Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Four Probe Method Setup
Uploaded by
devendrakphyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Four Probe Method Setup
Uploaded by
devendrakphyCopyright:
Available Formats
Four Probe Method
Resistivity of Semiconductor by Four Probe Method at different temperatures and determination of the Band-gap
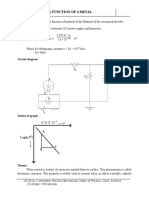
The Four Probe Method is one of the standard and most widely used method for the measurement of resistivity of semiconductors. The experimental arrangement is illustrated. In its useful form, the four probes are collinear. The error due to contact resistance, which is specially serious in the electrical measurement on semiconductors, is avoided by the use of two extra contacts (probes) between the current contacts. In this arrangement the contact resistance may all be high compare to the sample resistance, but as long as the resistance of the sample and contact resistances are small compared with the effective resistance of the voltage measuring device (potentiometer, electrometer or electronic voltmeter), the measured value will remain unaffected. Because of pressure contacts, the arrangement is also specially useful for quick measurement on different samples or sampling different parts of the same sample.
Description of the experimental set-up
1. Probes Arrangement
It has four individually spring loaded probes. The probes are collinear and equally spaced. The probes are mounted in a teflon bush, which ensure a good electrical insulation between the probes. A teflon spacer near the tips is also provided to keep the probes at equal distance. The whole arrangement is mounted on a suitable stand and leads are provided for the voltage measurement.
2. Sample
Germanium crystal in the form of a chip
3. Oven
It is a small oven for the variation of temperature of the crystal from the room temperature to about 200C (max.)
SES Instruments Pvt. Ltd.
452, Adarsh Nagar, Roorkee - 247 667, India. Phone : 91-1332-272852 Fax : 91-1332-277118 email : ses@sestechno.com website: www.sestechno.com
4. Four Probe Set-up, DFP-02
The set-up consists of three units in the same cabinet.
(i)
Multirange Digital Voltmeter
In this unit, intersil 3 digit single chip A/D Converter ICL 7107 has been used. It has high accuracy like auto zero to less than 10V, zero drift of less than 1V/ C, input bias current of 10pA max. and roll-over error of less than one count. Since the use of internal reference causes the degradation in performance due to internal heating, an external reference has been used. SPECIFICATIONS Range X1 (0-200mV) & X10 (0-2V) Resolution 100 V at X1 range Accuracy 0.1% of reading 1 digit Impedance 1M Display 3 digit, 7 segment LED (12.5mm height) with auto polarity and decimal indication Overload Indicator Sign of 1 on the left & blanking of other digits
(ii) Constant Current Generator
It is an IC regulated current generator to provide a constant current to the outer probes irrespective of the changing resistance of the sample due to change in temperatures. The basic scheme is to use the feedback principle to limit the load current of the supply to preset maximum value. Variations in the current are achieved by a potentiometer included for that purpose. The supply is a highly regulated and practically ripple free d.c. source. The current is measured by the digital panel meter. SPECIFICATIONS Open Circuit Voltage : 18V Current range : 0-20mA Resolution : 10A Accuracy: 0.25% of the reading 1 digit Load regulation: 0.03% for 0 to full load Line Regulation: 0.05% for 10% changes
(iii) Oven Power Supply
Suitable voltage for the oven is obtained through a step down transformer with a provision for low and high rates of heating. A glowing LED indicates, when the oven power supply is ON. The experimental set-up is complete in all respect Typical results obtained from this set-up are shown in the figure.
