Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013
Uploaded by
Jerrord ThomasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 11 Pop Quiz Jan 2013
Uploaded by
Jerrord ThomasCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS Grade 11 January 2013 Section B- Mechanics
Name:_________________________ Class: _________________________ Date: __________________________
TOTAL =
/20 =
SECTION A ANSWER ALL QUESTIONS Each question has four (4) possible answers a, b, c, d. Read each question carefully and circle the most suitable answer. 1. A child tries to push over a large empty oil drum. Where should the drum be pushed to topple it over with least force?
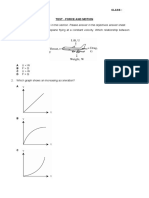
2. A student measures the speed of a trolley. At one instant, the speed of the trolley is 1.0 m / s and two seconds later the speed is 4.0 m / s. What is the acceleration of the trolley? A) 1.5 m / s B) 2.0 m / s C) 2.5 m / s D) 5.0 m / s 1. The speed-time graph shows the movement of a car.
2. Two men jump out of an aeroplane at the same time. One of the men opens his parachute and the other man remains in free-fall. Why is the man in free-fall moving faster than the parachutist? A) The man in free-fall experiences greater air resistance. B) The man in free-fall has a greater mass. C) The parachutist experiences greater air resistance. D) The parachutist has not reached terminal velocity. 3. Which part of the graph shows the limit of proportionality for an elastic solid?
What does the shaded area of the graph represent? A) the average acceleration of the car B) the average speed of the car C) the total distance travelled by the car D) the total travelling time of the car
A) B) C) D)
O OP P PQ
4. A student finds the centre of mass of a triangular lamina PQR. He drills a small hole at Q. He suspends the lamina from a pin through the hole at Q so that
Proper Preparation Prevents Poor Performance and Your attitude determines your altitude
Page 1
the lamina swings freely. He then hangs a plumbline from the pin at Q, as shown. He marks the position of the plumb-line on the lamina.
7. The graph shows part of a journey made by a cyclist. How far did the cyclist travel in 7 s? A) 28 m B) 30 m C) 32 m D) 42 m 8. A metal cone with a circular base is placed on a
To determine the location of the centre of mass, the student then repeats the experiment but with one change. What is the change? A) He suspends the lamina from the hole at Q, with R on the left and P on the right. B) He suspends the lamina from a pin through a hole at R. C) He uses a heavier weight on the plumb-line. D) He uses a longer plumb-line. 5. Which vehicle has an acceleration of 5 m / s? A) a bicycle, when its speed changes from rest to 2.5 m / s in 2 s B) a car, when its speed changes from rest to 15m / s in 5 s C) a lorry, when its speed changes from rest to 20m / s in 15 s D) a motorbike, when its speed changes from rest to 50 m / s in 10 s 6. A car accelerates from traffic lights for 10 s. It stays at a steady speed for 20 s and then brakes to a stop in 3 s. Which graph shows the journey?
flat surface. The stability of the cone depends on A) its weight only. B) the diameter of its base and the position of its centre of mass. C) the diameter of its base only. D) the position of its centre of mass only. 9. Which list contains only scalar quantities? A) acceleration, displacement, velocity B) distance, force, speed C) force, length, time D) length, mass, speed 10. A uniform metre rule is balanced by a 4 N weight as shown in the diagram. What is the weight W of the metre rule? A) 1N B) 4 N C) 16 N
D) 40 N
11. Which speed-time graph shows an object moving with non-uniform acceleration?
Proper Preparation Prevents Poor Performance and Your attitude determines your altitude
Page 2
15. The graph illustrates the motion of an object. Which feature of the graph represents the distance travelled by the object whilst moving at a constant speed? A) area S B) area S + area T C) area T D) the gradient at point X 16. A girl uses paper-clips to balance a toy bird on her finger as shown.
