Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conversion of Units - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
marx0506Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Conversion of Units - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia
Uploaded by
marx0506Copyright:
Available Formats
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Conversion of units
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Conversion of units is the conversion between different units of measurement for the same quantity, typically through multiplicative conversion factors .
Contents
1 Techniques 1.1 Process 1.2 Multiplication factors 1.3 Table ordering 2 Tables of conversion factors 2.1 Length 2.2 Area 2.3 Volume 2.4 Plane angle 2.5 Solid angle 2.6 Mass 2.7 Density 2.8 Time 2.9 Frequency 2.10 Speed or velocity 2.11 Flow (volume) 2.12 Acceleration 2.13 Force 2.14 Pressure or mechanical stress 2.15 Torque or moment of force 2.16 Energy 2.17 Power or heat flow rate 2.18 Action 2.19 Dynamic viscosity 2.20 Kinematic viscosity 2.21 Electric current 2.22 Electric charge 2.23 Electric dipole 2.24 Electromotive force, electric potential difference 2.25 Electrical resistance 2.26 Capacitance 2.27 Magnetic flux 2.28 Magnetic flux density 2.29 Inductance 2.30 Temperature
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 1/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
2.31 Information entropy 2.32 Luminous intensity 2.33 Luminance 2.34 Luminous flux 2.35 Illuminance 2.36 Radiation - source activity 2.37 Radiation - exposure 2.38 Radiation - absorbed dose 2.39 Radiation - equivalent dose 3 Software tools 3.1 General commercial sources of converters 4 In fiction 5 See also 6 References 7 External links
Techniques
Process
The process of conversion depends on the specific situation and the intended purpose. This may be governed by regulation, contract, Technical specifications or other published standards. Engineering judgment may include such factors as: The precision and accuracy of measurement and the associated uncertainty of measurement The statistical confidence interval or tolerance interval of the initial measurement The number of significant figures of the measurement The intended use of the measurement including the engineering tolerances Some conversions from one system of units to another need to be exact, without increasing or decreasing the precision of the first measurement. This is sometimes called soft conversion. It does not involve changing the physical configuration of the item being measured. By contrast, a hard conversion or an adaptive conversion may not be exactly equivalent. It changes the measurement to convenient and workable numbers and units in the new system. It sometimes involves a slightly different configuration, or size substitution, of the item. Nominal values are sometimes allowed and used.
Multiplication factors
Conversion between units in the metric system can be discerned by their prefixes (for example, 1 kilogram = 1000 grams, 1 milligram = 0.001 grams) and are thus not listed in this article. Exceptions are made if the unit is commonly known by another name (for example, 1 micron = 106 metre).
Table ordering
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 2/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Within each table, the units are listed alphabetically, and the SI units (base or derived) are highlighted.
