Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Triaxial Procedure
Uploaded by
Uduebor MichealCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Triaxial Procedure
Uploaded by
Uduebor MichealCopyright:
Available Formats
TREVI FOUNDATIONS GEOTECHNICAL RESEARCH LABORATORY FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY, AKURE
LABORATORY TEST EXPERIMENT PROCEDURES (TRIAXIAL TESTS)
GENERAL
FILLING THE RESERVOIR
Ensure that all valves are locked, except the water supply and vacuum release valves a. Put on the compressor pump and raise the black valve at the centre of the pump b. Open the valve outlet on the pump to let air into the gauge c. Open up all the valves to allow the air into the water keg and into the reservoir.
DE-AIRING THE WATER IN THE RESERVOIR
Ensure that all the valves are closed except the vacuum supply valve a. b. c. d. e. Put on the vacuum pump and release the black valve on top of it Run till satisfied that there are no more air bubbles rising within the reservoir Close the valve on top of the vacuum pump Close vacuum supply Open the vacuum release valve to release the pressure within the reservoir
FILLING THE AIR- WATER BLADDERS
Note: fill one bladder at a time, always start from cell pressure AIR a. Open air valve leading to bladder b. Close air valve when bladder stands erect, do not rotate the air knob WATER a. b. c. d. e. Open water inlet from reservoir Open deaired water inlet valve on panel Open water valves leading to bladder, do not open valve leading to cell (chamber) Open vent at the top of the air water bladder When it is filled, close the vent and close all the valves
UNCONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED TRIAXIAL TEST
A. B. C. D. Prepare Sample as specified in General. Setup sample inside Triaxial Cell as specified in General. Setup Air-Water Bladder as specified in General. Filling up the Triaxial chamber (Cell). a. Open De-aired water inlet valve to allow water into the system. b. Open valve B and C c. Switch volume change apparatus to By Pass. d. Open CP valve at the bottom of the cell. e. Open vent at the top of the cell to allow air to escape. f. Wait until water fills the chamber and displaces all the air in the cell. g. Close the vent at the top of the cell and all preceding water valves.
E. Applying pressure to the cell a. Using valve A, turn the knob clockwise to increase the pressure to the calculated overburden pressure by checking the pressure on the pressure transducer. Overburden Pressure = gh Bulk Density = Mass/Volume Mass Weight of sample Volume volume of mould h depth at which sample was recovered g - Acceleration due to gravity = 9.80665 m/s2 b. Open the valve to transfer the pressure into the cell chamber Check the pressure transducer to see if the pressure is still the same, if not increase to desired pressure. F. Applying pressure to the sample a. Setup the machine and set strain to 0.05mm/min. b. Setup the Datacomm software and activate channels 1, 6 and 9 to take readings c. Zero all transducer readings and set delay to 5secs. d. In time begin test to match up after software has begun to record (say about 2 secs after). e. Continue test up to 1 minute after failure of soil sample, reduction in the axial load or constant axial load corresponds to a failure state of sample.
