Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH 18
Uploaded by
France Mico SobrevegaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH 18
Uploaded by
France Mico SobrevegaCopyright:
Available Formats
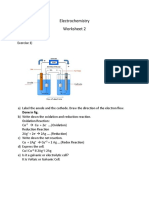
Chemists Daily Chapter 18-1
1. Assign oxidation numbers to each atom in: NiCl2 Nickel ion charge would be +2, so oxidation number is +2
Chloride ion charge would be 1, so each chlorine has an ox # of -1
Mg2TiO4
Oxygen ox # (from the rules) is -2
Magnesium ion charge would be +2, so oxidation number is +2
Titanium ox # of +4, so that the whole thing adds up to zero charge Oxygen ox # (from the rules) is -2
K2Cr2O7
Potassium ion charge would be +1, so oxidation number is +1
Chromium ox # of +6, so that the whole thing adds up to zero charge
HPO4-
Oxygen ox # (from the rules) is -2
Phosphorus ox # of +6, so that the whole thing adds up to 1 charge 2. Identify whether each reaction is a redox reaction. If so, identify the oxidizing agent,
Hydrogen ox # (from the rules) is +1
the reducing agent, the substance being oxidized, and the substance being reduced. Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) ZnCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
a.
Product ox # Zn is +2, H is 0, Cl is 1
Reactant ox # Zn is 0, H is +1, Cl is -1
was oxidized and is the reducing agent. reduced and is the oxidizing agent b. Cr2O7
2-
Since there is a change in ox #, this is a redox reaction.
Since hydrogens ox # decreased, it was
Since Zns ox # inceased, it
Product ox # Cr is +6, O is -2, H is +1
Reactant ox # Cr is +6, O is -2, H is +1
(aq)
2OH- (aq)
CrO4
2-
(aq)
H2O (l)
Since there is no change in ox #s, this is not a redox reaction Identify the substances oxidized and reduced in the reaction of calcium and chlorine to What are the oxidizing and reducing agents? + Cl2 CaCl2
3.
form calcium chloride.
Product ox # Ca is +2, Cl is 1 oxidizied)
Reactant ox # Ca is 0, Cl is 0
Balanced equation:
Ca
So oxidizing agent is Cl (which is reduced) and the reducing agent is Ca (which is
Chemists Daily Chapter 18-2
CH3OH (aq)
1. Balance the following equations: + Cr2O7
2-
CH3OH CH2O
Write half reactions:
(aq)
CH2O (aq)
Cr
3+
(aq)
in acidic solution
3+
Balance (not H or O) CH3OH CH2O Balance O using H2O CH3OH CH2O
Cr 2O7 Cr 2O7 Cr 2O7
+
2-
Cr
2-
2Cr
3+
2-
Balance H using H+
2Cr
3+
+ 7 H2 O 2Cr
3+
CH3OH CH2O + 2H
CH3OH CH2O + 2H + 2e+
Balance charge using eMake e- the same
14 H 14 H 14 H
3+
+ Cr2O7 + Cr2O7 + Cr2O7
2-
+ 7 H2 O
3+
2-
+ 6e- 2Cr
+ 7 H2 O + 7 H2 O
3CH3OH 3CH2O + 6H + 6e+
2-
Add and cancel 3CH3OH + 8 H
-
+ 6e- 2Cr
3+
+ Cr2O7 +
2-
3CH2O + 2Cr
+ 7 H2 O
Cl2 (g) Cl (aq) Cl2 Cl
-