Tables of conversion factors
This article gives lists of conversion factors for each of a number of physical quantities, which are listed in the index. For each physical quantity, a number of different units (some only of historical interest) are shown and expressed in terms of the corresponding SI unit. Legend Symbol (H) exactly equal to approximately equal to of chiefly historical interest Definition
digits indicates that digits repeat infinitely (e.g. 8.294 369 corresponds to 8.294 369 369 369 369 )
Length
Length Name of unit angstrom Symbol Definition 1 1010 m 0.1 nm Relation to SI units
astronomical unit AU barleycorn (H) bohr, atomic unit a0 of length cable length (imperial) cable length (International) cable length (US) chain (Gunter's; ch Surveyor's) cubit (H) ell (H) fathom ell fm
149 597 870 700 m Distance from 149 597 870 700 m [1] Earth to Sun = in (see note above about rounding) 8.46 103 m Bohr radius of hydrogen 5.291 772 0859 1011 3.6 1020 m
[2]
608 ft 1/10 nmi 720 ft 66 ft(US) 4 rods [3] Distance from fingers to elbow 18 in 45 in [4] (In England usually) 6 ft [4]
185.3184 m 185.2 m = 219.456 m 20.116 84 m 0.5 m = 1.143 m = 1.8288 m
3/35
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
fermi finger finger (cloth) foot (Benot) (H) foot (Cape) (H) foot (Clarke's) (H) foot (International) foot (US Survey)
fm
1 1015 m[4] 7/8 in 4 in
1 1015 m = 0.022 225 m = 0.1143 m 0.304 799 735 m
ft (Ben)
Legally defined as 1.033 English feet in 0.314 858 m 1859 ft (Cla) 0.304 797 2654 m 0.304 799 514 m 0.3048 m 1/3 yd 12 inches 0.3048 m 0.304 799 47 m 12003937 m [5] 13 mm 10 chains = 660 ft = 220 yd [4] 4 in [4] in lea 2.54 cm 1/36 yd 1/12 ft 3 US Statute miles [3] 24 light-hours 60 light-minutes 60 light-seconds 0.304 800 610 m = 0.3 103 m = 201.168 m 0.1016 m .0254 m = 4 828.032 m 2.590 206 837 12 1013 m 1.079 252 8488 1012 m 1.798 754 748 1010 m
foot (Indian) (H) ft Ind ft
foot (Sear's) (H) ft (Sear) ft (US)
french; charriere F furlong hand inch (International) league (land) light-day light-hour light-minute light-second light-year line link (Gunter's; Surveyor's) ly ln lnk fur
Distance light travels in one second in 299 792 458 m vacuum Distance light travels in vacuum in 365.25 days [6] 1/12 in [7] 1/100 ch [4] 0.66 ft 7.92in 1 ft [4] Distance light travels in 1299 792 458 of a second in vacuum.[8] = 9.460 730 472 5808 1015 m = 0.002 116 m = 0.201 168 m = 0.3048 m
link (Ramsden's; lnk Engineer's)
metre (SI base
1m
4/35
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
unit) mickey micron mil; thou mil
110 000 000 of the distance from equator to pole. 1200 in 1 103 in 10 km 6 082 ft mi 80 chains 5 280 ft 1 760 yd 6 000 ft 6 087 ft 5 280 US Survey feet (5 280 1 200 3 937) m 2 in [4] nm NL; nl 1 109 m 3 nmi [4] = 1.27 104 m 1 106 m 2.54 105 m = 10 000 m = 1 853.7936 m 1 609.344 m 1 828.8 m = 1 855.3176 m 1 609.347 219 m = 0.057 15 m 1 109 m = 5556 m = 1853.184 m 1852 m 1853.248 m = 0.762 m = 0.0762 m 3.085 677 82 1016 6 106 m [10] Dependent on point measures. 0.000 351 450 m
5/35
mil (Sweden and mil Norway) mile (geographical) (H) mile (international) mile (tactical or data) mile (telegraph) mi (H) mile (US Survey) nail (cloth) nanometer nautical league nautical mile (Admiralty) nautical mile (international) nautical mile (US pre 1954) pace palm parsec pica point (American, pt English) [11][12]
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
