Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Roles and Responsabilities
Uploaded by
Shanaka AshanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Roles and Responsabilities
Uploaded by
Shanaka AshanCopyright:
Available Formats
Project Roles and Responsibilities Template
Purpose
The purpose of this document is to provide a summary of the primary roles in the X project and the responsibilities associated with each role. A roles and responsibilities spreadsheet also maps the roles and assigned responsibilities on the date of creation. (These roles and responsibilities will change over the course of the project.)
Scope
The roles and responsibilities described encompass those of the internal X project team and its primary sponsors.
Authorized by
Mr. or Ms. X Project Manager Mr. or Ms. X Project Sponsor
Maintained by
Version
.01 .02 1.0
Date
Author
Description
Approved
Definitions
Term Role Responsibility Area of responsibility Artifact Definition A project role is an assignment on the project team. Project authority to take action, make decisions, and initiate action. Areas identified as important to the success of the project. A work product produced during the course of the project. Also called a deliverable. There are two categories of artifacts: 1) artifacts that lead to the finished product (i.e., requirements document) and 2) artifact used to manage the project (i.e., work breakdown structure planning document).
Acronyms
Acronym SME BA Subject matter expert Business analyst Description
2002 TechRepublic, Inc. www.techrepublic.com. All rights reserved.
Project Roles and Responsibilities Template
Summary
Within the X project environment, a clear definition of the roles and responsibilities that individuals play will be critical to the success of the project. Throughout the course of the project, the role an individual plays, or the hat that is worn, may change. In addition, an individual may play more than one role simultaneously. Individuals must understand the roles they play to know what responsibilities they have in making decisions, taking actions, reporting, and reviewing. Role definition benefits the project by: Bringing order to the chaos of a normal project. Allowing the team to reach perform stage of development faster. Keeping people from performing redundant activities. Creating a job description. Predetermining decision-making responsibility. Identifying personal responsibility for success at the beginning of the project. Reducing confusion about who does what when. Everyone on the project team holds the role, or wears the hat, of a project team member. Each team member is responsible for understanding the other roles and responsibilities. A detailed mapping of the X project roles and responsibilities is provided on the attached spreadsheet. Each project team member should refer to the matrix when assigned a role on the team. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
Project roles
A project role is an assignment on the project team. Its similar to a job description. A team member can have one or more roles at the same time. A persons role may be temporary or last for the life of the project. For example, one person may have the role of team lead, artifact owner, and SME. When the artifact is completed, baselined, and the project phase is complete, the person would relinquish those roles and take on the responsibility of the next role assigned. Some roles, like project sponsor, project manager, project control office, or project track lead, will last over the course of the project track, project, or program. At certain times, the persons wearing these hats may be asked to put on the hat of a different role, like business analyst (BA) or SME. While assuming that role, the responsibilities also change. To facilitate smooth team interactions and clear lines of authority and responsibility, every person on the team should identify which role he or she is filling when giving direction, making decisions, calling meetings, or reviewing artifacts.
Project responsibilities
When a team member is assigned a role on the project, he/she is given certain responsibility and the authority to take action or make decisions. On most projects, responsibilities usually fall into process steps: 1. Initiate: Start action on a project track, project phase, artifact, or task. As long as the action taken is within the scope of the project, the person who is given authority to initiate action can do so without being directed by management. Usually, initiating action takes place before a completed plan is in place. The major output of initiating is moving to the planning responsibility. The same person may or may not also be involved with the planning role. For example, the project manager may initiate a project track and turn it over to the project track lead for detailed planning. 2. Plan: Some roles require planning. The roles associated with planning are project manager, project track lead, and artifact owner. The person doing the planning can use other persons (business process SME, technical SME, project sponsor) to create effective plans. Major outputs of the planning responsibilities are an approved plan, an artifact, or the project.
