Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DC Machine Theory and Transformer Principles
Uploaded by
Polireddi Gopala KrishnaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DC Machine Theory and Transformer Principles
Uploaded by
Polireddi Gopala KrishnaCopyright:
Available Formats
Code No: C9909/RR
RR
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2012 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY ( Common to Electronics & Communication Engineering, Computer Science & Engineering, Information Technology, Computer Science & Systems Engineering, Electronics & Telematics, Electronics & Computer Engineering and Instrumentation & Control Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Compare the operation of a D.C. Generator and Motor, and mention one application of each machine. (b) A d.c. shunt machine connected to 250V mains has an armature resistance (including brushes) of 0.1 and the resistance of the eld circuit is 125. Find the ratio of the speed as a generator to the speed as a motor, the line current in each case being 80A. [8+8] 2. (a) Explain the various methods of speed control of a D.C. Shunt Motor. (b) A 460V d.c. series motor runs at 1000rpm taking a current of 40A. Calculate the speed and percentage change in torque if the load is reduced so that the motor is taking 30A. Total resistance of the armature and eld circuits is 0.8. Assume ux is proportional to the eld current. [8+8] 3. (a) Explain the principle of operation of transformer. Derive its e. m. f. equation. (b) A 1-phase transformer has 180 turns respectively in its secondary and primary windings. The respective resistances are 0.233 and 0.067. Calculate the equivalent resistance of i. the primary in terms of the secondary winding, ii. the secondary in terms of the primary winding, and iii. the total resistance of the transformer in terms of the primary.
[8+8]
4. (a) Obtain the equivalent circuit of a single-phase transformer. Explain how to evaluate the equivalent circuit of a transformer from open circuit & short circuit tests. [4+6] (b) A 5 kVA, 220 / 110 volts, 1-phase transformer has a maximum eciency of 96.97% at 0.8 p.f. lagging. It has a core loss of 50 watts and the full load regulation at 0.8 p.f. lagging is 5%. Find the eciency and regulation at full load 0.9 p.f. lagging. [6] 5. (a) Explain the Autotransformer starters used in induction motors. What are its advantages? [6+2] (b) A 200 kW, 3300 V, 6-pole, 50 Hz star-connected slip-ring induction motor has a star connected rotor. Stator to rotor turns ratio is 3.2. Rotor resistance and leakage reactance are 0.1 and 1 respectively. Neglect stator impedance. Find
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
1 of 2
Code No: C9909/RR
RR
i. current and torque at starting on rated voltage and with slip rings short circuited and ii. the external resistance required to reduce the starting current to 50 A with across-the-line starting. Compute also the starting torque under these conditions. [8]
6. (a) Explain the synchronous impedance method of computing the voltage regulation. (b) A 3 phase, 12 pole, star connected alternator has 180 slots with 10 conductors per slot and the conductors of each phase are connected in series. The coil span is 144 degrees (electrical). Determine the phase and line value of e.m.f. If the machine runs at 1600 r.p.m and the ux per pole is 0.06 Weber distributed sinusoidally over the pole. [8+8] 7. (a) Compare 3 induction motor with 3 synchronous motor if any four aspects. (b) The input to an 1100 V, 3 phase star connected synchronous motor is 60 A. The eective resistance and synchronous reactance per phase is 1 ohm and 30 ohm respectively. Find the power supplied to the motor and the induced e.m.f for a power factor of 0.95 leading. [6+10] 8. (a) Explain the operation of a single phase induction motor on the basis of double revolving eld theory. (b) Draw a typical torque-speed curve of a single-phase induction motor on the basis of double revolving eld theory. [8+8]
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
2 of 2
Code No: R22021
R10
SET - 1
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS (Com. to EEE, ECE, ECC, BME, EIE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Explain the operation of RC high-pass circuit when exponential input is applied. b) Verify V2 = pass circuit. 2. a) Draw the circuit diagram of emitter coupled clipper. Draw its transfer characteristics indicating all intercepts, slopes and voltage levels and derive the necessary equations. b) Give the circuits of different types of shunt clippers and explain their operation with the help of their transfer characteristics. a) Define i) Rise time ii) Fall time iii) Delay time iv) Storage time Explain the factors which contribute to the delay time of transistor. b) Draw and explain the circuit diagram of integrated positive RTL NOR gate. a) Draw the circuit and explain the operation of Schmitt Trigger with the help of transfer characteristics. Define UTP & LTP and also explain how the hysteresis can be eliminated. b) Design of self-bias bistable multivibrator using silicon n-p-n transistors whose junction voltages are VCE(sat) = 0.3 V, VBE (sat) = 0.7 V, VBE(cut-off) = 0 V and hFE (min) = 50, VCC= -VBB =9V, IC = 4 mA. a) With the help of a neat circuit diagram, explain the working of an emitter coupled monostable multivibrator. Derive an expression for the gate width of monostable multivibrator. b) Design an astable multivibrator to generate a square wave of 2 kHz frequency with a duty cycle of 35%. a) Explain the basic principle of a boostrap sweep generator. Draw the circuit and explain its operation. Derive the expression for its slope error. b) Find i) the sweep amplitude and ii) the slope error for the bootstrap sweep generator when a 2 kHz symmetrical square wave is applied as an input to it. The typical h-parameter values of transistors are hfe =90, 1/hoe = 35k , hie= 1k and hrc =1. Assume all forward-biased junction voltages are zero. a) What is synchronization? Why it is necessary in waveform generators? Explain the synchronization of a sweep circuit with symmetrical signals. b) What is phase jitter? Explain the method to eliminate it. a) Describe the operation of a triggered transistor blocking oscillator with emitter timing with the help of circuit diagram & necessary waveforms. Obtain the expression for the pulse width tp. b) Draw the circuit of a bidirectional sampling gate and derive the expression for its gain. Obtain the values of VC(min) and Vn (min). 1 of 1
2x V e 1 V = tanh x for a symmetrical square wave applied to a RC low 2x 2 e +1 2
( (
) )
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22021
R10
SET - 2
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS (Com. to EEE, ECE, ECC, BME, EIE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Prove that a low pass circuit acts as an integrator. Derive an expression for the output voltage levels under steady state conditions of a low pass circuit excited by a ramp input. b) What is an attenuator? How can an uncompensated attenuator be modified as a compensated attenuator. Give the comparison between perfect compensation, under compensation and over compensation.
2.
a) Draw the circuit diagram and explain the working of transistor clippers b) In the circuit shown below, Rs = R f = 100, Rr = , R = 10 K, C = 1f , Vr = 0 . A symmetrical square wave signal of amplitude 20V and frequency 5 KHz is applied at t = 0. Draw the output waveform
3.
a) Explain with the help of suitable waveforms the switching times of a diode switch. Derive the expression for reverse recovery time. b) Draw the circuit of CMOS NOR gate and explain its operation. Mention the advantages of CMOS over the other digital logic families.
4.
a) Define the transition time, resolving time and settling time of a bistable multivibrator. b) Draw the circuit and explain the operation of self bias bisable multivibrator. List the advantages of this circuit over a fixed-bias bistable multivibrator. Design a bistable multivibrator to meet the following specifications, VCC =-VBB=12V, IC(sat)=6mA, hFE(min) =25. Maximum trigger frequency = 25KHz. 1 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22021
R10
SET - 2
5.
a) Draw and explain the working of a collector-coupled Astable multivibrator. Derive the expression for frequency of oscillation. b) Calculate the component values of a monostable multivibrator developing an output pulse of 500s duration. Assume hFE (min)=25, ICE (sat) =5mA, VCC=10V,and VBB = -4V.
