Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Naming Alcohols
Uploaded by
Mary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Naming Alcohols
Uploaded by
Mary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaCopyright:
Available Formats
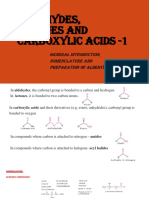
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY A Study Guide for alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amines and polymers
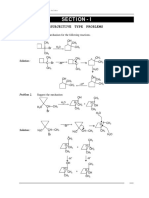
ALCOHOLS THE NAMING OF ALCOHOLS The iupac naming of alcohols begins by choosing the longest hydrocarbon chain containing the OH functional group. 1) Locate the OH group using the lowest possible numbering and 2) The ending e is removed form the base name replaced by ol. (The common naming system involves using the base name with a yl ending. Example methyl alcohol. Eg. CH3 CH2 CH2 OH 1- propanol EXERCISE 1. Name and classify each of the following (using the IUPAC system): b) HO CH2 CH CH3 l CH3 2-methyl-1-propanol CH3 CH CH2 -CH3 | OH 2 butanol
a) CH3 CH2 CH CH2 CH CH3 l l OH CH3 2o 5-methyl-3-hexanol OH | 2-methyl-2-propanol c) H3C C CH3 | 3o CH3 2.
1o
Draw the condensed structural formula for: c) 2 methyl 2- propanol CH3 OH \/ CH3-C-CH3
a) 2 pentanol CH3-CH2-CH2-CH-CH3 | OH b) 4,4 dimethyl -1- hexanol
HO
Questions 1. Write the reaction of how you would prepare 2-pentanol. Could you produce this in 100% yield? a. Add 1-pentene to water (Markovnikov Addition) and 2-pentanol will be prepared in a 100% yield
b. 2.
If you tried 2-pentene you would only get a 50/50 mixture of 2-pentanol and 3-pentanol
What functional group would be the result of the addition of KMnO 4 to: a) 2-butanol ketone b) 3-methyl-3-hexanol n.r. (alcohol) c) ethanol aldehyde or carboxylic acid Write the balanced chemical equation for the combustion of 1-propanol. 2 C3H7OH + 9 O2 6 CO2 + 8 H2O If methanol was oxidized to methanal (aldehyde) and KMnO4 was reduced to MnO2; give the balanced redox reaction if it took place in an acidic solution. CH3OH CH2O + 2H+ + 2e- (X3) 3e- + 4H+ + MnO41- MnO2 + 2H2O (X2) 2H+ + 2MnO41- + 3CH3OH 2 MnO2 + 4H2O + 3CH2O
3. 4.
ETHERS NAMING OF ETHERS 1) 2) Choose the longest alkyl group as the parent alkane. Treat the second alkyl group as the branch alkyl group. This is named by replacing the yl with oxy. The alkoxy group that is adding on to the main chain should be located onto the main chain with an appropriate number. CH3 CH2 O CH CH3 \ CH3 2- ethoxypropane
Eg. CH3 O CH2 CH3
methoxyethane
EXERCISE 1. Name the following ethers. 1-methoxybutane
a) CH3 CH2 CH2 CH2 O CH3 b) CH3CH2CH2CH2 O CHCH2CH2CHCH2CH3 | | CH3 CH3 c) CH3 CH O CH2 CH CH2 CH3 | | CH3 CH3 Draw the following ethers. a) 1-methoxy propane
2-butoxy-5-methylheptane
1-isopropoxy-2-methylbutane
2.
b) 3 ethoxy-4-methylheptane CH3 CH2 O CH3 | | CH3 CH2 CH CH CH2 CH2 CH3
CH3 O CH2 CH2 CH3
c) 2 methoxy 2- methylpropane CH3 O CH3 \ / CH3 C CH3
ALDEHYDES AND KETONES THE NAMING OF ALDEHYDES AND KETONES The naming of aldehydes and ketones begins by choosing the longest chain containing the carbonyl group to obtain the base name. The ending e is removed from the base name and replaced by the suffix al in the case of aldehydes and one in the case of ketones. Since the carbonyl group of an aldehyde is always at one end of the main chain, its position does not require a number. However, for ketones, we use a number to show the location of the carbonyl group (starting the count from the end closest to the carbonyl group). Examples: CH3 | CH3-CH-CH2-C-H 3-methylbutanal EXERCISE: 1. Name the following using IUPAC system: CH3 | O || b) CH3 O | || CH3 C C -H | CH3 O || O || CH3 |
CH3 C CH2 CH CH3 4-methyl-2-pentanone
a) CH3 CH CH2 CH2 C CH3
2. Draw the structural formula for: a) 3-pentanone CH3-CH2-CO-CH2-CH3 c) 2-methylpentanal O
||
b) butanal CH3-CH2-CH2-CHO d) 2,4-dimethyl-3-hexanone
|| O Questions 1. Write an equation for each of the following reactions: a) Balance the reaction between methanal and acidified Cr2O72- ions. Hint: This reaction is a redox reaction. Combine the following two half reactions to obtain a balanced equation.
