Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Six Remedies Available in Equity
Uploaded by
John RisvoldOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Six Remedies Available in Equity
Uploaded by
John RisvoldCopyright:
Available Formats
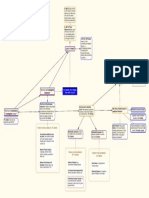
Equity Six (6) Remedies available at equity 1.
. Injunctive Relief is ordered (enjoined) to do or refrain from doing something (permanently or temporarily) A. Temporary Injunctive Relief i. irreparable harm need for relief no because trial will be too late (balance hardships) ii. s likelihood of success (require bond to reimburse ) B. Contrast: Temporary Restraining Order i. Test identical ii. Ex parte proceeding (no notice but good faith effort, no adversarial proceeding) iii. 10 day limitation C. Permanent Injunctive Relief (I Put Five Bucks Down) i. Inadequate legal remedy alternative No replevin, ejectment or money damages (too speculative, tort threatened, insolvent, irreparable injury, multiplicity of actions) ii. Property right (traditional) /protectable interest (modern) requirement iii. Feasibility of Enforcement (Negative no enforcement issues or Mandatory possible issues from supervision or compliance) iv. Balancing of Hardships a) must be gross disparity b) not if s conduct willful c) consider monetary award to d) consider hardship to public v. Defenses a) unclean hands improper conduct related to lawsuit b) laches waits so long unreasonable and prejudicial to (consider money damages) c) impossibility cannot carry out terms of injunction d) Free Speech (defamation or privacy publication branch injunction denied) D. Acts to bind: (i) parties (ii) ee and agents (iii) others acting in concert Trade Secret Misappropriation Trade Secret Taken (better if by improper conduct) Fiduciary duty? = Third party and taker can be enjoined Trademark/Trade Name Infringement Protectable mark Infringement? (likelihood of confusion tests)
Model Answer: In issue is whether plaintiff can obtain temporary injunctive relief. To do so, plaintiff must meet a two-part test: (i) Irreparable Injury (Discuss facts in time frame context) (ii) Likelihood of Success: (Discuss the probability. Impose bond requirement.) 2. Specific Performance is required to perform the contract (Cha-Cha Is My Dance) A. Contract is valid (more certainty and definiteness than money damages) B. Contract conditions of must be satisfied C. Inadequate legal remedy alternative (Sellers of land can get s.p.) (ok even with liquidated damages clause) D. Mutuality of remedy Court will reject the mutuality argument if it feels secure that the can and will perform. Provide for simultaneous performance E. Defenses i. Equitable defenses a. unclean hands b. laches c. unconscionability smell test at time of contract ii. Contract defenses a. mistake b. misrepresentation c. statute of frauds (look for: oral land contract. If so new rule: If one has rendered (i) valuable part performance, (ii) in reliance in the contract, this will take the case out of the statute of frauds and specific performance will be granted. Specials areas of specific performance Equitable conversion If, Specifically enforceable land sale contract then property interests of buyer and seller are switched. Occurs between execution and closing. o Death: Specifically enforceable contract executed. o Damage/Destruction Majority Rule: The risk of loss is on buyer, except if loss from negligence of seller. Modern Trend: The risk of loss is on he seller, except if at the time of loss the buyer has either legal title or possession. Whoever has risk of loss should get insurance, can be got through constructive trust. Personal services contracts o Personal services contract generally not specifically enforceable (enforcement problems and involuntary servitude) o Covenant not to compete must: protect a legitimate interest (unique services) and be reasonable in both geographic and durational scope.
