Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Simple Column Design Example
Uploaded by
berto2008Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Simple Column Design Example
Uploaded by
berto2008Copyright:
Available Formats
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section (GB)
CALCULATION SHEET
Document Ref: Title
SX004a-EN-GB
Sheet
of
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section EN 1993-1-1 Laurent Narboux Charles King
Date Date
Eurocode Ref Made by Checked by
Oct 2006 Oct 2006
Localized resource for UK
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section
Within this worked example on a pinned column UKC section in a simple structure, the column buckling resistance is calculated.
N Ed
N Ed
Created on Friday, January 18, 2008 This material is copyright - all rights reserved. Use of this document is subject to the terms and conditions of the Access Steel Licence Agreement
8,0
8,0
[m]
SN008
Lcr. = 1.0 L Lcr. = 0 .7 L
Partial factors
M0 = 1.0 M1 = 1.0
EN 1993-1-1 6.1 (1)
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section (GB)
CALCULATION SHEET
Document Ref: Title
SX004a-EN-GB
Sheet
of
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section EN 1993-1-1 Laurent Narboux Charles King
Date Date
Eurocode Ref Made by Checked by
Oct 2006 Oct 2006
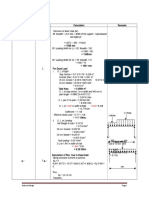
Basic data Design a column of a multi-storey building in consideration of the following data. Axial load : Column length : Buckling length : NEd = 2000 kN 8.00 m y-y axis: 1.0 8.00 = 8.00 m z-z axis: 0.7 8.00 = 5.60 m Steel grade : Section classification: S275 Class 2
z tf
UKC 305x305x97 Steel grade S275
Created on Friday, January 18, 2008 This material is copyright - all rights reserved. Use of this document is subject to the terms and conditions of the Access Steel Licence Agreement
BS4 Corus Advance
Depth Width Web thickness Flange thickness Fillet Section area
h = 307.9 mm b = 305.3 mm tw = 9.9 mm tf = 15.4 mm
z y
tw y h
r = 15.2 mm A = 123.4 cm2
Second moment of area /yy Iy = 22249 cm4 Second moment of area /zz Iz = 7308 cm4 Yield strength Steel grade S275 The maximum thickness is 15.4 mm < 40 mm, so : fy = 275 N/mm Note :
2
EN 1993-1-1 Table 3.1
When published, the National Annex may impose either the values of fy from the Table 3.1 or the values from the product standard. Here the values are the same.
x g
CALCULATION SHEET
i
Document Ref: Title
SX004a-EN-GB
Sheet
of
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section EN 1993-1-1 Laurent Narboux Charles King
Date Date
Eurocode Ref Made by
Oct 2006 Oct 2006
a y
Checked by
J p
Design buckling resistance of a compression member To determine the design column buckling resistance Nb,Rd, the reduction factor for the relevant buckling curve must be defined. This factor is determined by calculation of the non-dimensional slenderness based on the elastic critical force for the relevant buckling mode and the cross sectional resistance to normal forces. Elastic critical force Ncr The critical buckling force is calculated as follows :
, a y c
N cr, y =
d i
2 EI y Lcr, y
2
2 21000 22249 = 7205.3 kN 8002
N cr, z =
2 EI z 2 21000 7308 = = 4829.9 kN 2 560 2 Lcr, z
E is the Youngs modulus :
r l
E = 210000 N/mm2 Lcr,z = 5.60 m
L is the buckling length in the buckling plane considered: Lcr,y = 8.00 m
F a
Non-dimensional slenderness
The non-dimensional slenderness is given by :
n r
EN 1993-1-1 6.3.1.2 (1)
y =
o e
A fy N cr, y A fy N cr, z
123.4 27.5 = 0.686 7205.3 123.4 27.5 = 0.838 4829.9
d a
z =
For slenderness 0,2 or for
e m
N Ed 0,04 the buckling effects may be N cr ignored and only cross sectional checks apply.
EN 1993-1-1 6.3.1.2 (4)
C T
r h
e i
a s
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section (GB)
CALCULATION SHEET
Document Ref: Title
SX004a-EN-GB
Sheet
of
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section EN 1993-1-1 Laurent Narboux Charles King
Date Date
Eurocode Ref Made by Checked by
Oct 2006 Oct 2006
Reduction factor
For axial compression in members the value of depending on the nondimensional slenderness should be determined from the relevant buckling curve according to: 1 = but 1.0 2 EN 1993-1-1 2 + - 6.3.1.2 (1)
where : LT = 0.5 1 + - 0.2 +
is an imperfection factor.