G. Post test a. Open cell pressure valve and air release valves to drain off excess pressure b. Dissemble cell quickly c. Take out test sample and remove rubber membrane with the help of membrane stretcher d. Weigh the soil sample e. Sketch failure shape and failure plane in tested soil sample f. Take out soil from centre of the sample for water content determination
CONSOLIDATED UNDRAINED TRIAXIAL COMPRESSION TEST
A. B. C. D. E. Prepare the sample as specified in General. Setup sample in triaxial cell as specified in General. Setup air water bladder as specified in general. Setup the Volume Change apparatus as specified in General. Filling Up the Triaxial Cell a. Open the de-aired water inlet valve to allow water into the system b. Open Valves B and C c. Switch the volume change apparatus to by pass d. Open Valve Cp at the base of the cell chamber e. Open all the vents at the top of the chamber f. Wait until water fills the cell and displaces all the air in the air g. Close up all the vents and all valves h. Zero and measure the initial steady pore pressure of the specimen at this point by monitoring the pore pressure reading via the datacomm software i. F. Applying cell pressure ( To prevent swelling of the specimen when saturating) a. Ensure that the compressor pump is on b. Open valves A,B, C, and D c. Put on the pressure transducer at the top of the panel d. Using the pressure knob A, by turning clockwise increase the pressure to desired level e. Open the valve CP to transfer the pressure into the chamber f. Keep valve CP, A, C, and D open, close valve B g. Measure the steady pore pressure within the specimen at this point by monitoring the pore pressure reading via the datacomm software h. G. Applying Back Pressure (Saturation Stage) a. Open Valves A, B, C, and D b. Using pressure knob A, turn clockwise to increase pressure to the desired level ( ensure you keep a differential pressure between 5 10 % depending on the specimen type), by monitoring the pressure transducer c. Open valve BP at the base of the cell to transfer the pressure to the specimen d. Keep valve BP, A, C, and D open, close valve B H. % Saturation ( Skepton Value) Determination a. Measure the steady pore pressure within the specimen by monitoring the pore pressure reading via the datacomm software b. Increase the Cell pressure by a differential ( anything above 30kpa) c. Measure the steady pore pressure within the specimen by monitoring the pore pressure reading via the datacomm software d. Determine the skepton value by calculating
If saturation is not satisfactory ( within 0.95 0.99), increase back pressure to a differential of between 5- 10kpa Ensure that at least 95% saturation is achieved or when there is no more saturation, stop saturation. I. e. Close all unneeded valves Consolidation a. Close all valves b. Open valves A, B, C, and D c. Increase pressure to equal the addition of the overburden pressure of the soil at natural depth + current back pressure Consolidation Pressure = Calculated Overburden Pressure + Back Pressure
Transfer the pressure to the cell by opening the valve CP at the base of the cell chamber. Setup the volume change apparatus and switch it to measure volume change Measure the initial reading of the volume change apparatus Open valve BP at the base of the cell to allow excess drainage from the specimen into the volume change apparatus h. Leave the setup to consolidate for 24 hours and take readings as usual for consolidation test J. Compression (Shearing Stage) a. Only the valves leading to CP and the Pore pressure transducer valves should be left open b. Setup the Tritest machine and datacomm software to begin shearing of the specimen c. Take deformation and pore pressure readings until he sample fails K. Post test a. Open cell pressure valve and air release valves to drain off excess pressure b. Dissemble cell quickly c. Take out test sample and remove rubber membrane with the help of membrane stretcher d. Weigh the soil sample e. Sketch failure shape and failure plane in tested soil sample f. Take out soil from centre of the sample for water content determination
