Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment #1 - : By: Kumod Kumar Gupta (B09064) Kuldeep Purohit (Group Mate)
Uploaded by
Lalit KumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment #1 - : By: Kumod Kumar Gupta (B09064) Kuldeep Purohit (Group Mate)
Uploaded by
Lalit KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
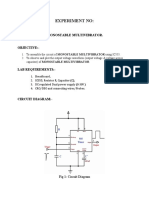
EXPERIMENT #1
OBJECTIVE: -
BY: KUMOD KUMAR GUPTA (B09064) KULDEEP PUROHIT (GROUP MATE)
________________________________________
Obtaining square wave from function generator. Convert this to a trigger pulse using wave-shaping circuit. Making variable pulse monostable multivibrator circuit using 555 timer IC. Vary the duty cycle using control voltage input in the timer to get pulse width modulated output.
WAVE SHAPING CIRCUIT:-
The wave shaping circuit is required to trigger the monostable circuit. Output of this circuit has the trigger pulse which goes low from high for a short duration.
Figure 1: Output (B) after the diode.
Figure 2: Output (A) after capacitor
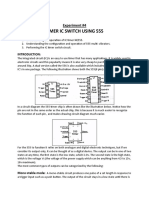
VARIABLE PULSE WIDTH MONOSTABLE CIRCUIT:-
HOW 555 TIMER OPERATES:-
When a negative pulse is applied to the trigger input of the timer, then comparator-2 detects it and compares it with +Vcc/3 at the +ve terminal of comparator and gives HIGH at the output, it will set the flip-flop and the output goes high, at the same time the transistor becomes off and the capacitor C charged up through the resistor R1 till it reaches +2Vcc/3, after that the comparator-1 will have high at its output and that will reset the flip-flop and turns the output back to its original state and at the same time transistor becomes ON and the capacitor will get discharged. Now, if we want to control the width of the output pulse then we may add a control voltage at the control terminal of the timer. Now instead of comparing threshold terminal with 2Vcc/3, the comparator-1 will compare with control voltage, if threshold voltage becomes greater than control voltage, then flip-flop
will be reset. So we see here that control voltage is a decisive factor for the width of the output pulse and so for the duty cycle.
3.00
Vc
0.00 5.00
output
-1.00 0.00 25.00u 50.00u Time (s) 75.00u 100.00u
Figure 3: Voltage through capacitor (simulation and experimental results)
The plot is showing Vc (across capacitor). The output we get will be ON up to the period of charging of the capacitor which is a function of resistance RA and capacitance C.
Varying the duty cycle: Now, to vary the duty cycle, we add an additional voltage source at the control voltage terminal of the timer. RESULTS: The PWM outputs at different values of control voltage are shown below:-
Figure 4: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 2.6V
Figure 5: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 2.8.
Figure 6: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 3.1V
Figure 7: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 3.4V
Figure 8: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 3.7V
Figure 9: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 3.9V
Figure 10: CONTROL VOLTAGE = 4.1V
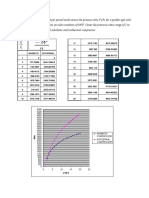
DUTY CYCLE vs CONTROL VOLTAGE
1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5
The above figure is showing the plot of duty cycle versus control voltage.
CONCLUSION: We successfully did the experiment in the lab and are able to vary the duty cycle of the output by varying the control input in the timer. We have obtained a trigger pulse by using the wave shaping circuit. We studied how to use 555 timer and all to get the pulse of the desired width and got them for different values of control voltage. Now we can use this PWM output as an input in DC-DC convertor as a gate driver circuit in MOSFET (switch).
