Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9A02306 Basic Electrical Engineering
Uploaded by
sivabharathamurthyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9A02306 Basic Electrical Engineering
Uploaded by
sivabharathamurthyCopyright:
Available Formats
Code: 9A02306 B.
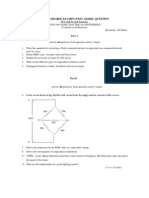
Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular and Supplementary Examinations, November 2012 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to CSS, IT and CSE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) Define and explain Kirchoffs laws. (b) Define and explain resistance, inductance and capacitance. 2 (a) (b) Explain the steps for solving a network problem using Thevenin's theorem. Find the current I in the circuit shown in fig. 7
Figure. 7
3 (a) (b)
Derive the expression for impedance of RLC parallel circuit A coil having a resistance of 10 ohms and an inductance of 0.2 H is connected in series with a 100106 F capacitor across a 230 V, 50 Hz supply, Calculate i) The active and reactive components of the current ii) the voltage across the coil, Draw the phasor diagram. Discuss the constructional features of transformers. Draw neat diagrams. Calculate the flux in the core of a single phase transformer having a primary voltage of 230 V, at 50 Hz and 50 turns. IF the flux density in the core is 1 Tesla, calculate the net cross sectional area of the core. Explain the types of DC generators in detail. A lap wound DC generator having 80 slots with 10 conductors per slot generates at no load emf of 400 V, when running at 1000 rpm. At what speed should it be rotated to generate a voltage of 220 V on open circuit. What is the significance of back emf generated in a DC machine, hence explain the principle of operation of a DC motor. A 100 V series motor takes 45 A when running at 750 rpm. Its armature resistance is 0.22 ohms, while the series field resistance is 0.13 ohms. Iron and frictional losses amounts to 750 W. Find the shaft power. A 3-phase, 2-pole 50 Hz induction motor has a slip of 4% at no-load and 6% at full load. Find (i) Synchronous speed (ii) Full-load speed (iii) No-load speed (iv) Frequency of rotor current at stand still (v) Frequency of rotor current at full load. With neat diagrams, explain the types of moving iron instruments with their working principles. *****
4 (a) (b)
5 (a) (b)
6 (a) (b)
Code: 9A02306 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular and Supplementary Examinations, November 2012 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to CSS, IT and CSE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) Derive an expression for the effective resistance of three resistors connected in parallel. (b) Derive an expression of energy stored in a capacitance from the fundamentals. (c) State Ohm's law. What are its limitations? 2 (a) (b) 3 (a) Explain passive elements in detail. Derive the equation for delta to star transformation
(b) 4 (a) (b)
In a series RLC circuit, an A.C. voltage of 120 0 V is applied at a frequency of 400 rad/sec. The input current leads the voltage by 63.5. Find the value of R if L = 25 mH and c = 50 F. What are the drops across L and C? Obtain RMS value of full wave rectifier. Derive an emf equation of a single phase transformer. The maximum flux density in the core of 250 /3000 Volts 50 HZ single phase transformer is 1.2 webers per square meter. If the emf per turn is 8 volts determine primary and secondary turns and area of the core. Explain the type of compound generator with neat circuit diagram. A long shunt, compound generator delivers a load current of 50 A at 500 V and has armature, series field and shunt field resistance of 0.05 ohm, 0.03 ohm and 250 ohm respectively. Calculate the generated emf and the armature current. Allow 1.0 V for branch for contact drop. A 200 V dc shunt motor develops an output of 16.9 kW when taking an input of 20.2 kW. The field winding resistance is 50 ohm and armature resistance is 0.06 ohm. Calculate the efficiency and power input when the output is 7.35 kW. A 3-phase, 4 poles, 50 Hz induction motor has a star-connected wound rotor. The rotor emf between slip rings at standstill is 50 V. The rotor resistance and standstill reactances are 0.3 and 3 respectively. Find (i) Rotor currents per phase at starting and slip rings short circuited (ii) Rotor currents per phase at starting if a star connected rheostat of 4 per phase is connected across the slip rings. (iii) Rotor emf when the motor is running at full load at 1450 rpm. (iv) Rotor current at full load and rotor power factor at full load Explain the type of eddy current damping control used in the measuring instruments with neat diagram. A moving coil instrument has a resistance of 12 and gives a full-scale deflection when carrying 50 mA. Show how it can be adopted to measure current up to 100 A. *****
5 (a) (b)
8 (a) (b)
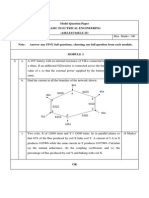
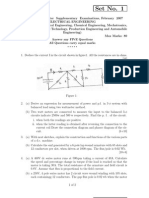
Code: 9A02306 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular and Supplementary Examinations, November 2012 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to CSS, IT and CSE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) Explain the passive elements in detail. (b) Three resistors of 5 ohm, 10 ohm and 15 ohm are joined in parallel. If the current in 10 ohm resistor is 3 A, what is the current in other resistors and the total current? 2 (a) (b) State and explain the Superposition theorem. Find the current in the 6 ohm resistor using Superposition theorem. as shown in fig.9