Write half reactions: Balance (not H or O)
ClO (aq)
in basic solution Cl2 ClO
-
Balance O using H2O Cl2 Balance H using H+ Cl2 Balance charge using eMake + 2e- 2Cl
-
Cl2
2Cl
Cl2 2ClO
2Cl
Cl2 + 2H2O 2ClO
2Cl
Cl2 + 2H2O 2ClO + 4H
-
Cl2
Add and cancel
They are
e- the same
Cl2 + 2H2O 2ClO + 4H + 2e+
2Cl2 + 2H2O 2Cl + 2ClO + 4H
-
Cancel H2O
4 OH- + 2Cl2 + 2H2O 2Cl + 2ClO + 4H2 O
-
Make H2O from H
4 OH- + 2Cl2 + 2H2O 2Cl + 2ClO + 4H
+
Add 4 OH- to each side
and OH-
+ 4 OH-
4 OH- + 2Cl2 2 OH- + Cl2
Reduce coefficients
-
2Cl + 2ClO + 2H2O
-
Cl + ClO + H2O
Chemists Daily Chapter 18-3
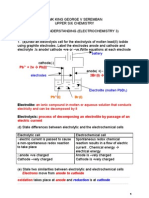
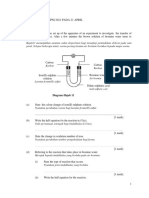
1. G iven the following cell notation: Cr (s) | Cr
3+
(aq)
||
Cu
2+
(aq)
Cu (s)
Write a balanced equation for the cell reaction and give a brief description of the cell. The anode is first: Cr (s) Cr
2+ 3+
The cathode is second: 2Cr (s) 3Cu
2+
Make the number of electrons the same and add the reactions to get: (aq) + 2Cr
3+
Cu
(aq)
+ 2e-
(aq)
+ 3e-
Cu (s)
+ 6e-
2+
(aq)
3Cu (s)
+ 6e-
2Cr (s)
3Cu
(aq)
2Cr
3+
(aq)
+ 3Cu (s)
3+
The cell is a chromium anode dipped into a solution of Cr salt bridge. cathode dipped into a solution of Cu
2+
ions.
The two solutions are connected by a
ions and a copper
2. W rite the shorthand notation for a galvanic cell that uses the reaction: Mg (s) + Fe
2+
(aq)
Mg
2+
(aq)
Fe (s)
Splitting into half reactions: Mg (s) Fe
2+
So Mg is oxidized (this is the anode) and the Fe is reduced (this is the cathode). Mg (s) | Mg
2+
(aq) + 2e- Fe (s)
Mg
2+
(aq)
2e-
(aq) || Fe
2+
(aq) | Fe (s)
Chemists Daily Chapter 18-4
1. A galvanic cell consists of a Mg electrode in a 1.0 M Mg(NO3)2 solution and a Ag electrode in a 1.0 M AgNO3 solution. Calculate the E for this cell.
The reduction potentials are: E (Ag /Ag)
+
E (Mg
2+
/Mg)
0.80 V
-2.37 V
Silver has the more positive reduction potential, so it will be reduced. So Ecell = EAg+/Ag EMg2+/Mg = 0.80 (-2.37) = 3.17 V
2. a.
Determine whether the following reactions are spontaneous as written: 2Al
3+
6I
3I2
2Al
Since E is negative the reaction is NOT spontaneous b. 3Fe Fe
2+ 2+
So Ecell
Al is reduced, I- is oxidized. = EAl3+/Al EI2/I-
(-1.66) (+0.54) = -2.20 V
2NO
4H2O
3Fe
2NO3
8H
Since E is negative the reaction is NOT spontaneous c. Cr 3Ca
3+
So Ecell
is reduced, NO is oxidized. = EFe2+/Fe -
ENO3-/NO =
(-0.45) (+0.96) = -1.41 V
2Cr
3+
2Cr
3Ca
2+
So Ecell
is reduced, Ca is oxidized. = ECr3+/Cr ECa2+/Ca
Since E is positive the reaction is spontaneous
(-0.74) (-2.87) = +2.13 V
Chemists Daily Chapter 18-5
1. A current of 0.452 A is passed through an electrolytic cell containing molten CaCl2 for 1.5 hours. formed at the electrode.