The oxidation half-reaction: The reduction half-reaction:
H2O + HCHO 6e- + 14 H+ +
Cr2O72-
HCOOH + 2H+ + 2 e> 2 Cr3+ + 7 H2O
(X3)
8H+ + 3HCHO + Cr2O72- 3HCOOH + 4H2O + 2 Cr3+
b)The reaction between propanal and hydrogen gas over platinum as a catalyst. CH3-CH2-CHO + H2,Pt CH3-CH2-OH 1-propanol
c) The oxidation of 2-methylpropanal with acidified potassium dichromate ions. CH3-CH-CHO + [O] CH3-CH-COOH | CH3 | CH3 2-methylpropanoic acid
2. Which alcohol would you oxidize to prepare a) pentanal and b) 3-pentanone. Write a balanced half reaction for each reaction. a) b) CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-OH CH3-CH2-CH-CH2-CH3 | CH3 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS THE NAMING OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS The IUPAC names of CARBOXYLIC ACIDS are obtained by selecting the longest carbon chain containing the CARBOXYL group and replace the ending of the alkane name with the ending oic acid. If an alkyl group is present, the numbering starts from the carbon of the carboxyl group. 1-pentanol 3-pentanol
EXAMPLE:
O ||
CH3 CH2 CH CH2 CH2 C OH | CH2 - CH3
4-ethylhexanoic acid
EXERCISE: 1. Name the following carboxylic acids using IUPAC system: a) CH3 CH3 \ / O || b) CH3 CH3 | |
CH3 CH2 C CH2 C OH 3,3-dimethylpentanoic acid
CH3 CH CH - COOH 2,3-dimethylbutanoic
2. Draw the condensed formula for: a) Heptanoic acid CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-COOH b) 4-methylhexanoic acid CH3-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2-COOH | CH3 QUESTIONS 1. What ions form when propanoic acid reacts with water? CH3-CH2-COOH + H2O CH3-CH2-COO- + H3O+ 2. Why does butanoic acid have a higher BP than 3-pentanone?
CH3-CH2-CH2-COOH and CH3-CH2-CO-CH2-CH3 have roughly the same London forces and both contain a carbonyl group (C=O) so they both have a polar area. However, they differ because butanoic acid has an OH bond so it has hydrogen bonding as an IMF.
3.
If ethanoic acid is reduced with H2, what two possible products can form? (name and draw their condensed structural formulas) CH3CHO + H2, Pt Ethanal CH3CH2OH ethanoic acid
CH3COOH + H2, Pt
4.
What alcohol needs to be oxidized to prepare 3-methylpentanoic acid? 3-methyl-1-pentanol
CH3-CH2-CH-CH2-CH2-OH
| CH3
Oxidation ADD A STRONG OXIDIZING AGENT TO THE FOLLOWING ORGANIC COMPOUNDS. NAME THE PRODUCTS. a) ethanol CH3-CH2-OH + [O] CH3-CHO + [O] ethanal CH3-COOH ethanoic acid
b) 3 - methyl-3-pentanol
CH3-CH2 C CH2 CH3 + [O] nr / \ CH3 OH CH3 CH CHO + [O] CH3 CH COOH | | CH3 CH3 2-methylpropanoic acid
c) 2 methylpropanal
d) 3,3 dimethyl -2-pentanol
O || CH3-CH2 C CH CH3 + [O] CH3-CH2 C C CH3 / \ \ / \ CH3 CH3 OH CH3 CH3 3,3 dimethyl -2- pentanone
REDUCTION REACTIONS
DRAW THE FOLLOWING COMPOUNDS AND SHOW THE REDUCTION PRODUCT. Name all the new compounds. a) 3-pentanone + H2, Pt O b) 3,4 dimethylpentanal CH3 CH CH CH2-CHO + H2, Pt | | CH3 CH3 OH CH3 CH CH CH2-CH2OH | CH3 3-pentanol
c) 2,4,4 trimethyl-2pentene + H2, Pt
2,2,4-trimethylpentane d) methanal HCHO + H2, Pt CH3OH methanol