d. e. f. g.
You might also like
- Unconsolidated UndrainedDocument9 pagesUnconsolidated UndrainedMohd Syafiq Akmal100% (2)
- Questions 1Document2 pagesQuestions 1AudreyWalangareDimalibotNo ratings yet
- Lab Procedure Water Flow LossesDocument2 pagesLab Procedure Water Flow LossesChanel AnnNo ratings yet
- CVG3109 - Lab - Consolidated Drained Tests For Sand - 2014Document11 pagesCVG3109 - Lab - Consolidated Drained Tests For Sand - 2014Rhedo.AbdNo ratings yet
- Triaxial Test: Consolidated UndrainedDocument9 pagesTriaxial Test: Consolidated UndrainedNguyễn Hòa100% (1)
- CU Triaxial Tests Using ELE DS7 SoftwareDocument13 pagesCU Triaxial Tests Using ELE DS7 SoftwareJuan Daniel Garcia VargasNo ratings yet
- Bimbingan 3Document19 pagesBimbingan 3SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli's Theorem ExperimentDocument3 pagesBernoulli's Theorem ExperimentShahiera ShafieNo ratings yet
- Surface Sampling of Reservoir FluidsDocument6 pagesSurface Sampling of Reservoir FluidsMuhammad MufarridNo ratings yet
- Calibration OF Volume TankDocument16 pagesCalibration OF Volume TankMelgie Mae Matulin Dikitanan100% (1)
- BS 1881-106 Air Content of Fresh ConcreteDocument2 pagesBS 1881-106 Air Content of Fresh Concreteibad ullahNo ratings yet
- Venturi meter experiment proceduresDocument2 pagesVenturi meter experiment proceduresAnonymous mRBbdopMKf100% (1)
- Porosity and Permeability LABORATORYDocument5 pagesPorosity and Permeability LABORATORYDavid OrtegonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Lab ReportDocument17 pagesChemical Lab Reportoprudra2000No ratings yet
- Adiabatic Batch ReactorDocument2 pagesAdiabatic Batch ReactorAshish VermaNo ratings yet
- Permeability of Soil Using The Falling Head MeathodDocument4 pagesPermeability of Soil Using The Falling Head MeathodSreekala Prabhasankar100% (3)
- SamplingDocument1 pageSamplingPopa Costin AugustinNo ratings yet
- Hydrotest ProcedureDocument3 pagesHydrotest Procedureaman131100% (2)
- Chest Tube Thoracostomy (CTT): Insertion, Care, ProblemsDocument7 pagesChest Tube Thoracostomy (CTT): Insertion, Care, ProblemsMikhaelEarlSantosTacordaNo ratings yet
- 5 Written QuestionsDocument28 pages5 Written QuestionsAshok YNo ratings yet
- Gas Diffusion ExperimentDocument18 pagesGas Diffusion ExperimentMuhammad NasrulNo ratings yet
- AREN 2110: Heat Engine ExperimentDocument8 pagesAREN 2110: Heat Engine ExperimentRafa ElaNo ratings yet
- Flowmeter DEMONSTRATIONDocument20 pagesFlowmeter DEMONSTRATIONAfiq IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 To Verify The Bernoulli's Theorem For Steady Flow of WaterDocument4 pagesExperiment 5 To Verify The Bernoulli's Theorem For Steady Flow of WaterMHS MHSNo ratings yet
- Blue Book Terms p4 276-352Document78 pagesBlue Book Terms p4 276-352John Paul EspañoNo ratings yet
- Manual For Continuous Distillation: 1. Week 1Document21 pagesManual For Continuous Distillation: 1. Week 1Richard ObinnaNo ratings yet
- charging and discharging refrigeratorDocument1 pagecharging and discharging refrigeratorMateo, Dale Vincent A.No ratings yet
- MAPUA HYDRAULICS LAB ENERGY LOSSES IN BENDSDocument7 pagesMAPUA HYDRAULICS LAB ENERGY LOSSES IN BENDSJohn Michael Menoza ZapantaNo ratings yet
- RT - Asnt Quetion BankDocument12 pagesRT - Asnt Quetion Bankprabhakaran.SNo ratings yet
- Cek Mesin AnestesiDocument3 pagesCek Mesin AnestesiAchmad MustikaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual MEC 212Document43 pagesLaboratory Manual MEC 212Kirandeep GandhamNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Department Bernoulli ExperimentDocument10 pagesHydraulics Department Bernoulli ExperimentPaul CamachoNo ratings yet
- Blue Book Terms p1 1 100Document101 pagesBlue Book Terms p1 1 100Listless ListlessNo ratings yet
- UU Triaxial TestDocument11 pagesUU Triaxial Testprinces_anaNo ratings yet
- 401 TestingDocument8 pages401 TestingMark Still DelarnaNo ratings yet
- Unit 24 Quiz HvacDocument4 pagesUnit 24 Quiz HvacNneedofallDanswers89% (9)
