,2007
12 The first three terms of a geometric progression are 27, 18, 12. Find the sum to infinity of the geometric
progression.
[3 marks]P1,2007
13 It is given that the first four terms of a geometric progression are 3, -6, 12 and x. Find the value of x.
[2 marks]P1,2008
14 The first three terms of an arithmetic progression are 46, 43 and 40. The nth term of this progression is
negative. Find the least value of n.
[3 marks]P1,2008
15 In a geometric progression, the first term is 4 and the common ratio is r. Given that the sum to infinity
of this progression is 16, find the value of r.
[2 marks]P1,2008
16 Given the geometric progression ,...,
9
20
,
3
10
, 5 find the sum to infinity of the progression.
[3 marks]P1,2009
17 Diagram shows three square cards.
The perimeters of the cards form an arithmetic progression. The terms of the progression are in
ascending order.
a. Write down the first three terms of the progression.
b. Find the common difference of the progression.
[2 marks]P1,2009
18 The first three terms of a geometric progression are x, 6, 12. Find
a. the value of x
b. the sum from the fourth term to the ninth term.
[4 marks]P1,2009
19 The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progression is given by ] 1 3 [
2
+ = n
n
S
n
.
Find
(a) The sum of the first 5 terms,
(b) The 5
th
term
[4 marks]P1,2010
3 cm
5 cm
7cm
P a g e | 14
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
20 It is given that 1, x
2
, x
4
, x
6
,. Is a geometric progression and its sum to infinity is 3.
Find
(a) the common ratio in terms of x,
(b) the positive value of x.
[3 marks]P1,2010
21 The first three terms of an arithmetic progression are 3h, k, h + 2.
(a) Express k in terms of h.
(b) Find the 10
th
term of the progression in terms of h.
[4 marks]P1,2010
LINEAR LAW
1 Diagram shows a straight line graph of
x
y
against x
Given that y = 6x x
2
, calculate the value
of k and of h.
[3 marks]P1,2004
2 The variables x and y are related by the equation y = kx
4
, where k is a constant.
a) Convert the equation y = kx
4
to linear form.
b) Diagram shows the straight line obtained by plotting y
10
log against x
10
log .
Find the value of
i) k
10
log
ii) h
[4 marks]P1,2005
(2, k)
(h, 3)
x
O
x
y
O
(0, 3)
(2, h)
y
10
log
x
10
log
P a g e | 15
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
3 Diagrams shows the curve y = -3x
2
+ 5 and the straight line graph obtained when y = -3x
2
+ 5 is
expressed in the linear form Y = 5X + c.
Express X and Y in terms of x and/or y
[3 marks]P1,2006
4 The variables x and y are related by the equation y
2
= 2x(10 x). A straight line graph is obtained by
plotting
x
y
2
against x, as shown in diagram.
Find the value of p and of q.
[3 marks]P1,2007
5 The variables x and y are related by the equation
x
k
y
5
= , where k is a constant.
a) Express the equation
x
k
y
5
= in its linear form used to
obtain the straight line graph shown in the diagram.
b) Find the value of k.
[4 marks]P1,2008
(p, 0)
(3, q)
x
y
2
x O
(0, -2)
y
10
log
x O
y
x
O
Y
X
O
-3
y = - 3x
2
+5
P a g e | 16
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
6 The variables x and y are related by the equation hy = kx
2
+ hk. A straight line graph is obtained by
plotting y against x
2
as shown in the diagram below.
[3 marks]P1,2010
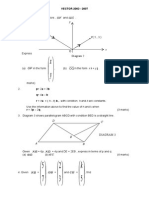
VECTORS
1 Given that O(-3, 4) and B(2, 16), find in terms of the unit vectors
~
i and
~
j
a) AB
b) the unit vector in the direction of AB [4 marks]P1,2004
2 Given that A(-2, 6), B(4, 2) and C(m, p), fin the value of m and of p such that
~
~
12 10 2 j i BC AB = + .
[4 marks]P1,2004
3 Diagram show vector OA drawn on a Cartesian plane
a) Express OA in the form
|
|
.
|
\
|
y
x
b) Find the unit vector in the direction of OA
[2 marks]P1,2005
4 Diagram shows a parallelogram, OPQR, drawn on a Cartesian plane
It is given that
~
~
4 6 j i OP + = and
~
~
5 4 j i PQ + = .
