Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kimia Garam Aras 3 Bank Soalan Jawapan
Uploaded by
Hazwani HashimOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kimia Garam Aras 3 Bank Soalan Jawapan
Uploaded by
Hazwani HashimCopyright:
Available Formats
SMK SEBAUH
Jawapan
SPM Kimia Tingkatan 4,5 - Soalan Kimia Garam Aras 3 Kertas 2
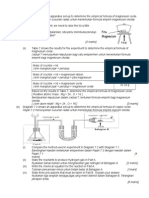
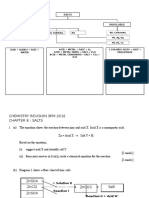
1. (a) i. Blue/Biru ii. CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) CuSO4 (aq) + H2O (l) CuO (p) + H2SO4 (ak) CuSO4 (ak) + H2O (ce) iii. To ensure all sulphuric acid reacted Untuk memastikan semua asid sulfurik bertindakbalas iv. Because excess sulphuric acid cannot be separated from the salt solution Disebabkan asid sulfurik berlebihan tidak boleh dipisahkan dari larutan garam v. Because copper is below hydrogen in the electrochemical series and reaction would not occur Disebabkan kuprum berada di bawah hidogen dalam siri elektrokimia dan tindak balas tidak akan berlaku (b) i. Manipulated variable = Impure copper(II) sulphate Pembolehubah dimanipulasi = Kuprum(II) sulfat tak tulen Responding variable = Pure copper(II) sulphate Pembolehubah bertindakbalas = Kuprum(II) sulfat tulen Fixed variable = Water Pemboleh ubah dimalarkan = Air ii. A pure form of copper(II) sulphate can be obtained by recrystallization Kuprum(II) sulfat tulen boleh dihasilkan secara penghabluran semula. iii. The solution is heated so as to evaporate some of the water in the solution. Larutan dipanaskan untuk mengewapkan sebahagian air dari larutan. (a) Sulphuric acid (b) To make sure that all the sulphuric acid completely reacted with the copper(II) oxide. (c) CuO(s) + H2SO4(aq) CuSO4 (aq) + H2O(g) (d) To make the filtrate saturated so that crystalisation will take place. (e) The saturated solution obtained is cooled so that crystalisation occurs. The mixture is then filtered and the crystals collected on the filter paper is rinsed with a little distilled water. (f) Number of mole of H2SO4 = = 0.02 moles So, number of moles of CuSO4 = 0.02 moles Mass of CuSO4 = 0.02(64 +32+64) = 3.2 g (g) Copper(II) oxide and copper(II) hydroxide. (a)
2.
3.
(b) The copper(II) carbonate green solid become black solid. (c) i. Copper(II) oxide and carbon dioxide ii. CuCO3(s) CuO(s) + CO2(g) (d) Number of moles of copper(II) carbonate = = 0.005 moles Maximum mass of copper(II) oxide = 0.005(64 + 16) = 0.4 g (e) CuCO3(s) + 2H+ (aq) Cu2+ (aq) + CO2 (g) + H2O(l) (f) The strip of zinc will becomes thinner, a brown solid will be deposited. Blue solution will become paler.
4.