mi
NM (Adm); nmi = 6080 ft (Adm) NM; nmi 1852 m [9] 1853.248 m 2.5 ft [4] 3 in [4] pc Distance of star with parallax shift of one arc second from a base of one astronomical unit 12 points 1/72.272 in
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
point (Didot; European)
[12][13]
1/12 1/72 of pied du roi; pt After 1878: 5/133 cm 1/72 in 1/72.27 in yd 16 ft 20 ft [4] 9 in [4] 2 in pm twp 1/1440 in
0.000 375 97 m; After 1878: 0.000 375 939 85 m = 0.000 352 7 m = 0.000 351 4598 m = 0.2286 m = 5.0292 m = 6.096 m = 0.2286 m 1 1012 m = 0.0508 m 1 1012 m = 1.7638 105 m 1.0021 1013 m [4]
point pt (PostScript) [11] point (TeX) [11] pt quarter rod; pole; perch rd (H) rope (H) span (H) spat [14] stick (H) stigma; bicron (picometre) twip yard (International) rope
x unit; siegbahn xu yd 0.9144 m [5] 3 ft 36 in
0.9144 m
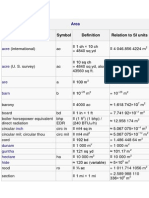
Area
Area Name of unit acre (international) acre (U. S. survey) are barn barony board bd boiler horsepower equivalent direct bhp radiation EDR circular inch circular mil; circular thou
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
Symbol ac ac a b
Definition 1 ch 10 ch = 4840 sq yd 10 sq ch = 4840 sq yd, also 43560 sq ft. 100 m2 1028 m2 4000 ac 1 in 1 ft (1 ft2) (1 bhp) / (240 BTUIT/h) /4 sq in
Relation to SI units 4 046.856 4224 m2 4 046.873 m2 [15] = 100 m2 = 1028 m2 1.618 742 107 m2 = 7.741 92 103 m2 12.958 174 m2 5.067 075 104 m2 5.067 075 1010 m2
6/35
circ in
circ mil /4 mil2
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
cord dunam guntha hectare hide rood section shed square (roofing) square chain (international) square chain (US Survey) square foot square foot (US Survey) square inch square kilometre sq ch sq ch sq ft sq ft sq in km2 ro ha
192 bd 1 000 m2 121 sq yd 10 000 m2 120 ac (variable) ac 1 mi 1 mi 1052 m2 10 ft 10 ft 66 ft 66 ft = 1/10 ac
= 1.486 448 64 m2 = 1 000 m2 101.17 m2 10 000 m2 5 105 m2 = 1 011.714 1056 m2 = 2.589 988 110 336 106 m2 = 1052 m2 = 9.290 304 m2 404.685 642 24 m2 9.290 304 102 m2 9.290 341 161 327 49 102 m2 6.4516 104 m2 = 106 m2
66 ft(US) 66 ft(US) = 1/10 ac 404.687 3 m2 1 ft 1 ft 1 ft (US) 1 ft (US) 1 in 1 in 1 km 1 km 1 lnk 1 lnk 0.66 ft(US) 0.66 ft(US) 1 lnk 1 lnk 1 ft 1 ft 1 m 1 m 1 mil 1 mil 1 mi 1 mi 1 mi (US) 1 mi (US) 1 rd 1 rd 1 yd 1 yd 1 000 m2 36 sq mi (US) 30 ac
square link (Gunter's)(International) sq lnk square link (Gunter's)(US Survey) square link (Ramsden's) square metre (SI unit) square mil; square thou square mile square mile (US Survey) square rod/pole/perch square yard (International) stremma township yardland sq lnk sq lnk m2 sq mil sq mi sq mi sq rd sq yd
1 lnk 1 lnk 0.66 ft 0.66 ft = 4.046 856 4224 102 m2 4.046 872 102 m2 = 0.09290304 m2 = 1 m2 = 6.4516 1010 m2 = 2.589 988 110 336 106 m2 2.589 998 47 106 m2 = 25.292 852 64 m2 0.836 127 36 m2 = 1 000 m2 9.323 994 107 m2 1.2 105 m2
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
7/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Volume
