Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anthropology Fields Guide
Uploaded by
Denisse LimOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anthropology Fields Guide
Uploaded by
Denisse LimCopyright:
Available Formats
Anthropology
Fields of Anthropology
June 4, 2012
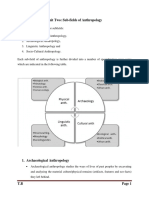
1) Biological (concerned most with human populations and how they vary biologically) a. Human paleontology/paleoanthropology Emergence of humans and their later evolution Studies fossils, bones, geological information on succession of climates, environments and plant and animal populations Paleontologists interested in behaviour and evolution of our closest relatives among mammals Primates b. Human variation How and why contemporary human populations differ in biological or physical characteristics Why do Eskimos and Africans have different body built? 2) Cultural a. Archaeology Study of past cultures Study artifacts (remains or past civilizations) ;; requires field work Most archaeologists deal with prehistory, time before written records. Historical archaeology studies the remains of recent people who left written records b. Archaeological/ anthropological linguistics i. Historical study of how languages changes over time and how they may be related (development) ii. Descriptive/ Structural How contemporary languages differ, especially in their construction (Discovering and recording the principles that determine how sounds and words are put in a speech) iii. Sociolinguistic study of how language is used in social context (what people speak about, how they interact conversationally, their attitudes towards speakers of other dialects/languages, and how people speak differently in different social contexts.) c. Ethnology (Cultural Anthropology) concerned with patterns of thought and behaviour(such as marriage customs, kinship organization, political and economic systems, religion, folk art and music, and with the many ways in which these patterns differ in contemporary societies) dynamics of culture (how cultures develop and change) relationship between beliefs and practices within a culture ***Ethnologists generally use data collected through observation and interviewing of living people, archaeologists must work with fragmentary remains of past cultures, then draw inferences from there. Type of Ethnologists i. Ethnographer o Usually spends a year or so living with, talking to, and observing the people whose customs he or she is studying provides customary behaviour and thought o Focus on how people live, know peoples culture o Various cultural studies to find out various sets of differences and similarities of people s culture
ii. Ethnohistorian o Prepared to study how the ways of life of a particular group of people have changed over time o Rely more on others documents (whereas ethnographers rely on their observations) o More concerned on history of people who did not leave written records o Tries to explain why certain changes in their life took place
Relevance of Anthropology Understanding of human beings everywhere Helps us avoid misunderstandings with people Alleviate some of the misunderstandings that arise between people of diff cultural groups from causes operating below level of consciousness As a world becoming interconnected, important to be able to respect cultural and physical differences, because it might lead to war if theres no respect
You might also like
- Anthropology: The Study of Human Diversity and Evolution Across Cultures and TimeDocument4 pagesAnthropology: The Study of Human Diversity and Evolution Across Cultures and TimeSign UpNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Unit Two PPPTDocument21 pagesAnthropology Unit Two PPPTesiyasmenNo ratings yet