ESTERS NAMING OF ESTERS In naming esters, we obtain the first part of the name from the name of the alkyl group attached to the oxygen; the second part is obtained by changing the -ic acid ending of the acid to -ate. EXAMPLES O || CH3 C O CH3 methyl ethanoate O || CH3 CH2 CH2 C O CH CH3 2 propylbutanoate | CH3
QUESTIONS I. Give the IUPAC name for: a) O || HC-O-CH2 CH2 CH3 Propyl methanoate b) O || CH2 CH3 |
CH3 CH2 - C O CH CH2 CH3 3-pentyl propanoate
2. There are two esters with the formula C3H6O2 a) Draw their condensed formulas. CH3-COO-CH3 AND HCOO-CH2-CH3
b) Give their IUPAC names methyl ethanoate and ethyl methanoate c) Identify the alcohol and the carboxylic acid used in the preparation of each ester. Methanol and ethanoic acid ethanol and methanoic acid
d) Name and draw the isomeric carboxylic acid. CH3-CH2-COOH propanoic acid
e) Compare the BP of either ester to (d). Propanoic acid has a higher BP because it has hydrogen bonding either ester has only a dipole force. London forces are roughly equal. 3. Write the esterification reaction between: a) ethanoic acid and ethanol. CH3-COOH + HOCH2-CH3 CH3 COO CH2-CH3
b) methanoic acid and 1-butanol. HCOOH + HOCH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 HCOO CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 c) propanoic acid and 2-methyl-2-propanol. CH3-CH2-COOH + HOC - C -CH3 CH3-CH2COO C -CH3 / \ CH3 CH3 / \ CH3 CH3
4. Write a balanced equation to show how each ester below is prepared a) CH3 CH2 COO CH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 - CH2 CH3 CH3-CH2-COOH + HOCH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 b) H COO CH2 CH2 CH2 CH3 HCOOH + HO-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH3 AMINES THE NAMING OF AMINES: The IUPAC names of amines are formed by adding the prefix amino- to the corresponding alkane name of the amine. As usual, numbers are used to indicate the carbon to which the amine substituent is attached. The functional group takes priority over the alkyl group. (In this course we will only have to name primary amines). CH3-NH2 CH3 CH CH2 CH CH2 CH3 | | 3-amino-5-methylhexane
aminomethane QUESTIONS
CH3
NH2
1. Name and classify the following amines. a) NH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH3 | NH2 1,3 diaminopropane 1,4-diamino-2-methyl b) NH2 NH2
c) NH2 CH2 CH2 CH2 CH CH CH3 | |
1-amino 4,5-dimethylhexane
CH3 CH3
2. Draw the structural formulas of four amines that have the molecular formula C 3H9N (two primary, one secondary, and one tertiary amine). Classify the amines and name the primary amines among them.
1) CH3-CH2-CH2-NH2 2) CH3- CH -CH3 | NH2 AMIDE NAMING OF AMIDES 1) 2) 3)
1-aminopropane primary 2-aminopropane primary
3) CH3-NH-CH2-CH3 4) CH3 \ CH3 - N CH3
-secondary -tertiary
Locate the carbonyl group and name the parent carboxylic acid. Replace the oic acid with the ending amide. A - Primary Amide if there are two hydrogen atoms bonded to the nitrogen. This name needs no prefix. B Secondary Amide if there is one alkyl group attached to the nitrogen. Name and locate the alkyl group, use the letter N to indicate that it is bonded to the nitrogen atom. C Tertiary Amide if there are two alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen. Name and locate each alkyl group alphabetically, use the letter N to locate before each group.
Eg.