6.
a) Define the terms slope error, displacement error and transmission error. b) Draw the circuit diagram of transistor current sweep generator and explain its working. c) Explain the technique used to improve the linearity of current sweeps.
7.
a) With the help of a neat circuit diagram and waveforms, explain the method to achieve frequency synchronization using pulse train as sync signals. b) Draw and explain the waveforms of a frequency division by an astable multivibrator.
8.
a) Draw the circuit of an astable blocking oscillator with a diode control and explain its operation. Plot the waveforms. Derive the expression for its frequency. b) With the help of a neat diagram, explain the working of a two-diode sampling gate. Derive expression for i) Gain , ii) (Vc) min, and iii) (Vn) min.
2 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22021
R10
SET - 3
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS (Com. to EEE, ECE, ECC, BME, EIE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Derive an expression for the output of low pass circuit excited by a step input. b) An RC low-pass filter is fed with a symmetrical square wave. The peak-to-peak amplitude of the input waveform is 10 V and its average value is zero. It is given that RC=T/2 where T is the period of the square wave. Determine the peak-to-peak amplitude of the output wave form. a) Explain the working of a two-level diode clipper with the help of circuit diagram, waveform and transfer characteristics. b) Draw the basic circuit diagram of negative peak clamper circuit and explain its operation. a) Briefly discuss the influence of breakdown voltages on the choice of supply voltage in a transistor switch. b) Explain the characteristics and implementation of the following digital logic family i) CMOS, ii) ECL a) With the help of a suitable circuit diagram, explain the methods of symmetric and un symmetric triggering of a bisable multivibrator. b) The self-biased flip-flop uses germanium transistors with VCE (sat) = 0.2 V, VBE (sat) =0.6 V and hFE(min) = 20, VCC =10 V, RC =1 k , R1 = 5k , R2 = 10 k and RE =500 Find i) The stable state voltages and currents ii) the maximum value of ICBO required. a) Explain the operation of a collector-coupled monostable multivibrator with the help of a neat circuit diagram and waveform. Derive an expression for the gate width. b) A collector coupled monostable multivibrator using n-p-n silicon transistors has the following parameters. VCC = 12 V, VBB = 4 V, RC = 1 k , R1 = R2 = R = 15 k , hFE = 35, rbb = 220 and C = 1000 pF. Neglect ICBO. i) Show that in the stable state one transistor is ON and the other is OFF. ii) Find the width of the output pulse. a) Describe the working principle of a practical transistor Miller sweep voltage waveform generator with the help of its circuit and its practical requirements. b) Obtain an expression for slope error in a current sweep circuit employing a practical yoke. Simplify this expression. Also derive an expression for sweep-speed mathematically. a) What is meant by synchronization with frequency division? Explain, with suitable waveforms, the procedure to obtain 3:1 and 5:1 synchronization. b) Explain the terms i) Phase delay ii) Phase jitters Write short notes on the following. a) Astable blocking oscillators b) Four diode sampling gates c) Effect of control voltage on bidirectional sampling gates. 1 of 1
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22021
R10
SET - 4
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS (Com. to EEE, ECE, ECC, BME, EIE) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Draw the output waveform of an RC high-pass circuit with a square wave input under different time constants. Explain the same. b) Explain RLC ringing circuit with a neat sketch
2.
a) State and prove clamping circuit theorem. b) Determine the output waveform for the biased clipping circuit for the square wave input.
3.
a) Describe how a transistor functions as a switch in the CE configuration in ON state and in OFF state. How does the temperature affect the saturation junction voltages of a transistor? b) Classify the basic families that belong to the bipolar families and to the MOS families. What is the major difference between TTL and ECL? Why does the propagation delay occur in logic circuits?
4.
a) Design a fixed-bias bistable multivibrator with supply voltages 12V, an n-p-n silicon device having VCE (sat) = 0.2 V, VBE (sat) = V = o.7 V and hFE (min) = 50 are used. Assume IC = 5 mA. b) What is necessity of triggering ? Explain about symmetrical and unsymmetrical triggering.
1 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22021
R10
SET - 4
5.
a) Draw the circuit diagram and explain the working of an astable multivibrator with the necessary waveforms. b) Design a one shot circuit to produce a pulse width of 5 msec. Assume hFE =30, VCE(sat)=0.3V, VBE(sat)=0.7V, IC=5 mA, VCC=6V,VBB=1.5V,Q1 ON and Q2 OFF
6.
a) Derive the relation between the slope, transmission and displacement errors. b) Explain the basic principles of Miller and Bootstrap time-base generators Compare Miller and Bootstrap time-base generators.
a) Mention the principle involved in the synchronization of voltage sweep waveform with a sinusoidal synchronization signal with neat waveforms. b) Describe frequency division employing a transistor astable multivibrator
8.
Explain the operation of, i) Monostable transistor blocking oscillator (base timing) with a circuit diagram and waveforms. Derive an expression for pulse width. ii) Four diode sampling gate and discuss its properties.
2 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 1
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2012 THERMAL ENGINEERING - I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Explain how specific fuel consumption varies with power for i) air standard cycle ii) fuel air cycle iii) actual cycle b) What is meant by burning time loss, explain with the help of p-v diagram
2.
a) Explain with a neat sketch, valve timing diagram for a four stroke SI engine b) Explain with a neat sketch, working of a simple carburetor
3.
a) Explain the combustion phenomenon in an S.I engine. b) Explain the effect of various engine variables on S.I engine knock.
4.
a) Explain the phenomenon of knock in C.I engines and compare it with S.I engine knock b) Explain with suitable sketches working of air cell combustion chamber
5.
a) Explain briefly the variables affecting performance characteristics
b) A six cylinder gasoline engine operates on a four stroke cycle. The bore of each cylinder is 80mm and the stroke is 100mm. The clearance volume per cylinder is 70cc. At a speed of 4000 rpm the fuel consumption is 20kg/h and the torque developed is 150 Nm. Calculate (i) brake power (ii) brake mean effective pressure (iii) brake thermal efficiency if the calorific value of the fuel is 43000 kJ/kg.
1 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 1
6.
a) Explain three methods usually adopted to control the quantity of air delivered by reciprocating air compressor and discuss its merits and demerits. b) A three stage compressor is used to compress air from 1.0 bar to 35 bar. The compression in all stages follows PV1.25 = C. The temperature of air at the inlet to the compressor is 300K. Neglecting the clearance and assuming perfect intercooling, find out the indicated power required in kW to deliver 15 m3 of air per minute measured at inlet conditions and intermediate pressures also. Take R = 0.287 kJ/kg K.
7.
a) Explain with simple sketch, working of a Lysholm compressor b) Air at a temperature of 300K flows in a centrifugal compressor running at 18000 rpm. Isentropic total head efficiency is 0.76, outer diameter of the blade tip is 550 mm, slip factor is 0.83, calculate i) temperature rise of air passing through the compressor ii) static pressure ratio. Assume that the absolute velocities of air at inlet and exit of the compressor are same.
