Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Remainder theorem and factor theorem for polynomials
Uploaded by
Reese PeartOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Remainder theorem and factor theorem for polynomials
Uploaded by
Reese PeartCopyright:
Available Formats
REMAINDER THEOREM If y = P(x) is a polynomial function, then a value of x that satisfies P(x) =0 is called a zero of the polynomial.
The zeros of P(x) are the same as the solutions to the equation P(x) =0. Example: 2 and -2 are zeros of the function P(x) = x2 4 because P(2) = 0 and P(-2) = 0. Also, 2 and -2 are the solutions of the equation x2 4 = 0.
Using the remainder theorem to evaluate a polynomial Example Use the remainder theorem to find P(-4) if P(x) = 2x4 10x2 + 30x 60.
Solution We can substitute for x = -4 in the expression. That is P(-4) = 2(-4)4 10(-4)2 + 30(-4) -60 = 2(256) 10(16) -120 -60 = 512-160-120-60 = 172 So the remainder is 172
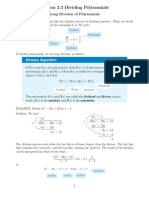
We can also use long division to find the remainder.
Another approach is to use synthetic division to find the remainder. -4 2 2 0 -8 -8 -10 32 22 30 -88 -58 -60 232 172
The remainder is 172. Also 2x4 10x2 + 30x 60 = (x+4)(2x3 8x2 + 22x 58) + 172
Example Use long division to find the remainder if 2x4 9x3 + 21x2 -26x +12 is divided by 2x-3. Solution
The remainder is 0. Also 2x4 9x3 + 21x2 - 26x + 12 = (2x-3)(x3 3x2 + 6x 4)
Example Use synthetic division to find the remainder if x4 16 is divided by x-2. Solution
The remainder is 0. Also x4 16 = (x-2)(x3 + 2x2 + 4x +8)
Students Exercise Calculate (x4 3x + 5) divided by (x 4) using long division and synthetic division. (Answer x4 3x + 5 = (x 4)(x3 + 4x2 + 16x +61) + 249)
FACTOR THEOREM
A number c is a zero of the polynomial function y = P(x) if and only if x-c is a factor of the polynomial. In other words, if P( c) = 0 then ( x-c) is a factor of the polynomial and vice versa. Example: 2 and -2 are zeros of the function P(x) = x2 4. Therefore (x 2) and (x + 2) are factors of x2 4.
Example Determine whether x + 4 is a factor of the polynomial P(x) = x3 13x + 12. If it is a factor then factor P(x) completely.
Solution Step 1: By the factor theorem, x + 4 is a factor of P(x) if and only if P(-4) = 0. P(-4) = (-4)3 13(-4) + 12= -64 + 52 + 12 = 0. Since P(-4) = 0, then x + 4 is a factor.
Step 2: The other factor is the quotient from synthetic division, so P(x) = (x+4)(x2 4x + 3) -4 1 1 0 -4 -4 -13 16 3 12 -12 0
Step 3: Factoring the quadratic term, we obtain P(x) = (x + 4) (x 3) (x 1)
Students Exercise 1. Factorise x3 7x 6 2. Solve the equation -2x3 + 11x2 -17x +6=0.