- MethodStatement CUTriaxial SaturationDocument2 pagesMethodStatement CUTriaxial SaturationDr Wong Kim YuenNo ratings yet
- 4c Lab3 Heat EnginesDocument4 pages4c Lab3 Heat EnginesAiza AliNo ratings yet
- Power Plant Coaching With ClueDocument352 pagesPower Plant Coaching With ClueEep JayNo ratings yet
- Flow Through An OrificeDocument8 pagesFlow Through An OrificeKevin VillaNo ratings yet
- Procedure: For The Procedure, We First Need To Set Up The Venturi and Manometer On Top of The Hydraulic BenchDocument2 pagesProcedure: For The Procedure, We First Need To Set Up The Venturi and Manometer On Top of The Hydraulic Benchkurou hazamaNo ratings yet
- Core Flooding Manual-1Document6 pagesCore Flooding Manual-1Boniphace JohnNo ratings yet
- A-1 PIPE Terms Coaching Part 1Document351 pagesA-1 PIPE Terms Coaching Part 1Ralph Adrian MielNo ratings yet
- Blue Book Terms Part 1 Powerpoint 2Document101 pagesBlue Book Terms Part 1 Powerpoint 2andradajc6No ratings yet
- Pressure Vacuum Vent Cap Test ProcedureDocument3 pagesPressure Vacuum Vent Cap Test ProcedureDadang Ibnu SetyawanNo ratings yet
- Rotary dryer multiple choice questionsDocument352 pagesRotary dryer multiple choice questionsHerson Fronda BucadNo ratings yet
- FM CompleteDocument19 pagesFM Completenini jasniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: MethodologyDocument2 pagesChapter 3: MethodologyM Shahrul IzuanNo ratings yet
- The Sample Is Sealed Inside A Rubber Membrane and Then Surround With WaterDocument6 pagesThe Sample Is Sealed Inside A Rubber Membrane and Then Surround With WaterhabiNo ratings yet
- OedometerDocument7 pagesOedometerDaniel ShinnickNo ratings yet
- Bernoulli Lab Report-CorrectDocument20 pagesBernoulli Lab Report-CorrectJerle ParondoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: Effect of Water and Air Flow Changes in Gas AbsorptionDocument10 pagesExperiment 1: Effect of Water and Air Flow Changes in Gas AbsorptionAzrol Azmir Long100% (2)
- Level TransmitterDocument16 pagesLevel Transmitterstolen mechieduc100% (2)
- Autoclave Harvey 5000Document16 pagesAutoclave Harvey 5000Cesar Alfonso Saldivar MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Coefficient of Discharge of A Venturi MeterDocument1 pageDetermination of Coefficient of Discharge of A Venturi MeterJoffer Gallamaso50% (2)
- EME3026. Expt 2, Jet Impact. T1-2016-17Document6 pagesEME3026. Expt 2, Jet Impact. T1-2016-17Theebbanraj A/L AsokanNo ratings yet
- Respiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManFrom EverandRespiration Calorimeters for Studying the Respiratory Exchange and Energy Transformations of ManNo ratings yet
- Marvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SFrom EverandMarvel Carbureter and Heat Control: As Used on Series 691 Nash Sixes Booklet SNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- Land 07 00020Document12 pagesLand 07 00020Uduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- S98 089 PDFDocument12 pagesS98 089 PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- S98 089 PDFDocument12 pagesS98 089 PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Presentation-Rigid-pavement Design-Fig-Current - 2019Document9 pagesPresentation-Rigid-pavement Design-Fig-Current - 2019Uduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Infrastructures 05 00007 v2 PDFDocument10 pagesInfrastructures 05 00007 v2 PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- NCDOT Research & Innovation Summit – Engineered Water Repellency in Frost Heave MitigationDocument14 pagesNCDOT Research & Innovation Summit – Engineered Water Repellency in Frost Heave MitigationUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Preparing and presenting at the virtual NCDOT SummitDocument2 pagesPreparing and presenting at the virtual NCDOT SummitUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- 7 Abaqus Conv GuidelinesDocument4 pages7 Abaqus Conv GuidelinesSrinivas RallabandiNo ratings yet
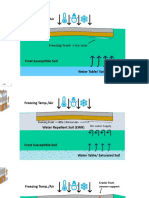