Name of unit acre-foot acre-inch barrel (imperial) barrel (petroleum) barrel (US dry) barrel (US fluid) board-foot bucket (imperial) bushel (imperial) bushel (US dry heaped) bushel (US dry level) butt, pipe coomb cord (firewood) cord-foot cubic fathom cubic foot cubic inch cubic metre (SI unit) cubic mile cubic yard cup (breakfast) cup (Canadian) cup (metric) cup (US customary) c (CA) c c (US) cu fm cu ft cu in m3 cu mi cu yd bl (imp) bl; bbl bl (US) Symbol ac ft Volume Definition 1 ac x 1 ft = 43 560 ft3 1 ac 1 in 36 gal (imp) 42 gal (US) 105 qt (US) = 105/32 bu (US lvl) 144 cu in 4 gal (imp) 8 gal (imp) 1 bu (US lvl) 2 150.42 cu in 126 gal (wine) 4 bu (imp) 8 ft 4 ft 4 ft 16 cu ft 1 fm 1 fm 1 fm 1 ft 1 ft 1 ft 1 in 1 in 1 in 1 m 1 m 1 m 1 mi 1 mi 1 mi 27 cu ft 10 fl oz (imp) 8 fl oz (imp) 250.0 106 m3 8 US fl oz 1/16 gal (US) 240 mL[16] 1/384 gi (imp) = pinch
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 8/35
Relation to SI units = 1 233.481 837 547 52 m3 = 102.790 153 128 96 m3 = 0.163 659 24 m3 = 0.158 987 294 928 m3 = 0.115 628 198 985 075 m3 = 0.119 240 471 196 m3 2.359 737 216 103 m3 = 0.018 184 36 m3 = 0.036 368 72 m3 = 0.044 048 837 7086 m3 = 0.035 239 070 166 88 m3 = 0.476 961 884 784 m3 = 0.145 474 88 m3 = 3.624 556 363 776 m3 = 0.453 069 545 472 m3 = 6.116 438 863 872 m3 0.028 316 846 592 m3 16.387 064 106 m3 1 m3 4 168 181 825.440 579 584 m3 0.764 554 857 984 m3 = 284.130 625 106 m3 = 227.3045 106 m3 = 250.0 106 m3 = 236.588 2365 106 m3 = 2.4 104 m3
fl bl (US) 31 gal (US) fbm bkt bu (imp) bu (US) bu (US lvl)
cup (US food nutrition labeling) c (US)
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
dash (imperial) dash (US) dessertspoon (imperial) drop (imperial) drop (imperial) (alt) drop (medical) drop (medical) drop (metric) drop (US) drop (US) (alt) drop (US) (alt) fifth firkin fluid drachm (imperial) fluid dram (US); US fluidram fluid scruple (imperial) gallon (beer) gallon (imperial) gallon (US dry) gallon (US fluid; Wine) gill (imperial); Noggin gill (US) hogshead (imperial) hogshead (US) jigger (bartending) kilderkin lambda last litre load
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
(imp)
= 369.961 751 302 08 3 109 m3
1/96 US fl oz = US pinch = 308.057 599 609 375 109 m3 1/12 gi (imp) gtt gtt 1/288 fl oz (imp) 1/1 824 gi (imp) 0.9964/12 ml 1/12 ml 1/20 mL gtt gtt gtt 1/360 US fl oz 1/456 US fl oz 1/576 US fl oz 1/5 US gal 9 gal (US) fl dr fl dr fl s beer gal fl oz (imp) US fl oz 1/24 fl oz (imp) 282 cu in = 11.838 776 0416 106 m3 = 98.656 467 013 8 109 m3 77.886 684 109 m3 = 83.03 109 m3 = 83.3 109 m3 = 50.0 109 m3 = 82.148 693 22916 109 m3 64.854 231 496 71 109 m3 51.342 933 268 23 109 m3 = 757.082 3568 106 m3 = 0.034 068 706 056 m3 = 3.551 632 8125 106 m3 = 3.696 691 195 3125 106 m3 = 1.183 877 60416 106 m3 = 4.621 152 048 103 m3 4.546 09 103 m3 = 4.404 883 770 86 103 m3 3.785 411 784 103 m3 = 142.065 3125 106 m3 = 118.294 118 25 106 m3 = 0.327 318 48 m3 = 0.238 480 942 392 m3 44.36 106 m3 = 0.081 829 62 m3 = 1 109 m3 = 2.909 4976 m3 0.001 m3 = 1.415 842 3296 m3
9/35
gal (imp) 4.546 09 L gal (US) gal (US) gi (imp); nog gi (US) bu (US lvl) 231 cu in 5 fl oz (imp) 4 US fl oz
hhd (imp) 2 bl (imp) hhd (US) 2 fl bl (US) 1 US fl oz 18 gal (imp) 1 mm3 80 bu (imp) L 1 dm3 [17] 50 cu ft
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
minim (imperial) minim (US) ounce (fluid imperial) ounce (fluid US customary) ounce (fluid US food nutrition labeling) peck (imperial) peck (US dry) perch pinch (imperial) pinch (US) pint (imperial) pint (US dry) pint (US fluid) pony pottle; quartern quart (imperial) quart (US dry) quart (US fluid) quarter; pail register ton sack (imperial); bag sack (US) seam shot strike (imperial) strike (US) tablespoon (Australian metric)
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
min min
1/480 fl oz (imp) = 1/60 fl dr (imp)