Find PR
[3 marks]P1,2005
y
x
2
O
(0 , 6)
Given the gradient of the straight line is 3,
find the value of h and of k.
O
x
y
R
Q
P
O
2 4 6 8 10 12
2
4
6
y
x
A
P a g e | 17
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
5 Diagram shows two vectors OA and AB
Express
a) OA in the form
|
|
.
|
\
|
y
x
b) AB in the form
~
~
j y i x +
[2 marks]P1,2006
6 The points P, Q and R are collinear. It is given that
~ ~
2 4 b a PQ = and ( )
~ ~
1 3 b k a QR + + = , where k is a
constant. Find
a) the value of k
b) the ratio of PQ : QR
[4 marks]P1,2006
7 The following information refers to the vectors
~
a and
~
b .
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
8
2
~
a ,
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
4
1
~
b
Find
a) the vector
~ ~
2 b a
b) the unit vector in the direction of
~ ~
2 b a [4 marks]P1,2007
8 The vector
~
a and
~
b are non-zero and non-parallel. It is given that ( ) ( )
~ ~
5 3 b k a h = + , where h and k are
constants. Find the value of
a) h
b) k [2 marks]P1,2008
9 Diagram shows a triangle PQR.
The point T lies on QR such that QT : TR = 3 : 1
Express in terms of
~
a
and
~
b :
a) QR
b) PT
[4 marks]P1,2008
10 Diagram shows a triangle PQR.
Given
~
3a PQ = ,
~
6b PR = and point S lies on QR such that
QR : SR = 2 : 1,
Express in terms of
~
a and
~
b
a) QR
b) SP [4 marks]P1,2009
O
-5
y
x
A(4, 3)
B
P
Q
T
R
4
~
a
4
~
b
P
R
S
Q
P a g e | 18
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
11 Given that j i a + =13 and j k i b = 7 , find
a) b a in form j y i x +
b) the value of k if 10 = b a [4 marks]P1,2009
12 Diagram shows the vector OR.
[3 marks]P1,2010
13 Diagram shows a triangle OAB and M is a point on AB.
[4 marks]P1,2010
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
1 Solve the equation x x x sin sin cos
2 2
= for 0
o
s x s 360
o
[4 marks]P1,2004
2 Solve the equation 5 sin 8 2 cos 3 = x x for 0
o
s x s 360
o
[4 marks]P1,2005
3 Solve the equation
o
x x 30 sin 4 sin sin 15
2
+ = 0
o
s x s 360
o
[4 marks]P1,2006
4 Solve the equation 0 cos 2 cot = + x x for 0
o
s x s 180
o
.
[4 marks]P1,2007
5 Given that sinu = p, where p is a constant and 90
o
s x s 180
o
. Find in terms of p
a) cosecu
b) sin2u
[3 marks]P1,2008
y
O
x
R(3 , 4)
Express in the form j y i x + :
(a) OR
(b) the unit vector in the direction of OR .
O
A
M
B
Given a OA 5 = , b OB 4 = , and 2AM = 3MB,
find
(a) AB
(b) OM
P a g e | 19
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
6 Solve the equation 0 cos sin 3 = cox x x , 0
o
s x s 360
o
.
[3 marks]P1,2009
7 It is given that
13
5
sin = A and
5
4
cos = B , where A is an obtuse angle and B is an acute angle. Find
a) tan A
b) cos (A B)
[3marks]P1,2009
8 Given cos u = p, find tan
2
u. [2 marks]P1,2010
PROBABILITY
1 A box contains 6 white marbles and k black marbles. If a marble is picked randomly from the box, the
probability of getting a black marble is
5
3
. Find the value of k.
[3 marks]P1,2004
2 Table shows the number of coloured cards in a box.
Two cards are drawn at random from the box.
Find the probability that both cards are of the same colour.
[3 marks]P1,2005
3 The probability that Hamid qualifies for the final of a track event is
5
2
while the probability that Mohan
qualifies is
3
1
. Find the probability that
a) both of them qualify for the final
b) only one of them qualifies for the final.
[3 marks]P1,2006
4 The probability that each shot fired by Ramli hits a targets is
3
1
.
a) If Ramli fires 10 shots, find the probability that exactly 2 shots hit the target.
b) If Ramli fires n shots, the probability that all the n shots hit the targets is
243
1
. Find the value of n.
