Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas Diskusi 2-DAC
Uploaded by
Romi Dwi SaputraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Tugas Diskusi 2-DAC
Uploaded by
Romi Dwi SaputraCopyright:
Available Formats
TUGAS DISKUSI KELOMPOK INSTRUMENTASI ELEKTRONIKA
DAC_Principle
DISUSUN OLEH :
Kunnu Purwanto 20020120065 Noor Rohmat 20020150008 Budi Indra Sudrajat 20020120049 Siswiyoko 20020120007 JURUSAN TEKNIK ELEKTRO FAKULTAS TEKNIK
UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH YOGYA KARTA
2006
1. Download bahan kuliah DAC (DAC principle.pdf) !
These are the result of download, Mr Dwijoko !!!
Chemistry 464 J. B. Callis, Instructor Spring Quarter, 2002
The Digital to Analog Converter
Definition: The digital to analog converter (DAC) is a device that converts digital numbers (binary) into analog voltages. Applications: In chemistry, these center around controlling or systematically varying one of the independent variables in an experiment. Consider for example the following: Voltammetry: Here the voltage is systematically varied and the resulting electrochemical current is measured. A device known as a potentiostat is used to set the voltage (potential) across two or more electrodes. In a computer controlled potentiostat the voltage is produced by means of a DAC. Mass Spectrometry: For the case of a magnetic sector mass spectrometer, the magnetic field is generated by an electromagnetic, the current through which determines the magnetic field and consequently, which ions traverse the system and reach the detector. Often, the magnet is driven by means of a DAC. Scanning Tunneling Microscopy: Two DACs are used in this application to control the x, y position of the sensing tip. Here, the scanning is affected by piezoelectric transducers that convert voltages to position on a scale as fine as Angstroms. Optical spectroscopy: In this case there is a need to insure that the lamp provides a constant source of photons. Often this accomplished by measuring the lamp intensity with an optical transducer such as a photodiode and feeding its signal back to the power supply that controls the output of the lamp. The actual signal is compared to a set point and a proper voltage calculated, often digitally. Then a DAC is used to send the desired voltage to the lamp. The Basic Principle of the DAC (1) Generate a current of magnitude proportional to the value of each bit in the parallel digital word. Then: (2) Sum the currents of all the bits that are logic 1.
Figure 1. Basic Principle of the DAC The Components of a DAC
Figure 2: Schematic Diagram of a DAC Input Register (Latch): Samples the digital data source at appropriate times and holds the data in parallel digital form for a steady input to the DAC. Reference Voltage: Voltage source used to supply power to the current generators.
Basic DAC: The network of current generators (resistors) and switches used to provide the currents proportional to the weight of each bit multiplied by its binary value. Summing Current to Voltage Converter: An operational amplifier used to sum the currents from all the bits and convert them to a voltage. Offset and gain controls are incorporated to adjust the overall binary number to the desired voltage transfer function.
The Binary Weighted Resistor Network DAC Circuit Principle: The resistor of the nth bit is calibrated to be proportional to 1/2 n so that when driven by the constant voltage source, the current is proportional to 2n. The sum of the currents for all the bits that are turned on is proportional to the value of the input datum (binary number).
Figure 3. Binary Resistor Network DAC Circuit Problem: consider a 12 bit DAC. The resistor values must range over 2048:1. The smallest R is set by the need to keep the current low, at least 5 K. This means that the highest R must be 10.24 M? . This consumes high power, places restrictive requirements on the current switches and makes for a difficult calibration.
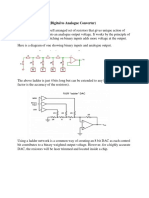
The Ladder Network DAC Circuit This circuit produces a current at each switch that is proportional to the value of the bit. Only two values of the resistances are needed, R and 2R. Such DACs are very inexpensive because they have proven very easy to construct and calibrate.
