Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Posterior Triangle
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Posterior Triangle
Uploaded by
kcxieCopyright:
Available Formats
Posterior Triangle
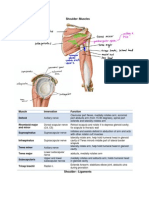
Posterior Triangle Muscle Platysma Innervation Cervical branch of facial nerve (CN VII) Accessory nerve (CN XI) Accessory nerve (CN XI) and C3, C4 nerves Dorsal scapular nerve (C5) and C3, C4 nerves C1-C3 by a branch of ansa cervicalis C4-C6 C3-C8 C4-C6 Function Draws corners of mouth inferiorly and widens it in expressions of sadness and fright. Draws skin of neck superiorly when teeth are clenched. Laterally flex head and neck, rotates head and neck to the opposite side. Together: flex head and neck Superior fibers elevate scapula, middle fibers retract scapula, inferior fibers depress scapula, superior and inferior together rotate scapula superiorly Elevates and inferiorly rotates scapula. Depress, retract, and steady hyoid Lateral flexion of neck, rotation of head and neck to the opposite side, elevation of first rib. Together: flex neck Laterally flex neck, elevation of first rib. Laterally flex neck, elevation of second rib.
Sternocleidomastoid
Trapezius
Levator scapulae Omohyoid Anterior scalene Middle scalene Posterior scalene
Fascia Investing layer of deep cervical fascia Prevertebral layer of deep cervical fascia
Most superficial layer, surrounds entire neck deep to skin/subcutaneous tissue Tubular sheath for vertebral column and muscles associated with it (longus colli and longus capitis anteriorly, scalenes laterally, deep cervical muscles posteriorly)
Posterior Triangle Clinical Correlates Affected structure muscles Clinical correlate torticollis: contraction of cervical mucles that produces twisting of neck and slanting of head (wry neck). Due fibrous tissue tumor in SCM, pulling infant's head at birth. Spasmodic torticollis: cervical dystonia. Begins in adulthood, involves bilateral combination of lateral neck muscles (SCM, trapezius). penetrating trauma/surgery/tumors/fractures. Weakness in turning head to one side against resistance, weakness/atrophy of trapezius. Drooping of shoulder, unilateral paralysis of the trapezius (pt cannot elevate and retract shoulde or elevate arm superior to horizontal) paralysis of half of diaphragm. Used in lung operation. Anesthesia injected on anterior surface of anterior scalene. inject anesthesia along posterior border of SCM at nerve point of the neck. central line placement "internal barometer," becomes prominent when venous pressure rises (heart failure, obstruction of superior vena cava, enlarged supraclavicular lymph nodes, incr intrathoracic pressure) can be seen deep to SCM superior to medial end of clavicle. reflects ECG recordings and right atrium pressure. usually right internal jugular vein because it is straighter and larger ligation to control bleeding from a branch. Occipital artery provides main collateral circulation surgical approach to carotid arteries, IJV, vagus, hypoglossal, cervical sympathetic trunk palpate artery between trachea and infrahyoid muscles atherosclerotic thickeningtransient ischemic attack: loss of neurological function. carotid endarterectomy: open artery at origin, strip of atherosclerotic plaque with intima.
SCM
nerves veins arteries
spinal accessory nerve (CN XI) phrenic nerve block cervical plexus subclavian vein external jugular vein internal jugular pulse internal jugular vein puncture external carotid artery carotid triangle carotid pulse carotid occlusion
You might also like
- Pediatrics NotesDocument25 pagesPediatrics Noteskcxie100% (12)
- Fever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialsDocument3 pagesFever of unknown origin evaluation and differentialskcxieNo ratings yet
- Genetic Conditions For USMLEDocument2 pagesGenetic Conditions For USMLEkcxieNo ratings yet
- ShoulderDocument4 pagesShoulderkcxieNo ratings yet
- Toxicology TableDocument20 pagesToxicology TablekcxieNo ratings yet
- Palmar HandDocument3 pagesPalmar HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Cavity TableDocument2 pagesPelvic Cavity TablekcxieNo ratings yet
- Cubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmDocument4 pagesCubital Fossa and Anterior ForearmkcxieNo ratings yet
- Lower LimbDocument1 pageLower LimbkcxieNo ratings yet
- Dorsal Forearm and HandDocument2 pagesDorsal Forearm and HandkcxieNo ratings yet