2002 TechRepublic, Inc. www.techrepublic.com. All rights reserved.
Project Roles and Responsibilities Template
3. Implement: Roles that are responsible for implementing a plan are usually those associated with completing tasks on the project plan. Some of these roles are: team lead, artifact owner, author, developer, and tester. The output of implementation is work produced to create an artifact that leads to building the finished product. 4. Monitor: The monitoring responsibility is assigned to a variety of roles. Monitoring is not to be confused with reporting. A status report may capture some of the results of monitoring. However, monitoring may also involve problem solving and coaching. Monitoring is an active responsibility. For example, a team lead will monitor the progress of the artifact owners and developers working on the tasks of the plan. If the artifact is not being produced to plan, that person has the responsibility of understanding what problems exist that prevent implementing the plan. It may be that the plan needs revision. If that's the case, the problem can be escalated to the role that had the planning responsibility and those who approved the plan. Conversely, the individual who is implementing the plan may not fully understand the specifications, plan, or objectives of the project. In that instance, the monitoring individual can coach the implementer with a review of the specifications, plans, or project objectives. Outputs of the monitoring responsibility are verification that the plan is on track, minor coaching, reporting, and requests for assistance. 5. Controlling: The roles that assume responsibility for controlling are those that own a process or artifact. For example, the project track lead, team lead, or artifact owner can take corrective action when the monitoring indicates the project or artifacts are not being created or produced as designed or planned. Controlling is a reactive responsibility. The same person may have the role of monitoring and controlling an artifact. Once monitoring responsibilities are fulfilled, the request for assistance can lead to a decision, counseling, new planning, and resetting scope. One aspect of controlling is the responsibility for preventing the project scope from changing after it has been baselined. This is accomplished through the core processes of change management and risk management. The owners and administrators of these two core processes have the responsibility for administering the processes. The scope change control and responsibility is built into the process and is not assumed by an individual. However, within the process, certain roles are identified that have the responsibility of making scope change decisions. 6. Closure: It is the responsibility to close out anything that was initiated. A project track, project phase, artifact, or task needs closure. It is usually the responsibility of the role of owner to conduct closure. Some tasks associated with closure are archiving drafts and baselined artifacts, contract closure, celebrating, reviewing, lessons learned, knowledge transfers, and hand-offs to the next user of the artifacts.
Deliverables responsibilities
Because this is a deliverables-based project, we have created two additional responsibilities: primary owner and secondary owner. These responsibilities are associated with either an artifact or a process. Primary owner: The responsibility of primary owner combines the responsibilities of planning, implementing, and monitoring. In addition, the responsibility includes assuring that the necessary quality, change, and risk processes are applied to the artifact or process. Secondary owner: The responsibility of secondary owner usually applies to project processes. For example, the change management process can have a primary owner who initiated, planned, and implemented the process. The responsibility of the secondary owner is monitoring and controlling. Additional responsibilities include holding meetings as required by the process, maintaining logs, and facilitating decisions.
Oversight responsibilities
Because the project has active sponsors, a business unit driving the project, and a client/project team relationship, we assign approval responsibilities: approval, reporting, and assigning.
2002 TechRepublic, Inc. www.techrepublic.com. All rights reserved.
Project Roles and Responsibilities Template
Approval: Responsibility for approval normally occurs with a plan, process, or decision that affects project scope, methodology, or artifact creation. Sponsors have approval responsibility for WBS, project processes, and other project plans. The project manager assumes responsibility for approving project work plans, artifact/QC plans, and QC sign-offs. The project track lead approves tasks, resource assignments, and work time estimates. The Sponsor approves the project managers request for acquiring new project resources. Reporting: Every project team member has the responsibility for reporting. A more complete description of the roles and responsibilities for reporting is provided in the communications plan. A high-level description of the responsibility is to have it roll up from team lead to project track lead to project manager to sponsor to advisory committee. Assigning: Assignment mostly covers acquiring and allocating resources to tasks. Although the responsibility for acquiring resources belongs to the project manager, the project track lead and project manager jointly assign them to ownership of artifacts and resources to tasks.
Roles and responsibilities matrix
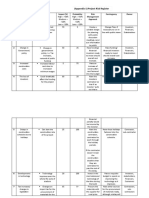
The roles and responsibilities for the X project are presented in the chart below. To read the chart, a project team member should determine what role one is playing at any point and what area of responsibility is of concern. See the chart legend for letter designations. They correspond to the responsibilities described in this document. For example, if a person is assigned as an artifact owner and wants to determine his or her responsibilities for the tasks to create the artifact, he or she would read across and find the letters: E, F, H. Referring to the chart legend, the artifact owner is responsible for E = implementing the task, F = controlling the task, and H = closing the task. (Note: You can substitute what weve provided here with your own team member titles or other tasks in your project that are not included here.)