12. When a body moves across a rough surface, a frictional force is produced. What is the effect of the paper-clips? A) They help to raise the centre of mass above her finger. B) They help to raise the centre of mass to her finger. C) They help to lower the centre of mass below her finger. D) They do not affect the centre of mass but increase the weight. 17. The diagram shows a wheelbarrow and its load, which have a total weight of 150 N. This is supported by a vertical force F at the ends of the handles.
Which statement about this force is always true? A) It acts in the direction of the motion. B) It is equal in value to the force producing the motion. C) It makes the body recoil in the opposite direction after stopping it. D) It opposes the motion across the surface. 13. The diagram shows a boy of weight 500 N sitting on a see-saw. He sits 2.0 m from the pivot.
What is the force F needed to balance the seesaw? A) 250N B) 750 N C) 1000 N D) 3000 N 14. An object that has a mass of 15 kg on the Earth is taken to the Moon. The gravitational field strength on the Earth is 10 N / kg and on the Moon is 1.6 N / kg. What are the mass and the weight of the object on the Moon?
What is the value of F? A )75 N B) 150 N C) 225 N D) 300 N 18. The diagrams show the cross-sections of different glasses. Which one is the least stable when filled with a liquid?
Proper Preparation Prevents Poor Performance and Your attitude determines your altitude
Page 3
END OF TEST
Proper Preparation Prevents Poor Performance and Your attitude determines your altitude
Page 4
You might also like
- T-Forces and Motion AssessmentDocument12 pagesT-Forces and Motion AssessmentGan Hock KiamNo ratings yet
- SPH4U Dynamics Test 1Document13 pagesSPH4U Dynamics Test 1Shehab MohamedNo ratings yet
- 8c Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument36 pages8c Physics Multiple Choice QuestionsMunad E Ali100% (1)
- Phy Test Paper 2023 FinalDocument21 pagesPhy Test Paper 2023 Finalshallom udehNo ratings yet
- Ch 8 Review: Circular Motion, Gravity, Work ProblemsDocument9 pagesCh 8 Review: Circular Motion, Gravity, Work ProblemsJunLi CaiNo ratings yet
- G - 12 Physics MODEL - 1Document6 pagesG - 12 Physics MODEL - 1henotech HDNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet Tow 9thDocument3 pagesWork Sheet Tow 9thFiraol TegenuNo ratings yet
- Modul 1Document13 pagesModul 1Ms PaulinaNo ratings yet
- Nmat Review Physics 1 (Module 1 Exercise) : DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheDocument3 pagesNmat Review Physics 1 (Module 1 Exercise) : DIRECTIONS: Select The Best Answer To Each of TheMia0% (1)
- AGA KHAN SCHOOLS, SOUTH First Term Examination, November 2020 Physics Class IX (Science Group) Paper I (ADocument12 pagesAGA KHAN SCHOOLS, SOUTH First Term Examination, November 2020 Physics Class IX (Science Group) Paper I (AHaseeb MirzaNo ratings yet
- Physics TestDocument5 pagesPhysics TestAnonymous FH0ak9INfUNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term IGCSE PhysicsDocument9 pagesMid-Term IGCSE Physicsgdsuta80% (5)
- Midterm 1 Practice ProblemsDocument10 pagesMidterm 1 Practice ProblemsMansoor Al TunijiNo ratings yet
- KAPALONG NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL 2ND QUARTER SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTDocument3 pagesKAPALONG NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL 2ND QUARTER SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENTApril Joy Lascuña100% (1)
- Modul 1 f4f5Document13 pagesModul 1 f4f5Tamil ArasuNo ratings yet
- SPH4C Physics Grade 12 College Exam Review Package Unit 1 MotionDocument30 pagesSPH4C Physics Grade 12 College Exam Review Package Unit 1 MotionKhristine Khate Odiaman MendezNo ratings yet