For h/b = 307.9/305.3= 1.01 < 1.2 and tf = 15.4< 100 mm
-
buckling about axis y-y: Buckling curve b, imperfection factor = 0.34
Created on Friday, January 18, 2008 This material is copyright - all rights reserved. Use of this document is subject to the terms and conditions of the Access Steel Licence Agreement
y = 0.5 [1 + 0.34 (0.686 - 0.2) + 0.6862 ] = 0.818
y =
-
1 0.818 + 0.8182 - 0.6862
= 0.791
buckling about axis z-z: Buckling curve c, imperfection factor = 0.49
z = 0.5 [1 + 0.49 (0.838 - 0.2) + 0.8382 ] = 1.007
z =
1 1.007 + 1.007 2 - 0.8382 = 0.639
= min (y; z ) = min (0.791; 0.639) = 0.639 < 1.0
(when > 1 then = 1)
Design buckling resistance of a compression member
N b, Rd = A fy
M1
= 0.639
123.4 27.5 = 2168 kN 1 .0
EN 1993-1-1 6.3.1.1 (3)
Then we check:
N Ed 2000 = = 0.92 < 1.0 OK N b, Rd 2168
EN 1993-1-1 6.3.1.1 (1)
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section (GB)
Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section SX004a-EN-GB
Quality Record
RESOURCE TITLE Reference LOCALISED RESOURCE DOCUMENT Name Created by Technical content checked by Editorial content checked by Laurent Narboux Charles King D C Iles Company SCI SCI SCI Date Oct 2006 Oct 2006 19/2/07 Example: Pinned column using non slender UKC section SX004a-EN-GB
Created on Friday, January 18, 2008 This material is copyright - all rights reserved. Use of this document is subject to the terms and conditions of the Access Steel Licence Agreement
You might also like
- Finite Element Analysis of Eccentric R.C.C FootingDocument72 pagesFinite Element Analysis of Eccentric R.C.C FootingJunaidAhmedNo ratings yet
- JassimDocument29 pagesJassimZain Communication0% (1)
- Column Design - As Per BS CodeDocument16 pagesColumn Design - As Per BS CodeYam BalaoingNo ratings yet
- COLUMN BASE PLATE DESIGN CALCULATIONS (BS5950-1:2000Document7 pagesCOLUMN BASE PLATE DESIGN CALCULATIONS (BS5950-1:2000Shakil Akhter100% (1)
- Design Loads and Assumptions for Elevated Station ConcourseDocument3 pagesDesign Loads and Assumptions for Elevated Station ConcourseHarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- GF SlabDocument8 pagesGF Slabcheligp1981No ratings yet
- GIRT DESIGN C140x60x20x4 BEAMDocument2 pagesGIRT DESIGN C140x60x20x4 BEAMYaşarUğurNo ratings yet
- Design of Connectionv.3Document15 pagesDesign of Connectionv.3Apple Grace S. Valencia100% (1)
- Wind Load IS875Document30 pagesWind Load IS875Pranjal Pareek100% (2)
- Masonry Wall Design - 2Document3 pagesMasonry Wall Design - 2Michael AbandeNo ratings yet
- Resistance Moment Calculations (Walls BS 8110) PDFDocument3 pagesResistance Moment Calculations (Walls BS 8110) PDFdhanya1995No ratings yet
- Purlin Design Limit StateDocument2 pagesPurlin Design Limit Stateerzahid ahmadNo ratings yet
- Vertical Loads On Building Frames: Assumptions For The Analysis of Girders Using Approximate AnalysisDocument10 pagesVertical Loads On Building Frames: Assumptions For The Analysis of Girders Using Approximate AnalysisNeven Ahmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet For Hilti HIT HY 200 Injectable Mortar in Concrete Technical Information ASSET DOC 8258686 PDFDocument41 pagesTechnical Data Sheet For Hilti HIT HY 200 Injectable Mortar in Concrete Technical Information ASSET DOC 8258686 PDFiabdillahNo ratings yet
- Staad Pro-Solid Elements-Cantilever BeamDocument18 pagesStaad Pro-Solid Elements-Cantilever BeamV.m. RajanNo ratings yet
- StruCad Evolution Getting Started TutorialDocument41 pagesStruCad Evolution Getting Started Tutorialnifty25No ratings yet
- Raft Foundation DesignDocument5 pagesRaft Foundation Designafiq100% (1)
- Time Period Calculation in ETABS As Per IS 1893 Part 1Document2 pagesTime Period Calculation in ETABS As Per IS 1893 Part 1NAYAN RANPURA100% (1)