Roles and responsibilities legend
A B C D E F G H I J L Primary ownership: Creation Secondary ownership: Administering Initiating Planning Implementing Controlling Monitoring Closing Approving Reporting Assigning
2002 TechRepublic, Inc. www.techrepublic.com. All rights reserved.
Project Roles and Responsibilities Template
Roles and responsibilities matrix
Project schedule Desktop Support External communications Internal communications WBS definition Project status Project scope
Project sponsor Project manager Project control office Project track lead Phase team lead Artifact owner Artifact author Artifact developer Business analyst SR. Business analyst Technical analyst System architect Methodology SME Subject matter expert Content provider Technical writer Business writer Quality assurance auditor Quality control technician G,J D,E C,D,F F E
C,F D,E F C,D,J
G C,J D,E,F,J J C,E,H D,E,F,H E,F,H E,F,F D G
I C D,L F C,D,E E,F,H E E E E E E
H E E D C D C,H
C C D
G C,E C,D E E C D C,G D
D E D G C G
E E E E J J J J
G,J
G,J H,J
2002 TechRepublic, Inc. www.techrepublic.com. All rights reserved.
Work Environment
Project task
Scheduling (rooms, meetings)
Resources
Project processes
Archiving
Artifact
You might also like
- Terms of ReferenceDocument2 pagesTerms of ReferenceSeble GetachewNo ratings yet
- 8 - Project Risk ManagementDocument64 pages8 - Project Risk ManagementMohammed AdelNo ratings yet
- F4-40-03 Context & Interested Parties RegisterDocument3 pagesF4-40-03 Context & Interested Parties RegisterGerritNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Project Risk ManagementDocument38 pagesChapter 12 Project Risk ManagementJaya ShresthaNo ratings yet
- KPI For ProjectDocument6 pagesKPI For ProjectAhmed Imtiaz Rao100% (1)
- Bec 3324: Project Management Year Iii - Semester Ii Session 7Document35 pagesBec 3324: Project Management Year Iii - Semester Ii Session 7Tharindu PereraNo ratings yet
- Project Risk Management TemplateDocument6 pagesProject Risk Management TemplateJr HaumaNo ratings yet
- Process Improvement PlanDocument10 pagesProcess Improvement PlanRamyaNo ratings yet
- L04 Qualitative Risk AnalysisDocument14 pagesL04 Qualitative Risk AnalysisDimitris KokkalisNo ratings yet
- Risk ManagementDocument127 pagesRisk ManagementAkhileshkumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Project Control Framework Handbook v2 April 2013Document58 pagesThe Project Control Framework Handbook v2 April 2013Angie DunnNo ratings yet
- HSBC Bank Malaysia Berhad ("The Bank") Board of Directors Terms of ReferenceDocument26 pagesHSBC Bank Malaysia Berhad ("The Bank") Board of Directors Terms of ReferenceAmrezaa IskandarNo ratings yet
- Pertmaster Risk RegisterDocument8 pagesPertmaster Risk RegisterDhanes PratitaNo ratings yet
- All ITTO For Risk ManagementDocument1 pageAll ITTO For Risk ManagementSohaib Omer SalihNo ratings yet
- Project Risk ManagementDocument16 pagesProject Risk ManagementMAXWELL gwatiringaNo ratings yet
- C M P (P N) : OST Anagement LAN Roject AMEDocument7 pagesC M P (P N) : OST Anagement LAN Roject AMERoqaia AlwanNo ratings yet
- Governance Management Plan: (Insert Department Name) (Insert Project Name)Document12 pagesGovernance Management Plan: (Insert Department Name) (Insert Project Name)ohhelloNo ratings yet
- Interface Management PDFDocument2 pagesInterface Management PDFEdwin HarrisNo ratings yet
- Roles and Responsibilities TemplateDocument5 pagesRoles and Responsibilities Templatebrajeshsinghfdd100% (2)
- Document Development Life CycleDocument2 pagesDocument Development Life Cyclekronos047100% (1)
- You Exec - Risk Management FreeDocument9 pagesYou Exec - Risk Management FreeJuan GómezNo ratings yet
- A Practical Approach To Creating A Risk Management PlanDocument4 pagesA Practical Approach To Creating A Risk Management PlanNicoleAbdon0% (1)
- Project ControlDocument23 pagesProject ControlSanduni jayarathneNo ratings yet