(a) (i) Y = Oxygen Z = Nitrogen dioxide X = Lead(II) oxide (ii) Add / pour sulphuric acid and iron(II) sulphate solution followed by concentrated sulphuric acid. Precipitate / brown ring formed (b) (i) Lead(II) ion/Pb2+ ion (ii) W2+ + 2I WI2/Pb2+ + 2I PbI2 (iii) W(II) hydroxide / lead(II) hydroxide (c) (i) Precipitate / white solid formed (ii) W(II) sulphate / Lead(II) sulphate (a) i. Lead(II) nitrate solution ii. Bubble the gas A through limewater. The limewater turns milky shows that gas A is carbon dioxide. iii. PbCO3 + 2HNO3 Pb (NO3)2 + CO2 + H2O (b) A white precipitate is formed in excess sodium hydroxide (c) i. Lead(II) carbonate; PbCO3 ii. Pb(NO3)2 + Na2CO3 Pb CO3 + 2NaNO3 iii. The mixture is filtered using filter funnel and filter paper. The precipitate (zink carbonate) is dry using a piece filter paper and the filtrate (zinc carbonate) is collected in conical flask. (a) i. Blue / Biru ii. CuO (s) + H2SO4 (aq) CuSO4 (aq) + H2O (l) iii. To ensure all the sulphuric acid has reacted Untuk memastikan semua asid bertindakbalas iv. Because excess sulphuric acid cannot be separated form the salt solution Kerana asid sulfurik berlebihan tidak boleh dipisahkan dari larutan garam v. Because copper is below hydrogen in the electrochemical series and reaction will not occur Kerana kuprum adalah di bawah hidrogen dalam siri elektrokimia dan tindakbalas tidak akan berlaku (b) i. Manipulated variable = Impure copper(II) sulphate Pembolehubah manipulasi = Kuprum(II) sulfat tak tulen Responding variable = Pure copper(II) sulphate Pembolehubah bergerakbalas = Kuprum(II) sulfat tulen Fixed variable = Water Pembolehubah tetap = Air ii. Pure copper(II) sulphate can be obtained by recrystallization Kuprum (II) sulfat tulen boleh diperolehi dengan kaedah pengkristalan semula iii. Step (b). The solution is heated so as to evaporate some of the water in the solution. Langkah (b). Larutan dipanaskan dan sebahagian air di dalam larutan akan merewap. (a) reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium [1 m] neutralisation of hydrochloric acid by magnesium oxide[1 m] reaction between hydrochloric acid and magnesium carbonate [1 m] (b) neutralisation of hydrochloric acid and magnesium oxide [1 m]
5.
6.
7.
[1 m] dilute hydrochloric acid is heated in a beaker [1 m] magnesium oxide powder is added until there is an excess of the insoluble oxid.
The hot colourless solution is filtered to remove the excess magnesium oxide. [1 m]
[1 m] The filtrate is poured into an evaporating dish and is heated until the volume of the solution left is 1/3 of the original volume [1 m]
[1 m ] The solution is then cooled or evaporated and then crystallised. [1 m] The remaining solution is filtered and the crystals are rinsed with a little distilled water and dried between two sheets of filter paper [1 m] (c) i. 2 cm3 of magnesium chloride solution are poured into a test tube, three drops of sodium hydroxide solution
8.
are added then in excess. The mixture is shaken gently. [1 m] White precipitate is formed and it is soluble in excess sodium hydroxide solution. [1 m] Another 2 cm3 of magnesium chloride solution is poured into a test tube, three drops of ammonia aqueous solution is then added in excess. The mixture is shaken gently. [1 m] An insoluble white precipitate formed in excess ammonia aqueous solution. [1 m] The cation is determine as magnesium ion [1 m] ii. 2 cm3 of magnesium chloride solution are poured into a test tube, excess dilute nitric acid is added followed by 1 cm3 of silver nitrate solution [1 m] A white precipitate is formed [1 m] The anion is determined as chloride ion. [1 m] (a) (i) X = Cu2+ ; Y = Fe2+ and Z = Fe3+ [2m] (ii) Cu(OH)2 ; Fe(OH)2 and Fe(OH)3 [2m] (b)
[8m] (c) Add a little sodium carbonate powder to 5 cm3 of solution from bottle 1. The evolution of gas that turns lime water milky will verify the presence of hydrogen ions in the acid. Tambahkan sedikit natrium karbonat kepada 5 cm3 larutan dari botol 1. Gas yang terhasil dan mengeruhkan air kapur dapat menentukan kehadiran ion hidrogen dalam asid. [2m] Add 2 cm3 of barium nitrate solution to 5 cm3 of solution from bottle 1. The formation of a white precipitate will verify the presence of sulphate ions. Tambahkan 2 cm3 larutan barium nitrat kepada 5 cm3 larutan dari botol 1. Pembentukan mendakan putih menentukan kehadiran ion sulfat. [2m] Add 1 cm3 of Nessler reagent to 5 cm3 of solution from bottle 2. The formation of brown precipitate will verify the presence of ammonium ions. Tambahkan 1 cm3 reagen Nessler kepada 5 cm3 larutan dari botol 2. Pembentukan mendakan perang menentukan kehadiran ion ammonium. [2m] Add a little of iron(II) sulphate and dilute sulphuric acid to 5 cm3 of solution from beaker 2, followed by concentrated sulphuric acid added slowly. The formation of brown ring will verify the presence of nitrate ions. Tambahkan sedikit ferum(II) sulfat dan larutan cair asid sulfurik kepada 5 cm3 larutan dari botol 2 diikuti oleh asid sulfurik pekat ditambah perlahan-lahan. Pembentukan cincin perang menentukan kehadiran ion nitrat. [2m] (a) A salt is the substance formed when the hydrogen ions of an acid are replaced by metal ions or
9.