3. Recission the original contract is considered voidable and rescinded (Good Dog) A. Grounds for rescission (7): (1) mistake (2) misrepresentation (3) coercion (4) undue influence (5) lack of capacity (6) failure of consideration (7) illegality (all make contract invalid) i. Mutual mistake: material fact = rescission, collateral fact no rescission ii. Unilateral mistake no rescission except if non-mistaken party knew or should have known (modern trend: exception for undue hardship) iii. Misrepresentation must show actual reliance B. Valid defenses i. unclean hands ii. laches iii. non-defense s negligence 4. Reformation contract does not accurately reflect the understanding reached cannot adversely affect subsequent BFP (Very Good Dog) A. Valid contract B. Grounds for reformation i. mutual mistake = reformation ii. unilateral mistake no reformation, except where non-mistaken party knew iii. misrepresentation = reformation C. Defenses i. unclean hands ii. laches iii. non-defenses: negligence of , statute of frauds, parol evidence rule 5. Constructive Trust ( has title) Imposed on improperly acquired property to which defendant now has title. serves as trustee and must return the property to the plaintiff. A. No adequate legal remedy (property unique) B. Tracing is allowed C. BFP prevails over D. prevails over unsecured creditors E. Use if property value has gone up 6. Equitable Lien ( has title) Imposed on improperly acquired property to which the defendant has title. Property subject to an immediate court-directed sale. Monies received go to the . If the proceeds of the sale are less than the fair market value of the property when it was taken, a deficiency judgment will issue for the difference and can be used against s other assets. A. No adequate legal remedy B. Tracing is allowed C. BFP prevails over D. prevails over unsecured creditors E. Use is property value has gone down F. Use if s property cannot be traced solely to s property
You might also like
- Il Bar Exam Outlines - EquityDocument4 pagesIl Bar Exam Outlines - EquityLewis GNo ratings yet
- Condensed Equity OutlineDocument5 pagesCondensed Equity Outlinecaribelita100% (1)
- IL Civ Pro Bar OutlineDocument6 pagesIL Civ Pro Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro II - Outline (Bahadur)Document8 pagesCiv Pro II - Outline (Bahadur)KayceeNo ratings yet
- Admissible:Inadmissible Character EvidenceDocument7 pagesAdmissible:Inadmissible Character Evidencemdean10No ratings yet
- Crim Pro Outline 3Document55 pagesCrim Pro Outline 3Margaret BoykinNo ratings yet
- Con Law WinDocument117 pagesCon Law WinAdam JacobsonNo ratings yet
- Civil-Procedure Outline Greiner BlueberryDocument55 pagesCivil-Procedure Outline Greiner BlueberryIsaac GelbfishNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Life SaverDocument14 pagesCriminal Law Life SaverHadi Onimisi TijaniNo ratings yet
- Crim Law OutlineDocument9 pagesCrim Law OutlineEmma Trawick BradleyNo ratings yet
- Crim Pro I Search and Seizure EssentialsDocument101 pagesCrim Pro I Search and Seizure EssentialsMariam BabayanNo ratings yet
- Pleading Requirements for Protestor Removal CaseDocument8 pagesPleading Requirements for Protestor Removal CaseDeserae WeitmannNo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law OutlineDocument19 pagesConstitutional Law OutlineThomas Jefferson100% (1)
- Davis EvidenceDocument101 pagesDavis EvidenceKaren DulaNo ratings yet
- Reverter vs. Right of EntryDocument1 pageReverter vs. Right of EntryflorinaNo ratings yet
- Military Justice Courts-MartialDocument18 pagesMilitary Justice Courts-MartialJose Gabriel CordovaNo ratings yet