- (Appendix 1) Project Risk RegisterDocument4 pages(Appendix 1) Project Risk RegisterDave RobertsNo ratings yet
- Gate Review DeadlinesDocument38 pagesGate Review Deadlinesअमित अम्बर गुप्ताNo ratings yet
- Risk Register for Project FlipDocument1 pageRisk Register for Project Flipravapu345No ratings yet
- Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesRoles and Responsibilitiespolters67% (3)
- Risk RegisterDocument4 pagesRisk RegisterSujan SarkarNo ratings yet
- SE Environmental Policy SampleDocument2 pagesSE Environmental Policy SampleJEXNo ratings yet
- Contractor Management GuidelinesDocument60 pagesContractor Management GuidelinesRickyNo ratings yet
- Cost Management PlanDocument14 pagesCost Management PlanohhelloNo ratings yet
- D1.2 Project Management Plan PDFDocument41 pagesD1.2 Project Management Plan PDFREYMOND SIREGARNo ratings yet
- Sample Risk Breakdown StructureDocument1 pageSample Risk Breakdown StructureAkhileshkumar PandeyNo ratings yet
- Project Risk Management 2016Document58 pagesProject Risk Management 2016venkaatram0% (1)
- Construction Auditingby Ron RisnerDocument2 pagesConstruction Auditingby Ron RisnerdemirciferhatNo ratings yet
- Process Group and Knowledge Area Interaction - Excel TemplateDocument4 pagesProcess Group and Knowledge Area Interaction - Excel TemplateHaroon Ahmed0% (1)
- Facilities Management RFP ExampleDocument74 pagesFacilities Management RFP Exampleeriel_ramos100% (1)
- PMP Comprehensive NotesDocument27 pagesPMP Comprehensive NotesAhmed Awed100% (1)
- Project Planning Transition ChecklistDocument3 pagesProject Planning Transition ChecklistBhupinder Singh100% (1)
- Project Manager Roles and ResponsibilitiesDocument5 pagesProject Manager Roles and ResponsibilitiesKandid2uNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan Build-out ProjectDocument6 pagesRisk Management Plan Build-out ProjectJohn Tonya BuckNo ratings yet
- Supporting Doc Risk MGMT Plan TDocument9 pagesSupporting Doc Risk MGMT Plan TSujiya KhanNo ratings yet
- Project Risk Assessment SpreadsheetDocument9 pagesProject Risk Assessment Spreadsheetfakhro100% (7)
- Roles and Responsibilities TemplateDocument5 pagesRoles and Responsibilities TemplateJeevan VicknesNo ratings yet
- A24 Appendix A Construction Risk Register PDFDocument6 pagesA24 Appendix A Construction Risk Register PDFHammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Contractor Performance PracticeDocument7 pagesContractor Performance PracticeJohn SambulaNo ratings yet
- 04 - Human Resource PlanDocument10 pages04 - Human Resource PlanMohammed AffrozeNo ratings yet
- Crisis Management & Business Continuity Planning: Andrew HilesDocument6 pagesCrisis Management & Business Continuity Planning: Andrew HilesJuvy Macapagal100% (1)
- Project Risk Management: Identify RisksDocument53 pagesProject Risk Management: Identify RisksYasi EemoNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesRisk Management Plan TemplateAlfonso Enrique Núñez Nieto100% (1)
- Quality: To Meet Product or Service Specifications and ExpectationsDocument13 pagesQuality: To Meet Product or Service Specifications and ExpectationsmaelikahNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment of Construction ProjectsDocument15 pagesRisk Assessment of Construction ProjectsAshokNo ratings yet
- Risk RegisterDocument9 pagesRisk RegisterKingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Project ExecutionDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Project ExecutionczuberekNo ratings yet
- Risk Register TemplateDocument20 pagesRisk Register TemplatesavasgNo ratings yet
- Risk Management Plan SampleDocument13 pagesRisk Management Plan SampleRonna GasconNo ratings yet
- Project Lesson Learned SummaryDocument1 pageProject Lesson Learned SummaryYousuf HussainNo ratings yet
- Project Roles and ResponsabilitiesDocument5 pagesProject Roles and ResponsabilitiesShanaka AshanNo ratings yet