[4 marks]P12007
5 The probability of Sarah being chosen as a school prefect is
5
3
while the probability of Aini being
chosen is
12
7
. Find the probability that
a) neither of them is chosen as a school prefect,
b) only one of them is chosen as a school prefect.
[4 marks]P1,2008
Colour Number of Cards
Black 5
Blue 4
Yellow 3
P a g e | 20
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
6 The probability that a student is a librarian is 0.2. Three students are chosen at random. Find the
probability that
a) all three are librarians,
b) only one of them is librarian.
[4 marks]P1,2009
7 In a selection of a class monitor, the probability that student X is chosen is
3
1
, while the probability that
either student X od student Y is chosen is
5
2
.
Find the probability that
(a) student Y is chosen,
(b) student X or student Y is not chosen.
[3 marks]P1,2010
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
1 X is a random variable of a normal distribution with a mean of 5.2 and variance of 1.44. Find
a) the Z score if X = 6.7
b) P(5.2 s X s 6.7)
[4 marks]P1,2004
2 The masses of students in a school has a normal distribution with mean of 54 kg and a standard
deviation of 12 kg. Find
a) the mass of the students which gives a standard score of 0.5,
b) the percentage of students with mass greater than 48 kg.
[4 marks]P1,2005
3 Diagram shows a standard normal distribution graph.
The probability represented by the area of the shaded
region is 0.3485.
(a) Find the value of k.
(b) X is a continuous random variable which is normally
distributed with a mean of 79 and a standard deviation
of 3. Find the value of X when the z-score is k.
[4 marks]P1,2006
4 X is a continuous random variable of a normal distribution with a mean of 52 and a standard deviation
of 10. Find
a) the z-score when X = 67.2
b) the value of k when P(z < k) = 0.8849
[4 marks]P1,2007
5 The masses of a group of students in a school have a normal distribution with a mean of 40 kg and a
standard deviation of 5 kg. Calculate the probability that a student chosen at random from this group has
a mass of
a) more than 45 kg
b) between 35 kg and 47.8 kg
[4 marks]P1,2008
O k
z
f(x)
0.3485
P a g e | 21
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
6 The masses of apples in a stall have a normal distribution with a mean of 200 g and a standard deviation
of 30 g.
a) Find the mass, in g, of an apple whose z-score is 0.5
b) If an apple is chosen at random, find the probability that the apple has a mass of at least 194 g.
[4 marks]P1,2009
7 The discrete random variable X has a binomial probability distribution with n = 4, where n is the number
of trials. Diagram shows the probability distribution of X.
[4 marks]P1,2010
16
1
4
1
k
P(X = x)
x
0 1 2 3 4
Find
(a) the value of k
(b) P(X 3)
P a g e | 22
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
FUNCTIONS