8.
a) A axial compressor having eight stages and 50% reaction design compresses air in a pressure ratio of 4:1. the air enters the compressor at 200C and flows with a constant speed of 90m/s. the rotating blades of the compressor rotates with a mean speed of 180 m/s. isentropic efficiency of the compressor may be taken as 82%. Calculate work done and blade angles. b) Explain with a suitable graph phenomenon of surging and chocking in a rotary compressor.
2 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 2
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2012 THERMAL ENGINEERING - I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Discuss the effects of the following variables on pressure and temperature at salient points of Otto cycle on the basis of fuel air cycle. i) compression ratio ii) fuel air ratio b) What is exhaust blow down loss. Discuss on the optimum opening position of the exhaust valve to reduce this loss. a) Explain with a neat sketch, port timing diagram for a two stroke CI engine b) Explain with a simple sketch, working of Bosch fuel injection system
a) Discuss the variables affecting flame speed in SI engines. b) Discuss about the basic requirements of SI engine combustion chambers
2.
3.
4.
a) Explain with suitable graphs combustion phenomenon in a CI engine b) Explain briefly the effect of engine variables on knock a) The fuel supply to a diesel engine has a gross calorific value of 44800 kJ/kg and contains 85.4% C and 12.3%H2. The average temperature of the exhaust gases is 2600C and the volumetric analysis gives CO2 : 5.77%, CO: 0.12%,O2: 13.09%,N2: 81.02% by difference. Find i) heat carried away by the exhaust gases expressed as percentage of heat supplied ii) the mass of air per kg of fuel in excess of the theoretically required for complete combustion. Take mean specific heat of dry air exhaust gas as 1kJ/kgK and atmospheric temperature as 170C. b) Discuss briefly methods available for improving performance of an engine a) Derive an expression for volumetric efficiency as a function of clearance ratio. b) A single stage single acting air compressor delivers 0.6 kg of air per minute at 6 bar. The temperature and pressure at the end of suction stroke are 300C and 1 bar. The bore and the stroke of the compressor are 100 mm and 150mm respectively. The clearance is 5% of the swept volume. Assume index of compression and expansion be 1.3. Find (i) volumetric efficiency of the compressor (ii) power required if the mechanical efficiency is 85% (iii) speed of the compressor. a) A centrifugal compressor with 70% isentropic efficiency delivers 20 kg of air per minute at a pressure of 3 bar. If the compressor receives air at 200C and at a pressure of 1 bar, find the actual temperature of air at exit. Also find the power required to run the compressor if its mechanical efficiency is 95%. b) Differentiate between axial and centrifugal compressors. a) Explain with suitable figures construction of a axial compressor with its velocity triangles. b) Derive a suitable expression for degree of reaction for an axial compressor.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 3
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2012 THERMAL ENGINEERING - I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a)Assuming fuel air cycle approximation, where does the maximum pressure and temperature occurs in a constant volume cycle and why. When is the maximum power produced. b) What is the effect of direct heat loss on p-v diagram of an Otto cycle engine, how much efficiency would be increased if the direct heat loss is completely recovered or eliminated?
2. a) Explain with a simple sketch, working of a battery ignition system. b) What is meant by SAE 40 and significance of the numerical value? Explain with a simple sketch working of a forced lubrication system.
3. a) What is delay period and what are the factors which affect delay period b) Explain with simple sketches, combustion chambers for SI engines
4. a) Explain with suitable graphs abnormal combustion in CI engine b) Explain briefly the three methods of generating swirls in CI engine combustion chambers.
5. a) The following details were noted in a test on a four-cylinder, four-stroke engine, diameter =100mm, speed of the engine = 1600mm, stroke = 120mm, fuel consumption = 0.2 kg/min; calorific value = 44000 kJ/kg, difference in tension on either side of the brake pulley = 40 kg, brake circumference is 300 cm. If the mechanical efficiency is 80%, calculate i) brake thermal efficiency ii) indicated thermal efficiency iii) indicated mean effective pressure and iv) brake specific fuel consumption b) What are the components in exhaust gas and why stringent norms are being enforced to reduce emissions.
1 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 3
6. a) What is the effect of atmospheric conditions on the output of the compressor, derive an expression for volumetric efficiency for ambient conditions b) An air compressor works between the pressure limits of 1.43 bar and 7.2 bar and sucks in 10m3 per minute of air at 15C. If the compression process varies from isentropic with = 1.4 to isothermal determine the work done per minute during compression process alone for both the cases. How will this get affected for compression process with compression index n = 1.25.
7. a) Discuss the fields of application of centrifugal and axial flow compressors. Explain why axial compressors are largely used for aviation gas turbines. b) A centrifugal compressor is desired to have a total pressure ratio of 3.5:1. The inlet eye of the compressor impeller is 30cm in diameter. The axial velocity at inlet is 130m/s and mass flow is 10 kg/s. The velocity in the delivery duct is 115 m/s. the tip speed of the impeller is 450m/s and runs at 16000 rpm with total head isentropic efficiency of 78% and pressure coefficient of 0.72. The ambient conditions are 1.013 bar and 150C. Calculate i) static pressure ratio ii) static pressure and temperature at inlet and outlet of compressor.
8. a) Explain with a simple sketch construction and working of a axial compressor. b) A symmetrical blading axial flow compressor has an airflow with axial velocity of 145 m/s. The blading is designed for 50% reaction at mean diameter. Pressure ratio is 1.5 and isentropic efficiency is 86 %. Assuming that the flow is of Vortex type, estimate the degree of reaction at the root and tip of the blade, if the ratio of inside diameter to outside diameter is 0.75. The inlet conditions to compressor correspond to standard state sea level
2 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 4
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations Dec 2012 THERMAL ENGINEERING - I (Com. to ME, AME) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Compare Carnot, Stirling and Ericsson cycles operating between the same source and sink temperatures with equal changes in specific volume. b) What are pumping and rubbing friction loss, compare the actual and fuel air cycle in a diesel engine.
2.
a) Explain with a simple sketch, working of a Wankel engine. b) What is the difference between air standard cycle approximation, fuel air cycle approximation and real cycle performance?
3.
a) What is abnormal combustion, explain with supportive figures the concept of abnormal combustion b) What are fuel requirements for a SI engine and what are the additives generally added to prevent knock during combustion.
4.
a) What is meant by combustion induced swirl, why turbulent type combustion chambers cause higher heat transfer than non turbulent type. b) Describe the methods of suppressing knock in CI engines.
5.
a) Explain with a suitable sketch principle of viscous air flow meter. What is the advantage over orifice meter? b) A four cylinder four stroke S.I engine has a compression ratio of 8 and bore of 100 mm, with stroke equal to bore. The volumetric efficiency of each cylinder is equal to 75%. The engine operates at a speed of 4800 r.p.m with an air-fuel ratio 15. Given that calorific value = 42 MJ/kg, atmospheric density = 1.12 kg/m3, mean effective pressure in the cylinder = 10bar and mechanical efficiency of the engine = 80%. Determine the indicated thermal efficiency and the brake power. 1 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22033
R10
SET - 4
6.
a) What is meant by volumetric efficiency of the compressor, Explain how clearance volume effects it. b) The free air delivery of a single cylinder single stage reciprocating air compressor is 2.5 m3/min. The ambient air is at STP conditions and delivery pressure is 7 bar. The clearance volume is 5% of the stroke volume and law of compression and expansion is PV1.25 = constant. If L = 1.2 D and compressor runs at 150 rpm, determine the size of the cylinder.