Figure.9
3 (a) (b) 4 (a) (b) 5 (a) (b)
Derive the equation for true power in an ac circuit. Derive the equation of impedance and power factor of RLC series circuit. Explain the principle of operation of a single phase transformer when it supplies lagging power factor load. Derive the emf equation of a single phase transformer and draw the no load phasor diagram Explain the types of DC generators in detail. A lap wound DC generator having 80 slots with 10 conductors per slot generates at no load emf of 400 V, when running at 1000 rpm. At what speed should it be rotated to generate a voltage of 220 V on open circuit. What is the significance of back emf generated in a DC machine, hence explain the principle of operation of a DC motor. A 100 V series motor takes 45 A when running at 750 rpm. Its armature resistance is 0.22 ohms, while the series field resistance is 0.13 ohms. Iron and frictional losses amounts to 750 W. Find the shaft power. A 3-phase, 2-pole 50 Hz induction motor has a slip of 4% at no-load and 6% at full load. Find (i) Synchronous speed (ii) Full-load speed (iii) No-load speed (iv) Frequency of rotor current at stand still (v) Frequency of rotor current at full load. With neat diagrams, explain the types of moving iron instruments with their working principles.
6 (a) (b)
*****
Code: 9A02306 B.Tech II Year I Semester (R09) Regular and Supplementary Examinations, November 2012 BASIC ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING (Common to CSS, IT and CSE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 70 Answer any FIVE questions All questions carry equal marks ***** 1 (a) (b) Explain Kirchoff's laws with an example. Consider a 230 V, 100 W incandescent lamp. Determine (i) the lamp resistance (ii) the lamp current and (iii) the energy consumed in 8 hours. Explain the following: Superposition theorem Thevinin's Theorem
2 (a) (b) 3 (a) (b)
Derive the equation for power factor of RLC circuit. An RC parallel circuit consists of a resistance of 10 ohm and an inductance of 0.04 F connected to a 100 V, 50 Hz source. Calculate (i) The total current (ii) power factor and (iii) the true power of the circuit. Explain the principal of operation of transformer. Derive its e. m. f. equation. Write short notes on the construction of transformers. Explain the type of compound generator with neat circuit diagram. A long shunt, compound generator delivers a load current of 50 A at 500 V and has armature, series field and shunt field resistance of 0.05 ohm, 0.03 ohm and 250 ohm respectively. Calculate the generated emf and the armature current. Allow 1.0 V for branch for contact drop. A 200 V dc shunt motor develops an output of 16.9 kW when taking an input of 20.2 kW. The field winding resistance is 50 ohm and armature resistance is 0.06 ohm. Calculate the efficiency and power input when the output is 7.35 kW. A 3-phase, 4 pole, 50 Hz induction motor has a star-connected wound rotor. The rotor emf between slip rings at standstill is 50 V. The rotor resistance and standstill reactances are 0.3 and 3 respectively. Find (i) Rotor currents per phase at starting and slip rings short circuited (ii) Rotor currents per phase at starting if a star connected rheostat of 4 per phase is connected across the slip rings. (iii) Rotor emf when the motor is running at full load at 1450 rpm. (iv) Rotor current at full load and rotor power factor at full load Explain the type of eddy current damping control used in the measuring instruments with neat diagram. A moving coil instrument has a resistance of 12 and gives a full-scale deflection when carrying 50 mA. Show how it can be adopted to measure current up to 100 A. *****
4 (a) (b) 5 (a) (b)
8 (a) (b)
You might also like
- 1GR-FE Engine Cooling System GuideDocument77 pages1GR-FE Engine Cooling System GuideMauricio Andrés Montenegro71% (7)
- Rewinding GeneratorsDocument4 pagesRewinding GeneratorsSherehan ShawkatNo ratings yet
- Foundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsFrom EverandFoundations of Electromagnetic Compatibility: with Practical ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- AC machines course policies and grading systemDocument23 pagesAC machines course policies and grading systemJessica Laine TumbagaNo ratings yet
- 9A02308 Electrical Machines - IDocument4 pages9A02308 Electrical Machines - IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument17 pagesDC MotorSiddique MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Core Loss TestingDocument8 pagesCore Loss Testingcompaq1501100% (1)
- Electrical Machines With SolutionsDocument82 pagesElectrical Machines With Solutionsvijay219100% (3)
- Mentor IIDocument114 pagesMentor IIHòa Trịnh0% (1)
- Dynamic Balancing EccentricityDocument11 pagesDynamic Balancing EccentricitygrahazenNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Automotive Parts Manufacturers & Auto Accessories SuppliersDocument10 pagesAutomotive Parts Manufacturers & Auto Accessories Suppliersumesh kumarNo ratings yet
- EMI Lab ManualDocument81 pagesEMI Lab Manualkiran_y2No ratings yet
- 3 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pages3 Basic Electrical EngineeringJyothsna VayyalaNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer Any FIVE Questions All Questions Carry Equal MarksDocument1 pageTime: 3 Hours Max Marks: 80 Answer Any FIVE Questions All Questions Carry Equal MarkssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A14301 Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pages9A14301 Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02407 Electrical Machines - IIDocument8 pages9A02407 Electrical Machines - IIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A14301 Electrical EngineeringDocument1 page9A14301 Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Set No. 1Document8 pagesSet No. 1raviteja1840No ratings yet