1 a) {x , y}
1 b) many to one
2) m =
2
5
, k =
8
1
3 a) 0 ,
2
= x
x
3b) x = 15
4a) 2
4b) 8
5a)
x
x 5 2
5b)
4
3
6) 2x + 5
7a) many to one
7b)
2
: x x f
8) m = 4
9a) m = 3
9b) h(x) = x + 1
10) x =8 , x = -2
11) a = 6 , b = -5
12a) t =
2
1
12b) 0 f(x) 9
13 a)
5
4
13 b) 25x
2
-1
14 a) 4
14 b) k = 3
15 a) 2 and 6
15 b) {p, q, r, s}
16 a) 8x 12
16 b) x =
2
3
17 a) 5
17 b) p = 32
18 a) {(1,p), (2,r), (3,5), (4,p)}
18 b) many to one
18 c) {p, r, s}
19 a)
2
1 x
19 b) 18
20 )
2
1
QUADRATIC EQUATIONS
1) 2x
2
+ 5x -3 = 0
2) x = 0.149 , x = 3.351
3) p = -4 , p = 8
4 a) x =
3
1
, x =-2
4 b)
12
2
k
h =
5) p = 5
6) p <
4
1
7) p >
10
1
QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS
1) -2 x 6
2a) k =1
2b) x = 1
2c) (1, -2)
3) p > 1
4a) p = -1
4b) q = 2
4c) x = 1
5a) x = 3
5b) f(x) = (x 3)
2
4
6) x < -4 , x > 1
7)
2
1
x 1
8) m = 1, n = 5
9a) p >0
9b) q = -3
9c) r = -4
10) 1 < x < 4
11a) p = 3
11b) x = -3
12) a = -2 , 2
13a) -1 , 3
13b) x = 1
14a) k = 1
14b)
f(x
)
x
1
3
(2,1)
1
-3
P a g e | 23
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
INDICES AND LOGARITHM
1) x = 3
2) 2p m -1
3) x = -3
4) x =
2
3
5) 3r 2p +1
6) x = 1
7) y = 2x
8) x =
8
9
9)
2
3 y x +
10) n =
2
1
11) x = -3
12) x = 9
13) n =2
14) p = q
3
15) x = -2
16)
3
2 b a +
COORDINATE GEOMETRY
1) y =
3
2
x + 3
2) 5x
2
+ 5y
2
+ 50x 6y 118 = 0
3) p =
k 2
1
4) B(2,3)
5) h = 2 , k =
3
1
6) p = -9 , p = 21
7a)
3
x
+
4
y
= 1
7b) 6x 8y + 7 = 0
8) t = 3 , t = 11
9) B(
4
3
,
2
5
)
10a) h = 8
10b) D(0,-2)
11) x
2
+ y
2
+ 6x - 8y = 0
STATISTICS
1) m = 25 - 9k
2
2) m = - 4 , 11
3a) 12
3b) 4
4a) 63
4b) k = 5
5a) 7.071
5b) 84.85
6) 4
CIRCULAR MEASURE
1) 7.675 cm
2a) 1.222
2b) 13.09 cm
3a) 0.7
3b) 26.2 cm
2
4a) 18.5
4b) 80.48
5a) 1.047 rad
5b) 30.70 cm
2
6a) 14.2
6b) 58.64
7) 59 cm
2
DIFFERENTIATION
1) 6x(6x 5)(2x 5)
2
2)
5
8
=
dt
dx
3)
8
27
4)
6
5
=
dt
dh
5) P(7,4)
6) 14(3x 5)
6
7a) 7
7b) y = 7p
8) k =
3
2
9) p = 16
10) y =
2
1
h
11) y = -x 3
12)
dt
dx
= - 0.0225
13a) k = 3
13b) y = 7 6
2
3
2
+ x x
14a) 4x 12
14b) x = 3
14c) 18
15) r = 4
PROGRESSIONS
P a g e | 24
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
1) p =
2
8
y
2) T
8
= 21, T
9
= 25 , T
10
= 29
3) T
7
= 510
4)
33
32
5i) x = 5
5ii) x = 4
6i) 4
6ii) 1100
7a) 3
7b) 7
8) p = 8
9a) T
1
= 64 , r =
2
1
9b)
3
2
42
10a) G.P
10b) Common ration, r =
2
1
11) d = 14
12) 81
13) 24
14) n = 17
15)
4
3
16) 3
17a) 12, 20, 28
17b) d = 8
18a) x = 3
18b) 1512
19a) 40
19b) 14
20a) x
2
20b) 0.8165
21a) k = 2h + 1
21b) 9 6h
LINEAR LAW
1) k = 4 , h = 3
2a) k x y
10 10 10
log log 4 log + =
2bi) 3
2bii) 11
3) X =
2
1
x
, Y =
2
x
y
4) p = 10 , q = 14
5a) k x y
10 10 10
log ) 5 log ( log + =
5b) k =
100
1
6) h = 2 , k = 6
VECTORS
1a) 5 i + 12 j
1b)
13
5
i +
13
12
j
2) m = 6 , p = -2
3a) 12i + 5j
3b)
13
12
i +
13
5
j
4) -10i + j
5a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
3
4
5b) 4i 8j
6a)
2
5
6b) 4 : 3
7a)
|
|
.