ammonium ions. [1 m] Example: Sodium chloride [1 m] (b) i. Insoluble salts can be prepared by double decomposition. [1 m] ii. an insoluble salt, PY is is prepared us described below: Two salt solutions, PX and PY are selected as the materials. [1 m] P and Q are cations while X and Y are anions. [1 m] The reaction is, PX(aq) + QY (aq) PY(s) + QX(aq) [1 m] PY is the insoluble salt and QX is a soluble salt. [1 m] The solutions are measured and mix in a beaker. The mixture is stirred. [1 m] Precipitate formed is filtered and the residue is rinsed with distilled water. [1 m] The residue is dried between sheets of filter papers. [1 m] (c) i. 2 cm3 of copper(II) chloride solution is poured into a test tube, [1 m] excess of dilute nitric acid is added followed by 1 cm3 of silver nitrate [1 m] White precipitate is formed [1 m] ii. 2 cm3 of copper(II) chloride solution are poured into a test tube, 1 cm3 of sodium hydroxide solution is added then excess [2 m] A blue precipitate is formed. It is soluble in excess sodium hydroxide solution. [1 m] 2 cm3 of copper(II) chloride solution is poured into a test tube, 1 cm3 of ammonia aqueous solution is added then in excess [2 m] A blue precipitate is formed and it dissolve in excess aqueous ammonia solution to form a dark blue solution. [2 m] 10. (a) Double decomposition reaction is a reaction involving two different salt aqueous solutions to produce an insoluble salt. [1 m] The first solution containing metal ions while the second solution containing non-metal ions for the salt. [1 m] Tindak balas penguraian ganda dua ialah tindak balas melibatkan dua larutan garam yang berlainan untuk menghasilkan garam tak larut. Larutan pertama mengandungi ion logam sementara larutan kedua mengandungi ion bukan logam bagi garam.
[3 m] b) Material: copper(II) carbonate powder, 0.5 mol dm3 nitric acid and distilled water. [1 m] Apparatus: measuring cylinder, beaker, glass rod, filter papers, filter funnel, tripod stand, retort stand Bunsen burner, and crucible. [1 m] Bahan: serbuk kuprum(II) karbonat,0.5 mol dm-3 asid nitrik dan air suling Radas: silinder penyukat, bikar, rod kaca, kertas turas, corong turas, kaki tiga, kaki retort dan penunu Bunsen, mangkuk pijar Procedure/Prosedur: 25 cm3 of nitric acid is measured s using measuring cylinder and then fi ll it into a beaker. The
beaker is then put on a tripod stand and heat it. [1 m] 25 cm3 asid nitrik disukat menggunakan silinder penyukat dan diisikan ke dalam bikar. Bikar kemudiannya diletakkan di atas kaki tiga dan dipanaskan Copper(II) carbonate powder is added little by little into the heated dilute nitric acid. [1 m] The mixture is stir using a glass rod. Stop adding when there is little copper(II) carbonate does not dissolving any more. [1 m] Serbuk kuprum(II) karbonat ditambahkan sedikit demi sedikit ke dalam asid nitrik cair yang dipanaskan. Campuran dikacau menggunakan rod kaca. Hentikan penambahan apabila sedikit kuprum(II) karbonat tidak lagi larut. Filter the resulting solution to remove the excess copper(II) carbonate. The filtrate is copper(II) sulphate solution. [1 m] Turaskan larutan yang terhasil untuk menyingkirkan lebihan kuprum(II) karbonat. Hasil turasan ialah larutan kuprum sulfat Copper(II) sulphate solution is transferred into a crucible, and then heat it until 1/3 of the initial volume for saturation. [1 m] Larutan kuprum(II) sulfat dipindahkan kepada mangkuk pijar dan dipanaskan sehingga 1/3 larutan awal penepuan The saturated solution is left to cool down until room temperature to encourage crystallisation to take place. [1 m] Larutan tepu dibiarkan sejuk sehingga suhu bilik untuk menggalakkan penghabluran berlaku The contain is filtered and rinsed with distilled water. [1 m] Kandungan dituraskan dan dibilas dengan air suling. The blue crystal, copper(II) sulphate is dried with filter paper [1 m] Hablur biru,kuprum(II) sulfat dikeringkan dengan kertas turas. Chemical equation: Persamaan kimia: Reaction between sodium carbonate solution and copper(II) chloride solution: Tindak balas antara larutan natrium karbonat dan larutan kuprum(II) klorida CuCO3 (aq) + HNO3(aq ) Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(l) [2 m]