= 59.193 880 208 3 109 m3
1/480 US fl oz = 1/60 US fl = 61.611 519 921 875 109 m3 dr 28.413 0625 106 m3 29.573 529 5625 106 m3 3 105 m3 = 9.092 18 103 m3 = 8.809 767 541 72 103 m3 = 0.700 841 953 152 m3 = 616.115 199 218 75 109 m3 = 568.261 25 106 m3 = 550.610 471 3575 106 m3 = 473.176 473 106 m3 = 22.180 147 171 875 106 m3 = 1.136 5225 103 m3 = 1.101 220 942 715 103 m3 = 946.352 946 106 m3 = 0.290 949 76 m3 = 2.831 684 6592 m3 = 0.109 106 16 m3[citation needed ] = 0.105 717 210 500 64 m3 = 0.281 912 561 335 04 m3[citation needed ] 29.57 106 m3 = 0.072 737 44 m3 = 0.070 478 140 333 76 m3 20.0 106 m3
10/35
fl oz (imp) 1/160 gal (imp) US fl oz US fl oz pk pk per 1/128 gal (US) 30 mL[16] 2 gal (imp) US lvl bu 16 ft 1 ft 1 ft
1/192 gi (imp) = tsp (imp) = 739.923 502 60416 109 m3 1/48 US fl oz = US tsp pt (imp) pt (US dry) gal (imp) 1/64 bu (US lvl) gal (US dry) 3/4 US fl oz
pt (US fl) gal (US)
gal (imp) = 80 fl oz (imp) = 2.273 045 103 m3 qt (imp) qt (US) qt (US) gal (imp) 1/32 bu (US lvl) = gal (US dry) gal (US fl) 8 bu (imp) 100 cu ft 3 bu (imp) 3 bu (US lvl) 8 bu (US lvl) 1 US fl oz 2 bu (imp) 2 bu (US lvl)
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
tablespoon (Canadian) tablespoon (imperial) tablespoon (metric) tablespoon (US customary) tablespoon (US food nutrition labeling) teaspoon (Canadian) teaspoon (imperial) teaspoon (metric) teaspoon (US customary) teaspoon (US food nutrition labeling) timber foot ton (displacement) ton (freight) ton (water) tun wey (US)
tbsp tbsp
fl oz (imp) 5/8 fl oz (imp)
= 14.206 531 25 106 m3 = 17.758 164 0625 106 m3 15.0 106 m3 = 14.786 764 7825 106 m3 = 1.5 105 m3 = 4.735 510 416 106 m3 = 5.919 388 02083 106 m3 = 5.0 106 m3 = 4.928 921 595 106 m3 = 5 106 m3 = 0.028 316 846 592 m3 = 0.991 089 630 72 m3 = 1.132 673 863 68 m3 = 1.018 324 16 m3 = 0.953 923 769 568 m3 = 1.409 562 806 6752 m3
tbsp tbsp tsp tsp
US fl oz 15 mL[16] 1/6 fl oz (imp) 1/24 gi (imp) 5.0 106 m3
tsp tsp
1/6 US fl oz 5 mL[16] 1 cu ft 35 cu ft 40 cu ft 28 bu (imp) 252 gal (wine) 40 bu (US lvl)
Plane angle
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
11/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Plane angle Name of unit angular mil arcminute; MOA arcsecond centesimal minute of arc centesimal second of arc degree (of arc) Symbol ' " ' 2/6400 rad 1/60 1/3600 1 grad/100 Definition Relation to SI units 0.981 748 103 rad 0.290 888 103 rad 4.848 137 106 rad 0.157 080 103 rad
"
1 grad/(10 000) 1/360 of a revolution /180 rad 1/400 of a revolution 2/400 rad 0.9 45 90 The angle subtended at the center of a circle by an arc whose length is equal to the circle's radius. One full revolution encompasses 2 radians. 60 30
1.570 796 106 rad 17.453 293 103 rad 15.707 963 103 rad 0.785 398 rad 1.570 796 rad = 1 rad 1.047 198 rad 0.523 599 rad
grad; grad gradian; gon octant quadrant radian (SI unit) sextant sign rad
Solid angle
Solid angle Name Symbol of unit square degree deg; sq.deg.; (/180) sr () The solid angle subtended at the center of a sphere of radius r by a portion of the surface of the sphere having an area r2. A sphere encompasses 4 sr.[14] Definition Relation to SI units 0.30462 103 sr
steradian sr (SI unit)
= 1 sr
Mass