- Mcculloch V. Maryland:: Theories of Constitutional InterpretationDocument14 pagesMcculloch V. Maryland:: Theories of Constitutional Interpretationfbarber13No ratings yet
- Strict Liability: Products Liability EssentialsDocument22 pagesStrict Liability: Products Liability EssentialsmattNo ratings yet
- 14th Amendment Rights Under the 4th, 5th, and 6thDocument84 pages14th Amendment Rights Under the 4th, 5th, and 6thpar hal100% (1)
- Fourth Amendment protections for searches and seizuresDocument44 pagesFourth Amendment protections for searches and seizuresschyler coxNo ratings yet
- Partnership Agreement ElementsDocument11 pagesPartnership Agreement ElementsPuneet SinghNo ratings yet
- State Action and Equal Protection Judicial ReviewDocument24 pagesState Action and Equal Protection Judicial ReviewNate Enzo100% (1)
- Con Law Outline 3Document25 pagesCon Law Outline 3Dana BlueNo ratings yet
- Rigos Bar Review Series "Uniform" Multistate Essay Exam (Mee) Review Conflicts of Law Magic Memory OutlinesDocument4 pagesRigos Bar Review Series "Uniform" Multistate Essay Exam (Mee) Review Conflicts of Law Magic Memory Outlinessomeguy813No ratings yet
- Crim. Law ATTACK Outline - Alschuler - Spring 2009 ChecklistDocument8 pagesCrim. Law ATTACK Outline - Alschuler - Spring 2009 ChecklistDaniel BarciaNo ratings yet
- Denno Crim Law Exams Part 2Document83 pagesDenno Crim Law Exams Part 2Jay SmithNo ratings yet
- Parties. ALIENAGE If One Party Is Citizen of Foreign State, Alienage Jdx. Satisfied, Except WhenDocument2 pagesParties. ALIENAGE If One Party Is Citizen of Foreign State, Alienage Jdx. Satisfied, Except WhenCory BakerNo ratings yet
- Evidence Class Outline 2 (1584)Document73 pagesEvidence Class Outline 2 (1584)Tiffany BrooksNo ratings yet
- Case ListDocument12 pagesCase ListLaura HoeyNo ratings yet
- Fall 2020 Barzuza CorporationsDocument12 pagesFall 2020 Barzuza Corporationsa thaynNo ratings yet
- Federal Rules of Evidence ChecklistDocument6 pagesFederal Rules of Evidence ChecklistJenny SeonNo ratings yet
- Con Attack OutlineDocument34 pagesCon Attack OutlineLarry RogersNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law OutlineDocument25 pagesCriminal Law OutlinechristiandemeNo ratings yet
- Land Use ControlsDocument17 pagesLand Use ControlsHaifaNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro Spring 2014Document23 pagesCiv Pro Spring 2014Zachary Figueroa100% (1)
- Introduction to Family Law and its DefinitionsDocument93 pagesIntroduction to Family Law and its Definitionsbiglank99No ratings yet
- Outline Laura Civil Procedure.Document97 pagesOutline Laura Civil Procedure.Mike Binka KusiNo ratings yet
- Rethinking Privacy: Fourth Amendment "Papers" and The Third Party DoctrineDocument54 pagesRethinking Privacy: Fourth Amendment "Papers" and The Third Party DoctrineThe Brennan Center for JusticeNo ratings yet
- Babich CivPro Fall 2017Document30 pagesBabich CivPro Fall 2017Jelani WatsonNo ratings yet
- Crim Law Cases + NotesDocument15 pagesCrim Law Cases + Notestwbrown1220No ratings yet
- Big Head Civ ProDocument55 pagesBig Head Civ ProSucolTeam6No ratings yet
- Contracts 2 Outline Spring20Document66 pagesContracts 2 Outline Spring20Amelia PooreNo ratings yet
- Arrest and Detention FlowchartDocument1 pageArrest and Detention FlowchartAliNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Outline: Actus Reus, Mens Rea, Sources & TheoriesDocument32 pagesCriminal Law Outline: Actus Reus, Mens Rea, Sources & TheoriesLeah GaydosNo ratings yet
- Section: MPC Common LawDocument4 pagesSection: MPC Common Lawrdt854100% (1)