Solution 1. (x + 1)(x 3)(x + 2) 2. So x = 2 or x = 0.5 or x = 3
You might also like
- FP2 Inequalities (Chapter 1)Document11 pagesFP2 Inequalities (Chapter 1)asifjuk6692No ratings yet
- Linear Equations in Two Variables: Table of ContentsDocument14 pagesLinear Equations in Two Variables: Table of ContentsJayson AbadNo ratings yet
- MI2026 ProblemsDocument35 pagesMI2026 ProblemsHưng Đoàn VănNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Discrete MathDocument3 pagesTest 1 Discrete MathMarcus McWile MorningstarNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Linear Equations in Two Variables CADocument10 pagesGrade 9 Linear Equations in Two Variables CAkuta100% (1)
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Sequences and SeriesDocument1 pageCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Sequences and SeriesOmprakash BanshiwalNo ratings yet
- Solve Simultaneous Equations Year 9 MathsDocument4 pagesSolve Simultaneous Equations Year 9 Mathseshal meNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 POLYNOMIALSDocument69 pagesTopic 1 POLYNOMIALSNorlianah Mohd ShahNo ratings yet
- Linear Equation Word Problems2Document9 pagesLinear Equation Word Problems2sasyedaNo ratings yet
- Factoring Polynomials Rev ExDocument2 pagesFactoring Polynomials Rev ExCoolman PoonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Quadratic FormulaDocument4 pagesLesson Plan Quadratic Formulaapi-309707623100% (1)
- Pre-Calculus Math 40s Standards Test - Trigonometry I QUESTIONSDocument17 pagesPre-Calculus Math 40s Standards Test - Trigonometry I QUESTIONShmdniltfiNo ratings yet
- Principles of Math 12 - Permutations and Combinations Lesson 3 PDFDocument9 pagesPrinciples of Math 12 - Permutations and Combinations Lesson 3 PDFaustinfruNo ratings yet
- Wks. Error Analysis Complex Fractions - 7.4Document1 pageWks. Error Analysis Complex Fractions - 7.4Susie GreenNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Math Grade 8 Linear Equations 3Document2 pagesWorksheet Math Grade 8 Linear Equations 3Ibrahimli KhadijaNo ratings yet
- Non Routine ProblemsDocument31 pagesNon Routine ProblemsmikiNo ratings yet
- Number TheoryDocument73 pagesNumber TheoryPawan KumarNo ratings yet
- Permutation and Combination PDFDocument10 pagesPermutation and Combination PDFBinoy PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Quadratic Functions and Factoring: Graphing Calculator Activity: Investigating Algebra ActivityDocument94 pagesChapter 1: Quadratic Functions and Factoring: Graphing Calculator Activity: Investigating Algebra ActivityHnin Hnin HtetNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: Permutation and Combination Grade 11 MathDocument2 pagesUnit 5: Permutation and Combination Grade 11 MathRobel YacobNo ratings yet
- Quadratics, Trigonometric Equation & SeriesDocument214 pagesQuadratics, Trigonometric Equation & SeriesSam VagniNo ratings yet
- 09 Mathematics Polynomials Test 01Document1 page09 Mathematics Polynomials Test 01sivsyadavNo ratings yet
- 2010 Highschool SolutionsDocument19 pages2010 Highschool SolutionsDheliaNo ratings yet
- (Chapter 2) Linear FunctionDocument17 pages(Chapter 2) Linear FunctiondenixngNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation 1Document29 pagesQuadratic Equation 1Athena Jane NapolisNo ratings yet
- Word Problems LCM and GCDDocument19 pagesWord Problems LCM and GCDAlejandra Cifuentes ElguetaNo ratings yet
- Remainder TheoremDocument2 pagesRemainder TheoremKurarin Jan MaikeruNo ratings yet
- Basic Triangle Congruence Lesson PlanDocument1 pageBasic Triangle Congruence Lesson Planapi-219434647No ratings yet
- Partial DerivativesDocument12 pagesPartial DerivativesSatyadeep YadavNo ratings yet
- Lecture2 HandDocument12 pagesLecture2 HandNicholas FosterNo ratings yet