- Design Z Section PurlinDocument9 pagesDesign Z Section PurlinSudipta HuiNo ratings yet
- Wood Armer Calculation (For Plate Elements) : Top (Hogging) ReinforcementDocument3 pagesWood Armer Calculation (For Plate Elements) : Top (Hogging) ReinforcementHASSAN SK MDNo ratings yet
- Design of TrussDocument29 pagesDesign of Trussfrancis100% (1)
- Crack Width Check For Water Tank BaseDocument4 pagesCrack Width Check For Water Tank BaseShamim Ahsan ZuberyNo ratings yet
- Plate GirderDocument6 pagesPlate GirderOkayNo ratings yet
- D.Kober Lectures 3+4 Silos PDFDocument69 pagesD.Kober Lectures 3+4 Silos PDFAmeen MazouniNo ratings yet
- TR12 PDFDocument24 pagesTR12 PDFramorusoNo ratings yet
- Footing Design DimensionsDocument3 pagesFooting Design DimensionsMesfinNo ratings yet
- 3285-SNS M-25 M-30 InterimDocument9 pages3285-SNS M-25 M-30 InterimErHarshGandhiNo ratings yet
- Steel Cap Plate Connections DesignDocument18 pagesSteel Cap Plate Connections DesignVinoth KumarNo ratings yet
- Stair Hand Rail Connection Design Calculation-WPCDocument12 pagesStair Hand Rail Connection Design Calculation-WPCUmesh ChamaraNo ratings yet
- Calculation PDFDocument126 pagesCalculation PDFmohammed almahrooqiNo ratings yet
- Sway Frame Steel Column DesignDocument1 pageSway Frame Steel Column DesignChirianu MarianNo ratings yet
- TSS 35 / 205 sheet thickness & load data for aluminium & steel roofingDocument1 pageTSS 35 / 205 sheet thickness & load data for aluminium & steel roofingAkhil VNNo ratings yet
- Steelwork Design Guide To BS 5950 Vol 1 Part B1 Dimensions & PropertiesDocument56 pagesSteelwork Design Guide To BS 5950 Vol 1 Part B1 Dimensions & PropertiessubamanivelNo ratings yet
- Steel Truss Roof Structure For Kattumana Porialar 24.4.2014Document6 pagesSteel Truss Roof Structure For Kattumana Porialar 24.4.2014Ahmad AnasNo ratings yet
- Eurocode Load Combination Cases (Quasi-Permanent, Frequent, Combination) For ULS and SLSDocument4 pagesEurocode Load Combination Cases (Quasi-Permanent, Frequent, Combination) For ULS and SLSlui him lunNo ratings yet
- View Topic - Pile Cap Design Using SafeDocument5 pagesView Topic - Pile Cap Design Using SafeParameswaran GanesanNo ratings yet
- Calculation Sheet Connection DesignDocument1 pageCalculation Sheet Connection DesignJay SenjaliaNo ratings yet
- Bolted Splice ConnectionDocument6 pagesBolted Splice ConnectionSeetharam Mahanthi100% (1)
- Slab With and Without OpeningDocument17 pagesSlab With and Without Openingstructure123No ratings yet
- Base Plate +and Foundation Bolt Design +connection Design 30-08-2021Document9 pagesBase Plate +and Foundation Bolt Design +connection Design 30-08-2021Deepanshu GargNo ratings yet
- Bondek I - Calculation Note - 1 Row of SupportDocument7 pagesBondek I - Calculation Note - 1 Row of Supporttrung1983No ratings yet
- Mathcad - Design Resistance For Individual FastnersDocument3 pagesMathcad - Design Resistance For Individual FastnersValentinNo ratings yet
- Design of Curved Monorail StructureDocument2 pagesDesign of Curved Monorail StructuredsanandaNo ratings yet
- Staircase Design: 8.28kN/m 15.57kN/mDocument3 pagesStaircase Design: 8.28kN/m 15.57kN/mBikki CyamaNo ratings yet
- RR Masonary Retaining WallDocument2 pagesRR Masonary Retaining WallRajesh GangwalNo ratings yet
- Raft DesignDocument8 pagesRaft Designomolewa joshuaNo ratings yet
- Design of Shear Wall Pier P1Document6 pagesDesign of Shear Wall Pier P1Nishan GajurelNo ratings yet
- Connection DesignDocument15 pagesConnection DesignRufus Cheng100% (1)
- Design of Tension Members - Info On Sag RodsDocument10 pagesDesign of Tension Members - Info On Sag RodsRichard FernandezNo ratings yet
- StAad ModelingDocument18 pagesStAad ModelingVineet Verma0% (1)
- Pile Design & Analysis of Single Piles. ExamplesDocument61 pagesPile Design & Analysis of Single Piles. ExamplesMohammed HussainNo ratings yet
