Professional Documents
Culture Documents
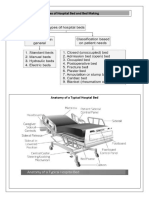
Bed Making
Uploaded by
Kai PesquiraCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Bed Making
Uploaded by
Kai PesquiraCopyright:
Available Formats
Bed Making Objectives: After 4 hours of varied classroom activities, the level I students will be able to: I.
Define the following terms:
I.1 Bed Making process of making the bed that will add to ones comfort. I.2 Fan Fold to lay one part over or against another part. I.3 Mitered corner used at most corners of the beds for sheets, blanket and bed spreads to secure bed cloths while beds are occupied. I.4 Toe Pleat a fold mode in the top bed clothes to provide additional space for patients toes. I.5 Foot Drop dropping of the foot from paralysis of the anterior muscle of the leg. I.6 Bed Cradle contains a cradle ( a device for holding the top covers of the feet). I.7 Magic Corner a special type of fold that serves as guide for an easier spreading of the linens. II. Enumerate the purpose of bed making
II.1Help patients to secure proper rest and comfort which are essential for health and refresh them by providing clean linen. 2.2 Provide care for patients to lessen fatigue. 2.3 Preventing patients from skin irritation. 2.4 To make bed look neat and clean and for psychological comfort and rest. 2.5 Changing beds is part of maintaining hygiene. 2.6 The client is able to carry in normal body activities. III. Discuss the types of bed
III.1 Closed Bed a bed which is made following the discharge of a patient in preparation for a new patient. The spread covers the top linens and extends to the head of the mattress and sometimes covers the pillow. The beddings and pillow are kept clean by this method. III.2 Open Bed frequently used to refer to the type of bed making employed when the bed has been assigned to a new patient, or it may refer to any bed occupied by a patient. Spread is turned under the top of the blanket. The top sheet is turned over the top of the blanket. Bed is opened to whatever width the patient desires. Usually, the top bedding is fan folded to the foot of the bed to make it easy for the patient to get in. III.3 Occupied Bed patient must remain in bed constantly. When finished, the top covers are made into a fold similar to the open bed. Making the bed using new linens while the patient is on the bed.
III.4
Unoccupied Bed
A. Closed Bed arranging clean bed lines in preparations for patient to be admitted. Bed isnt used; no patient in it. B. Open Bed arranging or preparing the bed for newly admitted patients. Could be faded diagonally and fan folded side wards. Top covers are folded back (easier for clients to get in) III.5 Post operative Bed arranging bed linens to receive the patient who had just undergone surgery III.6 Anesthetic Bed sometimes called recovery bed IV. Explain the principles of Bed Making
IV.1 Sociology nurse should listen as how to talk to patients; should know the subject of conversation interests the patient; alleviates stress. IV.2 Body Mechanics most important to prevent quick tiring, back problems, muscle pain and maintain body mechanics or alignment. IV.3 Anatomy and Physiology body events uneven points of pressure against different areas of the mattress and pressure is greatest of all points of prominence or of great weight. IV.4 Chemistry wooden blanket fibers may cause irritation to the patients skin, there must always be a sheet to separate blanket from patient, and strong detergent soaps may cause irritation if knees are not thoroughly rinsed. IV.5 Microbiology pathogenic microorganisms may be transferred from the source to a new host directly by contaminated linen; wash hands before and after making a bed, bed linen should be folded away from your body to minimize transfer of microorganisms to clothing; fanning bed clothing, stirs up bacteria in the air. IV.6 Physics (good posture should be maintained when changing linens) irritation bed sores. IV.7 Physiology comfort for the patient is the psychology basic idea beyond goal workmanship. V. Identify the different kinds of linen
V.1Linen made of softly generally like home linen but is made for hospital purposes. V.2Pillowcase use to cover the pillow. V.3Blanket large piece of cloth, often soft, woolen and is used for warmth as a bed cover. V.4Top Sheet used to cover the patient to provide warmth as a bed cover; made of thick cotton; thermal material. V.5Cotton Draw Sheet piece of cloth that covers rubber sheet and is used to absorb and protect moisture. V.6Bottom Sheet used to cover the bed after mattress cover. V.7Rubber Sheet used to protect the bottom sheet.