- Ankle and Sole of FootDocument4 pagesAnkle and Sole of FootkcxieNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Main Arteries and Veins of the NeckDocument43 pagesMain Arteries and Veins of the NeckAbishek JNo ratings yet
- The Anterior and Posterior Triangles of The NeckDocument10 pagesThe Anterior and Posterior Triangles of The NeckClair TomNo ratings yet
- Upper Extremity Venous Doppler Ultrasound PDFDocument12 pagesUpper Extremity Venous Doppler Ultrasound PDFLayla Salomão0% (1)
- How To Do Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation - Critical Care Medicine - MSD Manual Professional EditionDocument9 pagesHow To Do Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation - Critical Care Medicine - MSD Manual Professional EditionnaveenNo ratings yet
- Definition of JVPDocument16 pagesDefinition of JVPMimi ChukwuNo ratings yet
- Central Venous Access - 2019 (Gen, Ind-Contr)Document6 pagesCentral Venous Access - 2019 (Gen, Ind-Contr)Carlos NoronaNo ratings yet
- Complication of Neck Dissection & Its Management.: Dr. Sanjay Maharjan 1 Yr Resident, Ent-Hns, MTH, PokharaDocument37 pagesComplication of Neck Dissection & Its Management.: Dr. Sanjay Maharjan 1 Yr Resident, Ent-Hns, MTH, PokharaNitin SharmaNo ratings yet
- Dahl, Roald - The Collected Short Stories of Roald Dahl, Volume 1Document381 pagesDahl, Roald - The Collected Short Stories of Roald Dahl, Volume 1Xueying LiuNo ratings yet
- Dr. El Fiky Atlas Head & Neck Anatomy Mahmoud Abd AltawabDocument79 pagesDr. El Fiky Atlas Head & Neck Anatomy Mahmoud Abd AltawabHeba Hesham100% (11)
- Re Ca VADocument9 pagesRe Ca VAmanudanuNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Cardiovascular Examination OSCE GuideDocument24 pagesPaediatric Cardiovascular Examination OSCE GuideJeremiah KollieNo ratings yet
- Pa2 and Pa3 2Document14 pagesPa2 and Pa3 2Roger ViloNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System AssessmentDocument37 pagesPeripheral Vascular and Lymphatic System AssessmentSuzanne Rush100% (3)
- Anatomy of Head & Neck Muscles, Blood Vessels, and NervesDocument105 pagesAnatomy of Head & Neck Muscles, Blood Vessels, and NervesJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Venous Supply of Head, Neck and FaceDocument67 pagesVenous Supply of Head, Neck and FaceAlisha AranhaNo ratings yet
- JVP Guide: Assessing Jugular Venous Pulse Waves and PressureDocument53 pagesJVP Guide: Assessing Jugular Venous Pulse Waves and PressureJoshua JayakaranNo ratings yet
- CvsDocument35 pagesCvsVISS11No ratings yet
- 2011 @dentallib John Beumer III, Mark T Marunick, Salvatore J Esposito-171-229Document139 pages2011 @dentallib John Beumer III, Mark T Marunick, Salvatore J Esposito-171-229TariqNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Resonance Tractographyas A Method of Choice For Neuroimaging in Ocular Ischemic Syndrome Against The Background of HypertensionDocument4 pagesMagnetic Resonance Tractographyas A Method of Choice For Neuroimaging in Ocular Ischemic Syndrome Against The Background of HypertensionCentral Asian StudiesNo ratings yet
- BDS First Professional Anatomy Exam Model PaperDocument15 pagesBDS First Professional Anatomy Exam Model Paperfast-track for n2021No ratings yet
- 11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 2Document22 pages11 - Head & Neck (Blood Vessels) (FF) - Part 2checkmateNo ratings yet
- Guide to Respiratory Exam - OSCE ChecklistDocument33 pagesGuide to Respiratory Exam - OSCE ChecklistBasmah 7No ratings yet
- Analysis of 13 Cases of Venous Compromise in 178 Radial Forearm Free Flaps - Oral and Maxillofacial Surg 2012Document5 pagesAnalysis of 13 Cases of Venous Compromise in 178 Radial Forearm Free Flaps - Oral and Maxillofacial Surg 2012Nanna de VengerbergNo ratings yet
- JVP Examination For GPDocument43 pagesJVP Examination For GPYonathanHasudunganNo ratings yet
- Blood Collection in SwineDocument4 pagesBlood Collection in Swineelvhynd beiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Thyroid GlandDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Thyroid GlandShienna Marie SalvioNo ratings yet
- Bocca Functional Neck DissectionDocument4 pagesBocca Functional Neck DissectionNoma OlomuNo ratings yet
- Critical Care ProtocolsDocument19 pagesCritical Care ProtocolsPrabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Nicole Brown Simpson - Autopsy ReportDocument11 pagesNicole Brown Simpson - Autopsy Reporthwshaeffer63% (8)
- Central Venous Catheterization: Maret 2021Document39 pagesCentral Venous Catheterization: Maret 2021Rudy SiahaanNo ratings yet