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 12/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Notes: See Weight for detail of mass/weight distinction and conversion. Avoirdupois is a system of mass based on a pound of 16 ounces, while Troy weight is the system of mass where 12 troy ounces equals one troy pound. In this table, the unit gee is used to denote standard gravity in order to avoid confusion with the "g" symbol for grams. In physics, the pound of mass is sometimes written lbm to distinguish it from the pound-force (lbf). It should not be read as the mongrel unit "pound metre". Mass Name of unit atomic mass unit, unified atomic unit of mass, electron rest mass bag (coffee) bag (Portland cement) barge carat carat (metric) clove crith dalton dram (apothecary; troy) dram (avoirdupois) electronvolt gamma grain grave hundredweight (long) hundredweight (short); cental kilogram
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
Symbol u; AMU me 60 kg 94 lb av 22 sh tn kt ct 3 1/6 gr 200 mg 8 lb av
Definition
Relation to SI units 1.660 538 73 1027 1.3 1036 kg 9.109 382 15 1031 45 1039 kg [18] = 60 kg = 42.637 682 78 kg = 20 411.656 65 kg 205.196 548 333 mg = 200 mg = 3.628 738 96 kg 89.9349 mg 1.660 902 10 1027 1.3 1036 kg
Da dr t dr av eV gr G long cwt or cwt sh cwt kg 60 gr 27 11/32 gr 1 eV (energy unit) / c2 1 g 1/7000 lb av grave was the original name of the kilogram 112 lb av 100 lb av mass of the prototype near Paris ( mass of 1L of water)
= 3.887 9346 g = 1.771 845 195 3125 g = 1.7826 1036 kg = 1 g 64.798 91 mg 1 kg = 50.802 345 44 kg = 45.359 237 kg 1 kg (SI base unit)[8]
13/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
kip mark mite mite (metric) ounce (apothecary; troy) ounce (avoirdupois) ounce (US food nutrition labeling) pennyweight point pound pound (avoirdupois) pound (metric) pound (troy) quarter (imperial) quarter (informal) quarter, long (informal) quintal (metric) scruple (apothecary) sheet slug; geepound; hyl stone ton, assay (long) ton, assay (short) ton, long ton, short tonne (mts unit) wey Zentner
kip
1000 lb av 8 oz t 1/20 gr 1/20 g
= 453.592 37 kg = 248.827 8144 g = 3.239 9455 mg = 50 mg = 31.103 4768 g = 28.349 523 125 g = 28 g = 1.555 173 84 g = 2 mg = 0.45359237 kg 0.453 592 37 kg = 500 g = 0.373 241 7216 kg = 12.700 586 36 kg = 226.796 185 kg = 254.011 7272 kg = 100 kg = 1.295 9782 g = 647.9891 mg 14.593 903 kg = 6.350 293 18 kg 32.666 667 g 29.166 667 g = 1 016.046 9088 kg = 907.184 74 kg = 1 000 kg = 114.305 277 24 kg (variants exist)
oz t oz av oz dwt; pwt lb lb av lb t
1/12 lb t 1/16 lb 28 g[16] 1/20 oz t 1/100 ct slugft/s2 0.453 592 37 kg = 7000 grains 500 g 5 760 grains 1/4 long cwt = 2 st = 28 lb av short tn long tn
q s ap slug st AT AT
100 kg 20 gr 1/700 lb av 1 gee 1 lb av 1 s2/ft 14 lb av 1 mg 1 long tn 1 oz t 1 mg 1 sh tn 1 oz t
long tn or 2 240 lb ton sh tn t 2 000 lb 1 000 kg 252 lb = 18 st Ztr. Definitions vary; see [19] and.[14]
Density
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
14/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Name of unit gram per millilitre kilogram per cubic metre (SI unit) kilogram per litre ounce (avoirdupois) per cubic foot ounce (avoirdupois) per cubic inch
Density Symbol Definition g/mL kg/m3 kg/L oz/ft3 oz/in3 g/mL kg/m3 kg/L oz/ft3 oz/in3 oz/gal oz/gal lb/ft3 lb/in3 lb/gal lb/gal
Relation to SI units = 1,000 kg/m3 = 1 kg/m3 = 1,000 kg/m3 1.001 153 961 kg/m3 1.729 994 044 103 kg/m3 6.236 023 291 kg/m3 7.489 151 707 kg/m3 16.018 463 37 kg/m3 2.767 990 471 104 kg/m3 99.776 372 66 kg/m3 119.826 4273 kg/m3 515.378 8184 kg/m3