- Bolt Design (Blodget)Document4 pagesBolt Design (Blodget)Mayuresh KudveNo ratings yet
- Values of Effective-Length Factor K For Columns.Document1 pageValues of Effective-Length Factor K For Columns.ivan bolañosNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11-1 Bases by H.J. MtyanaDocument29 pagesLecture 11-1 Bases by H.J. MtyanaHarold Jackson Mtyana100% (1)
- Mat Chapter 18Document29 pagesMat Chapter 18hemant_durgawaleNo ratings yet
- Flow Chart - Frame AnalysisDocument4 pagesFlow Chart - Frame Analysisjmcc2No ratings yet
- Example - Buckling Resistance of A Pinned Column With Intermediate RestraintsDocument5 pagesExample - Buckling Resistance of A Pinned Column With Intermediate RestraintsAndreea NanNo ratings yet
- Ec3 Kolon HesabıDocument5 pagesEc3 Kolon HesabınaimalimliNo ratings yet
- Unrestrained Beam With End MomentsDocument9 pagesUnrestrained Beam With End MomentsNikos StathoulopoulosNo ratings yet
- En 15620 Steel Static Storage Systems - Adjustable Pallet Racking - Tolerances, Deformations and ClearancesDocument76 pagesEn 15620 Steel Static Storage Systems - Adjustable Pallet Racking - Tolerances, Deformations and ClearancesPaul Costan92% (12)
- Reinforced Concrete Column by Zinab EC2Document15 pagesReinforced Concrete Column by Zinab EC2berto2008No ratings yet
- 7 STEPS TO DEVELOPING AN AGILE MARKETING TEAMDocument17 pages7 STEPS TO DEVELOPING AN AGILE MARKETING TEAMberto2008No ratings yet
- En 15629 (2008)Document35 pagesEn 15629 (2008)berto2008100% (1)
- Worked Examples To Eurocode 2Document165 pagesWorked Examples To Eurocode 2amin6693225097% (30)
- Connection TutorialDocument1 pageConnection Tutorialberto2008No ratings yet
- Steel Column Design Eurocode 3Document2 pagesSteel Column Design Eurocode 3Jonp4ul_MiddletonNo ratings yet
- How To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2Document104 pagesHow To Design Concrete Structures Using Eurocode 2berto2008No ratings yet
- En 15095-2007+a1 (2008)Document45 pagesEn 15095-2007+a1 (2008)berto2008No ratings yet
- Connection Tutorial AnswersDocument2 pagesConnection Tutorial Answersberto2008No ratings yet
- Structrual Concrete Design To Eurocode 2 University of Sheffield Structural Engineering MastersDocument12 pagesStructrual Concrete Design To Eurocode 2 University of Sheffield Structural Engineering Mastersfatabass100% (3)
- ConnectionsDocument38 pagesConnectionsberto2008No ratings yet
- Columns Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3Document1 pageColumns Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3berto2008No ratings yet
- Connection Tutorial AnswersDocument2 pagesConnection Tutorial Answersberto2008No ratings yet
- Nominal MomentsDocument2 pagesNominal Momentsberto2008No ratings yet
- ColumnsDocument28 pagesColumnsberto2008No ratings yet
- Connections Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3Document1 pageConnections Tutorial: Behaviour and Design of Structures 3berto20080% (1)
- ConnectionsDocument38 pagesConnectionsberto2008No ratings yet
- Effective LengthsDocument8 pagesEffective Lengthsberto2008No ratings yet
- Effective Lengths - 2upDocument4 pagesEffective Lengths - 2upberto2008No ratings yet
- Column Tutorial AnswersDocument2 pagesColumn Tutorial Answersberto2008No ratings yet
- Column Sizing Chart PDFDocument7 pagesColumn Sizing Chart PDFberto2008No ratings yet
- SIMPLIFIED BENDING RESISTANCE CHECK ACCORDING TO EUROCODEDocument22 pagesSIMPLIFIED BENDING RESISTANCE CHECK ACCORDING TO EUROCODEberto2008No ratings yet
- Steel Beam DesignDocument39 pagesSteel Beam Designberto2008No ratings yet
- Steel Beams TutorialDocument1 pageSteel Beams Tutorialberto2008No ratings yet
- LT Buckling Beam Design - Simple Method - 2upDocument5 pagesLT Buckling Beam Design - Simple Method - 2upberto2008No ratings yet