- Graham Evidence Spring2013 2Document26 pagesGraham Evidence Spring2013 2sagacontNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law I Theory DimensionsDocument55 pagesCriminal Law I Theory DimensionsErin LillieNo ratings yet
- Ivil Rocedure: Ersonal Urisdiction HO CAN BE SuedDocument45 pagesIvil Rocedure: Ersonal Urisdiction HO CAN BE SuedVicki GokhmanNo ratings yet
- Con Law Cheat Sheet (Judicial Tests)Document4 pagesCon Law Cheat Sheet (Judicial Tests)Rachel CraneNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3 68-77 Assignment #5 106-115 Assignment #6 119-128Document16 pagesAssignment #3 68-77 Assignment #5 106-115 Assignment #6 119-128Marco FortadesNo ratings yet
- Flowchart Bankruptcy Proceedings Up To The Stage A Debtor Is Adjudged A BankruptDocument2 pagesFlowchart Bankruptcy Proceedings Up To The Stage A Debtor Is Adjudged A BankruptAudrey LimNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Outline (Metzger)Document21 pagesCriminal Law Outline (Metzger)jalisamwNo ratings yet
- Criminal Law Outline Spring 2010Document17 pagesCriminal Law Outline Spring 2010BUbobby24No ratings yet
- Brief PropertyDocument4 pagesBrief Propertyshakinmakin84No ratings yet
- Ahrens Criminal Law Fall 2009 OutlineDocument8 pagesAhrens Criminal Law Fall 2009 Outlinecsharp47No ratings yet
- Animal Law Outline Key ConceptsDocument25 pagesAnimal Law Outline Key ConceptsKatie SperawNo ratings yet
- Remedies Hutchinson - 2012Document57 pagesRemedies Hutchinson - 2012LegaleLegalNo ratings yet
- Administrative Law - Siegel - Spring 2007 - 3Document64 pagesAdministrative Law - Siegel - Spring 2007 - 3champion_egy325No ratings yet
- Law School Outline - Property - NYU School of Law - EstlundDocument55 pagesLaw School Outline - Property - NYU School of Law - Estlundeagleal5No ratings yet
- Anti-SLAPP Law Modernized: The Uniform Public Expression Protection ActFrom EverandAnti-SLAPP Law Modernized: The Uniform Public Expression Protection ActNo ratings yet
- Torts OutlineDocument30 pagesTorts OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Wills Bar OutlineDocument6 pagesWills Bar OutlineJohn Risvold50% (2)
- Creation, Transfer and Termination of Private TrustsDocument4 pagesCreation, Transfer and Termination of Private TrustsJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Family Law Bar OutlineDocument5 pagesFamily Law Bar OutlineJohn Risvold100% (1)
- Suretyship Bar OutlineDocument2 pagesSuretyship Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Secured Bar OutlineDocument3 pagesSecured Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Evidence OutlineDocument8 pagesEvidence OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Civ Pro Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesCiv Pro Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Contracts OutlineDocument35 pagesContracts OutlineJohn Risvold100% (1)
- Corporations Bar OutlineDocument4 pagesCorporations Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- Recognition of Foreign Judgments and Choice of Law ApproachesDocument4 pagesRecognition of Foreign Judgments and Choice of Law ApproachesJohn Risvold50% (2)
- Travis Risvold Final OutlineDocument28 pagesTravis Risvold Final OutlineJohn Risvold0% (1)
- Commercial Paper Bar OutlineDocument2 pagesCommercial Paper Bar OutlineJohn RisvoldNo ratings yet
- DENR Authority Over Small-Scale MiningDocument3 pagesDENR Authority Over Small-Scale MiningAdrian SimanganNo ratings yet
- Reversed Civrev Bqa 2016 1989Document225 pagesReversed Civrev Bqa 2016 1989doraemoan100% (1)
- Law PDFDocument250 pagesLaw PDFkennethNo ratings yet
- Pre-Trial Memorandum: Superior Court (Toronto Region)Document4 pagesPre-Trial Memorandum: Superior Court (Toronto Region)Azirah Yoj Ripalda HembraNo ratings yet