7.
a). Explain the working centrifugal compressor with a neat sketch and plot a variation of pressure and velocity of air passing through impeller and diffuser. b) A centrifugal compressor delivers 0.5 kg of air per second at a pressure of 1.8 bar and 1000C. The intake conditions are 200C and 1 bar. Find the isentropic efficiency of the compressor and the power required to drive it. Take n = 1.65 and Cp=1kJ/kgK.
8.
a) What modifications can be made to improve performance and decreasing number of stages in a axial compressor. b) An axial compressor stage has a mean diameter of 60cm and runs at 15000rpm. If the actual temperature rise and pressure ratio developed are 300C and 1.4 respectively. i) The power required to drive the compressor while delivering 57 Kg/s of air; assume mechanical efficiency of 86 % and an initial temperature of 350C. ii) The stage loading coefficient. iii) The stage efficiency and iv) The degree of reaction if the temperature at the rotor exits is 550C.
2 of 2
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22053
R10
SET - 1
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) What are the different types of database end users? Discuss the main activities of each. b) State the difference between a file management system and a database management system. Give an E-R diagram for a data base showing fatherhood, motherhood and spouse relationships among men and women. a) What is a view? How can it be created? Explain with an example. b) Explain about Set operators in Relational algebra a) How do triggers offer a powerful mechanism for dealing with the changes to database with Suitable example. b) Explain how the "GROUP By" clause works. What is the difference between the WHERE and HAVING clauses? Explain them with the help of an example for each. a) Define a functional dependency. Briefly describe reasoning about FDs. b) What are join dependencies? Why they are important in database design? a) How can you implement atomicity in transactions? Explain b) With a neat sketch discuss the states a transaction can be in. a) List the differences between cluster, primary and secondary indexes. b) What is index data structure? Briefly describe Hash-Based Indexing. a) Construct a B+ tree to insert the following key elements (order of the tree is 3) 5, 3, 4, 9, 7, 15, 14, 21, 22, 23. b) Mention the purpose of indexing. How this can be done by B+ tree? Explain.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22053
R10
SET - 2
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) With a neat sketch discuss the three-schema architecture of a DBMS. b) What is data independence? List the differences between logical data independence and physical data independence. Draw an E-R diagram for the data base of hospital with a set of patients and a set of medical doctors. With each patient, a log of the various tests conducted is also associated. a) How will you enforce integrity constraints in a relation? Explain with an example. b) Discuss in detail the operators SELECT, PROJECT, UNION with suitable examples. a) Consider the following relations :Employee (emplD, Name, SurName, address, DOB, sex, position,deptNo) Department (dtptNo, deptName, mgr, empID) Project (projNo, projName, deptNo) Work on (empID, projNo, hours worked) Write the SQL statements for the following: i) List the name and addresses of all employees who work for the IT department. ii) List the total hours worked by each employee, arranged in order of department number and within department, alphabetically by employee surname. iii) List the total number of employees in each department for those departments with more than 10 employees. iv) List the project number, project name and the number of employees who work on that project. b) Briefly describe join operations. a) What is normalization? Explain 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF with suitable example. b) What is MVD? What are MVD complementation and MVD argumentation? a) Explain the distinction between the terms serial schedule and serializable schedule. Give relevant example. b) Explain various recovery Schedules during transaction in detail a) Give the comparison of various file organizations. b) Briefly describe heap files and sorted files. a) Mention the purpose of indexing. How this can be done by B+ tree? Explain. b) Why is a B+ tree a better structure than a B-tree for implementation of an indexed sequential file? Explain this with an example. 1 of 1
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22053
R10
SET - 3
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Explain the role and functions of the database administrator. b) State the advantages and disadvantages of the three record based data models: network, hierarchical and relational. a) With suitable ER diagrams, briefly describe Relationships and Relationship sets. b) What is a key constraint? Briefly describe key constraints for ternary relationships. Given the relational schemes : ENROL (S#, C#, Section) - S# represents student number TEACH (Prof, C#, Section) - C# represents course number ADVISE (Prof, S#) - Prof is thesis advisor of S# PRE_REQ (C#, Pre_C#) - Pre_C# is prerequisite course GRADES (S#, C#, Grade, Year) STUDENT (S#, Sname) - Sname is student name Give queries expressed in relational algebra, and tuple relational calculus for the following: i) List all students taking courses with Zeba. ii) List all students taking at least one course that their advisor teaches. iii) List those professors who teach more than one section of the same course a) Briefly describe the DDL and DML command in SQL with syntaxes and examples each. b) Write short notes on types of joins. a) Define a primary key and a secondary key. In a record, non key fields are functionally dependent on the key . Explain with an example. b) What is FD? Explain the role of FD in the process of normalization. a) Discuss the ACID properties of a transaction. Give relevant example. b) Describe the concept of serilalizability with suitable example. a) Give the comparison of various file organizations. b) What is a concatenated key? Briefly describe composite search keys. a) Describe the structure of B+ tree and list the characteristics of a B+ tree b) What does ISAM stand for? Briefly describe the advantages of ISAM indexes.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: R22053
R10
SET - 4
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 75 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Explain the system structure of a database system with neat block diagram. b) State the differences between generalization and aggregation. Construct an E-R diagram for a car insurance company with a set of customers, each of which owns a number of cars. Each car has a number of recorded accidents associated with it. a) How will you enforce integrity constraints and how will you handle NULL values in relations? b) Give the syntaxes and semantics of tuple relational calculus. a) Consider the employee database, where the primary keys are underlined. Employee (empname, street, city) Works (empname, companyname, salary) Company (companyname, city) Manages (empname, managername) And given an expression in SQL for the following queries: i) Find the names of all employees who work for First Bank Corporation. ii) Find the names, street addresses, and cities of residence of all employees who work for First Bank Corporation and earn more than 200000 per annum. iii) Find the names of all employees in this database who live in the same city as the companies for which they work. b) What are nested queries? Explain with example a) Describe about the Multi-Valued Dependencies and Fourth normal form with suitable example. b) How can you identify join dependencies that must hold in a data base? a) Explain the four important properties of transaction that a DBMS must ensure to maintain database. b) Describe the concept of serilalizability with suitable example. a) What are the advantages and disadvantages of hash indices relative to B+- tree indices? b) What is an equality query? Briefly describe clustered index organization. Describe the structure of B+ tree and give the algorithm for search in the B+ tree with example. 1 of 1