|
\
|
12
5
7b)
13
12 5 j i +
8a) h = -3
8b) k = 5
9a) 4a 6b
9b) 3a +
2
3
b
10a) -3a + 6b
10b) - a - 4b
11a) 6i + (1 +k)j
11b) k = -9 , 7
12a) 3i + 4j
12b)
5
3
i +
5
4
j
13a) -5a + 4b
13b) 2a +
5
12
b
TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
1) x = 30
o
, 150
o
, 270
o
2) x = 41
o
49, 138
o
11
3) x = 23
o
35, 156
o
25, 199
o
28, 340
o
32
4) x = 90
o
, 210
o
, 270
o
, 330
o
5a)
p
1
5b)
2
1 2 p p
6) x = 19
o
28, 90
o
, 160
o
32, 270
o
7a)
12
5
P a g e | 25
Disediakan oleh Mohamad Esmandi Bin Hapni
7b)
65
33
8)
2
2
1
p
p
PROBABILITY
1) k = 9
2)
66
19
3a)
15
2
3b)
15
7
4a) 0.1951
4b) n = 5
5a)
16
1
5b)
60
29
6a) 0.008
6b) 0.384
7a)
15
1
7b)
5
3
PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTIONS
1a) 1.25
1b) 0.3944
2a) 60 kg
2b) 69.15%
3a) k = 1.03
3b) 82.09
4a) 1.52
4b) 1.2
5a) 0.1587
5b) 0.7819
6a) 215 g
6b) 0.5793
7a) k =
8
3
7b)
16
5
You might also like
- Koleksi Soalan SPM Paper 1Document34 pagesKoleksi Soalan SPM Paper 1Basri JaafarNo ratings yet
- Linear Law P1Document2 pagesLinear Law P1mohamad_bidari0% (1)
- Add Math SPM 2013Document36 pagesAdd Math SPM 2013tuntejaputeriNo ratings yet
- Add Maths SPM Forecast PapersDocument16 pagesAdd Maths SPM Forecast PapersShanmuganantha KathiraveluNo ratings yet
- Topik 1 FungsiDocument6 pagesTopik 1 Fungsifarahim67No ratings yet
- Chapter 12 II Transformations III SPM Past Year Questions 2Document8 pagesChapter 12 II Transformations III SPM Past Year Questions 2Samsiah Mustaffa100% (1)
- Trial SPM Maths Sarawak 2016 P2 AnswerDocument22 pagesTrial SPM Maths Sarawak 2016 P2 Answerwaichunko88% (8)
- Soalan Math Tambah Ting 4 Bab 4 Persamaan SerentakDocument3 pagesSoalan Math Tambah Ting 4 Bab 4 Persamaan SerentakChe Azhani Che OmarNo ratings yet
- Add Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Document18 pagesAdd Maths Form 4 Paper 1 Midterm 2012Thiyaku MaruthaNo ratings yet
- SPM Tips PhysicDocument2 pagesSPM Tips PhysicIzzuddin AzizanNo ratings yet
- Integration SPM ADocument1 pageIntegration SPM ARosmizar Ahmad0% (1)
- Key to excelling in Additional Mathematics/TITLEDocument124 pagesKey to excelling in Additional Mathematics/TITLEJia HuiNo ratings yet
- Circular Measure CalculationsDocument17 pagesCircular Measure CalculationsRahman AnwarNo ratings yet
- Tips For Additional MathematicsDocument5 pagesTips For Additional Mathematicssahmozac92% (12)
- Jom Tanya Sifu :15 Days Programme Part 1Document15 pagesJom Tanya Sifu :15 Days Programme Part 1Hayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2 Klon SPM Quad Eqn 2003 - 2014 - EdDocument32 pages2 Klon SPM Quad Eqn 2003 - 2014 - EdAnonymous 0fagPbbloNo ratings yet
- AddmathDocument30 pagesAddmathtuntejaputeriNo ratings yet
- Vector SPM 2003 - 2007Document4 pagesVector SPM 2003 - 2007Rosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Add. Maths Paper 1 SBP Form 4 Akhir 06Document20 pagesAdd. Maths Paper 1 SBP Form 4 Akhir 06Ameera Natasya86% (7)
- Add Math Index NumberDocument7 pagesAdd Math Index Numberkamil muhammadNo ratings yet
- AMATH QuadraticFunctionDocument14 pagesAMATH QuadraticFunctionLeneNo ratings yet
- Koleksi Soalan SPM Add MathsDocument17 pagesKoleksi Soalan SPM Add MathsCheegu EmmaNo ratings yet
- Score in Addmath SPM 2019Document37 pagesScore in Addmath SPM 2019andy100% (1)
- Kertas 2 SPM Matematik Tambahan 2004-2010Document49 pagesKertas 2 SPM Matematik Tambahan 2004-2010Cikgu Mohamad Esmandi HapniNo ratings yet
- MOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE PROBLEMSDocument4 pagesMOTION ALONG A STRAIGHT LINE PROBLEMSNi'mazakirah Ab Rahman100% (1)
- Modul 10 Set K2Document8 pagesModul 10 Set K2Ting ShiangNo ratings yet