- Clark County Jail Pre-Book Sheet: DefendantDocument5 pagesClark County Jail Pre-Book Sheet: DefendantKGW NewsNo ratings yet
- FGU Insurance Corporation vs. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 118889, March 23, 1998Document2 pagesFGU Insurance Corporation vs. Court of Appeals, G.R. No. 118889, March 23, 1998KimmyNo ratings yet
- Sanchez Villalobos ComplaintDocument29 pagesSanchez Villalobos ComplaintinforumdocsNo ratings yet
- SAME SEX MARRIAGE TABOO IN INDIADocument10 pagesSAME SEX MARRIAGE TABOO IN INDIAanushka kashyap100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Agrarian Reform PoliciesDocument24 pagesChapter 11 Agrarian Reform PoliciesJohn Lloyd GaringNo ratings yet
- Labor Law OutlineDocument40 pagesLabor Law OutlineDave CadalsoNo ratings yet
- Legal citations made simpleDocument42 pagesLegal citations made simpleTanushkaNo ratings yet
- Curious Case of Agnes Raguinan, Teacher: AsiseeitDocument7 pagesCurious Case of Agnes Raguinan, Teacher: AsiseeitJason JavierNo ratings yet
- Court upholds homestead rights over agrarian reform lawDocument1 pageCourt upholds homestead rights over agrarian reform lawMigs RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Republic Vs Ortigas 717 SCRA 601, GR 171496 (March 3, 2014)Document8 pagesRepublic Vs Ortigas 717 SCRA 601, GR 171496 (March 3, 2014)Lu CasNo ratings yet
- Humber Ferry FlyerDocument1 pageHumber Ferry FlyerTabitha HowardNo ratings yet
- Gabe Kaimowitz v. The Florida Bar, Its Agents, Employees and Assignees, 996 F.2d 1151, 11th Cir. (1993)Document7 pagesGabe Kaimowitz v. The Florida Bar, Its Agents, Employees and Assignees, 996 F.2d 1151, 11th Cir. (1993)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Law and Child AbuseDocument21 pagesLaw and Child AbuseMuhd Assyahidanllah Mohd Mokhtar100% (2)
- Mangahas vs. Paredes, 2007Document4 pagesMangahas vs. Paredes, 2007SophiaFrancescaEspinosaNo ratings yet
- Lex Communique Moot Court Competition Researcher TestDocument4 pagesLex Communique Moot Court Competition Researcher TestYashdeep LakraNo ratings yet
- Savoie Plea Agreement RedactedDocument20 pagesSavoie Plea Agreement RedactedCLDC_GSNo ratings yet
- National Service Training Program1: Ms - Viray (Module 3 - IT1&HRS1)Document3 pagesNational Service Training Program1: Ms - Viray (Module 3 - IT1&HRS1)Guki SuzukiNo ratings yet
- Bhagwandas Goverdhandas Kedia V Girdharilal Parshottamdas & CoDocument15 pagesBhagwandas Goverdhandas Kedia V Girdharilal Parshottamdas & CoIKIGAINo ratings yet
- Republic vs. AndayaDocument9 pagesRepublic vs. AndayaBoyTibs100% (1)
- Karnataka Police Department Directions PDFDocument2 pagesKarnataka Police Department Directions PDFGovindNo ratings yet
- 11 June 85 XXXXXXX XXXXXXXXX Baguio City Richelda Q. Estrada Brgy Sta Barbara, Agoo, La Union (Or Premarital)Document9 pages11 June 85 XXXXXXX XXXXXXXXX Baguio City Richelda Q. Estrada Brgy Sta Barbara, Agoo, La Union (Or Premarital)Jomar BoronganNo ratings yet
- United States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitDocument18 pagesUnited States Court of Appeals, Fourth CircuitScribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Legal Latin Maxims: BALLB II Semester and LLB VI SemesterDocument10 pagesLegal Latin Maxims: BALLB II Semester and LLB VI SemesterRishabh JainNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 164774Document1 pageG.R. No. 164774Mai LegriaNo ratings yet
- Middlebrooks OrderDocument79 pagesMiddlebrooks OrderJohn ByrneNo ratings yet
- Antolin PDFDocument20 pagesAntolin PDFRochelle Ann EstradaNo ratings yet