O || CH3-CH-C-NH2 | CH3 2-methylpropanamide
O || CH3-CH2-CH2-C-NH-CH2-CH3
O || CH3-C-N-CH3 \ CH2-CH3 N-ethyl-N-methylethanamide
N-ethylbutanamide
EXERCISE 1. Name and classify the following amides. a) O || CH3-CH2-CH-CH2-C-NH2 | CH2-CH3 3-ethylpentanamide 1o b) O || CH3-CH-CH-C-NH-CH3 | | CH3 CH3 N methyl-2,3-dimethylbutanamide 2O c) O || CH3 CH2-C-N-CH2-CH2-CH3 \ CH2-CH2-CH3 N,N - dipropylpropanamide 3O
2. Give the condensed structural formulas for the following amides classify each. a) N-methylpentanamide b) N,N-diethylbutanamide c) hexanamide CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CH2-CO-NH2 1O
CH3-CH2-CH2-CH2-CO-NH-CH3 CH3-CH2-CH2-CO-NH-CH2-CH3 2O \ 3O CH2-CH3
You might also like
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 1 AlkaneDocument44 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 1 AlkaneridwanNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Organic Chemistry, 7e Marc Loudon, Jim Parise Test BankDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Organic Chemistry, 7e Marc Loudon, Jim Parise Test BankNail BaskoNo ratings yet
- Food Analysis TechniquesDocument42 pagesFood Analysis TechniquesPiku100% (4)
- Masteranswersorganic 4 UDocument9 pagesMasteranswersorganic 4 Ukriss WongNo ratings yet
- Alkyl GroupsDocument10 pagesAlkyl GroupsMyrrh Oliver CasinabeNo ratings yet
- Notes Functional GroupsDocument5 pagesNotes Functional GroupsFrank GaoNo ratings yet
- 12 - Nomenclature Questions TPP by Sir ShafeyDocument4 pages12 - Nomenclature Questions TPP by Sir Shafeyaftabhajano080No ratings yet
- ESTERSDocument31 pagesESTERSSaadiah MohammadNo ratings yet
- Chem CHPT 6 Learning Module 2Document57 pagesChem CHPT 6 Learning Module 2Patrick Joshua GregorioNo ratings yet
- IUPAC NomenclatureDocument18 pagesIUPAC NomenclatureSachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Alkane-Full Notes FazliDocument47 pagesAlkane-Full Notes Fazlijokowi123No ratings yet
- 3 NomenclatureDocument45 pages3 Nomenclaturerusnah chungNo ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument31 pagesOrganic ChemistrySameep Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: General Properties and NomenclatureDocument20 pagesAlkanes: General Properties and NomenclatureLaely INNo ratings yet
- Alkanes: Contain Single Bonds CH - CH - CH - CH Saturated Hydrocarbon Substitution ReactionDocument28 pagesAlkanes: Contain Single Bonds CH - CH - CH - CH Saturated Hydrocarbon Substitution ReactionHesham El-RoussassiNo ratings yet
- Naming Organic CompoundsDocument9 pagesNaming Organic CompoundsRonikeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument35 pagesChapter 19 - Introduction To Organic ChemistryDF91100% (10)
- Organic Compounds Naming GuideDocument33 pagesOrganic Compounds Naming GuideSaritha Ramanadh100% (1)
- Understanding AlkanesDocument20 pagesUnderstanding AlkanesLaely INNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument45 pagesHYDROCARBONSTherese Eva Marie DequitoNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry: AlkanesDocument39 pagesOrganic Chemistry: AlkanesYu DhaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons ChapterDocument45 pagesHydrocarbons ChapterkjjkimkmkNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds-3Document32 pagesNomenclature of Organic Compounds-3Muhammad ArhamNo ratings yet
- IUPAC TH E O0bBdNyDocument21 pagesIUPAC TH E O0bBdNyChutiyaNo ratings yet
- Learner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemDocument82 pagesLearner q2 Week 67 Gen - ChemrikrikNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and Organic CompoundsDocument38 pagesAlkanes and Organic CompoundsMary Darice WongNo ratings yet
- Kakhasan Atom Karbon Dan Gugus FungsinyaDocument34 pagesKakhasan Atom Karbon Dan Gugus FungsinyaAllright ShitNo ratings yet
- Notes HydrocarbonsDocument9 pagesNotes HydrocarbonsShiina MashiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Intro To OrganicDocument8 pagesChapter 15 Intro To OrganicLisa DentonNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 1Document110 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1Mahmoud RslanNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds 1 7Document7 pagesCarbonyl Compounds 1 7vishalgowni8888No ratings yet
- Organic ChemistryDocument44 pagesOrganic ChemistryKushashwa Ravi ShrimaliNo ratings yet
- Alkenes NotesDocument60 pagesAlkenes NotesLenz KnightNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Part 2Document27 pagesNomenclature Part 2gcxnhmzNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Hydrocarbon Q 1:explain Classification of Hydrocarbons (3 Mark)Document16 pagesChapter - 6 Hydrocarbon Q 1:explain Classification of Hydrocarbons (3 Mark)api-233404189No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Nomenclature and Isomerism GuideDocument20 pagesOrganic Chemistry Nomenclature and Isomerism GuideRyantyler13No ratings yet