- Design Charts For Non-Composite Beams 2upDocument3 pagesDesign Charts For Non-Composite Beams 2upberto2008No ratings yet
- NCCI Simplified LT-Buckling Calcs 2upDocument5 pagesNCCI Simplified LT-Buckling Calcs 2upberto2008No ratings yet
- Design Charts For Composite Beams 2upDocument3 pagesDesign Charts For Composite Beams 2upberto2008No ratings yet
- Canevas HND 2020Document594 pagesCanevas HND 2020Folegwe Folegwe100% (2)
- Garment DyeingDocument25 pagesGarment DyeingSivakumar KNo ratings yet
- ECBC Version June 2009 (All Changed Text)Document95 pagesECBC Version June 2009 (All Changed Text)Kumar BiplabNo ratings yet
- IACS Common Structural Rules Knowledge Centre Q&AsDocument10 pagesIACS Common Structural Rules Knowledge Centre Q&Astotoq51No ratings yet
- Cavitation or NotDocument3 pagesCavitation or NotChanFKNo ratings yet
- List of Welding StandardsDocument5 pagesList of Welding StandardsSandip Das100% (1)
- Different Types of Bituminous Surfaces.: 1. Prime CoatDocument5 pagesDifferent Types of Bituminous Surfaces.: 1. Prime CoatSreerag RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Gentron Pro2 10000 ManualDocument43 pagesGentron Pro2 10000 Manualjustinp200125000% (1)
- Multipurpose Valves For Liquid Withdrawal of LP-Gas and NH Containers A8017D & A8020DDocument1 pageMultipurpose Valves For Liquid Withdrawal of LP-Gas and NH Containers A8017D & A8020DLPG Equipment Consulting and ServicesNo ratings yet
- Slurry Sampling: Slurry Sampling For On-Line Analysis and AccountingDocument8 pagesSlurry Sampling: Slurry Sampling For On-Line Analysis and Accountingsnarf273No ratings yet
- Republic Act 9003Document17 pagesRepublic Act 9003Elijah FelipeNo ratings yet
- WasteWater Engineering 1516 Sem 1Document7 pagesWasteWater Engineering 1516 Sem 1Tidus FarronNo ratings yet
- Manitou Telescopico Mrt2150 E3 Parts ManualsDocument20 pagesManitou Telescopico Mrt2150 E3 Parts Manualswilliam100% (20)
- Diesel Injector FailureDocument19 pagesDiesel Injector FailureWayne Mcmeekan100% (2)
- Copper AlloysDocument1 pageCopper AlloysuzairmetallurgistNo ratings yet
- The Potentialofusingnanofluids InPEMfuelcellcoolingsystemsDocument17 pagesThe Potentialofusingnanofluids InPEMfuelcellcoolingsystemsMario MandžukićNo ratings yet
- LEATHER CHEMISTRY GUIDEDocument16 pagesLEATHER CHEMISTRY GUIDESaravana Vel50% (2)
- Internal Water TreatmentDocument41 pagesInternal Water TreatmentKristian S0% (1)
- M45 Grade As Per Is 10262Document4 pagesM45 Grade As Per Is 10262Ashok RajanavarNo ratings yet
- Method Statement Dismantle Tower CraneDocument2 pagesMethod Statement Dismantle Tower Cranejesusgameboy33% (3)
- Denim Washing FinalDocument27 pagesDenim Washing FinaljayantNo ratings yet
- Utilisation of calcined mussel shells as partial cement replacementDocument8 pagesUtilisation of calcined mussel shells as partial cement replacementEugene Clark EridaoNo ratings yet
- Spark TestingDocument23 pagesSpark TestingJad MacintoshNo ratings yet
- Asnzs 3000+5033Document3 pagesAsnzs 3000+5033IceMan3No ratings yet
- Identificationof ScalesDocument2 pagesIdentificationof ScalesAmina MekkakiaNo ratings yet
- Prestressed ConcreteDocument15 pagesPrestressed ConcreteSheryll de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Tzidc 200Document24 pagesTzidc 200Thanh Luan NguyenNo ratings yet
- STSDocument50 pagesSTSpcuycsNo ratings yet
- Sgm2 and Sgm3 Fan Drive Gear Motors Technical Information: OpencircuitgearDocument78 pagesSgm2 and Sgm3 Fan Drive Gear Motors Technical Information: Opencircuitgeara_salehiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Advanced Separation Techniques B.E. 6 SemesterDocument13 pagesGujarat Technological University: Advanced Separation Techniques B.E. 6 SemesterBhavin KapadiaNo ratings yet