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0222
R07
SET - 1
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 LINEAR DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a). Derive the output voltage of an op - amp based differential amplifier. b) Compare and contrast an ideal OP-AMP and practical OP-AMP. a) Explain how an op - amp can be used as comparator? Draw the diagram obtain the expression for the output. b) Write short notes on Voltage regulators. a) Explain thermal drift and slew rate. b) Explain the operations of band reject and all pass filters a) What is the purpose of low pass filter in a phase locked loop? Describe different types of low pass filters used in PLL. b) Using a block diagram explain the functioning of 565. a) With the help of a neat circuit diagram and waveforms, explain the operation of a dual slope ADC. What are its special features? b) Draw the circuit of weighted resistor DAC and derive expression for output analog voltage Vo. a) Which is the fastest non-saturated logic gate/ Draw the circuit and explain its operation? b) What are the advantages and disadvantages of CMOS over TTL gate? a) Explain the function of a Parity generator with an example. b) With a truth table explain the logic of a Half-Subtractor. a) List out the differences between sequential and combinational circuits. b) Explain the function of static and Dynamic RAMS
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0222
R07
SET - 2
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 LINEAR DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Explain the use of constant bias circuit in operation of differential amplifier. b) List out electrical characteristics of an op - amp. a) Explain the sample and hold circuits. b) List the features of 723. a) Explain the operations of LPF and HPF filters. b) With a neat figure explain the method of obtaining a triangular wave form using OP amp. a) Draw the circuit of PLL as frequency multiplier and explain its working. b) Explain the application of 555 timer as linear ramp generator. a) With the help of a neat circuit diagram and waveforms, explain the operation of a successive approximation ADC. What are its special features? b) LSB of a 9 - bit DAC is represented by 19.6mv. If an input of 9 zero bits is represented by 0 volts. i) Find the output of the DAC for an input 10110 1101 and 01101 1011. ii) What is the Full scale reading (FSR) of this DAC? a) Explain the operation and verify the truth table of Totem-pole TTL NAND gate. b) Give the characteristics and advantages of MOS logic. a) Explain the function of an Encoder with truth table. b) Design a Half adder using NAND gates only. a) Design a Decade counter and explain its operation. b) Explain the function of synchronous DRAM.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0222
R07
SET - 3
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 LINEAR DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Explain the modes of operation of non-inverting differential amplifier. b) Write short notes on chip size and circuit complexity of IC. a) Why is it necessary to use an external offset voltage compensating network with practical OP-AMP circuits? b) Explain the function of V to I converters. a) Explain, How to obtain triangular wave using a square wave generator. b) Explain the working of a RC oscillator. a) Draw the circuit of Schmitt trigger using 555 timer and explain its operation. b) Draw the block schematic of a PLL describing the function of each block briefly. a) With the help of a neat circuit diagram and waveforms, explain the operation of a parallel comparator type ADC. b) Draw the circuit of weighted resistor DAC and derive expression for output analog voltage Vo. a) List out the advantages and applications of MOS logic. b) Distinguish between static and dynamic power dissipation of a CMOS circuit. a) Explain the function of a3 to 8 line Decoder with its truth table. b) Design 1:8 demultiplexer using two 1:4 demultiplexer. a) Explain the function of ROM architecture. b) List out the application of shift registers and counters.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0222
R07
SET - 4
II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 LINEAR DIGITAL IC APPLICATIONS (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
a) Explain the modes of operation of inverting differential OP amp b) List out features of 741 OP amp. a) List out the AC characteristics of an op-amp and discuss about them? b) Explain the operation of Schmitt trigger a) With a neat block diagram explain the features of VCO. b) With suitable circuit diagram explain the operation of a triangular wave generator using a comparator and a integrator. a) Give the functional block diagram of VCO NE 565 and explain its working and necessary expression for free running or center frequency. b) The circuit of a inverting summing amplifier is designed with R1 = R =1Kohm, and R2 = 2R1, R3 = 2R2, and Rn = 2Rn-1, the input voltages v1,v2,and vn can be 0 to 10 V. For n = 4, what is the smallest output voltage if at least one input is nonzero? a) What are the basic blocks in an Analog to Digital converter and explain counter type ADC. b) Compare merits and demerits of A/D converters. a) Compare MOS and CMOS logic b) Draw the schematic circuits of CMOS NAND and CMOS NOR gates and explain the function of both with truth table. a) Explain the function of a BCD to Binary converter. b) Convert gray code 1001001011110010 to binary. Explain the operation of conversion. a) Draw the circuit diagram and truth table and explain the operation of a JK flip flop.. b) Explain the function of RAM architecture.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0423
R07
SET - 1
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Convert the given Gray code number to equivalent binary 1001001011110010. b) Convert (A0F9.0EB)16 to decimal, binary, and octal. a) Simplify the following Boolean expressions using the Boolean theorems. i) (A+B+C) (B+C) + (A+D) (A+C) ii) (A+B) (A+B) (A+B) b) Why a NAND and NOR gates are known as universal gates? Realize all the basic gates using NAND and NOR a) Minimize the following expressions using K-map and realize using NAND Gates. f = m (1, 3, 5, 8, 9, 11, 15) +d (2, 13) b) Minimize the following expression using K-map and realize using NOR Gates. f = M (1, 2, 3, 8, 9, 10, 11, 15). d (7, 1, 5) a) Describe the operations performed by the following logic circuits with an example i) Comparator ii) Decoder iii) Encoder b) Explain the operation of a 3-to-8 decoder 74LS138. Realize 4-to-16 decoder using two 3-to-8 decoders. a) Is an X-OR function a threshold function? Justify. b) Realize the following function using a PROM of size 8x3 F = m(1,2,4,6) a) Explain the differences between asynchronous and synchronous counters. Design a MOD-10 ripple counter. b) Design and construct MOD-5 synchronous counter using JK flip flops. a) What are the Moore and Melay machines? Compare them. b) Explain the procedure for state minimization using the partition technique. a) Name the elements of an ASM chart and define each one of them. b) Explain the control subsystem implementation of weighing machine. 1 of 1
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0423
R07
SET - 2
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Solve for x i) (367)8=(x) 2 ii) (378.93)10 = (x) 8 iii) (B9F.AE)16 = (x) 8 b) Convert (163.875)10 to binary, octal, hexadecimal.
iv) (16)10 = (100) x
2.