You might also like
- IC 555 TimerDocument11 pagesIC 555 TimersaifaljanahiNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Tutorial Timmer 555Document9 pagesTutorial Timmer 555gabrielamedeletNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 00 Table of ContentsDocument26 pages00 Table of ContentsNana Agyeman AntwiNo ratings yet
- UC3845 Technical ExplanationDocument15 pagesUC3845 Technical ExplanationankurmalviyaNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Bsee201 B - Fluid MechanicsDocument150 pagesBsee201 B - Fluid MechanicsMarvin GagarinNo ratings yet
- Advance Concrete PDFDocument33 pagesAdvance Concrete PDFUdom RithNo ratings yet
- Speed Control of DC Motor Using PDocument22 pagesSpeed Control of DC Motor Using PAnanth Sai YadavNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- 555 Applications NoteDocument19 pages555 Applications NoteIsaac Herrera100% (1)
- Lalit Kumar (B10061) Manoj Kumar (B10062) Mohit Goyal (B10063)Document19 pagesLalit Kumar (B10061) Manoj Kumar (B10062) Mohit Goyal (B10063)Lalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Method Statement of Pipeline WorksDocument13 pagesMethod Statement of Pipeline Worksमनिसभेटुवाल86% (21)
- Astable Multivibrator Using IC 555 TimerDocument3 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using IC 555 TimermanishaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Special Ics The 555 Timer IcDocument10 pagesUNIT-4 Special Ics The 555 Timer IcVerloves LoveNo ratings yet
- 0 Lab6 Astable MultivibratorDocument3 pages0 Lab6 Astable Multivibratorchandu3072002No ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument3 pagesAstable MultivibratorTushar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lic Eec-501 Notes Unit5 Iftm UniversityDocument14 pagesLic Eec-501 Notes Unit5 Iftm UniversitySougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- PWM Signal GeneratorsDocument3 pagesPWM Signal GeneratorsjalalhNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer PDFDocument76 pages555 Timer PDFronaldo19940% (1)
- 555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi VibratorDocument29 pages555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi VibratorsrvdharNo ratings yet
- 555 TimerDocument76 pages555 TimerSai Krishna KodaliNo ratings yet
- Variable Frequency Drive: Abstract-The DC To AC Converters Is Known AsDocument4 pagesVariable Frequency Drive: Abstract-The DC To AC Converters Is Known AsDiego AragónNo ratings yet
- PWM Signal Generators: Testing Status: Mixed. Some Untested, Some SPICE SimulatedDocument15 pagesPWM Signal Generators: Testing Status: Mixed. Some Untested, Some SPICE SimulatedSivareddy MudiyalaNo ratings yet
- Operational AmplifierDocument10 pagesOperational AmplifierSalman AliNo ratings yet
- Sepic Converter Design and Operation: by Gregory SharpDocument21 pagesSepic Converter Design and Operation: by Gregory SharpSingam SridharNo ratings yet
- Ac Servo Speed Torque Characteristics Measurement Unit - PREMIERDocument14 pagesAc Servo Speed Torque Characteristics Measurement Unit - PREMIERAAYUSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- A High Efficiency Boost Converter For TFT-LCD Bias SupplyDocument4 pagesA High Efficiency Boost Converter For TFT-LCD Bias SupplyHamid BoualiNo ratings yet
- Speed Control Brushless DCDocument27 pagesSpeed Control Brushless DCstanley FNo ratings yet
- Lab#10: Design and Study of IC 555 Multivibrator Circuits (2 Turns)Document11 pagesLab#10: Design and Study of IC 555 Multivibrator Circuits (2 Turns)Ayushman ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Modified Motor PDFDocument11 pagesModified Motor PDFMD. SHAEKH ZAHAB CHOWDHURYNo ratings yet