- Simple IUPAC NomenclatureDocument15 pagesSimple IUPAC Nomenclatureapi-3757218100% (6)
- Complete Organic Chemistry NotesDocument161 pagesComplete Organic Chemistry NotesNelima Stella mercyNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Untuk Murid MHTDocument36 pagesOrganic Chemistry Untuk Murid MHTSuwandi Science13No ratings yet
- Aldehydes and Ketones - 1-MergedDocument94 pagesAldehydes and Ketones - 1-MergedseNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Hydrocarbon AlkaneDocument45 pagesCh2 Hydrocarbon AlkaneAlimah AzeliNo ratings yet
- Friends Boys School: Organic Chemistry SL / 12 IBDocument47 pagesFriends Boys School: Organic Chemistry SL / 12 IBKays Abu einNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument69 pagesWeek 3 Alkanes and Cycloalkanesjojojhinno rosalesNo ratings yet
- Tata Nama Alcohols and EthersDocument4 pagesTata Nama Alcohols and EthersNur ElidaNo ratings yet
- Objectives: UNIT 3. HydrocarbonsDocument52 pagesObjectives: UNIT 3. HydrocarbonsMarcelaNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic acid derivatives lectureDocument19 pagesCarboxylic acid derivatives lectureMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic CompoundsDocument16 pagesIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compoundspromit guha0% (1)
- Alkanes and CycloalkanesDocument5 pagesAlkanes and CycloalkanesAlineNo ratings yet
- 5 Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsDocument15 pages5 Basic Concepts and HydrocarbonsAnastasia ErshNo ratings yet
- ) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicDocument11 pages) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicPkrajen PillaiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Chemistry: Quarter 1 - Week 5Document5 pagesConsumer Chemistry: Quarter 1 - Week 5Princess Loraine DuyagNo ratings yet
- 21 NomenclaturaDocument17 pages21 NomenclaturapalesandraNo ratings yet
- Alcohols and Ethers Compounds Names Structures ReactionsDocument4 pagesAlcohols and Ethers Compounds Names Structures ReactionsAde RakhaNo ratings yet
- Kuliah 1Document70 pagesKuliah 1AzizNo ratings yet
- Carbonyl Compounds: Properties and ReactionsDocument87 pagesCarbonyl Compounds: Properties and ReactionsHafizszul FeyzulNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature Bansal Iit Jee Organic PDFDocument24 pagesNomenclature Bansal Iit Jee Organic PDFa143deendayal0% (2)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Organic ChemistryRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Assembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsFrom EverandAssembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsNo ratings yet
- Physical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976From EverandPhysical Organic Chemistry — 3: Plenary Lectures Presented at the Third IUPAC Conference on Physical Organic Chemistry, Montpellier, France, 6 - 10 September, 1976A. FruchierNo ratings yet
- Molecular Devices: An Introduction to Technomimetics and its Biological ApplicationsFrom EverandMolecular Devices: An Introduction to Technomimetics and its Biological ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- MusicDocument3 pagesMusicMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Jude Deveraux's Booklist With SummaryDocument4 pagesJude Deveraux's Booklist With SummaryMary Margaret "MM" A. Avena100% (1)
- PHL 5 - Unit I IntroductionDocument18 pagesPHL 5 - Unit I IntroductionfeidnaNo ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Organic CompoundsDocument11 pagesIdentification of Unknown Organic Compoundsiris_gundranNo ratings yet
- Uta No Prince-Sama LyricsDocument4 pagesUta No Prince-Sama LyricsMary Margaret Asprec AvenaNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (201) - Lecture MedtechDocument8 pagesPHYSICS (201) - Lecture MedtechMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Characterisitcs of CultureDocument1 pageCharacterisitcs of CultureMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Christina Dodd Complete BooklistDocument1 pageChristina Dodd Complete BooklistMary Margaret "MM" A. Avena50% (2)
- Wiki NomenclatureDocument5 pagesWiki NomenclatureMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Geometry of Molecules ChartDocument4 pagesGeometry of Molecules ChartMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Physiological ApparatusDocument32 pagesPhysiological ApparatusCzarina Barcelon Daos100% (12)