V.8Mattress Cover piece of cloth to cover mattress V.9Woolen blanket large rectangle piece of soft fabric often with bound edges used especially for warmth as a bed covering should be light, warm and large enough to cover whatever shoulder and to tuck in well at foot and extend over sides of the bed. VI. Differentiate the common bed positions:
6.1 Flat mattress is completely horizontal; client sleeping in a variety of bed positions, such as back-lying, side-lying and prone (face down). To maintain spinal alignment for client with spinal injuries. To assist client to move and turn in bed. Bed making by nurse. 6.2 Fowlers Position semi position in which head of bed is raised to angle of at least 45 degrees. Knees may be flexed or horizontal. Convenient for eating, reading, visiting, watching TV. Relief from lying positions and to promote lung expansion for client with respiratory problem. To assist a client to a position on the edge of the bed. 6.3 Semi Fowlers Position head of bed raised only 30 degrees angle. Relief from lying position and to promote lung expansion 6.4 Trendelenburgs Position head of bed lowered and rose in a straight line. Promote venous circulation in certain clients and provide postural drainage of basal lungs lobes. 6.5 Reverse Trendeleburgs Position head of bed raised and the foot lowered. Straight tilt in direction opposite to trendelenburgs position. To promote stomach emptying and prevent esophageal reflexes in clients with niatal hernea. VII. State the guidelines of bed making
VII.1 Wash hands before you begin and after you finish bed making. VII.2 Soiled linen should never be come in contact with nurses uniform. VII.3 Linen of the client is never placed on another clients bed. VII.4 Soiled linen is placed directly in a potable linen hanger or locked in a pillow case at the end of the bed before it is gathered up in a disposable linen hanger. VII.5 Soiled linen is never shaken in the air to avoid spreading of microorganism. VII.6 Consume time and energy by gathering all necessary materials. VII.7 Before you start bed making, you are supposed to have environmental sanitation. VII.8 Be sure to maintain body mechanics while performing the procedure.
You might also like
- The VedasDocument6 pagesThe VedasKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- The VedasDocument6 pagesThe VedasKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Surrogacy AgreementDocument29 pagesSurrogacy AgreementMacduff RonnieNo ratings yet
- Lab Test Results 7 2015Document3 pagesLab Test Results 7 2015Antzee Dancee0% (1)
- Ayurvedic KalpaDocument171 pagesAyurvedic KalparagalwarNo ratings yet
- Positioning & Draping: Positio Ning & DrapinDocument8 pagesPositioning & Draping: Positio Ning & DrapinBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology AnswersDocument4 pagesRespiratory Physiology AnswersRamya100% (2)
- CHECKLIST-On-Shampooing Patient's Hair in Bed265Document2 pagesCHECKLIST-On-Shampooing Patient's Hair in Bed265Blessie Fernandez0% (1)
- Pressure Sores Beds and Mattresses Against Pressure SoresDocument16 pagesPressure Sores Beds and Mattresses Against Pressure SoresChris PapadimitriouNo ratings yet
- MRCP PacesDocument243 pagesMRCP PacesTank Tank94% (17)
- Revised Market Potential Estimates for Biopure's Hemopure Based on Competitive LandscapeDocument4 pagesRevised Market Potential Estimates for Biopure's Hemopure Based on Competitive Landscapeargand_xw9097No ratings yet
- Gowning and Gloving EvaluationDocument2 pagesGowning and Gloving EvaluationAbegael BuyayaweNo ratings yet
- Nursing Bullets: Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewerDocument44 pagesNursing Bullets: Fundamentals of Nursing ReviewerErl DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Body Mechanics and MobilityDocument24 pagesBody Mechanics and MobilitySori KasasaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Historical Perspectives of Nursing InformaticsDocument33 pagesLesson 1.1: Historical Perspectives of Nursing InformaticsJustine Jean GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Care of The Clients With CancerDocument78 pagesCare of The Clients With Cancercasandra moranteNo ratings yet