You might also like
- Basics of EN 206:2013Document41 pagesBasics of EN 206:2013اسماعيل جودة100% (1)
- 600mm Concrete Drain DesignDocument8 pages600mm Concrete Drain Designkian hongNo ratings yet
- 04 - Planning SI and Interpretation of Results PDFDocument16 pages04 - Planning SI and Interpretation of Results PDFDaniel YongNo ratings yet
- Manufactured Substances in IndustryDocument13 pagesManufactured Substances in IndustryNorsuriani AwangNo ratings yet
- Exercise Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesExercise Rate of ReactionNurulkamilah KhairirNo ratings yet
- Civil Fiber-Reinforced ConcreteDocument15 pagesCivil Fiber-Reinforced ConcreteHELLO WORLDNo ratings yet
- Green Building in Malaysia - Safri (Autosaved)Document19 pagesGreen Building in Malaysia - Safri (Autosaved)farahazuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DCC5152Document35 pagesChapter 1 DCC5152Nora Ismail67% (9)
- Malaysia's GBI promotes green buildingsDocument2 pagesMalaysia's GBI promotes green buildingsTayaabaranNo ratings yet
- The Definition of Green BuildingDocument7 pagesThe Definition of Green BuildingDinidu PradeepNo ratings yet
- Project ECW567 CP ODL v2Document3 pagesProject ECW567 CP ODL v2Sapek 4c5No ratings yet
- ENGINEERING ETHICS AND REGULATIONDocument54 pagesENGINEERING ETHICS AND REGULATIONjhjjhNo ratings yet
- JKR SIRIM PrePDFDocument4 pagesJKR SIRIM PrePDFkhairul AnwarNo ratings yet
- GBI RNC Residential Tool V1.0 FinalDocument14 pagesGBI RNC Residential Tool V1.0 FinalNorFarah ShahiraNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineer Resume SummaryDocument4 pagesCivil Engineer Resume Summaryanandkumarrs6No ratings yet
- Latihan Gabungan Alkana N AlkenaDocument6 pagesLatihan Gabungan Alkana N AlkenaJuni FarhanaNo ratings yet
- SPAN Guidelines For Voluntary Water Efficient Products Labelling SchemeDocument41 pagesSPAN Guidelines For Voluntary Water Efficient Products Labelling SchemeThor Yi ChunNo ratings yet
- Assignment Individu CEM571 Sept 2015Document5 pagesAssignment Individu CEM571 Sept 2015nurulselangorNo ratings yet
- Perencanaan GedungDocument34 pagesPerencanaan GedungMochammad Zulfikri ArifinNo ratings yet
- Please Submit The Assignment On - During The Class. Late Submission Will Not Be Evaluated. 4 Person in One GroupDocument3 pagesPlease Submit The Assignment On - During The Class. Late Submission Will Not Be Evaluated. 4 Person in One GroupThurgah VshinyNo ratings yet
- PEKA Form 4 Chemistry Experiments ListDocument14 pagesPEKA Form 4 Chemistry Experiments Listmagentiran100% (1)
- WAJA CHP.2 Carbon Compounds 2Document35 pagesWAJA CHP.2 Carbon Compounds 2Safwan MazlanNo ratings yet
- SBJDocument10 pagesSBJShyboyzz JusopizNo ratings yet
- Menjawab Dan MengingatDocument5 pagesMenjawab Dan Mengingatsensnaliquid0% (1)
- Science Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkaliDocument38 pagesScience Form 2: 5.5 Acid and AlkalinurafziNo ratings yet
- EAHE System Performance FactorsDocument18 pagesEAHE System Performance FactorsSandeep ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 SKEMADocument11 pagesTrial Kedah Biology SPM 2013 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Chap 8 Part 2Document3 pagesChap 8 Part 2Naguib ZakariaNo ratings yet
- SM K DATO’ ZULKIFLI MUHAMMAD SCIENCE F3 PLANDocument2 pagesSM K DATO’ ZULKIFLI MUHAMMAD SCIENCE F3 PLANSHIAMALA DEVI A/P MUTHUSAMY MoeNo ratings yet