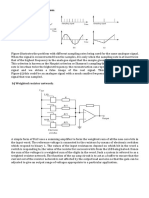
Figure 4. The ladder Network DAC Circuit. Limitations in Digital to Analog Conversion Resolution: The fraction of the full-scale range represented by the smallest change of the input number, e.g. 1 part in 212 for a twelve bit DAC. Accuracy: The difference between the expected and measured output voltage in terms of the change caused by changing the least significant bit (LSB). Most converters are specified to be accurate to at least +/- LSB. Linearity: The nearness of the transfer function from binary value to output voltage to a linear function. Usually specified to +/- LSB.
Monotonicity: A DAC is nonmonotonic if there is a momentary reversal in the expected direction of change. Zero Offset: The output for an input code of zero. This is generally within 1/2 LSB for unipolar DACs, but for bipolar DACs an error in the offset circuit can cause considerable zero offset. Stability: The constancy of the full-scale output with age and with variations in temperature and power supply. Settling Time: The time required for the output signal to settle within 1/2 LSB of its final value after a given change in input scale (usually full scale). Settling time is usually limited by the output amplifier rise time. Glitches: Transients that appear at the output when new digital data are applied.
Figure 5. Graphs illustrating the definitions of four common digital conversion errors:
(A) Transfer curve, 1/2 LSB offset at zero. (B) Linear transfer curve, but with 1 LSB error. (C) +/- 1/2 LSB nonlinearity (implies 1 LSB possible error); 1 LSB differential nonlinearity (implies monotonicity). (D) Nonmonotonic (must be > +/+ 1/2 LSB nonlinear).
2.
Tentukan fungsi utama DAC ! Mengkonversi bilangan digital (biner) ke analog. DAC ini menerima masukan digital paralel dan mengubahnya ke nilai tegangan (atau arus) yang disajikan masukan biner. Jika ini diulang untuk masukan digital yang berurutan akan terbentuk gelombang analog. Dalam penerapannya unit ini secara umum digunakan sebagai unit pengendali sistemstis dari salah satu variabel dalam sebuah percobaan, sebagai contoh : - Voltmeter : DAC dapat digunakan untuk pengukuran secara sistematik baik pengukuran tegangan (voltage) dan arus (current). - Spektrometer: Dalam hal ini, medan magnet dibangkitkankan oleh elektromagnetik, arus yang lewat menentukan medan magnet ,dan sebagai akibatnya ion-ion melintasi sistem dan mencapai detector. - Spektroskop optik : Dalam hal ini ada satu keperluan untuk menjamin bahwa lampu membagi sumber konstanta foton. Hal ini sering dilakukan dengan pengukuran intensitas lampu menggunakan sebuah transduser optis seperti fotodiode dan mengumpan sinyal balik ke power supply yang mengendalikan output lampu. Sinyal yang terjadi dibandingkan terhadap setpoint dan tegangannya dihitung. DAC digunakan untuk mengirimkan tegangan lampu sesuai yang dikehendaki.. - Scanning Tunneling Microskop : dua DAC yang digunakan dalam alat ini berfungsi untuk mengontrol posisi sinyal x dan y.
3.
Apa arti gambar 1 : Basic Principle of the DAC di halaman 2 !
a. Membangkitkan besarnya arus propotional ke harga setiap bit pada perintah digital parallel. b. Kemudian, menjumlah semua arus bit-bit bernilai logika 1
4. Jelaskan prinsip kerja masing-masing blok diagram dari gambar 2 di bawah, dimulai dari kiri (masukan) hingga Vo (keluaran) !