You might also like
- Nonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodFrom EverandNonlinear Dynamic in Engineering by Akbari-Ganji’S MethodNo ratings yet
- Classical Statistics-IDocument47 pagesClassical Statistics-IKailasaNo ratings yet
- In Electrical Electronic MeasurementDocument29 pagesIn Electrical Electronic Measurementsiddhartha bharadwajNo ratings yet
- Models - Plasma.drift Diffusion TutorialDocument14 pagesModels - Plasma.drift Diffusion TutorialbkmmizanNo ratings yet
- Exp03-Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy Using NaI (TL)Document10 pagesExp03-Gamma-Ray Spectroscopy Using NaI (TL)Muhammad ToharohNo ratings yet
- Orazem EIS Spring 2008Document306 pagesOrazem EIS Spring 2008Bangkit Rachmat HilcaNo ratings yet
- Energy Gap of SemiconductorDocument7 pagesEnergy Gap of SemiconductorVyshu MaminiduNo ratings yet
- 8.work Function of MetalDocument3 pages8.work Function of MetalRavi Kanth M NNo ratings yet
- Einstein Relations: Prof - Siva PrasadDocument11 pagesEinstein Relations: Prof - Siva PrasadRenuNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Engineering FundamentalsDocument42 pagesNuclear Engineering FundamentalsJustine CabuayNo ratings yet
- B.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualDocument87 pagesB.tech Applied Physics Lab ManualSwastika sainNo ratings yet
- E.over.m RatioDocument8 pagesE.over.m Ratiobrain221304No ratings yet
- DTU Engineering Physics CurriculumDocument63 pagesDTU Engineering Physics CurriculumParth Chopra100% (1)
- HV EngineeringDocument132 pagesHV EngineeringHumayun AhsanNo ratings yet
- Determination of Plancks Constant Using The Photoelectric EffectDocument5 pagesDetermination of Plancks Constant Using The Photoelectric EffectJp SwanepoelNo ratings yet
- Basics of Impedance Spectroscopy: ( 1% of The Entire Topic!)Document79 pagesBasics of Impedance Spectroscopy: ( 1% of The Entire Topic!)ManoranjanNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab Report AnalysisDocument76 pagesPhysics Lab Report AnalysisWaseem Akram50% (2)
- The Michelson InterferometerDocument6 pagesThe Michelson Interferometermarygreeno1No ratings yet
- Analysis of Dielectric ResponseDocument221 pagesAnalysis of Dielectric ResponsearunjothiNo ratings yet
- Gamma Rays: ObjectDocument15 pagesGamma Rays: ObjectSting GonsalisNo ratings yet
- Susceptibility of MNCL2Document23 pagesSusceptibility of MNCL2AshwamedhNo ratings yet
- 4PP ResistivityDocument9 pages4PP ResistivityViet Pham QuangNo ratings yet
- Boukamp 2020 J. Phys. Energy 2 042001Document25 pagesBoukamp 2020 J. Phys. Energy 2 042001Jayveer JoshiNo ratings yet
- L8 - Foster's Reactance TheoremDocument18 pagesL8 - Foster's Reactance TheoremBretBarraquio0% (1)
- Transverse Vibration of Stretched Strings: Politecnico Di Milano M.Sc. in Mechanical EngineeringDocument15 pagesTransverse Vibration of Stretched Strings: Politecnico Di Milano M.Sc. in Mechanical EngineeringArnab B.No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Microwave DevicesDocument18 pagesChapter 10 Microwave DevicesAghna Tiyas MandalNo ratings yet
- Question No 1: Experiment: To Measure Electrical Conductivity by Using Two Probe or Four Probe MethodDocument17 pagesQuestion No 1: Experiment: To Measure Electrical Conductivity by Using Two Probe or Four Probe Methodzrish100% (1)
- Chapter 7-AC STEADY STATE ANALYSIS. Cruicial TopicDocument55 pagesChapter 7-AC STEADY STATE ANALYSIS. Cruicial TopicDouglas OngomNo ratings yet
- Hysteresis in Ferromagnetic Materials ExperimentDocument8 pagesHysteresis in Ferromagnetic Materials ExperimentbpmurtaNo ratings yet
- Pre Lab 3Document2 pagesPre Lab 3Ami ShahNo ratings yet