- Dewan KG Perwira Jaya 1Document1 pageDewan KG Perwira Jaya 1Fahmie SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Synthetic Fibers For Crack ControlDocument9 pagesSynthetic Fibers For Crack ControlourebooksNo ratings yet
- Exam KAFA Akhir Tahun 2022 Tahun 3Document6 pagesExam KAFA Akhir Tahun 2022 Tahun 3Maisarah AK0% (2)
- SPM English 1119 Item Analysis Template (Blank)Document8 pagesSPM English 1119 Item Analysis Template (Blank)AdlinaNo ratings yet
- C2005 Ukur Kejuruteraan 2Document125 pagesC2005 Ukur Kejuruteraan 2azmir100% (2)
- Continuous Variation MethodDocument1 pageContinuous Variation Methoddalilac100% (1)
- MASS DIFFUSION TUTORIAL: WILKE-CHANG AND STOKES-EINSTEINDocument3 pagesMASS DIFFUSION TUTORIAL: WILKE-CHANG AND STOKES-EINSTEINPreethpalNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Biology Answering TechniquesDocument3 pagesPaper 3 Biology Answering Techniquesriyashree100% (1)
- RM DCC1023 Jun 2015Document9 pagesRM DCC1023 Jun 2015WanNorAsmaNo ratings yet
- Jawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraDocument63 pagesJawapan Bagi Bahan Bengkel Seminar Kimia SPM 2014 Oleh Cikgu AduraCikgu FaizalNo ratings yet
- PPD Pasir Gudang Johor Modul Hots Kbat Kimia Tingkatan 5Document1 pagePPD Pasir Gudang Johor Modul Hots Kbat Kimia Tingkatan 5chongpeisiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document6 pagesExperiment 3Napsiah NasuchiNo ratings yet
- Guidebook 2 Concrete Tests Oct 2010Document77 pagesGuidebook 2 Concrete Tests Oct 2010syakiroh100% (3)
- Effect of Pressure, Mixing and Temperature on Acetic Acid-Baking Soda ReactionDocument11 pagesEffect of Pressure, Mixing and Temperature on Acetic Acid-Baking Soda ReactionElaine PuiNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document4 pagesExperiment 5idaayudwitasariNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - SPM Model Question Paper 3Document7 pagesChemistry - SPM Model Question Paper 3Law Jin YaoNo ratings yet
- Demolition and site clearance measurementDocument18 pagesDemolition and site clearance measurementJoanne Tan100% (1)
- Kertas Kerja Update (KK) KbsDocument10 pagesKertas Kerja Update (KK) KbsMohd Ezuan Atok100% (1)
- Lab Report DETERMINATION OF PERCENT COMPOSITION IN HYDRATE COMPUNDSDocument6 pagesLab Report DETERMINATION OF PERCENT COMPOSITION IN HYDRATE COMPUNDSRikachu100% (1)
- GC Section 6 MasterDocument24 pagesGC Section 6 Masterapi-246009015No ratings yet
- Pengiraan TiangDocument7 pagesPengiraan TiangfyqaeNo ratings yet
- Booklet (Dca30123 - Working Drawing 2) - Sesi 2 20212022)Document56 pagesBooklet (Dca30123 - Working Drawing 2) - Sesi 2 20212022)HanaAnuarNo ratings yet
- Bill No. 6 - Blok Asrama LelakiDocument36 pagesBill No. 6 - Blok Asrama Lelakisitti drwsNo ratings yet
- Moment® Post Tensioning System Brochure - Ver2Document12 pagesMoment® Post Tensioning System Brochure - Ver2mdkmlNo ratings yet
- Assgn 1 DQS154 PDFDocument4 pagesAssgn 1 DQS154 PDFAce50% (2)
- Answer All The Questions./ Jawab SEMUA Soalan: Section A/Bahagian ADocument12 pagesAnswer All The Questions./ Jawab SEMUA Soalan: Section A/Bahagian AnurulNo ratings yet
- Chemistry SPM 2016 SaltDocument2 pagesChemistry SPM 2016 SaltAzie Nurul AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Tapak Analisis ItemDocument99 pagesTapak Analisis ItemGiovanna AdlimNo ratings yet
- FST556 FibreDocument5 pagesFST556 FibreCtNo ratings yet
- Tetraamin Copper (II) Sulphate SynthesisDocument9 pagesTetraamin Copper (II) Sulphate SynthesisIntan SaviraNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1 ADocument7 pagesExperiment 1 AJunne TanNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument14 pages1 SM PDFSiti HamsyiahNo ratings yet