- Ss 1 PHDocument3 pagesSs 1 PHPrince BurnaNo ratings yet
- Test of Competence: A. Cross Out The Correct Answer. (35 Points)Document4 pagesTest of Competence: A. Cross Out The Correct Answer. (35 Points)Ms Yosela MaharaniNo ratings yet
- Ch2 MCQuestions - Blank 2016Document13 pagesCh2 MCQuestions - Blank 2016utheinsweNo ratings yet
- Physics SolvedDocument16 pagesPhysics SolvedAbhijeet Singh PanwarNo ratings yet
- Physics 11Document9 pagesPhysics 11NasimaNo ratings yet
- Review Exam2Document5 pagesReview Exam2EliezerNo ratings yet
- PCS120 Fall 2014 Final ExaminationDocument15 pagesPCS120 Fall 2014 Final ExaminationAbdulrahman Jijawi100% (1)
- Test Bank For Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Douglas C Giancoli DownloadDocument38 pagesTest Bank For Physics Principles With Applications 7th Edition Douglas C Giancoli Downloadmarissaarmstrongpbfzemcsji100% (18)
- Physics 1401 - Exam 1 Review - Chapter 1,2Document23 pagesPhysics 1401 - Exam 1 Review - Chapter 1,2shoaibNo ratings yet
- Physics 1401 (Chapters 1-5) Review - Chapter 1,2Document33 pagesPhysics 1401 (Chapters 1-5) Review - Chapter 1,2FRANCISCO JERHYL KEITH G.No ratings yet
- This Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE MarkingDocument19 pagesThis Test Contains A Total of 10 Objective Type Questions. Each Question Carries 1 Mark. There Is NO NEGATIVE Markingvarunkohliin100% (1)
- Practica IiDocument9 pagesPractica IiEduardo FernandezNo ratings yet
- 103 F 05 Exam 1Document7 pages103 F 05 Exam 1Raufzha AnandaNo ratings yet
- 00 - Lab #14-Final Exam Review SOLUTIONSDocument6 pages00 - Lab #14-Final Exam Review SOLUTIONSOg DiNo ratings yet
- Ucm - AP ProblemsDocument13 pagesUcm - AP ProblemsCarlos OrtizNo ratings yet
- Physics 201 (003N) Fall 2010 - Midterm I.AnswersDocument7 pagesPhysics 201 (003N) Fall 2010 - Midterm I.AnswersXiao LinNo ratings yet
- MIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1 TEST IDocument12 pagesMIDTERM EXAMINATION in GENERAL PHYSICS 1 TEST Izamora pegafiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test of Matirc Class by Sir Irfan AliDocument2 pagesMCQ Test of Matirc Class by Sir Irfan AliirfanNo ratings yet
- Word of Life International School Mid - Term Two Exams 2021 Grade 9 Physics (MC) Time: 50 Minutes Answer All The QuestionsDocument10 pagesWord of Life International School Mid - Term Two Exams 2021 Grade 9 Physics (MC) Time: 50 Minutes Answer All The QuestionsWilber TuryasiimaNo ratings yet
- I. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesI. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Encircle The Letter of The Correct AnswerNeil VelascoNo ratings yet
- Test-Questions-Physics IDocument7 pagesTest-Questions-Physics INheszie Cortez MendozaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: KinematicsDocument38 pagesMultiple Choice Cumulative Review: Part I: Kinematics张书No ratings yet
- Phy 203 - Exam I (2007)Document4 pagesPhy 203 - Exam I (2007)Jose-Rico GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Force and Motion: Key Concepts of Forces, Moments, Equilibrium, Energy, Work and PowerDocument62 pagesForce and Motion: Key Concepts of Forces, Moments, Equilibrium, Energy, Work and PowerMerin0% (1)
- PretestDocument6 pagesPretestEdna Mae CruzNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Document7 pagesSample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Sukhwinder KumarNo ratings yet
- MODUL 1 FizikDocument14 pagesMODUL 1 FizikMohd HafizuddinNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Modul WAJADocument14 pagesPhysics Form 4 Modul WAJARamanath RamNo ratings yet
- Physics Exam Review 2014Document7 pagesPhysics Exam Review 2014Salix MattNo ratings yet