ounce (avoirdupois) per gallon (imperial) oz/gal ounce (avoirdupois) per gallon (US fluid) oz/gal pound (avoirdupois) per cubic foot pound (avoirdupois) per cubic inch lb/ft3 lb/in3
pound (avoirdupois) per gallon (imperial) lb/gal pound (avoirdupois) per gallon (US fluid) lb/gal slug per cubic foot
slug/ft3 slug/ft3
Time
Name of unit Symbol atomic unit of time Callippic cycle century day day (sidereal) decade fortnight helek Hipparchic cycle hour h c d d dec fn au a0/(c) 441 mo (hollow) + 499 mo (full) = 76 a of 365.25 d 100 a (see below for definition of year length) = 24 h Time needed for the Earth to rotate once around its axis, determined from successive transits of a very distant astronomical object across an observer's meridian (International Celestial Reference Frame) 10 a (see below for definition of year length) 2 wk 1/1 080 h 4 Callippic cycles - 1 d 60 min Time Definition Relation to SI units 2.418 884 254 1017 s = 2.398 3776 109 s = 100 years = 1440 min = 86 400 s 86 164.1 s = 10 years = 1 209 600 s = 3.3 s = 9.593 424 109 s = 3 600 s
15/35
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
jiffy ke (quarter of an hour) ke (traditional) lustre; lustrum Metonic cycle; enneadecaeteris millennium milliday minute moment month (full) month (Greg. av.) month (synodic) octaeteris
1/60 s 1/100 s h = 1/96 d 1/100 d 5 a of 365 d 110 mo (hollow) + 125 mo (full) = 6940 d 19 a 1 000 a (see below for definition of year length)
= .016 s = 10 ms = 60 60 / 4 s = 900 s = 60 / 4 min = 15 min = 24 60 60 / 100 s = 864 s = 24 * 60 / 100 min = 14.4 min = 1.5768 108 s = 5.996 16 108 s = 1000 years = 24 60 60 / 1 000 s = 86.4 s = 60 s = 90 s = 2 592 000 s 2.6297 106 s = 2 505 600 s 2.551 106 s = 2.524 608 108 s 1.351 211 868 1043 s
jiffy (alternate) ja
md min mo mo
1/1 000 d 60 s, due to leap seconds sometimes 59 s or 61 s, 90 s 30 d[20] Average Gregorian month = 1 a (Gregorian average) / 12 = 365.242 5 d / 12 = 30.436 875 d 29 d[20] Cycle time of moon phases 29.530 589 d (Average) = 48 mo (full) + 48 mo (hollow) + 3 mo (full)[21][22] = 8 a of 365.25 d = 2922 d (G/c5)
month (hollow) mo mo
Planck time
second
time of 9 192 631 770 periods of the radiation corresponding to the transition between the 2 hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom at 0 K[8] (but other seconds are (SI base unit) sometimes used in astronomy). Also that time it takes for light to travel a distance of 299,792,458 meters. 108 s 106 s 1 461 a of 365 d = 10 ns = 1 s = 4.607 4096 1010 s = 100 fs = 168 h = 10 080 min
16/35
shake sigma Sothic cycle svedberg week S wk
1013 s 7d
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
= 604 800 s year (Gregorian) year (Julian) year (sidereal) year (tropical) = 365.2425 d average, calculated from common years (365 a, y, or d) plus leap years (366 d) on most years divisible by 4. See yr leap year for details. a, y, or = 365.25 d average, calculated from common years (365 d) yr plus one leap year (366 d) every four years a, y, or time taken for Sun to return to the same position with yr respect to the stars of the celestial sphere a, y, or Length of time it takes for the Sun to return to the same yr position in the cycle of seasons = 31 556 952 s = 31 557 600 s 365.256 363 d 31 558 149.7632 s 365.242 190 d 31 556 925 s
Where UTC is observed, the length of time units longer than 1 s may increase or decrease by 1 s if a leap second occurs during the time interval of interest.