2+
Write the electrode reactions and calculate the quantity of products (in grams)
Cathode: Ca Anode:
2Cl- (l) Cl2 (g)
(l)
+ 2e- Ca (l) + 2e-
1.50 hours x (60 min/hr) x (60 sec/min) = 5.40 x 10 Charge = current x time
3
seconds
(2.44 x 10
Charge = 0.452 A x (5.40 x 10
C) x (1 mole e- / 96485 C) = 0.0253 mole e-
seconds) = 2.44 x 10 As = 2.44 x 10
3
Anode:
Cathode: 0.0253 mole e- x (1 mole Ca/2 mole e-) x (40.08 g/mol) = 0.507 g Ca 0.0253 mole e- x (1 mole Cl2/2 mole e-) x (70.906 g/mol) = 0.897 g Cl2
Using the half reactions:
2. A constant current is passed through an electrolytic cell containing molten MgCl2 for 18 hours. If 4.8 x 10
5
grams of Cl2 are obtained, what was the current (in amperes)? + 2e-
Anode:
1.31 x 10
4.8 x 10
2Cl- (l) Cl2 (g)
9
grams
C = 1.31 x 10
x (1 mole Cl2/70.906 g) x (2 mole e-/1 mole Cl2) x (96485 C/mol e-) =
9
As
18 hrs x (3600 sec/hr) = 6.48 x 10 1.31 x 10 3.
9
sec
4
As / 6.48 x 10
sec = 2.02 x 10
NaCl with a constant current of 30,000 A? obtained as a byproduct?
+
How many hours are required to produce 1000 kg of sodium by electrolysis of molten How many liters of Cl2 at STP will be
4.350 x 10 4.350 x 10
1000 kg Na x (1000 g / 1 kg) x (1 mol Na/22.99 g) x (1 mol e-/1 mole Na) =
4
Anode:
Cathode: Na
2Cl- (l) Cl2 (g) mole e-
(l)
+ e-
Na (l) + 2e-
4 9
4.197 x 10 4.350 x 10
As / 30,000 A = 1.399 x 10
mole e- x (96485 C / 1 mole e-) = 4.197 x 10
5
sec = 38.86 hrs
C = 4.197 x 10
As
mole e- x (1 mol Cl2 / 2 mole e-) = 2.175 x 10 STP: 1 atm and 273 K
mole Cl2
V =
PV = nRT
(2.175 x 10
mole) (0.082057 Latm/molK) (273 K) / 1 atm = 4.872 x 10
Chemists Daily Chapter 18-6
1. Calculate the standard free energy change and Kc for the following reaction at 25 C. Sn (s) + 2Cu
2+
(aq)
Sn
2+
(aq)
2Cu
(aq)
Half reactions: Oxidation: So Ecell = Sn
G = - 58 kJ (recall that C = J/V) Ecell = (RT/nF) (ln K) K = 6.4 x 10
9
G = -(2 mole e-) (96485 C/mole e-) (0.29 V)
G = -nFE
ECu2+/Cu+
Sn -
2+
ESn2+/Sn
+ 2e-
(0.16) (-0.14) = +0.29 V
Reduction:
2Cu
2+
+ 2e-
2Cu
ln K = nEcell / 0.0257 V = (2) (0.29 V) / 0.0257 V = 22.6
Note 0.0257 V is the result of RT/F for 25 C 2. Predict whether the following reaction would proceed spontaneously as written at 298 K: Co (s) + Fe
2+
Ecell
Oxidation: =
The half reactions: EFe2+/Fe -
Given that [Co
2+
] = 0.15 M and [Fe
2+
(aq) Co
2+
2+
] = 0.68 M
(aq)
Fe (s)
Co Co
E = Ecell (0.0257 V / n) ln Q Q = [Co
2+
ECo2+/Co
+ 2e=
(-0.45) (-0.28) = -0.17 V
Reduction: Fe
2+
+ 2e- Fe
From the overall reaction (recalling that pure solids do not appear in Q expression) E = (-0.17) (0.0257 V / 2) (ln 0.22) = -0.15 V ] / [Fe
2+
0.15 / 0.68 = 0.22
Since E is negative, the reaction is NOT spontaneous in the direction written 3. A galvanic cell was set up using the following reaction: Mg (s) + Cd
2+
(aq)
Mg
2+
(aq)
Cd (s)
this cell was measured to be 1.54 V. The half reactions: Ecell = ECd2+/Cd -
electrode was dipped into a solution of unknown Cd
The magnesium electrode was dipped into a 1.0 M solution of MgSO4 and the cadmium
2+
What is the Cd
2+
concentration.
concentration?