Agar masukan berupa sinyal digital dapat diubah ke bentuk sinyal analog maka diperlukan beberapa block berupa input register, DAC dasar, tegangan acuan, pembangkit arus keluar ke bentuk tegangan. Adapun fungsi/ prinsip kerja masing-masing block yaitu:
Input Register : mencuplik data berupa sinyal digital pada saat yang tepat setelah ada pengaturan input strobe dan menahan data dalam bentuk sinyal digital paralel untuk digunakan sebagai masukan pada Basic DAC. Reference Voltage : sumber tegangan yang digunakan untuk mensuplai tenaga ke generator arus. Basic DAC : jaringan generator arus (resistor) dan sakelar-sakelar, yang dipakai untuk membagi proporsi arus ke bobot setiap bit dikalikan nilai binernya. Summing Current to Voltage Converter : penguat operasi yang digunakan untuk menjumlah arus dari semua bit dan mengkonversikan bit-bitnya ke bentuk tegangan. Offset and gain controls digabungkan untuk menyesuaikan jumlah bit berlebih pada fungsi alih tegangan yang dikehendaki.
5. Apa yang dimaksud dengan error 1 LSB atau 1.5 LSB ? jelaskan jawaban anda ! Error + 1 LSB atau + 1.5 LSB adalah perbedaan antara tegangan keluaran yang diharapkan dengan tegangan keluaran yang diukur, yang mana hal ini disebabkan oleh perubahan + 1 LSB (bit terrendah) atau + 1,5 LSB
You might also like
- ADCDocument25 pagesADCsaddam Muhammad FadilaNo ratings yet
- ColocviuDocument6 pagesColocviuAndra BordeaNo ratings yet
- Data Conversion DevicesDocument6 pagesData Conversion Devicesriya vermaNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 5.LDR Based Highways Road Light Failed Intimation Using GSMDocument44 pages5.LDR Based Highways Road Light Failed Intimation Using GSMfotronichs velloreNo ratings yet
- Analog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIIDocument50 pagesAnalog-To-Digital Conversion Btech IIILisa BhagatNo ratings yet
- DLC Lab - 10Document7 pagesDLC Lab - 10Didarul Alam AlifNo ratings yet
- Current Steering DacDocument6 pagesCurrent Steering Dacfahmi rasiqNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual DAC-SignedDocument10 pagesLab Manual DAC-Signedabidrk_21789100% (2)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document23 pagesChapter 4Tejan Kumar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Shanon's Sampling TheormDocument2 pagesModule 5 Shanon's Sampling TheormamarnathNo ratings yet
- Analog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog ConversionsDocument20 pagesAnalog-to-Digital and Digital-to-Analog ConversionsArif HassanNo ratings yet
- Using A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowDocument10 pagesUsing A BJT As A Switch: An Example: BelowPrakhar BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 (2 mark)Document2 pagesUnit-5 (2 mark)sharmilakumari sNo ratings yet
- DAC ConverterDocument10 pagesDAC ConverterAmarnath M DamodaranNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument53 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterArryshah DahmiaNo ratings yet
- DEC LAB REPORT-06Document9 pagesDEC LAB REPORT-06anon_776365175No ratings yet
- Adc - DacDocument4 pagesAdc - DacShaheer TariqNo ratings yet
- Adc ConversionDocument20 pagesAdc Conversionhemantec100% (1)
- DLC LAB - 10 - Student - ManualDocument8 pagesDLC LAB - 10 - Student - ManualImtiaj SajinNo ratings yet
- Electronic ConvertersDocument18 pagesElectronic ConvertersKairredin Mahamed HusenNo ratings yet
- Electronic ConvertersDocument18 pagesElectronic ConvertersKairredin Mahamed HusenNo ratings yet
- Dac and Adc Circuits: Topic OutcomeDocument9 pagesDac and Adc Circuits: Topic OutcomeSegfred NavarroNo ratings yet
- ADC and DACDocument4 pagesADC and DACjeniferNo ratings yet