- Polynomials-Multiply-Factor Quiz WorksheetDocument7 pagesPolynomials-Multiply-Factor Quiz WorksheetJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Roman NumeralDocument2 pagesRoman Numeralไพรวัล ดวงตา67% (3)
- College Algebra Final Exam MC ReviewDocument11 pagesCollege Algebra Final Exam MC ReviewJoric MagusaraNo ratings yet
- Remainder Factor TheoremsDocument3 pagesRemainder Factor TheoremsJohn Goh100% (1)
- Lesson Plans Ed Tpa Task 1Document6 pagesLesson Plans Ed Tpa Task 1api-218854185No ratings yet
- Circle Circle Circle CircleDocument21 pagesCircle Circle Circle Circlerpk_14No ratings yet
- Putnam First100Document11 pagesPutnam First100Slow HandNo ratings yet
- FINAL Painless Algebra For DavaoDocument28 pagesFINAL Painless Algebra For DavaozapleekillsNo ratings yet
- Amc 12A: 69th AnnualDocument33 pagesAmc 12A: 69th AnnualNghiaNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective: We Will Add and Subtract Positive and Negative IntegersDocument38 pagesLearning Objective: We Will Add and Subtract Positive and Negative IntegersAngeline CuriosoNo ratings yet
- SAT Math Function Quiz: f(x) and z(q) ValuesDocument3 pagesSAT Math Function Quiz: f(x) and z(q) Valuessuhaila.gNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 QuestionDocument9 pagesAlgebra 2 QuestionGeorge Ezar N. QuiriadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Omer Baktir 1Document10 pagesLesson Plan Omer Baktir 1api-501227468No ratings yet
- Latin SquaresDocument65 pagesLatin Squarestoumazi0% (1)
- Statistics Lesson Plan Residual Plots FinalDocument7 pagesStatistics Lesson Plan Residual Plots Finalapi-482776194No ratings yet
- Divisibility RulesDocument13 pagesDivisibility RulesJeffrey Catacutan FloresNo ratings yet
- Answers To Previous PAT Tests OxfordDocument181 pagesAnswers To Previous PAT Tests OxfordPatricia Sheppard100% (2)
- 7.5lines and Planes in SpaceDocument38 pages7.5lines and Planes in SpacePrabhdeep SinghNo ratings yet
- ALGEBRADocument8 pagesALGEBRAafoo1234No ratings yet
- Lecture Notes MTH302 Before MTT MyersDocument88 pagesLecture Notes MTH302 Before MTT MyersAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Ch18 PDF Official Sat Study Guide Passport Advanced MathDocument14 pagesCh18 PDF Official Sat Study Guide Passport Advanced MathyawahabNo ratings yet
- Chapter8 Probability PDFDocument13 pagesChapter8 Probability PDFAriston EtormaNo ratings yet
- Dividing Polynomials Using Long DivisionDocument2 pagesDividing Polynomials Using Long DivisionHero MirasolNo ratings yet
- Different Forms of A Straight Line's EquationDocument6 pagesDifferent Forms of A Straight Line's EquationCharalampidis Dimitris100% (1)
- Quadratics Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesQuadratics Lesson PlanJeanne MalonzoNo ratings yet
- Kama SutraDocument7 pagesKama SutraMorbacovNo ratings yet
- Advanced Algeb ProjectDocument17 pagesAdvanced Algeb ProjectdiomNo ratings yet
- HSC Maths Extension 1 NotesDocument5 pagesHSC Maths Extension 1 Notesleozhou951100% (1)
- MuscleDocument62 pagesMuscleReese PeartNo ratings yet
- Energy BalanceDocument4 pagesEnergy BalanceReese PeartNo ratings yet
- GWEP AppFormDocument2 pagesGWEP AppFormReese PeartNo ratings yet
- Mass SpectrometryDocument3 pagesMass SpectrometryReese PeartNo ratings yet
- CXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and MagnetismDocument22 pagesCXC-CSEC Physics - Electricity and Magnetismdela275% (8)
- What Can I Do With a Biochemistry DegreeDocument1 pageWhat Can I Do With a Biochemistry DegreeReese PeartNo ratings yet
- Paper 32Document7 pagesPaper 32Raymond ScottNo ratings yet
- Paper - 3 June 95Document5 pagesPaper - 3 June 95Raymond ScottNo ratings yet