- G11 Revision Worksheet Sem - 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesG11 Revision Worksheet Sem - 1 SolutionsterabaapNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Assignment SA1 Class 9 CBSEDocument5 pagesPHYSICS Assignment SA1 Class 9 CBSEgurdeepsarora8738100% (1)
- PHYSICS Revision Assignment SA1Document5 pagesPHYSICS Revision Assignment SA1gurdeepsarora8738No ratings yet
- Physics (1) (1) FinalDocument5 pagesPhysics (1) (1) Finalvandanacharan79No ratings yet
- 2100ex2s03 PDFDocument7 pages2100ex2s03 PDFAnubhav SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Uniform Circular Motion: PSI AP Physics 1Document6 pagesUniform Circular Motion: PSI AP Physics 1Boldie LutwigNo ratings yet
- Hye C11 Physics QP 1 11 2023Document7 pagesHye C11 Physics QP 1 11 2023devdutta.nevaseNo ratings yet
- This Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All QuestionsDocument8 pagesThis Paper Consists of 50 Questions. Each Question Is Followed by Four Options. Choose The Best Option For Each Question Then Blacken The Correct Space On The Answer Sheet. Answer All Questionsjoe zulkefliNo ratings yet
- Physics 2007 EUEEDocument8 pagesPhysics 2007 EUEElikinaw demisieNo ratings yet
- TestDocument6 pagesTesthongling24No ratings yet
- Reviwer in Gen. Physics 1Document4 pagesReviwer in Gen. Physics 1Romero, Ken Angelo B.No ratings yet
- Physics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument37 pagesPhysics For Scientists and Engineers A Strategic Approach With Modern Physics 4Th Edition Knight Test Bank Full Chapter PDFwadeperlid9d98k88% (8)
- Section A and B MechanicsDocument7 pagesSection A and B MechanicsJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- List of Common FormulaeDocument6 pagesList of Common FormulaeJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Lab 1.revisedDocument38 pagesPower Systems Lab 1.revisedJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- CSEC Section D - Waves Past Paper QuestionsDocument46 pagesCSEC Section D - Waves Past Paper QuestionsJerrord Thomas100% (7)
- List of Common FormulaeDocument6 pagesList of Common FormulaeJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Csec Physics Manual 2012-15Document27 pagesCsec Physics Manual 2012-15Jerrord Thomas100% (15)
- Grade 11 - Week 2 - Sept 17 GÇô Sept 21, 2012Document5 pagesGrade 11 - Week 2 - Sept 17 GÇô Sept 21, 2012Jerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument16 pagesSyllabusJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Monthly Test - Waves February 2012 - Option BDocument4 pagesGrade 11 Monthly Test - Waves February 2012 - Option BJerrord Thomas100% (1)
- List of Common FormulaeDocument6 pagesList of Common FormulaeJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- List of Common FormulaeDocument6 pagesList of Common FormulaeJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- Static Electricity LessonDocument56 pagesStatic Electricity LessonJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- List of Common FormulaeDocument6 pagesList of Common FormulaeJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- List of Common FormulaeDocument6 pagesList of Common FormulaeJerrord ThomasNo ratings yet
- RadioactivityDocument22 pagesRadioactivityJerrord Thomas100% (1)
- Runner of Francis Turbine:) Cot Cot (Document5 pagesRunner of Francis Turbine:) Cot Cot (Arun Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Kelvin-Helmholtz Instability and Roll-up ExplainedDocument7 pagesKelvin-Helmholtz Instability and Roll-up ExplainedSanjay Kumar AdvaniNo ratings yet
- Mechanism Design Guide to Joints and DOFDocument8 pagesMechanism Design Guide to Joints and DOFAsaduz ZamanNo ratings yet