The potential of
Oxidation:
Mg Mg
2+
E = Ecell (0.0257 V / n) ln Q Q = [Mg
2+
EMg2+/Mg
+ 2e-
(-0.40) (-2.37) = +1.97 V
Reduction: Cd
2+
+ 2e- Cd
From the overall reaction (recalling that pure solids do not appear in Q expression) ] / [Cd
2+
1.0 / [Cd
2+
You might also like
- CH 302 13 Electrochemistry ProblemsDocument2 pagesCH 302 13 Electrochemistry ProblemsJenemarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Worksheet 2: Done in FigDocument8 pagesElectrochemistry Worksheet 2: Done in Figrezwanur rahmanNo ratings yet
- Non Sibi High School: Andover's Chem 550/580: Advanced Chemistry Chapter 16, Review Quiz 1 AnswersDocument6 pagesNon Sibi High School: Andover's Chem 550/580: Advanced Chemistry Chapter 16, Review Quiz 1 AnswersAlexis TranNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Electrochemistry - AnswersDocument10 pagesTutorial 3 Electrochemistry - AnswerssgarrabNo ratings yet
- Bab 6Document26 pagesBab 6Risna NurhanisaNo ratings yet
- Malate + NAD Oxaloacetate + NADH + HDocument14 pagesMalate + NAD Oxaloacetate + NADH + HRonaldNo ratings yet
- Exercises For Electrochemistry ReviewDocument10 pagesExercises For Electrochemistry Reviewlyandle minNo ratings yet
- Echem WKST KeyDocument7 pagesEchem WKST KeyNurul Hana OmarNo ratings yet
- Module 7 Problem Set Answer KeyDocument3 pagesModule 7 Problem Set Answer KeyPauline Grace CadusaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document20 pagesChapter 11helloblarg100% (1)
- Redox Dan Electrochemistry (Kimia)Document65 pagesRedox Dan Electrochemistry (Kimia)Rocky Simon HiaNo ratings yet
- Solved QuestionsDocument11 pagesSolved Questionspankaj16fbNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme Term 2 TrialDocument3 pagesAnswer Scheme Term 2 TrialTing TCNo ratings yet
- 20 Petrucci10e CSMDocument66 pages20 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Revision Chapter 9-13Document123 pagesRevision Chapter 9-13Ummul-KNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 1stDocument31 pagesElectrochemistry 1stKent DosejoNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Understanding - AnswersDocument11 pagesElectrochem Understanding - AnswersSiva NeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument74 pagesChapter 4 - Electrochemistryhoboslayer97No ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document28 pagesChapter 10helloblarg100% (3)
- CHEM2310 Electrochemistry Tutorial Solutions - Typed - Nov 2013Document4 pagesCHEM2310 Electrochemistry Tutorial Solutions - Typed - Nov 2013ClaytonMitchellJr.No ratings yet
- Soal ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesSoal ElectrochemistryHerlinda OktaNo ratings yet
- ERDMANN EXAM 3 SPRING 2019 CH 117 REVIEWDocument6 pagesERDMANN EXAM 3 SPRING 2019 CH 117 REVIEWharlow6winfield6adamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2300: Problem Set 6 Professor: C. E. LoaderDocument8 pagesChemistry 2300: Problem Set 6 Professor: C. E. LoaderIlham TanamasNo ratings yet
- Redox and Electrochemistry PDFDocument95 pagesRedox and Electrochemistry PDFErnest NsabimanaNo ratings yet
- Soal (1) (Repaired)Document9 pagesSoal (1) (Repaired)Inda AlwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Redox Reaction 2021 - p1Document31 pagesChapter 4 - Redox Reaction 2021 - p1Laela VutriNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Galvanic CellsDocument5 pagesElectrochemistry Assignment: Oxidation-Reduction Reactions and Galvanic CellsKester Yuree L. GimongalaNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Problem Set 2Document5 pagesSolutions To Problem Set 2Andy Nguyen100% (1)
- NOTES ElectrochemistryDocument30 pagesNOTES ElectrochemistryAlexander LeeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and NanomaterialsDocument76 pagesElectrochemistry and NanomaterialsCharles Arthel ReyNo ratings yet
- 02 ElectrochemistryDocument6 pages02 ElectrochemistryGeorgette RepunteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2Mustafidzul MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Tutorial SolutionsDocument30 pagesElectrochem Tutorial SolutionsDarren LimNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Electron Transfer and Electric CurrentDocument38 pagesElectrochemistry: Electron Transfer and Electric CurrentJerung FixNo ratings yet
- CHE1000 & 1010 - Tutorial Sheet 5 Marking KeyDocument10 pagesCHE1000 & 1010 - Tutorial Sheet 5 Marking Keychimfwembeemmanuel712No ratings yet