- Timer Ic: Ic 555: GE T5 - Digital, Analog Circuits and InstrumentationDocument5 pagesTimer Ic: Ic 555: GE T5 - Digital, Analog Circuits and InstrumentationFavourite MoviesNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Experiments ECE-P-672Document9 pagesPower Electronics Experiments ECE-P-672Sai SomayajulaNo ratings yet
- Drives Manual Final EeeDocument60 pagesDrives Manual Final EeenandhakumarmeNo ratings yet
- DC-DC Converter Tutorial: Application Note 2031Document10 pagesDC-DC Converter Tutorial: Application Note 2031Mou LaliNo ratings yet
- Multivibrador Com Ci 555Document11 pagesMultivibrador Com Ci 555joselito1juniorNo ratings yet
- Closed Loop Operation of Buck DC-DC Converter Using Discrete Pi ControlDocument4 pagesClosed Loop Operation of Buck DC-DC Converter Using Discrete Pi ControlPrajeesh PrakashNo ratings yet
- Multivibrator CircuitsDocument11 pagesMultivibrator CircuitsSatyaki ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- MATLAB Based Analysis and Simulation of Multilevel InvertersDocument3 pagesMATLAB Based Analysis and Simulation of Multilevel InvertersArunkumar ValusaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ChitodeDocument17 pagesPower Electronics ChitodeKumarNo ratings yet
- Electronics Exercise 2: The 555 Timer and It's Applications: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesElectronics Exercise 2: The 555 Timer and It's Applications: ObjectiveMichael AjayiNo ratings yet
- Lab 4Document6 pagesLab 4Carlos RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi VibratorDocument28 pages555 Timer As Mono Stable Multi VibratordererNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document8 pagesLab 10A. AlghamdiNo ratings yet
- A Novel Switch Mode Dc-To-Ac Converter With Nonlinear Robust ControlDocument21 pagesA Novel Switch Mode Dc-To-Ac Converter With Nonlinear Robust Controlapi-19799369No ratings yet
- LIC Unit IVDocument32 pagesLIC Unit IVDINESH KUMAR DRAVIDAMANINo ratings yet
- Ti Adc 2012 Team 28 4 Phase 1aDocument13 pagesTi Adc 2012 Team 28 4 Phase 1ahv_chillal88No ratings yet
- Monostable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesMonostable MultivibratorSakshi GosaviNo ratings yet
- Experiment No - 2: ObjectiveDocument5 pagesExperiment No - 2: ObjectiveMehar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lab Psim SCRDocument3 pagesLab Psim SCRNoah Tiago De GutierrezNo ratings yet
- SPEED CONTROL OF SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR" BY USING TRIAC - PPTDocument30 pagesSPEED CONTROL OF SINGLE PHASE INDUCTION MOTOR" BY USING TRIAC - PPTGökhan KAYA100% (2)
- IC Questions With Ans AnilsirDocument22 pagesIC Questions With Ans AnilsirAniil J Kumaar50% (2)
- Lic Reports FinalDocument11 pagesLic Reports FinalE L Sai BalajiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Induction MotorsDocument17 pagesLaboratory Induction MotorsEsteban GilNo ratings yet
- Switching Power Supply Theory and ApplicationsDocument40 pagesSwitching Power Supply Theory and ApplicationsascensorimNo ratings yet
- Timer Ic Switch Using 555: Experiment #4Document7 pagesTimer Ic Switch Using 555: Experiment #4Zeeshan RafiqNo ratings yet
- IC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsDocument11 pagesIC 555 Multivibrator CircuitsKaran YadavNo ratings yet
- Appliance Timer: Working of The CircuitDocument5 pagesAppliance Timer: Working of The CircuitMamon GhoshNo ratings yet
- 3.1555 TIMER:: Schematic SymbolDocument10 pages3.1555 TIMER:: Schematic SymbolnagpradasNo ratings yet
- Practical Application of Timer ICDocument5 pagesPractical Application of Timer ICManojkumarNo ratings yet
- IC Regulated Power Supply TutorialDocument8 pagesIC Regulated Power Supply TutorialGugun GunawanNo ratings yet
- Ec 2404 - Electronic System Design LabDocument66 pagesEc 2404 - Electronic System Design LabjebadanielNo ratings yet