- Module 16 PMR Trapezium and Scale Drawing ProblemsDocument6 pagesModule 16 PMR Trapezium and Scale Drawing ProblemsDerek MaNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Add Maths Final P2Document16 pagesForm 4 Add Maths Final P2Liew Kok YeeNo ratings yet
- Add Math p2 Trial SPM SBP 2007Document11 pagesAdd Math p2 Trial SPM SBP 2007Carolyn Chang Boon ChuiNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument5 pagesQuadratic EquationNg Kok ChingNo ratings yet
- PT3 RevisionDocument26 pagesPT3 RevisionAnonymous Kx8TAybnXQNo ratings yet
- SPM Trigonometry Functions Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageSPM Trigonometry Functions Problems and SolutionsRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Latihan Ungkapan AlgebraDocument2 pagesLatihan Ungkapan Algebrabenjoe100% (1)
- Topical Exercise - Algebraic ExpressionsDocument4 pagesTopical Exercise - Algebraic ExpressionsHazri Mohd HamzahNo ratings yet
- Soalan-Soalan Percubaan SPM Chapter 1:functions: KelantanDocument2 pagesSoalan-Soalan Percubaan SPM Chapter 1:functions: KelantanYuh HaurNo ratings yet
- Revision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsDocument4 pagesRevision - Additional Mathematics F4.1 - FunctionsJiaRenTeohNo ratings yet
- Matrices SPM 2015-2019Document3 pagesMatrices SPM 2015-2019Fatihah Md NoorNo ratings yet
- PANITIA MATEMATIK TAMBAHANDocument162 pagesPANITIA MATEMATIK TAMBAHANFazlina MustafaNo ratings yet
- Answers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)Document2 pagesAnswers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)compeil100% (2)
- AMATH Index NumberDocument20 pagesAMATH Index NumberLeneNo ratings yet
- SPM AddMath Linear LawDocument21 pagesSPM AddMath Linear LawLeneNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Test with 20 QuestionsDocument14 pagesTrigonometry Test with 20 QuestionsMohd TaufekNo ratings yet
- SPM 2003-2007 VECTORS, TRIGONOMETRY, PROBABILITY ANSWERSDocument9 pagesSPM 2003-2007 VECTORS, TRIGONOMETRY, PROBABILITY ANSWERSRosmizar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 II Set EnrichDocument11 pagesChapter 5 II Set Enrichjuriah binti ibrahim100% (1)
- Form 2 - Chapter 13Document8 pagesForm 2 - Chapter 13Adibah AliasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Introduction To SetsDocument7 pagesChapter 11 Introduction To SetsJu WenNo ratings yet
- SPM Questions (Differentiation) - Paper 2Document4 pagesSPM Questions (Differentiation) - Paper 2Sanjey RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Bab 4 Modul PBDDocument16 pagesForm 4 Bab 4 Modul PBDdianaNo ratings yet
- Kertas 1Document41 pagesKertas 1whuiseanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsDocument8 pagesChapter 3: Quadratic FunctionsHayati Aini AhmadNo ratings yet
- Additional Maths functions coordinate geometryDocument81 pagesAdditional Maths functions coordinate geometrySaya MenangNo ratings yet
- KOLEKSI SOALAN SPM MATEMATIK TAMBAHAN KERTAS 1Document15 pagesKOLEKSI SOALAN SPM MATEMATIK TAMBAHAN KERTAS 1John NgooNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionDocument62 pagesSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionShatesh Kumar Chandrahasan100% (2)
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionsDocument61 pagesSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionsAvvy21No ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionDocument62 pagesSPM Add Maths Pass Year QuestionJanice Yizing91% (23)
- SPM Past Questions Add MathsDocument61 pagesSPM Past Questions Add MathsAnonymous IyNfIgG4Z100% (2)
- Cgnash Pencetus Bijak Matematik: X X X X HDocument1 pageCgnash Pencetus Bijak Matematik: X X X X HcgnashNo ratings yet
