Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Superconductors
Uploaded by
Faris ShahinCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Superconductors
Uploaded by
Faris ShahinCopyright:
Available Formats
Superconductors Superconductors are substances which have the ability to conduct electricity without resistance.
First observed in Hg by Kamerlingh Onnes (1853-1921) in 1911.
4.2 K is the critical temperature (TC) for Hg. Material Zn Ae Sn Pb Nb Nb3Sn Nb3Ge YBa2Cu3O7 HgBa2Ca2Cu3O8 TC (K) 0.88 1.19 3.72 7.18 9.46 18.05 23.2 92 134
Breakthrough Discovery of high-temperature copper oxide-based superconductors by J. Georg Bednorg and K. Alex Muller, scientists at the IBM Zurich Research Laboratory in Switzerland. Material: an oxide of barium, lanthanum and copper with TC : 30K Nobel Prize in physics (1987) Theory of conventional superconductors in metals was advanced by John Bardeen, L.N. Cooper and J.R. Schrieffer in 1957 and is generally called BCS theory. The trio was awarded Nobel Prize in physics in 1972. In theory, 2 electrons can interact via distortions in the array of lattice ions so that there is on a net attraction between the electrons. As a result, the two electrons are bound into an entity called Cooper pair. Besides zero electrical resistance, superconductors also show diamagnetic property (in diamagnetism, the magnetization is in the opposite direction of the applied field) As the material which is placed in a uniform magnetic field (where value is smaller than the critical magnetic field HC), is called below TC, the magnetic flux inside the material is excluded from the material. This is called Meissner Effect.
a) Normal state b) Superconductivity state
Effect of a magnetic field Below TC superconductivity can be destroyed by the application of a strong magnetic field. At any temperature, the minimum field required to destroyed superconductivity is called the critical field (HC) of the material. Thus the value of the critical field depends on the temperature of the superconductivity material.
HC = HO{
Tayns law
Ho : critical field at 0K (absolute zero, typically at the value of 5000A/m
Isotope effect It is found that the transition temperature TC are inversely proportional to the square roots of the atomic weight of the isotope of a single superconductor. Thus, M TC = constant where is a constant and is approximately equal to 0.5. For example the atomic weight of isotope of Hg are from 199.5 to 203.4 atomic mass units. Therefore their transition temperature/critical temperature are from 4.185K to 4.146K respectively. Effect of pressure By applying very high pressure, we can bring TC of a material nearer to room temperature. TC pressure at high pressure
Effect of heavy current The superconductivity properties of conductors disappear when a sufficiently heavy current is passed through them. Since when current flows through a conductor it will set up the magnetic field this destroys the superconductivity state. According to Silsbees Rule, for a superconducting wire
IC = 2
when IC is the critical current and r is the radius of the wire.
Application: Superconductivity materials are used for a) MRI (Magnetic resonance imaging) b) Maglev train (Magnetic Levitation) c) Squid (superconducting quantum interference device)
You might also like
- 4.2 DiodeDocument1 page4.2 DiodeFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- What Did Mathematics Do To Physics?Document34 pagesWhat Did Mathematics Do To Physics?Faris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Logic GatesDocument1 page4.4 Logic GatesFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Generation of ElectricityDocument1 page3.5 Generation of ElectricityFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Experiment: 4.3 Understanding TransistorDocument1 pageExperiment: 4.3 Understanding TransistorFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Applications of Spin CoatingDocument10 pagesApplications of Spin CoatingFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Al Attas Philosophy of Science by AdiasetiaDocument50 pagesAl Attas Philosophy of Science by AdiasetiaFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics: One Dimensional Potential WellDocument17 pagesQuantum Mechanics: One Dimensional Potential WellFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 5.2 Radioactive DecayDocument1 page5.2 Radioactive DecayFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics: One Dimensional Potential WellDocument17 pagesQuantum Mechanics: One Dimensional Potential WellFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Analyzing EM InductionDocument1 page3.3 Analyzing EM InductionFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Classical Electromagnetism - FitzpatrickDocument227 pagesClassical Electromagnetism - Fitzpatrickgamekingd07No ratings yet