- Freezing Temp./Air: Freezing Front - Ice LensDocument4 pagesFreezing Temp./Air: Freezing Front - Ice LensUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Engineered Water Repellency in Frost Heave MitigationDocument1 pageEngineered Water Repellency in Frost Heave MitigationUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Abaqus - Cae Users ManualDocument1,306 pagesAbaqus - Cae Users ManualSarhan Karray100% (1)
- COMSOL For PB and MPB Eq in ModelingDocument10 pagesCOMSOL For PB and MPB Eq in ModelingUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Wang Developing A PDFDocument175 pagesWang Developing A PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Articulo 2Document10 pagesArticulo 2Adriano ZvNo ratings yet
- UNC Charlotte 5-Year Academic CalendarDocument1 pageUNC Charlotte 5-Year Academic CalendarUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Marriage Ethics For SinglesDocument38 pagesMarriage Ethics For SinglesUduebor Micheal100% (1)
- Ola, Fadugba, Uduebor - 2018 - In-Situ Chemical Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Groundwater (A Case Study of Baruwa Community, Lag PDFDocument13 pagesOla, Fadugba, Uduebor - 2018 - In-Situ Chemical Oxidation of Hydrocarbon Contaminated Groundwater (A Case Study of Baruwa Community, Lag PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Aderinola O.S., Uduebor M. A., Owolabi T.A - 2015 - COST PREDICTION MODELS OF COMPONENTS OF BUILDING AND CIVIL ENGINEERING CONSTRUCTION PDFDocument10 pagesAderinola O.S., Uduebor M. A., Owolabi T.A - 2015 - COST PREDICTION MODELS OF COMPONENTS OF BUILDING AND CIVIL ENGINEERING CONSTRUCTION PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Cve 306 - 1 - Origin of SoilsDocument7 pagesCve 306 - 1 - Origin of SoilsUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Oluyemi-Ayibiowu, Uduebor - 2019 - Effect of Compactive Effort On Compaction Characteristics of Lateritic Soil Stabilized With Terrasil PDFDocument6 pagesOluyemi-Ayibiowu, Uduebor - 2019 - Effect of Compactive Effort On Compaction Characteristics of Lateritic Soil Stabilized With Terrasil PDFUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Digigrub - CrestaTechDocument7 pagesDigigrub - CrestaTechUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Remediation by Natural Attenuation at Baruwa, Lagos NigeriaDocument7 pagesHydrocarbon Remediation by Natural Attenuation at Baruwa, Lagos NigeriaUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Man and His Cosmic EnvironmentDocument18 pagesMan and His Cosmic EnvironmentUduebor Micheal0% (1)
- Lecture Presentation 1 - Materials and AggregatesDocument68 pagesLecture Presentation 1 - Materials and AggregatesUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Ucs LabDocument14 pagesUcs LabUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- PoemsDocument1 pagePoemsUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Man and His OriginDocument16 pagesMan and His OriginUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Long Term Assessment of Hydrocarbon Contamination in Baruwa Community, Lagos, NigeriaDocument35 pagesLong Term Assessment of Hydrocarbon Contamination in Baruwa Community, Lagos, NigeriaUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Ministry of GraceDocument4 pagesMinistry of GraceUduebor MichealNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Unsaturated Geotechnical Properties of Tropical Soil in Southwestern NigeriaDocument37 pagesAssessment of Unsaturated Geotechnical Properties of Tropical Soil in Southwestern NigeriaUduebor Micheal100% (1)
- An Approach To Evaluate Hydraulic Conductivity of Soil Based On CPTU TestDocument13 pagesAn Approach To Evaluate Hydraulic Conductivity of Soil Based On CPTU TestAmin HashemiNo ratings yet
- R. F. Craig (Auth.) - Soil Mechanics - Solutions Manual-Springer US (1992)Document80 pagesR. F. Craig (Auth.) - Soil Mechanics - Solutions Manual-Springer US (1992)Samuel Bandeira100% (2)
- Pore-pressure coefficients in earth dam design and constructionDocument5 pagesPore-pressure coefficients in earth dam design and constructionRodolfo100% (1)