a) Obtain dual of the following Boolean expressions i) AB+A(B+C)+B(B+D) ii) A+B+ABC. b) Obtain the compliment of the following Boolean expressions i) AB+ABC+ABCD+ABCDE. ii) ABEF+ABEF+ABEF. a) Minimize the following expression using K-map and realize using NAND Gates. F (A,B,C,D) = m (0,1,2,9,11) +d(8,10,14,15). b) Minimize the following expression using K-map and realize using NOR gates. f = M(0,4,6,7,8,12,13,14,15) a) Explain the differences between a MUX and a DEMUX. Realize 16-input multiplexer by cascading of two 8-input multiplexers 74151. b) Realize the function f(A,B,C,D) = (1,4,6,10,14) + d (0,8,11,15) using i) 16:1 MUX ii) 8:1 MUX a) Give the comparison between PROM, PLA and PAL. b) Implement the following Boolean function with PLA F(A,B,C) = m(0,1,2,4) a) What is a shift register? Explain about the following modes of operations in a four bit shift register i) shift right ii) shift left iii) bidirectional. b) Explain the differences between ring and Johnson counters. Design and explain the operation of a decade Johnson counter. a) What are the capabilities and limitations of finite state machines? b) Explain the procedure for state minimization using merger graph and merger table. a) Differentiate between an ASM chart and a conventional flow chart. b) Explain in detail the ASM technique of designing a sequential circuit. 1 of 1
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0423
R07
SET - 3
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Solve for x i) (257)8 =(x) 2 ii) (21.625)10 = (x) 8 iii) (BC.2)16 = (x) 8 iv) (33)10 = (201) x b) Express the Decimal Digits 0-9 in BCD, 2421, 84-2-1 and Excess-3. a) Prove the following Boolean theorems i) AB+AC = (A+C)(A+B) ii) AB+AC+BC = AB+AC b) Simplify the following Boolean expressions i) ABC+AB+ABC ii) ACD+ABCD. a) Minimize the following expressions using K-map and realize using NAND Gates. f = m(0,1,4,5,6,7,9,11,15) +d (10,14) b) Minimize the following expression using K-map and realize using NOR Gates. f = M(1,4,5,11,12,14) . d (6,7,15) a) Implement full adder with 4 to 1 multiplexer. b) Implement 64 x 1 multiplexer with four 16 x 1 and one 4 x 1 multiplexer. a) Give the logic implementation of a32x4 bit ROM using decoder of suitable size. b) Implement the following Boolean function with PLA F(A,B,C) = m(1,5,6,7) a) Draw and explain 4-bit universal shift register. b) Explain the differences between asynchronous and synchronous counters. Design a MOD-6 ripple counter. a) What are the Moore and Melay machines? Compare them. b) Explain the procedure for state minimization using merger graph and merger table. a) Draw and explain ASM chart for a weighing machine. b) Explain in detail about salient features of ASM chart.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0423
R07
SET - 4
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 SWITCHING THEORY AND LOGIC DESIGN (Electronics and Communications Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) Covert 105.1510 to binary, octal, hexadecimal. b) what is hamming code? How is the hamming code word tested and corrected. a) State and prove i) commutative, ii) associative, iii) distributive, iv) idempotence, v) distributive laws of Boolean algebra. b) State and prove i) consensus theorem, ii) transposition theorem, iii)De-Morgans theorem. Minimize the following expressions using K-map and realize using NAND Gates. f = m(5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14,15) f = m(0,1,4,5,6,7,9,11,15) +d (10,14) a) Explain the differences between a MUX and a DEMUX. Realize 16-input multiplexer by cascading of two 8-input multiplexers 74151. b) Realize the function f(A,B,C,D) = m(1,2,5,8,10,14) + d( 6,7,15) using i) 16:1 MUX ii) 8:1 MUX iii) 4:1 MUX. a) Explain steps to implement a Boolean function using threshold gate. b) Write the program table to implement a BCD to XS-3 code conversion using PLA. a) Explain the operation of R-S master slave flip flop. Explain its truth table b) Explain about the realization of SR flip-flop, JK flip-flop using D flip-flop. a) What are the capabilities and limitations of finite state machines? b) Explain the procedure for state minimization using the partition technique. a) Draw and explain the ASM chart for a binary multiplier. b) Explain the data path subsystem for a weighing machine.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0523
R07
SET - 1
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. What is a data base system? Explain about various applications of it in detail.
2.
What is a data? Explain about various data models in detail.
3.
Explain in detail how database design is done?
4.
a) What is a table? Differentiate between tables and views in detail. b) Explain about destroying and altering tables and views in detail.
5.
a) What is a basic SQL query? Differentiate between basic and nested queries. b) What is a NULL value? How would you disallow NULL values?
6.
a) Explain about comparision operators in detail. b) What is decomposition? Explain the problems caused by decomposition.
7.
What is recovery? Explain about various types of recovery in detail.
8.
Write short notes on the following. a) Cluster indexes. b) Hash based indexing. c) Tree based indexing.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0523
R07
SET - 2
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
1.
What is DBMS? Differentiate between data base systems and file systems in detail.
2.
a) Explain about various data base languages in detail. b) Differentiate between DDL and DML in detail.
3.
a) What is an attribute? Differentiate between attribute and entity . b) Explain about additional features of ER model in detail.
4.
Explain about logical data base design in detail.
5.
a) What is a select operation? Differentiate between select and project operations. b) Explain about division operation with an example.
6.
a) Explain about various aggregative operators in detail. b) What is a trigger? Explain the significance of it.
7.
a) What is atomicity? Explain about the implementation of it in detail. b) Explain about lock based protocols in detail.
8.
Write short notes on the following. a) Performance tuning b) ISAM c) Primary index. 1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0523
R07
SET - 3
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) What is data? Explain about various views of it in detail. b) Explain about ER model in detail.
2.
Explain about the data base system structure in detail.
3.
a) What is an ER diagram? Draw an ER diagram for a library management system. b) Explain about various types of relationship in detail.
4.
What is a query? Explain about querying relational data in detail.
5.
What is a join? Explain about various types of joins with clear examples.
6.
a) What is a schema? Explain the reasons for schema refinement . b) Explain about fourth normal form in detail.
7.
Explain about file organization and indexing in detail.
8.
Write short notes on the following. a) Log based recovery b) Advanced recovery systems c) Granularity.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: V0523
R07
SET - 4
II B. Tech II Semester, Supplementary Examinations, Dec 2012 DATA BASE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (Com. to CSE, IT) Time: 3 hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry Equal Marks ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ 1. a) What is data abstraction? Explain the significance of it in detail. b) Differentiate between abstract and detailed data.
2.
Explain about the history of data base systems in detail.
3.
What is a large enterprise? Explain about conceptual data design for large enterprises in detail.
4.
a) What is an integrity constraint? Explain the significance of it. b) How would you enforce integrity constraints?
5.
What is a relational calculus? Explain about the tuple and domain relational calculus in detail.
6.
a) What is redundancy? Explain the problems caused by redundancy in detail. b) Explain about BCNF in detail.
7.
a) What is a concurrent transaction? Explain about recovery with concurrent transactions. b) Explain about remote back-up systems in detail.
8.
Write short notes on the following. a) Functional dependency. b) Third normal form c) Storage manager.