- First Order Active Filters (LPF, HPF) : (A) Low Pass FilterDocument12 pagesFirst Order Active Filters (LPF, HPF) : (A) Low Pass FilterVRNo ratings yet
- 01 Lissajous Curves Experiment ManualDocument3 pages01 Lissajous Curves Experiment ManualDeo CaviteNo ratings yet
- ZSimpWin EIS Software Technical Note on Kramers-Kronig ExtrapolationDocument13 pagesZSimpWin EIS Software Technical Note on Kramers-Kronig ExtrapolationChaitanya RaiNo ratings yet
- Skin Effect and Dielectric Loss Models of Power Cables 04784562Document8 pagesSkin Effect and Dielectric Loss Models of Power Cables 04784562Gilberto Mejía100% (1)
- SeminarDocument12 pagesSeminarAkshay Tiwari100% (1)
- 15A04403 Electromagnetic Theory & Transmission LinesDocument2 pages15A04403 Electromagnetic Theory & Transmission LinesRadhika MahankaliNo ratings yet
- Generalised Cockcroft-Walton voltage multipliers driven by multiphase square wavesDocument2 pagesGeneralised Cockcroft-Walton voltage multipliers driven by multiphase square wavesfeelblastNo ratings yet
- Measure Unknown Inductance Using Maxwell BridgeDocument2 pagesMeasure Unknown Inductance Using Maxwell Bridgemigman99No ratings yet
- Measurement of Inductance by Phasor Diagram Method PhysicsDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Inductance by Phasor Diagram Method PhysicsnileshugemugeNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Introduction To Quantum MechanicsDocument32 pagesChapter2 Introduction To Quantum MechanicsTahsin MorshedNo ratings yet
- RL Series Circuit ReportDocument11 pagesRL Series Circuit Reportfedley sikolia100% (1)
- 4c Lab9 Photoelectric EffectDocument4 pages4c Lab9 Photoelectric Effectk03mNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes PDFDocument138 pagesPhysics Notes PDFVishak Mendon100% (1)
- Applied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFDocument204 pagesApplied Reactor Technology - Henryk Anglart PDFdogclutchNo ratings yet
- Franck Hertz ExperimentDocument15 pagesFranck Hertz Experimentlalal345No ratings yet
- Homework 6Document5 pagesHomework 6Stephen RandallNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Energy Band Gap ExperimentDocument6 pagesLaboratory Manual For Energy Band Gap ExperimentVedant WathNo ratings yet
- Charging & Discharging Capacitor CircuitDocument4 pagesCharging & Discharging Capacitor CircuitHemanth GedelaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Langmuir Probes - Hiden Analytical Tech Info Sheet531Document8 pagesIntroduction To Langmuir Probes - Hiden Analytical Tech Info Sheet531alexaNo ratings yet
- Zeeman Effect PDFDocument32 pagesZeeman Effect PDFDEEPA YADAVNo ratings yet
- 2-Basic Concepts of Nuclear Physics and Overview of ReactorDocument67 pages2-Basic Concepts of Nuclear Physics and Overview of ReactorswamikashyapNo ratings yet
- (Experiment 3) BJT - Common Emiter Amplifier PDFDocument9 pages(Experiment 3) BJT - Common Emiter Amplifier PDFArik JuniarNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 ElectrostaticsDocument46 pagesUNIT 1 ElectrostaticsHimanshu BhandariNo ratings yet
- Wave Behavior of Particle and De-Broglie Hypothesis and Its TestingDocument8 pagesWave Behavior of Particle and De-Broglie Hypothesis and Its TestingUsman Masood PhysicistNo ratings yet
- Shreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 Entc Experiment No. 1 Characterization of RTDDocument49 pagesShreyash Bhimanwar 111907050 Entc Experiment No. 1 Characterization of RTDshreyash100% (1)
- Electrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsFrom EverandElectrical Overstress (EOS): Devices, Circuits and SystemsNo ratings yet
- Four Probe Experiment Dfp 02 Basic ModelDocument2 pagesFour Probe Experiment Dfp 02 Basic Modelagarkarpallavi8No ratings yet