- KTS - Sarao.bakus Temple of Eternal FiireDocument176 pagesKTS - Sarao.bakus Temple of Eternal FiireK.T.S. SaraoNo ratings yet
- Modicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetDocument14 pagesModicon TM172PDG42R DatasheetRonnie SolomonNo ratings yet
- 5.case Study: Effects of Homeopathic Medicines in AdultsDocument2 pages5.case Study: Effects of Homeopathic Medicines in AdultsAMEEN ARTSNo ratings yet
- 2021 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart FailureDocument137 pages2021 ESC Guidelines For The Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute and Chronic Heart FailuredianNo ratings yet
- Life Below WaterDocument10 pagesLife Below Watertrisha sobito0% (1)
- Chapter 5 Coordinate GeometryDocument33 pagesChapter 5 Coordinate GeometryKalNo ratings yet
- Steel StaircaseDocument17 pagesSteel StaircaseKarthick CrazeiNo ratings yet
- Ped 201 Toddler Observation LabDocument6 pagesPed 201 Toddler Observation Labapi-477856901No ratings yet
- Introducing Inspira's: Managed Noc & Itoc ServicesDocument2 pagesIntroducing Inspira's: Managed Noc & Itoc ServicesmahimaNo ratings yet
- Production Management Midterm ReviewDocument21 pagesProduction Management Midterm Reviewielsiu21184No ratings yet
- Sanoj Kumar - OriginalDocument5 pagesSanoj Kumar - OriginalHamid SaifNo ratings yet
- Syllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesSyllabi - EE 5004 - Power ElectronicsKalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- Practice: Circles and ArcsDocument2 pagesPractice: Circles and ArcsTIANA ARILENo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (CHM 127)Document105 pagesChapter 3 (CHM 127)FiqajasmeNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech 15Document16 pagesParts of Speech 15lost finNo ratings yet
- PDPM Iiitdm Jabalpur: LASER Beam Machining AdvancementsDocument12 pagesPDPM Iiitdm Jabalpur: LASER Beam Machining AdvancementsDeva RajNo ratings yet
- GSM Based Power Grid Monitoring SystemDocument41 pagesGSM Based Power Grid Monitoring SystemPreetham SurepallyNo ratings yet
- Perioperative HypothermiaDocument4 pagesPerioperative Hypothermiasri utari masyitahNo ratings yet
- ###Questions Model PDFDocument2 pages###Questions Model PDFDave DMNo ratings yet
- NQ-NQM Panelboards and Qonq Load Centers Information Manual 80043-712-06 Rev.02 06-2015 2 PiezasDocument144 pagesNQ-NQM Panelboards and Qonq Load Centers Information Manual 80043-712-06 Rev.02 06-2015 2 PiezasNadia EspinozaNo ratings yet
- South African Flora GlossaryDocument47 pagesSouth African Flora Glossarymr.bryceNo ratings yet
- Procedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20Document6 pagesProcedure - AC Circuits and Signal Modulation - W20ChocoNo ratings yet
- 11 F.Y.B.Sc - Chemistry PDFDocument22 pages11 F.Y.B.Sc - Chemistry PDFmalini PatilNo ratings yet
- VCDS Scan Reveals Faults in HVAC, ABS and Transmission SystemsDocument4 pagesVCDS Scan Reveals Faults in HVAC, ABS and Transmission SystemsDan MirceaNo ratings yet
- Large and Medium Manufacturing Industry Survey Report 2018Document778 pagesLarge and Medium Manufacturing Industry Survey Report 2018melakuNo ratings yet
- 3.1 The Truth About Air TravelDocument14 pages3.1 The Truth About Air TravelСвітлана Свирид0% (1)
- Regular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionsDocument3 pagesRegular Manual Cleaning: Mimaki Printer Maintenance and Long-Term Storage OptionshumbyxNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Projectile WSDocument3 pagesHorizontal Projectile WSForsbergPhysicsNo ratings yet
- M10 - Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate Using Polystyrene in Lightweight CHB-CE-503Document19 pagesM10 - Partial Replacement of Fine Aggregate Using Polystyrene in Lightweight CHB-CE-503Michelle LeeNo ratings yet