- 1zlaboratory ProceduresDocument81 pages1zlaboratory ProceduresJAYNE NICOLE M. MOTILLA (Warka)100% (1)
- Open GlovingDocument13 pagesOpen GlovingShing Mae MarieNo ratings yet
- Bed MakingDocument63 pagesBed MakingHerzl Loraine Prio100% (1)
- Principles of Sterile Technique: Them That Varies. These Principles Are Applied in TheDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Sterile Technique: Them That Varies. These Principles Are Applied in Thecoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Ozone Therapy in DentistryDocument16 pagesOzone Therapy in Dentistryshreya das100% (1)
- RLE Bag TechniqueDocument22 pagesRLE Bag TechniqueJa Flores100% (1)
- Essential Newborn Care ProtocolDocument30 pagesEssential Newborn Care ProtocolGwendareign ElizanNo ratings yet
- Principles OF Sterile Technique: Prepared By: Mrs. R. M. Dimalibot RM, RN ManDocument36 pagesPrinciples OF Sterile Technique: Prepared By: Mrs. R. M. Dimalibot RM, RN ManCerisse RemoNo ratings yet
- Mar ChecklistDocument18 pagesMar ChecklistMin MawNo ratings yet
- MALNUTRITIONDocument23 pagesMALNUTRITIONPrincess Alane MorenoNo ratings yet
- NCM 105 - NDDocument2 pagesNCM 105 - NDYsabelle GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Through The Lifespan and Diet and Disease BackupDocument67 pagesNutrition Through The Lifespan and Diet and Disease BackupJessica SnowNo ratings yet
- Orthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic CenterDocument7 pagesOrthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic Centerhannjazz100% (5)
- Family Health AssessmentDocument13 pagesFamily Health AssessmentKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Bioethics Final ExaminationDocument11 pagesBioethics Final ExaminationJonah reiNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care With ChecklistDocument5 pagesTracheostomy Care With ChecklistHollan GaliciaNo ratings yet
- Stufflebeam 2003 The Cipp Model For Evaluation by Daniel L StufflebeamDocument68 pagesStufflebeam 2003 The Cipp Model For Evaluation by Daniel L StufflebeamAnonymous T5PT3U100% (1)
- Surgical InstrumentDocument10 pagesSurgical InstrumentBabylyn PuruggananNo ratings yet
- Care of Mother and Child Nursing ModuleDocument37 pagesCare of Mother and Child Nursing ModuleFregen Mae ApoyaNo ratings yet
- Safety Data Sheet: Ultrasil® VN 3 (Insilco)Document6 pagesSafety Data Sheet: Ultrasil® VN 3 (Insilco)Bharat ChatrathNo ratings yet
- Checklist Unoccupied PDFDocument1 pageChecklist Unoccupied PDFJas SofiaNo ratings yet
- Types of Bed and MattressDocument30 pagesTypes of Bed and MattressConvalescent Nursing HomeNo ratings yet
- Core Bedmaking SkillsDocument22 pagesCore Bedmaking SkillsDyrom Aquino TorioNo ratings yet
- TEPID SPONGE BATHDocument3 pagesTEPID SPONGE BATHJeonoh FloridaNo ratings yet
- How to Perform Suctioning for an Intubated PatientDocument24 pagesHow to Perform Suctioning for an Intubated PatientLanz LlnsNo ratings yet
- NUTRITIONALASSESSMENT27102018PSMDocument48 pagesNUTRITIONALASSESSMENT27102018PSMRomani Pal100% (1)
- Foundation of Nursing AsepsisDocument34 pagesFoundation of Nursing AsepsisYemaya84No ratings yet
- Perilite and Hot SitzDocument11 pagesPerilite and Hot SitzJyra Mae TaganasNo ratings yet
- Case Study ScriptDocument5 pagesCase Study ScriptTRECHIA DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Perineal CareDocument3 pagesPerineal CareNikko Rafael RobillosNo ratings yet
- HandwashingDocument35 pagesHandwashingJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNo ratings yet
- Return Demonstration Evaluation Tool For: Unoccupied BedDocument9 pagesReturn Demonstration Evaluation Tool For: Unoccupied BedAshley Blaise JoreNo ratings yet
- SDG - Decent Work and Economic GrowthDocument17 pagesSDG - Decent Work and Economic GrowthMuhammad AzharNo ratings yet
- The Normal Anthropometric Measurements For HealthyDocument43 pagesThe Normal Anthropometric Measurements For HealthyAli Mohamed BurhanNo ratings yet