- Tugas ElektrokimiaDocument5 pagesTugas ElektrokimiaYasser PatelNo ratings yet
- 05 Petrucci10e CSMDocument45 pages05 Petrucci10e CSMAlexNo ratings yet
- Discovering Electrochemical Cells: PGCC CHM 102 SinexDocument36 pagesDiscovering Electrochemical Cells: PGCC CHM 102 Sinexavi0341No ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering - Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesChemical Engineering - Redox Reactions & ElectrochemistryAndreaForteRuizNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 AnswersDocument5 pagesChapter9 AnswersedytfuyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 ElectrochemistryDocument76 pagesChapter 10 ElectrochemistryPatrickNo ratings yet
- Review: Balancing Redox ReactionsDocument16 pagesReview: Balancing Redox Reactionsjanda bodongNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 1Document4 pagesProblem Set No. 1Queen Alyana BernabeNo ratings yet
- MCQ Prelims 2006Document12 pagesMCQ Prelims 2006Sherman HoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19 ElectrochemistryDocument33 pagesChapter 19 Electrochemistrymv08_zeppelinNo ratings yet
- CHEM1901 Answers to Problem Sheet 10Document7 pagesCHEM1901 Answers to Problem Sheet 10PaoleneNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry ReactionsDocument37 pagesElectrochemistry ReactionsmecsolNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and its applicationsDocument39 pagesElectrochemistry and its applicationsHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry: Unit: 2Document11 pagesStoichiometry: Unit: 2Premangshu GhoshalNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry FundamentalsDocument77 pagesElectrochemistry Fundamentalsvittyfung100% (1)
- The Transition Elements: Practice ExamplesDocument15 pagesThe Transition Elements: Practice Exampleskennethleo69No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryAnis IssabellaNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Chemistry Topperlearning Sample Paper3Document23 pagesClass 11 Chemistry Topperlearning Sample Paper3phultushiblsNo ratings yet
- 222 Fall 2013 Exam 2 KeyDocument6 pages222 Fall 2013 Exam 2 KeymyNo ratings yet
- Redox Reactions ExplainedDocument6 pagesRedox Reactions ExplainedTheresaNo ratings yet
- 201-Electrochem Revised PDFDocument42 pages201-Electrochem Revised PDFAjay AjayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Redox ReactionsDocument23 pagesChapter 8 Redox Reactionsapi-19916399No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsFrom EverandCritical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants Involving 8-Hydroxyquinoline and Its Metal Chelates: Critical Evaluation of Equilibrium Constants in Solution: Part B: Equilibrium Constants of Liquid-Liquid Distribution SystemsNo ratings yet
- Structural Model and Direct Stiffness MethodDocument17 pagesStructural Model and Direct Stiffness MethodFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Sobrevega-Seismic Performance C-SMRFDocument9 pagesSobrevega-Seismic Performance C-SMRFFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Matlab Modal AnalysisDocument5 pagesMatlab Modal AnalysisFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Behavior of Steel Structures in Fire-Resistant ConstructionDocument11 pagesFactors Affecting The Behavior of Steel Structures in Fire-Resistant ConstructionFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- FEM Finite Element Method IntroductionDocument101 pagesFEM Finite Element Method IntroductionAlessandro MuragliaNo ratings yet
- Direct Stiffness Method ThermalDocument17 pagesDirect Stiffness Method ThermalFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Single Page Integral Table PDFDocument2 pagesSingle Page Integral Table PDFEduardo MazariegosNo ratings yet
- Yin 2015 ThesisDocument185 pagesYin 2015 ThesisFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Mango How ToDocument2 pagesMango How ToFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- From A Flat MirrorDocument3 pagesFrom A Flat MirrorFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- LensesDocument2 pagesLensesFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Climate ChangeDocument8 pagesClimate Changenicanor06No ratings yet