- R-2R Ladder DAC PDFDocument6 pagesR-2R Ladder DAC PDFChimi WangmoNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital Converter and Vise VersDocument7 pagesAnalog To Digital Converter and Vise VersSpyx MeniNo ratings yet
- Project 2 ElectronicDocument23 pagesProject 2 ElectronicOmar Eduardo Rios GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 4 ADC PDFDocument16 pagesExperiment No. 4 ADC PDFRia Cordova0% (1)
- Communication Systems Lab Manual ExperimentsDocument37 pagesCommunication Systems Lab Manual Experimentsnidheeshlal10No ratings yet
- Dec Exp 6 Student ManualDocument5 pagesDec Exp 6 Student ManualSakib MahmudNo ratings yet
- DACDocument28 pagesDACRohith Mohan100% (1)
- Mechatronics - 302050: Lecture Notes / PPT Unit IiiDocument29 pagesMechatronics - 302050: Lecture Notes / PPT Unit IiiRajesh GangwarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document42 pagesChapter 5Ram Bahadur KhadkaNo ratings yet
- Unit5 - ADC - DAC - Notes - Unit 5Document16 pagesUnit5 - ADC - DAC - Notes - Unit 5Chinmai NimgadeNo ratings yet
- A Continuously Varying Physical Quantity by A Sequence of Discrete Numerical ValuesDocument24 pagesA Continuously Varying Physical Quantity by A Sequence of Discrete Numerical ValuesnunuNo ratings yet
- 06 Wireless ReportDocument17 pages06 Wireless ReportshastryNo ratings yet
- Digital To Analog ConvertersDocument9 pagesDigital To Analog ConvertersAlisha KshetriNo ratings yet
- integratedelectronicsUNIT 3convertersDocument11 pagesintegratedelectronicsUNIT 3convertersYogeshwaranNo ratings yet
- Digital-To-Analog Converter: Ideally Sampled SignalDocument8 pagesDigital-To-Analog Converter: Ideally Sampled SignalJMSTavaresNo ratings yet
- Cadence Based Imlementation of SuccessiveApproximation ADC Using 45nm Cmos TechnologyDocument6 pagesCadence Based Imlementation of SuccessiveApproximation ADC Using 45nm Cmos TechnologyUtsavNo ratings yet
- Adc DacDocument59 pagesAdc Dacamallia nadhiaratnaNo ratings yet
- Analog To Digital ConverterDocument11 pagesAnalog To Digital ConverterFf Fr100% (1)
- Digital Electronics-10 PDFDocument8 pagesDigital Electronics-10 PDFTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power Supply ExplainedDocument14 pagesDC Regulated Power Supply ExplainedMegha Projects100% (2)
- Successive Approximation ADCDocument4 pagesSuccessive Approximation ADCnvenkatesh485No ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of DAC On The Basis of Capacitor ArrayDocument4 pagesDesign and Simulation of DAC On The Basis of Capacitor ArrayAmitNo ratings yet
- DC Regulated Power SupplyDocument15 pagesDC Regulated Power SupplyMegha Projects100% (1)
- A/D & D/A Converter FundamentalsDocument16 pagesA/D & D/A Converter Fundamentalsgeet_battaNo ratings yet
- EE 120 - Interfacing With The Analog WorldDocument8 pagesEE 120 - Interfacing With The Analog WorldAids SumaldeNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Student Report on Flash ADC DesignDocument10 pagesMechanical Engineering Student Report on Flash ADC DesignMohamed Adam Ahmed Fouad Mohamed FAHMYNo ratings yet
- Rohini 17734667959Document7 pagesRohini 17734667959diegogachet1618No ratings yet
- Project Report Regulated Power SupplyDocument36 pagesProject Report Regulated Power SupplyPeerzada Wahid73% (11)
- Ch.7 Data AcquisitionDocument9 pagesCh.7 Data AcquisitionaattishNo ratings yet
- Unit Iv Adc & Dac 2 MarksDocument5 pagesUnit Iv Adc & Dac 2 MarkssasirekhaNo ratings yet
- DATA CONVERTER AND CONTROL SYSTEM LAB MANUAL EXPERIMENTSDocument45 pagesDATA CONVERTER AND CONTROL SYSTEM LAB MANUAL EXPERIMENTSSavita Kiran BNo ratings yet
- Digital Pulse Counter DocumentationDocument28 pagesDigital Pulse Counter Documentationpndd4c6100% (1)
- Dac PDFDocument7 pagesDac PDFsanthoshNo ratings yet