- AppNote03 Uc3842Document14 pagesAppNote03 Uc3842Heriberto Flores AmpieNo ratings yet
- CH - 01 - Electric Charges and FieldsDocument32 pagesCH - 01 - Electric Charges and FieldsLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Biology: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedDocument9 pagesBiology: © Ncert Not To Be RepublishedLalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Assignment-1 (B10061)Document4 pagesAssignment-1 (B10061)Lalit KumarNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization: - by Rama Krishna Thelagathoti (M.Tech CSE From IIT Madras)Document118 pagesComputer Organization: - by Rama Krishna Thelagathoti (M.Tech CSE From IIT Madras)iamy2ramsNo ratings yet
- GMSYS Release NotesDocument2 pagesGMSYS Release NotesrenzoquimNo ratings yet
- 211 A3 211 Summary ResultsDocument14 pages211 A3 211 Summary ResultsElmer Gonzalo Sullca ZapataNo ratings yet
- Uponor Dop Klett CPR 20 Ic 251 V 001Document3 pagesUponor Dop Klett CPR 20 Ic 251 V 001jamppajoo2No ratings yet
- NAEC Approved Continuing Education 2018marchDocument26 pagesNAEC Approved Continuing Education 2018marchRuano Andreola StumpfNo ratings yet
- Exception Handling Notes For Vtu StudentsDocument42 pagesException Handling Notes For Vtu StudentshelloNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering PDFDocument3 pagesCivil Engineering PDFchetan c patilNo ratings yet
- 9.16. Prepare A Plot of Work Per Pound Mole Versus The Pressue Ratio PDocument6 pages9.16. Prepare A Plot of Work Per Pound Mole Versus The Pressue Ratio PttussenoNo ratings yet
- Key Features Boilermaker Proven, Legendary ReliabilityDocument2 pagesKey Features Boilermaker Proven, Legendary ReliabilityManuel Cantoral CortazarNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument34 pagesUntitledRayudu VVSNo ratings yet
- Refining Mechanical PulpingDocument12 pagesRefining Mechanical PulpingMahdia MahmudNo ratings yet
- Manual Kls MartinDocument27 pagesManual Kls MartinChris AliNo ratings yet
- WS500 Operator WorkstationDocument2 pagesWS500 Operator WorkstationNayants GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Ehe 07Document286 pagesEhe 07api-348272721No ratings yet
- Kalzip - Vapour Layer FR 0822 PDFDocument2 pagesKalzip - Vapour Layer FR 0822 PDFBerat CakmakliNo ratings yet
- Variable Displacements Axial Piston Pumps: Edition: 06/06.2020 Replaces: MVP 05 T ADocument72 pagesVariable Displacements Axial Piston Pumps: Edition: 06/06.2020 Replaces: MVP 05 T ARidha AbbassiNo ratings yet
- Subsea AccumulatorsDocument4 pagesSubsea AccumulatorsAbdul Hameed OmarNo ratings yet
- Debug 1214Document2 pagesDebug 1214Faizah Ayulia NawitaNo ratings yet
- DNF Stand PipeDocument3 pagesDNF Stand PipeChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Tensile Properties of Ground Coffee Waste Reinforced Polyethylene CompositeDocument4 pagesTensile Properties of Ground Coffee Waste Reinforced Polyethylene CompositemhmmdzulvaNo ratings yet
- Software Hardware ListDocument2 pagesSoftware Hardware ListjackNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis DATADocument60 pagesFinal Thesis DATAdahaletushar75No ratings yet
- Unit 5 GeosyntheticsDocument315 pagesUnit 5 Geosyntheticskowshik1737551No ratings yet
- Computer Netwroks 15CS52: Venugopala Rao A S Assistant Professor (Senior) Dept of CSE, SMVITM BantakalDocument12 pagesComputer Netwroks 15CS52: Venugopala Rao A S Assistant Professor (Senior) Dept of CSE, SMVITM BantakalVenugopal RaoNo ratings yet
- Cfw300 Manual 1Document124 pagesCfw300 Manual 1maurilioNo ratings yet
- AKSML 230 - 33 KV - Sheet1Document2 pagesAKSML 230 - 33 KV - Sheet1Arif HossenNo ratings yet
- Bosch Powerpack-BrochureDocument16 pagesBosch Powerpack-BrochurengazawooNo ratings yet