1 of 1
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
Code No: T0501/R05
Set No. 1
II B.Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, December 2012 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS (Computer Science & Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. If A (n) = an xn + ...... + a1x + a0 then the derivative of A(x) is A1 (x) = n an xn1 + ...+a1 write an algorithm that produces the value of a polynomial and its derivative at a point x=v. Determine the number of required arithmetic operations. [16] 2. (a) Show that the best case running time of Quick sort on a sequence of size n with distinct elements is O(nlog(n)). (b) Why is it important that Strassens algorithm does not use commutative in the multiplication of 2x2 matrices? Explain. [8+8] 3. (a) Prove that if the weights on the edges of a connected undirected graph are distinct then there is a unique minimum spanning tree. (b) Explain the general characteristics of Greedy method. [8+8] 4. (a) Write a pseudocode for a linear time algorithm that generates the optimal Binary search tree from the root table. (b) Find the minimum number of operations required for the following chain matrix multiplication using dynamic programming. A(30,40) * B(40,5) * C(5,15) * D(15,6). [8+8] 5. (a) Write a pseudocode for nding the strongly connected components of directed graph. Also analyze its time complexity. (b) Explain the Inorder traversal of a tree with an example. [8+8] 6. (a) Draw and explain the portion of the tree for 4-queens problem that is generated during backtracking. (b) Explain the applications of Backtracking. [10+6] 7. Solve the TSP problem having the following cost matrix using branch and bound technique. [16] A A X 4 B C 4 D 7 B 5 X 2 6 C 2 1 X 8 D 3 5 3 X
8. (a) Explain the satisability problem and write the algorithm for the same. (b) Dierentiate between NP-complete and NP-Hard. [10+6]
|'''|'|'|''||''|'''|
1 of 1
You might also like
- Tutorial Load C-C PDFDocument3 pagesTutorial Load C-C PDFEyad A. FeilatNo ratings yet
- 5Document100 pages5arvind pandeyNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Electric BrakingDocument12 pagesInduction Motor Electric Brakingmastanamma.Y100% (1)
- Frog Leg WindingDocument9 pagesFrog Leg WindingAbhijeet RedekarNo ratings yet
- Tests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual LabDocument4 pagesTests On Single Phase Transformer (Procedure) - Analog Signals, Network and Measurement Laboratory - Electrical Engineering - IIT KHARAGPUR Virtual Labvjvijay88No ratings yet
- Types of Cams GuideDocument21 pagesTypes of Cams GuideHarikrishna ShenoyNo ratings yet
- SHEET 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesSHEET 1 Solution171148 171148No ratings yet
- ME8391 ETD by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument167 pagesME8391 ETD by WWW - Learnengineering.inERRAMESH1989No ratings yet
- Vehicle Performance Curves Explained for Light Vehicle ApplicationsDocument6 pagesVehicle Performance Curves Explained for Light Vehicle ApplicationsPratik008No ratings yet
- Power Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-7 Hydro-Water Power PlantDocument84 pagesPower Plant Lecture Notes - CHAPTER-7 Hydro-Water Power PlantHiteshNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Start/Run Induction Motor LabDocument9 pagesCapacitor Start/Run Induction Motor LabMarcos Roberto ReinertNo ratings yet
- Assignment Problems HVDCDocument2 pagesAssignment Problems HVDCSelva KumarNo ratings yet
- Special - Electrical - Machines QBDocument25 pagesSpecial - Electrical - Machines QBVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- PE QuestionBankDocument6 pagesPE QuestionBankRakshith0% (1)
- AC Voltage Controller: Shahid IqbalDocument39 pagesAC Voltage Controller: Shahid IqbalZack ZoldyckNo ratings yet
- DC Machines: Parts of DC MachineDocument51 pagesDC Machines: Parts of DC MachineKUMARNo ratings yet
- EENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Document4 pagesEENG492 Extended Assignment Spring 2019-2020 - v4Jamil NahraNo ratings yet
- 2-The Variable LoadDocument14 pages2-The Variable LoadPotatoFryNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Machines Tutorial Sheets (EL-208Document10 pagesAsynchronous Machines Tutorial Sheets (EL-208Kushagra BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Assignment of Control EngineeringDocument1 pageAssignment of Control EngineeringahmadNo ratings yet
- Vidyarthiplus Question Bank on Special Electrical MachinesDocument13 pagesVidyarthiplus Question Bank on Special Electrical MachinesjagadeeshNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsDocument4 pagesElectrical Machines I Lab Twisted QuestionsPranav MenonNo ratings yet
- M Bayu Irpan F 4EBDocument5 pagesM Bayu Irpan F 4EBBayu Jarai100% (1)
- Bearing Selection - Bearing Sample 2A V2Document3 pagesBearing Selection - Bearing Sample 2A V2Suchi Suchi SuchiNo ratings yet
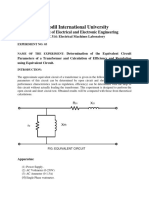
- Determination of The Equivalent Circuit Parameters of A Transformer and Calculation of Efficiency and Regulation Using Equivalent CircuitDocument4 pagesDetermination of The Equivalent Circuit Parameters of A Transformer and Calculation of Efficiency and Regulation Using Equivalent CircuitMd Rion100% (1)
- Hw5 SolutionDocument1 pageHw5 SolutionUmair AbbasNo ratings yet
- A7dca BSDZVCFDocument2 pagesA7dca BSDZVCFRAJANo ratings yet
- Flywheel ProblemsDocument51 pagesFlywheel Problemsgiriaj kokareNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Optimal Design of DC Machine Unit-02/Lecture-01Document31 pagesUnit - 2 Optimal Design of DC Machine Unit-02/Lecture-01madeehaNo ratings yet
- Assignment No.: 2 (Topic Name: Rolling Contact BearingDocument1 pageAssignment No.: 2 (Topic Name: Rolling Contact BearingJai Sharma0% (1)
- Assignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleDocument24 pagesAssignment and Its Solution - Airstandardcycle and VapourcycleMatthias100% (1)
- Epe 1.3 - Power Electronic Control of DC DrivesDocument1 pageEpe 1.3 - Power Electronic Control of DC DrivesPhani Kumar MallelaNo ratings yet
- ICE Assignment Chapter 1Document3 pagesICE Assignment Chapter 1ahmadNo ratings yet
- Part BDocument10 pagesPart BVenkat ManiNo ratings yet
- Brayton CycleDocument5 pagesBrayton CycleDanang Wahdiat Aulia IshaqNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machine Design Question Bank - As Per VTU SyllabusDocument20 pagesElectrical Machine Design Question Bank - As Per VTU SyllabusManjunathNo ratings yet
- 11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Document22 pages11.a.ii - ME03031 QA 1Bakkiya Raj100% (1)
- CH 14Document11 pagesCH 14hirenpatel_universalNo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: What Is The Difference Between Refrigeration & Air Conditioning?Document8 pagesUNIT-1: What Is The Difference Between Refrigeration & Air Conditioning?Udit NarayanNo ratings yet
- (Mini Project-Shaft Design) : The University of Jordan School of EngineeringDocument5 pages(Mini Project-Shaft Design) : The University of Jordan School of EngineeringMou'ath AlhajjajNo ratings yet
- Sheatpoweer Steam Turbine22Document3 pagesSheatpoweer Steam Turbine22Omeed ArtsNo ratings yet
- Engine Testing LabDocument3 pagesEngine Testing LabSachi MensiNo ratings yet
- Presentation On Intstrumentation & Control Included Topics:-Deflection & Null Type InstrumentsDocument18 pagesPresentation On Intstrumentation & Control Included Topics:-Deflection & Null Type InstrumentsAakash ahujaNo ratings yet