- 5.1 Nucleus of AtomDocument1 page5.1 Nucleus of AtomFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Chemical SensorDocument14 pagesChapter 2: Chemical SensorFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Selected Poems - Rumi (17 Pages)Document17 pagesSelected Poems - Rumi (17 Pages)Faris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Thesis GuidelinesDocument6 pagesThesis GuidelinesFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Jalalul-Din Rumi - Selected Poems of RumiDocument46 pagesJalalul-Din Rumi - Selected Poems of RumiFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To SensorDocument13 pagesIntroduction To SensorFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Capacitive SensorDocument29 pagesCapacitive SensorFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- A Selection of Poetry by Rumi (33p) PDFDocument33 pagesA Selection of Poetry by Rumi (33p) PDFarslanahmedkhawaja100% (3)
- Thesis GuidelinesDocument6 pagesThesis GuidelinesFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Number SystemsDocument24 pagesNumber SystemsShishupal SinghNo ratings yet
- 1D SensorsDocument23 pages1D SensorsFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Selected Poems - Rumi (17 Pages)Document17 pagesSelected Poems - Rumi (17 Pages)Faris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Thermodynamics and Statistical MechanicsDocument502 pagesLecture Notes On Thermodynamics and Statistical MechanicsM Naufal Aqil FarhanNo ratings yet
- The Manners of The Student of Knowledge - Shaikh Dr. Muhammad Bin Saeed RaslanDocument71 pagesThe Manners of The Student of Knowledge - Shaikh Dr. Muhammad Bin Saeed RaslanMountainofknowledge100% (3)
- The Manners of The Student of Knowledge - Shaikh Dr. Muhammad Bin Saeed RaslanDocument71 pagesThe Manners of The Student of Knowledge - Shaikh Dr. Muhammad Bin Saeed RaslanMountainofknowledge100% (3)
- Quantum Hall EffectDocument3 pagesQuantum Hall EffectFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Band Theory of SolidDocument9 pagesBand Theory of SolidFaris ShahinNo ratings yet
- Physics Olympiad Error and Data Analysis NoteDocument7 pagesPhysics Olympiad Error and Data Analysis NoteScience Olympiad Blog100% (1)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Niosh Lift Push PullDocument15 pagesNiosh Lift Push Pullahuan huanNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - ComplexationDocument48 pagesTopic 2 - ComplexationLokesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Kaeser SK 19Document75 pagesService Manual Kaeser SK 19Joe100% (8)
- Application of Mecanum WheelsDocument12 pagesApplication of Mecanum WheelsMithun JohnNo ratings yet
- Mathematics in The Modern WorldDocument15 pagesMathematics in The Modern WorldMikaela MelegritoNo ratings yet
- BENNET 840 MallinckrodtDocument12 pagesBENNET 840 MallinckrodtmartynbbNo ratings yet
- BOF Plant Write UpDocument20 pagesBOF Plant Write UpKalyan HalderNo ratings yet
- 1PH7 MotorDocument244 pages1PH7 MotorgetNo ratings yet
- Crystallinity in Polymers-1Document19 pagesCrystallinity in Polymers-1anbuchelvanNo ratings yet
- 1 - SetsDocument2 pages1 - SetsHerald MulanoNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Validation ProtocolDocument6 pagesCleaning Validation ProtocolVega life sciences100% (1)
- AyanamsaDocument30 pagesAyanamsahari1833% (6)
- Kemira, Leonard Dan Bethel Acid FormicDocument22 pagesKemira, Leonard Dan Bethel Acid FormicBen Yudha SatriaNo ratings yet
- Grade Xii Book III FinalDocument158 pagesGrade Xii Book III FinalEdwinNo ratings yet
- Fundatii Turbine EolieneDocument8 pagesFundatii Turbine EolieneTudor PopNo ratings yet
- SSPC Pa 2Document16 pagesSSPC Pa 2Rony Ruiz100% (5)
- P 4 - Q 4Document4 pagesP 4 - Q 4Rodriguez MamaniNo ratings yet
- Drillability IndexDocument10 pagesDrillability Indexeduardoenrique08289100% (1)
- Current Electricity WorksheetDocument6 pagesCurrent Electricity WorksheetRohan ChackoNo ratings yet
- Construction Site Earthwork CalculationDocument4 pagesConstruction Site Earthwork CalculationmasteriragaNo ratings yet
- (Clement Hal) Clement, Hal - Needle 1 - NeedleDocument120 pages(Clement Hal) Clement, Hal - Needle 1 - Needledicoursfigure100% (1)
- Prefixes and SuffixesDocument15 pagesPrefixes and SuffixesRita Otero100% (1)
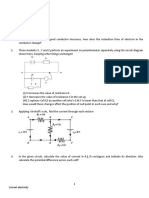
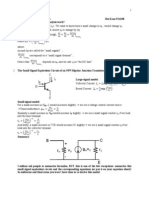
- Small Signal AnalysisDocument4 pagesSmall Signal Analysissamaiyasamp3No ratings yet
- Assignment N1Document9 pagesAssignment N1Rania ChNo ratings yet
- FireWall Rebr WebDocument24 pagesFireWall Rebr Webuyab1989No ratings yet
- TemptDocument13 pagesTemptJhun Lerry TayanNo ratings yet
- Aee1 SkriptDocument186 pagesAee1 SkriptCristian PanaNo ratings yet
- 1.'motivation For SoC Design - by Raveendra SomanaDocument13 pages1.'motivation For SoC Design - by Raveendra SomanaSantosh Shivapuji100% (1)
- DBT 203 Metal Extractive Technology: Topic 1: Extracting Metal From OresDocument24 pagesDBT 203 Metal Extractive Technology: Topic 1: Extracting Metal From OresSollehah SuhaimiNo ratings yet
- Evert Hoek Results CalcDocument6 pagesEvert Hoek Results CalcKanaiyalal N. ShethNo ratings yet