- Project Roles and ResponsabilitiesDocument5 pagesProject Roles and ResponsabilitiesShanaka AshanNo ratings yet
- Project Director Role ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesProject Director Role ResponsibilitiesShanaka AshanNo ratings yet
- Floor Area RatioDocument3 pagesFloor Area RatioShanaka AshanNo ratings yet
- Project Engineer Job ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageProject Engineer Job ResponsibilitiesShanaka AshanNo ratings yet
- Marcet Boiler: Page 1/2 12/2009Document2 pagesMarcet Boiler: Page 1/2 12/2009Shanaka AshanNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument6 pagesThermodynamicsVijay NidagalkarNo ratings yet
- Your One Source In Water Systems Product Catalog 2008Document44 pagesYour One Source In Water Systems Product Catalog 2008Gerry Dan ChanliongcoNo ratings yet
- SUMMER TRAINING REPORT AT Elin Electronics Ltd. Gzb.Document54 pagesSUMMER TRAINING REPORT AT Elin Electronics Ltd. Gzb.Ravi Kumar100% (3)
- NV 24 Globe ActuatorDocument12 pagesNV 24 Globe ActuatorRodrigo AlvesNo ratings yet
- Motori Industriali Serie ASC Da 160 A 315mmDocument52 pagesMotori Industriali Serie ASC Da 160 A 315mmdungga1No ratings yet
- BIT3251 BIT3251 BIT3251 BIT3251 應用指南 應用指南 應用指南 應用指南: Beyond Innovation TechnologyDocument10 pagesBIT3251 BIT3251 BIT3251 BIT3251 應用指南 應用指南 應用指南 應用指南: Beyond Innovation TechnologyHamza AbbasiNo ratings yet
- DAILY DRILLING REPORTDocument2 pagesDAILY DRILLING REPORTThế Tài HoàngNo ratings yet
- Gulf Harmony AW 46 Data SheetDocument1 pageGulf Harmony AW 46 Data SheetRezaNo ratings yet
- Oracle PLSQL Best Practices and Tuning PDFDocument270 pagesOracle PLSQL Best Practices and Tuning PDFKeyur Pandya100% (1)
- CMM49 14 01 MtocDocument2 pagesCMM49 14 01 MtocMichail K100% (1)
- IECDocument52 pagesIECM.r. Munish100% (2)
- Sda-02-Dd-02 - Pile & Pile Cap - Sheet-1 - R0Document1 pageSda-02-Dd-02 - Pile & Pile Cap - Sheet-1 - R0Himani PatelNo ratings yet
- Unitrans ZXONM E300 (V3.17) Installation ManualDocument35 pagesUnitrans ZXONM E300 (V3.17) Installation ManualMohamed YagoubNo ratings yet
- Step by Step Process To Run BEX Report in BackgroundDocument23 pagesStep by Step Process To Run BEX Report in Backgroundalcast007No ratings yet
- Catalog Filters PDFDocument53 pagesCatalog Filters PDFAlexandre Hugen100% (1)
- PF0060 KR QUANTEC Pro en PDFDocument2 pagesPF0060 KR QUANTEC Pro en PDFdanipopa_scribdNo ratings yet
- InRoom Tech Data 31010 ApcDocument92 pagesInRoom Tech Data 31010 ApcRolandoNo ratings yet
- Notice: Applications, Hearings, Determinations, Etc.: Southern Star Central Gas Pipeline, Inc.Document2 pagesNotice: Applications, Hearings, Determinations, Etc.: Southern Star Central Gas Pipeline, Inc.Justia.comNo ratings yet
- StradaDocument4 pagesStradayzk14No ratings yet
- HuskyDocument10 pagesHuskypreetimurali100% (1)
- Barangay Profile: (BP DCF No. 1 S. 2022)Document4 pagesBarangay Profile: (BP DCF No. 1 S. 2022)AiMae BaobaoenNo ratings yet
- Manual (4906-9127)Document6 pagesManual (4906-9127)LuisCabreraOroscoNo ratings yet
- Orace Rac TafDocument4 pagesOrace Rac TafNst TnagarNo ratings yet
- Jinal Black BookDocument7 pagesJinal Black Bookhardik patel0% (1)
- Blast Furnace Cooling System MonitoringDocument27 pagesBlast Furnace Cooling System MonitoringAnil MistryNo ratings yet
- iPLON India SolutionsDocument4 pagesiPLON India Solutionssudhirm16No ratings yet
- Finaldc 2Document10 pagesFinaldc 2Noel BactonNo ratings yet
- NATO Tactical Nuclear Weapons in EuropeDocument35 pagesNATO Tactical Nuclear Weapons in EuropeMaria Mont' SerratNo ratings yet
- BASH Shell Scripting SyllabusDocument4 pagesBASH Shell Scripting SyllabusAdzmely Mansor100% (1)
- Dome AbcsDocument1 pageDome AbcsRiddhi BhutadaNo ratings yet
- Why Geomechanical Reservoir KpiDocument43 pagesWhy Geomechanical Reservoir KpiKevin MusterNo ratings yet