- Cmps QBFFDocument80 pagesCmps QBFFFeliscio Ascione FelicioNo ratings yet
- Marks: 0.00 User Answer Sheet Rank: 7: Report QuestionDocument17 pagesMarks: 0.00 User Answer Sheet Rank: 7: Report Questionchandrachurom5538100% (1)
- Electric Vehicle Motor TypesDocument20 pagesElectric Vehicle Motor TypesRahulNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesIntroduction to Kinematics of MachinesEmmanuelRomaresNo ratings yet
- Assignment (Electric Power Utilization EE16105)Document4 pagesAssignment (Electric Power Utilization EE16105)Prasenjit DeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3younkushanks0% (1)
- Marking Scheme of MST-I AST-308Document3 pagesMarking Scheme of MST-I AST-308Ranjit Kour0% (1)
- Heat Exchangers Types & Applications, LMTD Derivation & ProblemsDocument11 pagesHeat Exchangers Types & Applications, LMTD Derivation & Problemsananth2012No ratings yet
- Calculate energy savings and project NPV for equipment upgradesDocument6 pagesCalculate energy savings and project NPV for equipment upgrades61EEPrabhat PalNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Based Medicine Reminder PDFDocument55 pagesMicrocontroller Based Medicine Reminder PDFjadhav priti NanaNo ratings yet
- Drives Manual Final EeeDocument60 pagesDrives Manual Final EeenandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- CYCLOCONVERTERSDocument2 pagesCYCLOCONVERTERSAmit ParchakeNo ratings yet
- Code No: V0421/R07 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, Apr – 2011 PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS (Com. to ECE, BME, ECCDocument4 pagesCode No: V0421/R07 II B.Tech II Semester, Regular Examinations, Apr – 2011 PULSE AND DIGITAL CIRCUITS (Com. to ECE, BME, ECCLavanya_123No ratings yet
- for Electrical Technology DocumentDocument4 pagesfor Electrical Technology Documentteodoro berouNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- 4th B.tech - I&II Semester-08052015Document1 page4th B.tech - I&II Semester-08052015Polireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Practice Paper IqDocument9 pagesPractice Paper IqSugam Sharma100% (1)
- New Children's Money Back: Benefits Illustration SummaryDocument2 pagesNew Children's Money Back: Benefits Illustration SummaryPolireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 2 Reversed Carnot CycleDocument2 pages2 Reversed Carnot CycleAlok GargNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Chapter - 6Document13 pagesLife Processes: Chapter - 6milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes: Chapter - 6Document13 pagesLife Processes: Chapter - 6milind dhamaniyaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument10 pagesTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig Functionsmonelmetal100% (1)
- Bell Coleman CycleDocument5 pagesBell Coleman CycleAshara Aakash100% (2)
- R10 III I Mid TimeTableDocument4 pagesR10 III I Mid TimeTableStanns Institutions ChiralaNo ratings yet
- JNTU Kakinada Exam Fees RatesDocument2 pagesJNTU Kakinada Exam Fees RatesPolireddi Gopala Krishna78% (9)
- IC Engine Testing and Performance ParametersDocument31 pagesIC Engine Testing and Performance ParametersPolireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Cooling SystemsDocument22 pagesAircraft Cooling SystemsPolireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Air Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)Document15 pagesAir Cycle Refrigeration Systems (Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur)emawz21No ratings yet
- Combustion in Si EnginesDocument40 pagesCombustion in Si EnginesPolireddi Gopala Krishna100% (4)
- Combustion in Si EnginesDocument40 pagesCombustion in Si EnginesPolireddi Gopala Krishna100% (4)
- Set No: 1: Code No: V3203/R07Document50 pagesSet No: 1: Code No: V3203/R07Polireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Te 2 SyllabusDocument3 pagesTe 2 SyllabusPolireddi Gopala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Daker DK Plus 2000: General FeaturesDocument2 pagesDaker DK Plus 2000: General Featuresovidiu ovidiusNo ratings yet
- RC Coupled Amplifier Experiment ReportDocument6 pagesRC Coupled Amplifier Experiment ReportTahsin Zaman TalhaNo ratings yet
- Free Dump Don't Pay For It: H19-301.prepaway - Premium.exam.60qDocument17 pagesFree Dump Don't Pay For It: H19-301.prepaway - Premium.exam.60qMoe KaungkinNo ratings yet
- GSE Model 675: Technical Reference ManualDocument84 pagesGSE Model 675: Technical Reference ManualAlec Hernandez GomezNo ratings yet
- Iot ConfigurationDocument12 pagesIot ConfigurationTechnos_IncNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohammad Salah: by Mechatronics Engineering Department The Hashemite UniversityDocument15 pagesDr. Mohammad Salah: by Mechatronics Engineering Department The Hashemite UniversityMais AlsharifNo ratings yet
- Star Online Publication: Case Number: Release Date: Symptom/Vehicle IssueDocument2 pagesStar Online Publication: Case Number: Release Date: Symptom/Vehicle IssueThomas AndersonNo ratings yet
- MAC 600 Service Manual: GE HealthcareDocument127 pagesMAC 600 Service Manual: GE HealthcareMAXWELL OLIVEIRA DOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Delta Tester 9424 Training ModuleDocument35 pagesDelta Tester 9424 Training ModuleNini FarribasNo ratings yet
- GPL32200A EMUBOARD SchematicDocument9 pagesGPL32200A EMUBOARD SchematicFrancis TaisantNo ratings yet
- Indoor Integrated Power System: TP48200B-N20B2Document8 pagesIndoor Integrated Power System: TP48200B-N20B2Equipo Técnico STLNo ratings yet
- Electronics Circuits IIDocument50 pagesElectronics Circuits IIjopi60No ratings yet
- CWS-100 ObjectivesDocument4 pagesCWS-100 Objectiveshalakahiki82No ratings yet
- Eastron SDM630MCT Smart Meter Modbus Protocol GuideDocument24 pagesEastron SDM630MCT Smart Meter Modbus Protocol GuideÁlvaroAnabalónSalamancaNo ratings yet
- Restricted Earth-Fault Relay Spaj 115 C: Product GuideDocument10 pagesRestricted Earth-Fault Relay Spaj 115 C: Product GuideShah RoshanNo ratings yet
- Mixed NeuromorphicDocument4 pagesMixed NeuromorphicPeter Wagih ZakiNo ratings yet
- How CRT and LCD monitors display imagesDocument11 pagesHow CRT and LCD monitors display imagesบรมวุฒิ ราญคำรัตน์No ratings yet
- Termostato kjr-12b ManualesDocument32 pagesTermostato kjr-12b ManualesIvar Denicia DelgadilloNo ratings yet
- MCQ Est1Document2 pagesMCQ Est1Marc Liam LuNo ratings yet
- Manual RADIO TECSUN PL ) PDFDocument26 pagesManual RADIO TECSUN PL ) PDFilie tcaciucNo ratings yet
- Colegio de Dagupan Midterm Examination AC Apparatus Set ADocument6 pagesColegio de Dagupan Midterm Examination AC Apparatus Set AJohnloyd M. DYNo ratings yet
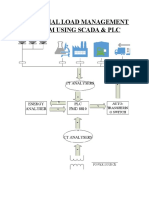
- INDUSTRIAL LOAD MANAGEMENT WITH SCADA & PLCDocument7 pagesINDUSTRIAL LOAD MANAGEMENT WITH SCADA & PLCMuhammad Naveed SultanNo ratings yet
- Dem240128d SBH PW N D TouchDocument20 pagesDem240128d SBH PW N D TouchCatalin PancescuNo ratings yet
- ZEN User Guide Version EDocument10 pagesZEN User Guide Version EphilippeNo ratings yet
- SA MAX7000 DiagramaDocument15 pagesSA MAX7000 DiagramaCesra HM100% (1)
- AMPmetrics v2 PDFDocument14 pagesAMPmetrics v2 PDFJoshua RobinsonNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer IC - WikipediaDocument20 pages555 Timer IC - WikipediaJuniorNo ratings yet
- Bolide+Pricelist+4!26!2021 CUSTOMERSDocument38 pagesBolide+Pricelist+4!26!2021 CUSTOMERSAcademia IntelNo ratings yet
- FCS DiagnosticsDocument187 pagesFCS Diagnosticsmaddygaddy0% (1)
- Solutions2CMOS CircuitDesign AllenDocument509 pagesSolutions2CMOS CircuitDesign AllenAnil KumarNo ratings yet