- 77 Ways to Use a Bio DegreeDocument1 page77 Ways to Use a Bio DegreeReese PeartNo ratings yet
- Remainder theorem and factor theorem for polynomialsDocument5 pagesRemainder theorem and factor theorem for polynomialsReese PeartNo ratings yet
- 11 2 ET V1 S1 - Introduction PDFDocument12 pages11 2 ET V1 S1 - Introduction PDFshahbaz jokhioNo ratings yet
- Flarenet Data Import From ExcelDocument15 pagesFlarenet Data Import From ExcelAbhay BhoirNo ratings yet
- Capstone ResearchDocument27 pagesCapstone ResearchRefugio, Quince MacamNo ratings yet
- Test PaperDocument2 pagesTest PaperLiliana BajdechiNo ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of The Readings About Rizal LawDocument4 pagesPros and Cons of The Readings About Rizal LawDaryl James Nucum33% (3)
- Customs and Traditions of Moros in The Philippine Island of He WestDocument4 pagesCustoms and Traditions of Moros in The Philippine Island of He Westkitty fordasNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Properties of English Syntax Some Remarks On The Essence of Human LanguageDocument3 pagesSome Basic Properties of English Syntax Some Remarks On The Essence of Human Languagewawan100% (1)
- Analysis of The Cockroach by Kevin HalliganDocument2 pagesAnalysis of The Cockroach by Kevin HalliganAbdulhusein786100% (1)
- Reporting ReviewerDocument26 pagesReporting ReviewerSTEPHANIE ANNE DACALANIONo ratings yet
- VHDL Module 5Document26 pagesVHDL Module 5Hemanth KumarNo ratings yet
- Hamel Basis, Additive Functions, and Cauchy's Functional EquationDocument6 pagesHamel Basis, Additive Functions, and Cauchy's Functional EquationVincent TeyekpitiNo ratings yet
- IMD StationsDocument15 pagesIMD Stationschinna rajaNo ratings yet
- The Happy Linguist by 3 Minute LanguagesDocument921 pagesThe Happy Linguist by 3 Minute LanguagesAlexandre KrulNo ratings yet
- Install Visual Basic 6Document3 pagesInstall Visual Basic 6avijit babuNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Riset Sains Manajemen: Volume 2, Nomor 3, 2018Document9 pagesJurnal Riset Sains Manajemen: Volume 2, Nomor 3, 2018Deedii DdkrnwnNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDetailed Lesson PlanAntonetteNo ratings yet
- Free BTC Bot Mining Script1646983482Document3 pagesFree BTC Bot Mining Script1646983482José DanielNo ratings yet
- GCP ACE NotesDocument127 pagesGCP ACE NotesyuvarajNo ratings yet
- PPL UNIT 1a PDFDocument11 pagesPPL UNIT 1a PDFsatya sriNo ratings yet
- Huawei Routing Overview CommandDocument26 pagesHuawei Routing Overview Commandeijasahamed100% (1)
- Instruction Booklet For Creating A Custom Kakejiku (Wall Scroll)Document10 pagesInstruction Booklet For Creating A Custom Kakejiku (Wall Scroll)Claudio OyarzunNo ratings yet
- 7 - Spreadsheets and DatabasesDocument3 pages7 - Spreadsheets and DatabasesМакс КальмусNo ratings yet
- Third Quarter Test in Prac 1Document38 pagesThird Quarter Test in Prac 1Cynthia LuayNo ratings yet
- Linguistic FunctionsDocument42 pagesLinguistic FunctionsRussel John CalloNo ratings yet
- BAKKER, S. J (2009), The Noun Phrase in Ancient GreekDocument336 pagesBAKKER, S. J (2009), The Noun Phrase in Ancient GreekIstván Drimál100% (1)
- Serampore MissionDocument193 pagesSerampore MissionLakshminatha DasaNo ratings yet
- Lib Burst GeneratedDocument8 pagesLib Burst Generatedlisbert lisNo ratings yet
- Day5-3-Asynchronous Programming - 2 Hours - 080220Document5 pagesDay5-3-Asynchronous Programming - 2 Hours - 080220noorfatima.okitNo ratings yet
- lesson1.PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION ACT.1-4, Jhondavesurbano, BSED-SCIENCE1ADocument6 pageslesson1.PURPOSIVE COMMUNICATION ACT.1-4, Jhondavesurbano, BSED-SCIENCE1AJhon Dave Surbano100% (1)
- Redfish Ref Guide 2.0Document30 pagesRedfish Ref Guide 2.0MontaneNo ratings yet