- Soalan SPM Paper 1Document34 pagesSoalan SPM Paper 1Anandraj GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Functions Paper 1Document12 pagesFunctions Paper 1Mohamad Shahir IsmailNo ratings yet
- Modul Amuk P1 SoalanDocument34 pagesModul Amuk P1 SoalanSukHarunNo ratings yet
- SPM AddMath ProgressionDocument16 pagesSPM AddMath ProgressionLeneNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus Concepts ExplainedDocument53 pagesVector Calculus Concepts ExplainedNurul Hanifah0% (2)
- Strategic Intervention MaterialDocument25 pagesStrategic Intervention MaterialJenny Martinez SaberdoNo ratings yet
- DiZenzo-A Note On The Gradient of A Multi-ImageDocument10 pagesDiZenzo-A Note On The Gradient of A Multi-ImageMaider MarinNo ratings yet
- Railway Engineering Curves and Super Elevation - Circular CurvesDocument13 pagesRailway Engineering Curves and Super Elevation - Circular CurvesThomas BautistaNo ratings yet
- XII - Maths - CirclesDocument12 pagesXII - Maths - CirclesNaveen GargNo ratings yet
- CH 01 HWDocument31 pagesCH 01 HWClayton KwokNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/21Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: MATHEMATICS 0580/21Eman AbdellatifNo ratings yet
- 2012 Edexcel Higher A Paper 2Document19 pages2012 Edexcel Higher A Paper 2Brenda WaltersNo ratings yet
- Omplex Nalysis: C 2014 Ron BuckmireDocument4 pagesOmplex Nalysis: C 2014 Ron BuckmireSasikalaNo ratings yet
- 6 Prosiding ICM2E 2017Document434 pages6 Prosiding ICM2E 2017Andinuralfia syahrirNo ratings yet
- Comment On Phoranomus and Dynamica de PotentiaDocument23 pagesComment On Phoranomus and Dynamica de Potentiarelax_mpg6406100% (1)
- Iit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0Document16 pagesIit Jee TRIGNOMETRY FORMULAS2.0ARYAN SINGHNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Machine TheoryDocument25 pagesIntroduction to Machine TheoryAli Khan Niazi100% (1)
- ME5203 EndSem 2021Document3 pagesME5203 EndSem 2021Bikash Gupta me21m054No ratings yet
- Mechanical Analysis of Thin-Walled Conical StructureDocument11 pagesMechanical Analysis of Thin-Walled Conical StructureJohn RoyNo ratings yet
- Gr.6 Third Periodical Test in MathDocument9 pagesGr.6 Third Periodical Test in MathPein NagatoNo ratings yet
- 3D Geometry in Geogebra - The Plane Through 3 PointsDocument6 pages3D Geometry in Geogebra - The Plane Through 3 PointsVinsens DiastaraNo ratings yet
- HW 1 SolutionDocument2 pagesHW 1 Solutionvictor capacuteNo ratings yet
- The 66th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2005Document1 pageThe 66th William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition Saturday, December 3, 2005Ciprian TimofteNo ratings yet
- Short History of TrigonometryDocument7 pagesShort History of TrigonometryAmazimg Abbah QouNo ratings yet
- Applications of Triple Integrals.Document4 pagesApplications of Triple Integrals.Tom Jones100% (1)
- Fundamentals-Of-Aerodynamics-6th-Edition-Anderson SolutionDocument12 pagesFundamentals-Of-Aerodynamics-6th-Edition-Anderson SolutionBẢO NGÔ HÀ GIA100% (1)
- Att Nov22Document1 pageAtt Nov22NebulaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 C8, 8.2 Circles and PolygonsDocument36 pagesGrade 6 C8, 8.2 Circles and PolygonsJustin Jumar B. AceronNo ratings yet
- Computer Analysis of Drill Point GeometryDocument14 pagesComputer Analysis of Drill Point GeometryLuis FelipeNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry RatiosDocument27 pagesTrigonometry RatiosElla de la Cruz Gulanes100% (1)
- 24 2 Properties Fourier TrnsformDocument13 pages24 2 Properties Fourier TrnsformHassan AllawiNo ratings yet
- M2 Forces and MomentsDocument46 pagesM2 Forces and MomentsErle100% (1)