- Chap-2-Sub Fields of AnthropologyDocument29 pagesChap-2-Sub Fields of Anthropologylemma4aNo ratings yet
- Antro AssigDocument5 pagesAntro Assigeyob abejeNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two SSNDocument9 pagesChapter Two SSNNikodimos BacosNo ratings yet
- .Antropology PP For Tepi Class - 1669541754000Document126 pages.Antropology PP For Tepi Class - 1669541754000reshadmuktar930No ratings yet
- Unit twoDocument24 pagesUnit twomogesalemu573No ratings yet
- Anthro-Short NoteDocument24 pagesAnthro-Short Notebirukmes2309No ratings yet
- Ermi Antro INTRODUCTIONDocument5 pagesErmi Antro INTRODUCTIONeyob abejeNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Is The Study of HumansDocument2 pagesAnthropology Is The Study of HumansLaura SacdalanNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Four Sub Fields of AnthropologyDocument11 pagesDiscuss The Four Sub Fields of AnthropologyKerala MekuriyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes in Ssci 4 (Socio-Anthropology) : Lesson 1Document5 pagesLecture Notes in Ssci 4 (Socio-Anthropology) : Lesson 1Deanne Mitzi SomolloNo ratings yet
- SOCANTHRODocument11 pagesSOCANTHROChristine AloyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Cultural Anthropology Chapter 1Document12 pagesIntroduction to Cultural Anthropology Chapter 1Lauren SabatinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter TwoDocument9 pagesChapter TwoMiliyonNo ratings yet
- Socio AnthroDocument17 pagesSocio AnthroMary Rose Sefulan SivaNo ratings yet
- What Is Anthropology - Fields of Anthropology PDFDocument5 pagesWhat Is Anthropology - Fields of Anthropology PDFAnonymous nHxkffNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anthropology: Department of Forensic Odontology, Faculty of Dentistry Airlangga UniversityDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Anthropology: Department of Forensic Odontology, Faculty of Dentistry Airlangga UniversityJanice HamdaniNo ratings yet
- Main Sub-fields of AnthropologyDocument23 pagesMain Sub-fields of AnthropologyBismah IbrarNo ratings yet
- What Is AnthropologyDocument9 pagesWhat Is AnthropologyLove NessieNo ratings yet
- Cultural Anthropology (ANTH 102)Document204 pagesCultural Anthropology (ANTH 102)mengleang measNo ratings yet
- What is Anthropology? The Study of HumanityDocument17 pagesWhat is Anthropology? The Study of HumanityNicole Geraldine Anne DagacanNo ratings yet
- What Is AnthropologyDocument2 pagesWhat Is AnthropologyROHAN KARALENo ratings yet
- Areas of Specialization .Document5 pagesAreas of Specialization .rosemariegalindo70No ratings yet
- What Is AnthropologyDocument10 pagesWhat Is AnthropologyAniaNo ratings yet
- Social Anthropology (Anth 1012) : Ministry of Science and Higher EducationDocument47 pagesSocial Anthropology (Anth 1012) : Ministry of Science and Higher EducationErmi Zuru100% (5)
- Anthropology Unit 1Document6 pagesAnthropology Unit 1Elsabet SamuelNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Basic Concepts in AnthropologyDocument11 pagesLesson 3 Basic Concepts in AnthropologySARAH JANE CAPSANo ratings yet
- Anthropology Chapter 1: Introducing Anthropology and Its Subject MatterDocument14 pagesAnthropology Chapter 1: Introducing Anthropology and Its Subject MatterHaromsa Bulto100% (1)
- Anthropology Note @NoteHeroBot (Chapters 1 & 2)Document28 pagesAnthropology Note @NoteHeroBot (Chapters 1 & 2)Mihretab DawitNo ratings yet
- Anthropology Unit 1 - 0907211459o7Document25 pagesAnthropology Unit 1 - 0907211459o7brightsunNo ratings yet
- Husen PPT AnthroDocument207 pagesHusen PPT AnthroYoomif TubeNo ratings yet
- Fields of AnthropologyDocument9 pagesFields of AnthropologyNaumanNo ratings yet
- Paper-I Unit 1 Ancient HistoryDocument6 pagesPaper-I Unit 1 Ancient Historyakhand kishoreNo ratings yet