- Many Similarities To Higher Vertebrates and in Man. 2. Ease of Manipulation 3. Inexpensive 4. AvailabilityDocument28 pagesMany Similarities To Higher Vertebrates and in Man. 2. Ease of Manipulation 3. Inexpensive 4. AvailabilityClaire Anne CaringalNo ratings yet
- Health Maintance Organization (HMO) Avena, Mma.: CDH 412 - DGCDocument8 pagesHealth Maintance Organization (HMO) Avena, Mma.: CDH 412 - DGCMary Margaret "MM" A. Avena0% (1)
- CDH 412 Hmo ReportDocument3 pagesCDH 412 Hmo ReportMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Functional GroupsDocument9 pagesFunctional GroupsMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Addition of VectorsDocument9 pagesAddition of VectorsMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Supply and DemandaDocument15 pagesSupply and DemandaJoshue SandovalNo ratings yet
- Health Maintance Organization (HMO) Avena, Mma.: CDH 412 - DGCDocument8 pagesHealth Maintance Organization (HMO) Avena, Mma.: CDH 412 - DGCMary Margaret "MM" A. Avena0% (1)
- PhysicsDocument1 pagePhysicsMary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Uta No Prince-Sama LyricsDocument4 pagesUta No Prince-Sama LyricsMary Margaret Asprec AvenaNo ratings yet
- DHT Booth Rules...Document1 pageDHT Booth Rules...Mary Margaret "MM" A. AvenaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Thermochemistry: StudentDocument28 pagesChapter 6 Thermochemistry: StudentKing Ray TabalbaNo ratings yet
- Numericals XI FinalDocument33 pagesNumericals XI FinalKhan SarfarazNo ratings yet
- Organic I Reactions (Complete) PDFDocument10 pagesOrganic I Reactions (Complete) PDFStarrx714No ratings yet
- Chemetall - (Data Sheet) Oakite 33Document3 pagesChemetall - (Data Sheet) Oakite 33Pubcrawl100% (1)
- Análisis AmbientalDocument16 pagesAnálisis AmbientalJ. M.No ratings yet
- Alkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-02 - Solved ProblemsDocument13 pagesAlkyl Halides & Aryl Halides-02 - Solved ProblemsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- Sedifilt Oil & Gas Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesSedifilt Oil & Gas Brochure PDFAalap DerasaryNo ratings yet
- 2018-07-01 Chemistry Times PDFDocument68 pages2018-07-01 Chemistry Times PDFMilena KafkaNo ratings yet
- Petrobras N-2912Document10 pagesPetrobras N-2912dylkanNo ratings yet
- Waste WaterDocument106 pagesWaste WaterLing Li100% (1)
- Fibres PPT 1Document19 pagesFibres PPT 1rajesh duaNo ratings yet
- Vapour Pressure LabDocument8 pagesVapour Pressure LabTuqeer MuhammadNo ratings yet
- LT 2662a Brochure Design Guide For Bonding Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers Volume 3 2011Document82 pagesLT 2662a Brochure Design Guide For Bonding Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers Volume 3 2011OzkanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Investigatory Project On AntacidsDocument13 pagesChemistry Investigatory Project On AntacidsJoderick Sherwin100% (1)
- 1.2.4 HDG - Painting Issues PDFDocument2 pages1.2.4 HDG - Painting Issues PDFAnonymous 1AAjd0No ratings yet
- DPP (Concentration Terms)Document56 pagesDPP (Concentration Terms)kedarnath jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 RdmeetingDocument4 pagesExperiment 3 RdmeetingDia SariNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document8 pagesTutorial 3Azrul RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Cast Irons - Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument6 pagesCast Irons - Engineering Materials & Metallurgy Questions and Answers - SanfoundrySample UseNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For ProteinsDocument8 pagesQualitative Tests For ProteinsFaye Cortez100% (1)
- Zeta-Potential Measurements On Micro Bubbles GeneratedDocument9 pagesZeta-Potential Measurements On Micro Bubbles Generatedggg123789No ratings yet
- Periodic Table Chart A4 WebDocument2 pagesPeriodic Table Chart A4 WebvibinNo ratings yet
- High Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyDocument69 pagesHigh Performance Thin Layer ChromatographyAliefanugerahsani Attabe100% (1)
- Textiles Presentation (Final) - April 2017Document37 pagesTextiles Presentation (Final) - April 2017Natalia RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Diagnostic TestDocument3 pagesChemistry Diagnostic TestJohn John RoacheNo ratings yet
- ASTM D4458-15 Iones de Cloruro en Agua CongénitaDocument4 pagesASTM D4458-15 Iones de Cloruro en Agua CongénitaAngel MurilloNo ratings yet
- PREOSDocument18 pagesPREOSLija BinuNo ratings yet
- Viskrings Seals SDSDocument6 pagesViskrings Seals SDSTarik ConceptNo ratings yet