- EQS - Exercise & Quiz Solution SheetDocument1 pageEQS - Exercise & Quiz Solution SheetFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- CHM11-3 LT#1 Electronic Structure of The AtomDocument1 pageCHM11-3 LT#1 Electronic Structure of The AtomFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Properties of BambooDocument11 pagesMechanical Properties of BambooPedro Rodriguez RosalesNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Exam Review 2Document11 pagesDiagnostic Exam Review 2France Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- APA DocumentationDocument4 pagesAPA DocumentationDerya FerhatNo ratings yet
- TaiwanDocument12 pagesTaiwanFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Potential Thesis TopicsDocument3 pagesPotential Thesis TopicsFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- ESE 150: Environmental DisturbancesDocument5 pagesESE 150: Environmental DisturbancesFrance Mico SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Electrogravimetry and CoulometryDocument36 pagesUnit 5 Electrogravimetry and CoulometryAzzah Dyah Pramata67% (3)
- Chapter 1Document4 pagesChapter 1Pritjot GillNo ratings yet
- Nernst EquationDocument6 pagesNernst EquationLysa 22No ratings yet
- JEE Main Syllabus PDFDocument44 pagesJEE Main Syllabus PDFAkash KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry and its applicationsDocument39 pagesElectrochemistry and its applicationsHaider AliNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Series & Galvanic Cells ExplainedDocument12 pagesElectrochemical Series & Galvanic Cells ExplainedEve BonellNo ratings yet
- APV Corrosion Handbook 1035 01 08 2008 US tcm11-7079Document8 pagesAPV Corrosion Handbook 1035 01 08 2008 US tcm11-7079Ahmed Ibrahim Ahmed EissaNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - CHAPTER IDocument31 pagesMicrosoft Word - CHAPTER IIbrahim Elhosary100% (1)
- Electrolyte identification (40Document45 pagesElectrolyte identification (40Mimie Yasmin KamalNo ratings yet
- Chem Xii (PB) QPDocument16 pagesChem Xii (PB) QPKojo TiNo ratings yet
- Battery ResumeDocument30 pagesBattery ResumeEduardo ValleNo ratings yet
- Wa0002Document164 pagesWa0002wilson simfukweNo ratings yet
- Seminar ReportDocument32 pagesSeminar ReportMandar WajpeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells GuideDocument32 pagesElectrochemical Cells Guidemamta2111No ratings yet
- HISTORY OF ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLSDocument10 pagesHISTORY OF ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLSNabilah OthmanNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cell - Definition, Description, Types, ApplicationsDocument4 pagesElectrochemical Cell - Definition, Description, Types, ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Pre-Laboratory Activity: Chemical Activity and Corrosion of MetalsDocument4 pagesPre-Laboratory Activity: Chemical Activity and Corrosion of MetalsMigs MlaNo ratings yet
- Study Material 12th Chemistry 2023-24Document146 pagesStudy Material 12th Chemistry 2023-24Aneek ChakrovartyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry TutorialsDocument28 pagesChemistry TutorialsDomionNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis ExperimentDocument17 pagesElectrolysis ExperimentIntan CahyaningrumNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7Document30 pagesQuiz 7Juba W AllenNo ratings yet
- TEST SERIES For JEE-2020Document7 pagesTEST SERIES For JEE-2020Aashika DhareNo ratings yet
- Mse 453 Lecture 3Document5 pagesMse 453 Lecture 3francis6qwamena6qorrNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry GuideDocument78 pagesElectrochemistry GuideNik Muhammad Firdaus100% (1)
- Latihan PDPR Kimia SPM 2021 Pada 21 AprilDocument8 pagesLatihan PDPR Kimia SPM 2021 Pada 21 Aprilexo kaihunNo ratings yet
- Federal Public Service Commission Chemistry ExamDocument2 pagesFederal Public Service Commission Chemistry ExamIqra SaleemNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis of Molten and Aqueous SolutionsDocument20 pagesElectrolysis of Molten and Aqueous SolutionsahlonggNo ratings yet
- Tutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokDocument27 pagesTutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokoscarbecNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument32 pagesElectrochemistryRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- ORP Vs FRCDocument12 pagesORP Vs FRCShesharam Chouhan100% (1)