- Park Ch. 1 - A1000 - Spring13Document21 pagesPark Ch. 1 - A1000 - Spring13lingyeeNo ratings yet
- AnthropologyDocument8 pagesAnthropologyHabib ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Antro Solomon Chp2pdfDocument120 pagesAntro Solomon Chp2pdf1bonsaadugnaNo ratings yet
- What Is Cultural Anthropology? Branches of Anthropology?Document5 pagesWhat Is Cultural Anthropology? Branches of Anthropology?moazzamikram75% (4)
- Unit 2-Anth 1012, EditedDocument30 pagesUnit 2-Anth 1012, Editedkm4874430No ratings yet
- Anthropology SubfieldsDocument47 pagesAnthropology SubfieldsNatty NigussieNo ratings yet
- History & Branches of Anthropology (Study of Human SocietiesDocument39 pagesHistory & Branches of Anthropology (Study of Human SocietiesJella GeroncaNo ratings yet
- Study of The Various Aspects of Humans in The Past To PresentDocument12 pagesStudy of The Various Aspects of Humans in The Past To PresentAian EsportunoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Cultural AnthropogyDocument16 pagesIntroduction To Cultural AnthropogyAndziso CairoNo ratings yet
- Anthropology 02Document21 pagesAnthropology 02Kathlyn Apple AmanteNo ratings yet
- Branches of SociologyDocument32 pagesBranches of SociologyDani QureshiNo ratings yet
- Anthropology HRM (Updated)Document23 pagesAnthropology HRM (Updated)Celeste BelcinaNo ratings yet
- The Multÿ Yea Yow yowANTHROPOLOGY PDFDocument7 pagesThe Multÿ Yea Yow yowANTHROPOLOGY PDFJestonie ManuelNo ratings yet
- Socio Cultural AnthropologyDocument13 pagesSocio Cultural AnthropologyRhe yaNo ratings yet
- FullDocument94 pagesFullCharles Anthony RamosNo ratings yet
- What Is AnthropologyDocument19 pagesWhat Is AnthropologyofikNo ratings yet
- Assignment Sumbitted To Mam Tyabba by Maryam Mumtaz Class BS (7) Linguistics Roll Number BSF1702734Document9 pagesAssignment Sumbitted To Mam Tyabba by Maryam Mumtaz Class BS (7) Linguistics Roll Number BSF1702734ShamOo MaLikNo ratings yet
- Social Science DisciplinesDocument23 pagesSocial Science Disciplinesangie vibarNo ratings yet
- Fields of AnthropologyDocument3 pagesFields of Anthropologyfredpaul esperoNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Anthropology NotesDocument3 pagesUcsp Anthropology NotesDonna Rose M. BalamadNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Multiple ChoiceDocument20 pagesExam 1 Multiple ChoiceragcajunNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1a - What Is AnthroSocDocument27 pagesLecture 1a - What Is AnthroSocNisha AshaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Social AnthropologyDocument148 pagesIntroduction To Social AnthropologyEarmias GumanteNo ratings yet
- What Is AnthropologyDocument19 pagesWhat Is AnthropologyJuno PajelNo ratings yet
- Imagining Serengeti: A History of Landscape Memory in Tanzania from Earliest Times to the PresentFrom EverandImagining Serengeti: A History of Landscape Memory in Tanzania from Earliest Times to the PresentNo ratings yet
- Meeting Customer Expectations with Quality ManagementDocument4 pagesMeeting Customer Expectations with Quality ManagementDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- ECONONE Definition of Terms HWDocument3 pagesECONONE Definition of Terms HWDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- Management On Organization: Management EthicsDocument6 pagesManagement On Organization: Management EthicsDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- ECONONE Definition of Terms HWDocument3 pagesECONONE Definition of Terms HWDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ArchaeologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To ArchaeologyDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- Cri ThinDocument1 pageCri ThinDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- What Is Critical Thinking and Why It CountsDocument4 pagesWhat Is Critical Thinking and Why It CountsDenisse LimNo ratings yet