- R5211002-Electrical TechnologyDocument4 pagesR5211002-Electrical TechnologysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2anji513No ratings yet
- Rr220402 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesRr220402 Electrical TechnologySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Rr211001 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesRr211001 Electrical TechnologySrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines Exam with Transformer and Induction Motor QuestionsDocument8 pagesElectrical Machines Exam with Transformer and Induction Motor QuestionsmadhueeNo ratings yet
- R7 100506 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageR7 100506 Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- r05311801 Electrical EngineeringDocument9 pagesr05311801 Electrical EngineeringDumiso BaloyiNo ratings yet
- rr220402 Electrical TechnologyDocument8 pagesrr220402 Electrical TechnologySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- BEE Important QuestionsDocument6 pagesBEE Important QuestionsBilal Ahmed100% (2)
- Basic Electrical & Electronic Engineering NotesDocument23 pagesBasic Electrical & Electronic Engineering NotesJay PandyaNo ratings yet
- Rr211001electricaltechnologyDocument8 pagesRr211001electricaltechnologysridiviNo ratings yet
- 9A02306 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument1 page9A02306 Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical Engineering Exam QuestionsDocument5 pagesBasic Electrical Engineering Exam QuestionsShareef KhanNo ratings yet
- KEE101 Electrical Imp Ques SSDocument2 pagesKEE101 Electrical Imp Ques SStathagat maitrayNo ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- Rr210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesRr210303 Electrical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- Em 2 SupplyDocument4 pagesEm 2 Supplykrishn murariNo ratings yet
- ElectricalDocument4 pagesElectricalAkhilesh Kumar MishraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering Exam: Kirchoff's Laws, Series Resonance, InductanceDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering Exam: Kirchoff's Laws, Series Resonance, InductanceKanish KarNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May - 2013 Electrical Machines - IiDocument8 pagesII B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May - 2013 Electrical Machines - IiAR-TNo ratings yet
- 16 Mark Questions - BEEEDocument5 pages16 Mark Questions - BEEEVignesh GNo ratings yet
- 9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIDocument4 pages9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- EmDocument6 pagesEmSatya NarayanaNo ratings yet
- 9a02306-Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument5 pages9a02306-Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- r059210302 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 pagesr059210302 Electrical Engineeringprakash.paruchuriNo ratings yet
- r059211001 Electrical Technology 1Document8 pagesr059211001 Electrical Technology 1api-3818050No ratings yet
- 9a02308 Electrical Mechines IDocument4 pages9a02308 Electrical Mechines IsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02401 Principles of Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pages9A02401 Principles of Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Bee Model Question Paper-2Document3 pagesBee Model Question Paper-2Emmanuel JosephNo ratings yet
- DC Generator and Motor TheoryDocument4 pagesDC Generator and Motor Theorysatya_vanapalli3422No ratings yet
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 pagesR09 Set No. 2Eu AumentadoNo ratings yet
- R5 100506 Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument1 pageR5 100506 Basic Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02504 Power ElectronicsDocument4 pages9A02504 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- for Electrical Technology DocumentDocument4 pagesfor Electrical Technology Documentteodoro berouNo ratings yet
- R5210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument2 pagesR5210303 Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- bt31R0719 p1 19 11 09rahulDocument29 pagesbt31R0719 p1 19 11 09rahulpravallika1210No ratings yet
- T127 - Question Bank - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument6 pagesT127 - Question Bank - Basic Electrical Engineeringharish babu aluruNo ratings yet
- V Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsDocument3 pagesV Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsSumant ReddyNo ratings yet
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Machines - 1Document8 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Machines - 1Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment BEE CompleteDocument5 pagesAssignment BEE CompleteHarshit YadavNo ratings yet
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 pagesRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- May 2010Document8 pagesMay 2010Viswa ChaitanyaNo ratings yet
- r7310205 Electrical Machines IIIDocument4 pagesr7310205 Electrical Machines IIIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Ee 1202 Electrical Machines IDocument3 pagesEe 1202 Electrical Machines IsubhazNo ratings yet