- Fundal Height DefinedDocument2 pagesFundal Height Definedervin0122No ratings yet
- Legaspi - Preparing Medication From A Vial ChecklistDocument4 pagesLegaspi - Preparing Medication From A Vial ChecklistJason LumayaNo ratings yet
- Cleansing Bed Bath: General ObjectivesDocument3 pagesCleansing Bed Bath: General ObjectivesPauline AñesNo ratings yet
- DispencingDocument19 pagesDispencingushaeatakotaNo ratings yet
- Home Visit: Barangay Health ServicesDocument32 pagesHome Visit: Barangay Health ServicesNessa Layos MorilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson Notes - Bed BathDocument5 pagesLesson Notes - Bed BathNicole Marin-ChingNo ratings yet
- Principles of Aseptic Technique in An Operating Room1Document2 pagesPrinciples of Aseptic Technique in An Operating Room1Joezerk Jhon Biel100% (1)
- Clinical Laboratory Techniques GuideDocument41 pagesClinical Laboratory Techniques GuideBalaji GandhiNo ratings yet
- Heimlich Maneuver PDFDocument7 pagesHeimlich Maneuver PDFMark DomingoNo ratings yet
- Bag TechniqueDocument3 pagesBag TechniqueBryan DimenNo ratings yet
- SHAMPOOING HAIR IN BED: 27-STEP PROCEDUREDocument3 pagesSHAMPOOING HAIR IN BED: 27-STEP PROCEDUREDuchess Juliane Jose MirambelNo ratings yet
- Fundal Height: Regala, Bianca Ysabelle M. RLE Group IV BSN Ii-BDocument15 pagesFundal Height: Regala, Bianca Ysabelle M. RLE Group IV BSN Ii-BBiway RegalaNo ratings yet
- Ncma216.Pharma Chemotherapeutics Part 1 Antimicrobial AgentsDocument50 pagesNcma216.Pharma Chemotherapeutics Part 1 Antimicrobial AgentsKhams TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Post Mortem Care ProceduresDocument4 pagesPost Mortem Care Proceduresamal abdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- 4sowing and Planting EquipmentsDocument102 pages4sowing and Planting EquipmentsLelisa TolesaNo ratings yet
- Making Beds: PerformanceDocument2 pagesMaking Beds: PerformanceNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- NURSING IS AN ART AND SCIENCEDocument6 pagesNURSING IS AN ART AND SCIENCEJo PigarNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and DietDocument11 pagesNutrition and DietMarie Nelle Escriba LimpocoNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric MeasurementDocument2 pagesAnthropometric MeasurementJames ClarkNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 R Laboratory Skills Pre Lim 2ND SemDocument23 pagesNCM 103 R Laboratory Skills Pre Lim 2ND SemCharles Matthew ErasmoNo ratings yet
- Final Examination Reviewer (Nha 100) Post Test C11Document13 pagesFinal Examination Reviewer (Nha 100) Post Test C11Prince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- NCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Document51 pagesNCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Richelle Joy Durano RegatunaNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument13 pagesSurgical InstrumentsMeshael HernandezNo ratings yet
- Bed MakingDocument5 pagesBed MakingHero ElevadoNo ratings yet
- Viii - Bed MakingDocument7 pagesViii - Bed MakingTuTitNo ratings yet
- D2220912Document1 pageD2220912Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Barili CulturalDocument13 pagesBarili CulturalKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Torrens System and Land Titles ExplainedDocument38 pagesTorrens System and Land Titles ExplainedKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Pesquira, John Kylle C. - Ace-Re-Assessment-Of-Fees-Acknowledgement-ReceiptDocument3 pagesPesquira, John Kylle C. - Ace-Re-Assessment-Of-Fees-Acknowledgement-ReceiptKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Final Rport of TBDocument26 pagesFinal Rport of TBKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Palawan Itinerary 2022Document2 pagesPalawan Itinerary 2022Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- D2220912Document1 pageD2220912Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- D2220912Document1 pageD2220912Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- D2220912Document1 pageD2220912Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- SCRPITDocument5 pagesSCRPITKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- D3 PrefsDocument1 pageD3 PrefsfreebookmanNo ratings yet