- Community and Civil SocietyDocument67 pagesCommunity and Civil SocietyLeticia CamachoNo ratings yet
- Baumann PDFDocument3 pagesBaumann PDFSomebody'sHeartbeatNo ratings yet
- Institutionalisation of History, Sociology and AnthropologyDocument11 pagesInstitutionalisation of History, Sociology and Anthropologyshweta sinhaNo ratings yet
- Maynes, May Jo & Walter, Ann. Family - History - and - World - History - From - Domestication - To - BiopoliticsDocument26 pagesMaynes, May Jo & Walter, Ann. Family - History - and - World - History - From - Domestication - To - BiopoliticsHenrique Espada LimaNo ratings yet
- Casajus Brother DjinnDocument16 pagesCasajus Brother DjinnDuveyrierNo ratings yet
- Sociology of Kinship AssignmentDocument7 pagesSociology of Kinship AssignmentAman VermaNo ratings yet
- Scheidel - Studying The State PDFDocument32 pagesScheidel - Studying The State PDFMo Za PiNo ratings yet
- KINSHIP TERMS + Iravati KarveDocument9 pagesKINSHIP TERMS + Iravati KarveMelissa SmithNo ratings yet
- Facts About BrazilDocument9 pagesFacts About BrazilHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Self 113 2019-2020: Mr. Michael Angelo Liwanag, RPMDocument54 pagesUnderstanding The Self 113 2019-2020: Mr. Michael Angelo Liwanag, RPMCliff DomionNo ratings yet
- George BerkowskiDocument61 pagesGeorge Berkowskijeca1304No ratings yet
- Harris (1976) Emic EticDocument23 pagesHarris (1976) Emic EticAiram AlonsoNo ratings yet
- 03ALevi Strauss, StructuralAnalysisinLinguisticsandAnthropologyDocument5 pages03ALevi Strauss, StructuralAnalysisinLinguisticsandAnthropologyGaram KwonNo ratings yet
- Why Religion Is Nothing Special But Is CentralDocument8 pagesWhy Religion Is Nothing Special But Is CentralAthanasiosKoutoupasNo ratings yet
- Mgsu MaDocument11 pagesMgsu Majagjeet singhNo ratings yet
- 5 6069129908435550654 PDFDocument192 pages5 6069129908435550654 PDFalluri bhaskarNo ratings yet
- Caribbean FamiliesDocument3 pagesCaribbean FamiliesMARK DEFREITASNo ratings yet
- Reuss-Ianni Two Cops CulturesDocument32 pagesReuss-Ianni Two Cops CulturesDaniel GOMEZNo ratings yet
- Chuktia Bhunjia: A Neglected Tribe of Orissa, IndiaDocument11 pagesChuktia Bhunjia: A Neglected Tribe of Orissa, IndiaR A JUNo ratings yet
- Marriage Laws Customs and Practices in Uganda A Casebook GuideDocument297 pagesMarriage Laws Customs and Practices in Uganda A Casebook GuideEdward Biryetega100% (1)
- Tiruray Ethnic Group of PhilippinesDocument3 pagesTiruray Ethnic Group of PhilippinesChuzell Lasam67% (3)
- ALAVI - Peasant Classes and Primordial LoyaltiesDocument40 pagesALAVI - Peasant Classes and Primordial LoyaltiesSergio OrozcoNo ratings yet
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Ucsp (Kinship by Blood)Document4 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Ucsp (Kinship by Blood)rosa4rosata1100% (2)
- Cultural Anthropology, Ant102 Spring 2020: Marcia Good, PHDDocument2 pagesCultural Anthropology, Ant102 Spring 2020: Marcia Good, PHDUnnati ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Belfiore Murder Among Friends PDFDocument301 pagesBelfiore Murder Among Friends PDFMiguel García Audelo100% (3)
- Meyer FortesDocument22 pagesMeyer Fortesmister.de.bancada01No ratings yet
- Module 2 Institutions Family, Marriage and Kinship - Part IDocument4 pagesModule 2 Institutions Family, Marriage and Kinship - Part IMIR SARTAJNo ratings yet
- Yoffee 1993Document19 pagesYoffee 1993Javier SandovalNo ratings yet
- Virgin Birth - Proceedings of The Royal Anthropological - Leach EdmundDocument12 pagesVirgin Birth - Proceedings of The Royal Anthropological - Leach EdmundhadlyynNo ratings yet
- Kinship, Marriage and The HouseholdDocument26 pagesKinship, Marriage and The Householdsenior high100% (1)