- 2006 07Document4 pages2006 07goyal.167009No ratings yet
- 9A02301 Electrical Engineering & Electronics EngineeringDocument1 page9A02301 Electrical Engineering & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Impedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsFrom EverandImpedance Spectroscopy: Theory, Experiment, and ApplicationsEvgenij BarsoukovNo ratings yet
- Control Systems (CS) Notes As Per JntuaDocument203 pagesControl Systems (CS) Notes As Per Jntuasivabharathamurthy100% (3)
- 07A4EC01 Environmental StudiesDocument1 page07A4EC01 Environmental StudiessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SSC Telugu (FL) (AP)Document232 pagesSSC Telugu (FL) (AP)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicDocument1 pageR5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7410407 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageR7410407 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- SSC Social Textbook (AP)Document100 pagesSSC Social Textbook (AP)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7410506 Mobile ComputingDocument1 pageR7410506 Mobile ComputingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A05707 Software Project ManagementDocument4 pages9A05707 Software Project ManagementsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310406 Digital CommunicationsDocument1 pageR7310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311506 Operating SystemsDocument1 pageR7311506 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A13701 Robotics and AutomationDocument4 pages9A13701 Robotics and AutomationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDocument1 pageR7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Code: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)Document1 pageCode: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)sivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessesDocument1 pageR7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311205 Distributed DatabasesDocument1 pageR7311205 Distributed DatabasessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R5310204 Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageR5310204 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7311006 Process Control InstrumentationDocument1 pageR7311006 Process Control InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310306 Heat TransferDocument1 pageR7310306 Heat Transfersivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- 9A10505 Principles of CommunicationsDocument4 pages9A10505 Principles of CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310206 Linear Systems AnalysisDocument1 pageR7310206 Linear Systems AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- R7310106 Engineering GeologyDocument1 pageR7310106 Engineering GeologysivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationsDocument4 pages9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A15502 Digital System DesignDocument4 pages9A15502 Digital System Designsivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- R5310406 Digital CommunicationsDocument1 pageR5310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessesDocument4 pages9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDocument8 pages9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDocument4 pages9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A05505 Operating SystemsDocument4 pages9A05505 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- 9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIDocument4 pages9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- TCLDocument198 pagesTCLVaisakVenugopal100% (1)
- Armature Reaction in Alternator or Synchronous GeneratorDocument4 pagesArmature Reaction in Alternator or Synchronous GeneratorNimeshNo ratings yet
- TI Analog Applications Journal 4 2013Document41 pagesTI Analog Applications Journal 4 2013jupsilundNo ratings yet
- Emd NotesDocument182 pagesEmd Notesvpzfaris0% (1)
- Lundmark Sonja PHDDocument123 pagesLundmark Sonja PHDZahra ShiraviNo ratings yet
- BEEE NotesDocument8 pagesBEEE NotesSrinathReddyNo ratings yet
- Synchronous GeneratorDocument9 pagesSynchronous GeneratorPathum SudasingheNo ratings yet
- Low Cost High Power DensityDocument7 pagesLow Cost High Power Densityrakeshee2007No ratings yet
- DC G ObjDocument3 pagesDC G Objpurushg62No ratings yet
- Unit - 3: Losses and Efficiency of DC MachinesDocument12 pagesUnit - 3: Losses and Efficiency of DC MachinesNisha JosephNo ratings yet
- Unit IDocument69 pagesUnit IThangam MaheshNo ratings yet
- De La Salle University Dasmarinas: Experiment No. 4 DC Shunt MotorDocument6 pagesDe La Salle University Dasmarinas: Experiment No. 4 DC Shunt MotorMizhar GerardoNo ratings yet
- LVDT John Ramirez and Darwin ValenzuelaDocument15 pagesLVDT John Ramirez and Darwin Valenzuelanikhilrane91_7522800No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentraviNo ratings yet
- Generating Electricity from Speed BreakersDocument23 pagesGenerating Electricity from Speed BreakersKrishna ManeNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Introduction.: Part-ADocument12 pagesUnit-1 Introduction.: Part-AnandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Commutation Process & Excitation MethodsDocument23 pagesQuestions & Answers On Commutation Process & Excitation Methodskibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Wp50 DraftDocument40 pagesWp50 DraftMutazYM1No ratings yet
- EEE 267: DC motor speed and torque calculationsDocument5 pagesEEE 267: DC motor speed and torque calculationsmaakbdNo ratings yet