- (USBR) - 2011 - Chapter 4 Static Stability Analysis PDFDocument159 pages(USBR) - 2011 - Chapter 4 Static Stability Analysis PDFEvandro_J100% (2)
- Settle3D: Settlement and Consolidation AnalysisDocument60 pagesSettle3D: Settlement and Consolidation AnalysisChristian Mesa CorreaNo ratings yet
- E2 12 02 06 PDFDocument8 pagesE2 12 02 06 PDFshrikant sutarNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument12 pagesSoil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsleGionNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Performance of The Excavation For The Chicago-State Subway Renovation Project and Its Effects On Adjacent StructuresDocument303 pagesAnalysis and Performance of The Excavation For The Chicago-State Subway Renovation Project and Its Effects On Adjacent StructuresMaryanti EnikNo ratings yet
- Notes 4 - Stresses in SoilsDocument45 pagesNotes 4 - Stresses in SoilsWen Sen SimNo ratings yet
- Soil Improvement Works For An Offshore Land ReclamationDocument13 pagesSoil Improvement Works For An Offshore Land ReclamationDoThanhTungNo ratings yet
- Objective Question On Unit No.2 Permeability & SeepageDocument10 pagesObjective Question On Unit No.2 Permeability & SeepageKalyani ingole100% (1)
- Lecture1 - Stresses in Soil (Students)Document122 pagesLecture1 - Stresses in Soil (Students)edger100% (1)
- Chapter 3. Professor Roy E. Olson On Con PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 3. Professor Roy E. Olson On Con PDFVitor AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Full Thesis ANALYSIS OF WELLBORE INSTABILITY WHILE DRILLING EXPLORATORY WELLS IN BANGLADESHDocument92 pagesFull Thesis ANALYSIS OF WELLBORE INSTABILITY WHILE DRILLING EXPLORATORY WELLS IN BANGLADESHAhmed GharbiNo ratings yet
- Modulos Resilient in Granulas Soils PDFDocument25 pagesModulos Resilient in Granulas Soils PDFLuisRodrigoPerezPintoNo ratings yet
- Sm1 Labclass Sand CastleDocument2 pagesSm1 Labclass Sand CastleRobert PrinceNo ratings yet
- Undrained Effective Stress AnalysisDocument5 pagesUndrained Effective Stress AnalysisVa Ni SkyNo ratings yet
- 62 Determination Load Sharing Effects Sprayed Concrete Tunnel LiningsDocument8 pages62 Determination Load Sharing Effects Sprayed Concrete Tunnel Liningsp_ignatiusNo ratings yet
- Problem Set in Effective StressesDocument2 pagesProblem Set in Effective StressesYandi ChilNo ratings yet
- 1 - Earth PressureDocument14 pages1 - Earth PressureclearcastingNo ratings yet
- E1EA0 Toth J Gravitational Systems of Groundwater Flow Theory EvalDocument311 pagesE1EA0 Toth J Gravitational Systems of Groundwater Flow Theory EvalNatalya Rakhbari100% (2)
- Consolidated Undrained Triaxial Compression Test For Cohesive SoilsDocument11 pagesConsolidated Undrained Triaxial Compression Test For Cohesive SoilsNikhilNo ratings yet
- Lacasse (1988) Design Parameters of Clays From in Situ and Laboratory TestsDocument47 pagesLacasse (1988) Design Parameters of Clays From in Situ and Laboratory TestsbryanerickjorgebNo ratings yet
- SLOPE PROTECTION Guide To Road Slope Proctection Works CH 3Document14 pagesSLOPE PROTECTION Guide To Road Slope Proctection Works CH 3Federico Singh Amadineep86% (7)
- Geop. ArtDocument8 pagesGeop. ArtEduardo MassaNo ratings yet
- Effective Stress in Saturated and Partly Saturated SoilsDocument21 pagesEffective Stress in Saturated and Partly Saturated SoilsAnonymous GnfGTwNo ratings yet
- JewellDocument30 pagesJewellmr_fanta_sticNo ratings yet
- 3D - On The Influence of Face Pressure, Grouting Pressure and TBM Design in Soft Ground TunnellingDocument12 pages3D - On The Influence of Face Pressure, Grouting Pressure and TBM Design in Soft Ground TunnellingTai TienNo ratings yet
- 6 Stresses in SoilsDocument23 pages6 Stresses in SoilsJenina LogmaoNo ratings yet
- CE 332 Geotechnical Engineering I: Lecture 1: Stress in The Ground (Total & Effective Stresses Within A Soil Mass)Document24 pagesCE 332 Geotechnical Engineering I: Lecture 1: Stress in The Ground (Total & Effective Stresses Within A Soil Mass)Nickson KomsNo ratings yet