- Different Parts of A Plant CellDocument3 pagesDifferent Parts of A Plant CellKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- D3 PrefsDocument1 pageD3 PrefsfreebookmanNo ratings yet
- PL94654243Document14 pagesPL94654243Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Effects of Mercury Awareness Among Pharmacy StudentsDocument1 pageEffects of Mercury Awareness Among Pharmacy StudentsKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Excuse LetterDocument1 pageExcuse LetterKai Pesquira100% (1)
- Global Assessment of FunctioningDocument2 pagesGlobal Assessment of FunctioningKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Diffuse Type SystemDocument1 pageDiffuse Type SystemKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Adult DisordersDocument2 pagesAdult DisordersKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Charm (Chapter 5 10-18-2010)Document4 pagesCharm (Chapter 5 10-18-2010)Kai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of A Young Dicot RootDocument3 pagesAnatomy of A Young Dicot RootVanessa Leuterio0% (2)
- Ang Among English ThesisDocument12 pagesAng Among English ThesisKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- DepressionDocument2 pagesDepressionKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Management Information SystemsDocument17 pagesPharmaceutical Management Information SystemsKai Pesquira100% (3)
- Han Dynasty: China's Golden Age 202 BC-220 ADDocument14 pagesHan Dynasty: China's Golden Age 202 BC-220 ADKai PesquiraNo ratings yet
- Broadline Epar Public Assessment Report enDocument25 pagesBroadline Epar Public Assessment Report enPablo OrricoNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansDocument26 pagesNutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansFitriNo ratings yet
- Local Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmDocument1 pageLocal Anesthetic Systemic Toxicity AlgorithmSydney JenningsNo ratings yet
- Community Acquired PneumoniaDocument63 pagesCommunity Acquired PneumoniaLet BorlagdanNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Dosage Calculations A Multi Method Approach 0132158620Document13 pagesSolution Manual For Dosage Calculations A Multi Method Approach 0132158620RandallValdezypfqw100% (86)
- Melanoma Cancer PresentationDocument13 pagesMelanoma Cancer PresentationMerlyn JeejoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacovigilance Classification & CodingDocument42 pagesPharmacovigilance Classification & Codingrakesh meher0% (1)
- Personal health data for nursing studentDocument8 pagesPersonal health data for nursing studentJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- The Generic Pharmacy (Powerpoint)Document7 pagesThe Generic Pharmacy (Powerpoint)Ronelyn BritoNo ratings yet
- To Compare Rosuvastatin With Atorvastatin in Terms of Mean Change in LDL C in Patient With Diabetes PDFDocument7 pagesTo Compare Rosuvastatin With Atorvastatin in Terms of Mean Change in LDL C in Patient With Diabetes PDFJez RarangNo ratings yet
- Class III Cavity Treatment (Procedure, Materials)Document2 pagesClass III Cavity Treatment (Procedure, Materials)Manos KritikosNo ratings yet
- Proctor Tobacco History Report Canadian Trial Rapport - Expert - ProctorDocument112 pagesProctor Tobacco History Report Canadian Trial Rapport - Expert - Proctorkirk_hartley_1No ratings yet
- Copy (1) of New Text DocumentDocument2 pagesCopy (1) of New Text DocumentAkchat JainNo ratings yet
- Patch ClampDocument4 pagesPatch ClampXael GarciaNo ratings yet
- Dance BenefitsDocument9 pagesDance Benefitsapi-253454922No ratings yet
- Regulation5362014 Qa enDocument143 pagesRegulation5362014 Qa enmeiNo ratings yet
- Maxillofacial Privileges QGHDocument4 pagesMaxillofacial Privileges QGHSanam FaheemNo ratings yet
- MInTFM Programme Brochure 2019Document12 pagesMInTFM Programme Brochure 2019Shoban RajNo ratings yet
- BarryKuebler Lesson1 AssignmentDocument4 pagesBarryKuebler Lesson1 AssignmentBarry KueblerNo ratings yet