- Preliminary HSC Pdhpe: CQ3 - How Do Biomechanical Principles Influence Movement?Document15 pagesPreliminary HSC Pdhpe: CQ3 - How Do Biomechanical Principles Influence Movement?progamerNo ratings yet
- The Two-Body Problem: Classical Dynamics Michaelmas 2014Document3 pagesThe Two-Body Problem: Classical Dynamics Michaelmas 2014ram kumarNo ratings yet
- EERC-82-09 Fluid-Structure Interactions Added Mass Computations For Incompressible FluidDocument126 pagesEERC-82-09 Fluid-Structure Interactions Added Mass Computations For Incompressible FluidBMWrider1453No ratings yet
- DSP Lab 1Document7 pagesDSP Lab 1anji.guvvalaNo ratings yet
- US NAVY Antennas and Wave PropagationDocument98 pagesUS NAVY Antennas and Wave PropagationHammna AshrafNo ratings yet
- Control Surfaces Hinge Moment Calculation For High Aspect Ratio WingDocument27 pagesControl Surfaces Hinge Moment Calculation For High Aspect Ratio WingPaulo HenriqueNo ratings yet
- Solutionsfor Uniformly Accelerated Motion Problems Worksheets CH 6Document3 pagesSolutionsfor Uniformly Accelerated Motion Problems Worksheets CH 6Abreham GirmaNo ratings yet
- Final Lab Report General Physics III LaboratoryDocument6 pagesFinal Lab Report General Physics III LaboratoryMuhammad FauzanilNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing - ETS Course Notes - Issue 17 - PPDocument116 pagesUltrasonic Testing - ETS Course Notes - Issue 17 - PPmajidNo ratings yet
- Torsional Vibration 4.1 What Is Torsional Vibration?: M I K QDocument7 pagesTorsional Vibration 4.1 What Is Torsional Vibration?: M I K QMohammad Muhtasim Mashfy, 170011054No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument8 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and MatterSakshi100% (2)
- Bragg's Law, Derivation and ApplicationDocument13 pagesBragg's Law, Derivation and ApplicationShahnawaz HussainNo ratings yet
- Lecture3 Ch2 WavesDocument24 pagesLecture3 Ch2 WavesLukinNo ratings yet
- Sae J266-2018Document34 pagesSae J266-2018tiramisuweitaoNo ratings yet
- Flow Pass A Circular CylinderDocument3 pagesFlow Pass A Circular CylinderAdry AqilNo ratings yet
- Classical MechanicsDocument14 pagesClassical MechanicswhatthemailNo ratings yet
- DGE502/EGE502 NGEC 2 Readings in Philippine HistoryTITLE Quantity, Definition, and Vector/Scalar Table TITLE Solving Projectile Motion Problems Step-by-StepDocument7 pagesDGE502/EGE502 NGEC 2 Readings in Philippine HistoryTITLE Quantity, Definition, and Vector/Scalar Table TITLE Solving Projectile Motion Problems Step-by-Stepaki sintaNo ratings yet
- Motion in Two Dimension - Practice ProblemsDocument15 pagesMotion in Two Dimension - Practice ProblemsAvik PatraNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Journal BearingDocument12 pagesDynamics of Journal BearingHarsh RaoNo ratings yet
- Project report on Coriolis force and its applicationsDocument33 pagesProject report on Coriolis force and its applicationsRakesh Kumar AcharjyaNo ratings yet
- Physics ReviewerDocument24 pagesPhysics ReviewerHazir HaslefttheroomNo ratings yet
- Gradually Varied Unsteady Flow PDFDocument7 pagesGradually Varied Unsteady Flow PDFDeepankumar Athiyannan0% (1)
- HW2 SolutionDocument5 pagesHW2 Solutionmrm3zaNo ratings yet
- 28 The Diagram Shows An Experiment Which Has Been Set Up To Demonstrate Two-Source InterferenceDocument42 pages28 The Diagram Shows An Experiment Which Has Been Set Up To Demonstrate Two-Source InterferencekoeliaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mechanics - KL - Ramachandran SDocument744 pagesEngineering Mechanics - KL - Ramachandran SFe Fernandez100% (1)
- Practice Test 01 - Physics - Arjuna JEE 2024Document2 pagesPractice Test 01 - Physics - Arjuna JEE 2024kochharmadhav0No ratings yet
- Weekly Assessment Number 3Document1 pageWeekly Assessment Number 3Marissa FontanilNo ratings yet