Frequency
Frequency Name of unit Symbol hertz (SI unit) revolutions per minute Hz rpm Definition Number of cycles per second One unit rpm equals one rotation completed around a fixed axis in one minute of time. Relation to SI units = 1 Hz = 1/s 0.104 719 755 rad/s
Speed or velocity
Speed Name of Symbol unit foot per hour foot per minute foot per second furlong per fortnight inch per hour inch per minute iph ipm fph fpm fps 1 ft/h 1 ft/min 1 ft/s furlong/fortnight 1 in/hr 1 in/min Definition Relation to SI units 8.466 667 105 m/s = 5.08 103 m/s = 3.048 101 m/s 1.663 095 104 m/s 7.05 556 106 m/s 4.23 333 104 m/s
17/35
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
inch per second kilometre per hour knot
ips
1 in/s
= 2.54 102 m/s = 1/3.6 m/s 2.777 778 101 m/s 0.514 444 m/s = 0.514 773 m/s
km/h kn, kt
1 km/h 1 NM/h = 1.852 km/h 1 NM (Adm)/h = 1.853 184 km/h[citation needed ]
knot kn (Admiralty) mach number
Ratio of the speed to the speed of sound in the medium. Varies especially with temperature. About 1225 km/h (761 mph) in air at sea 340 to 295 m/s level to about 1062 km/h (660 mph) at jet altitudes (12,200 metres for aircraft [23] (40,000 ft)). Unitless 1 m/s 1 mi/h 1 mi/min 1 mi/s 299 792 458 m/s = 1 m/s = 0.447 04 m/s = 26.8224 m/s = 1 609.344 m/s = 299 792 458 m/s
metre per second (SI m/s unit) mile per hour mile per minute mile per second speed of light in vacuum mph mpm mps c
speed of s sound in air
Varies especially with temperature. About 1225 km/h (761 mph) in air 340 to 295 m/s at at sea level to about 1062 km/h (660 mph) at jet altitudes. aircraft altitudes
A velocity consists of a speed combined with a direction; the speed part of the velocity takes units of speed.
Flow (volume)
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
18/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Flow Name of unit cubic foot per minute cubic foot per second cubic inch per minute cubic inch per second ft3/s in3/min in3/s Symbol Definition 1 ft3/s 1 in3/s 1 m3/s Relation to SI units = 0.028 316 846 592 m3/s = 1.638 7064 105 m3/s = 1 m3/s = 4.381 263 638 108 m3/s = 1.051 503 273 106 m3/s CFM[citation needed ] 1 ft3/min = 4.719 474 432 104 m3/s 1 in3/min = 2.731 1773 107 m3/s
cubic metre per second (SI unit) m3/s gallon (US fluid) per day gallon (US fluid) per hour gallon (US fluid) per minute litre per minute
GPD[citation needed ] 1 gal/d GPH[citation needed ] 1 gal/h
GPM[citation needed ] 1 gal/min = 6.309 019 64 105 m3/s LPM[citation needed ] 1 L/min = 1.6 105 m3/s
Acceleration
Acceleration Name of unit foot per hour per second foot per minute per second foot per second squared gal; galileo inch per minute per second inch per second squared knot per second Symbol fph/s fpm/s fps2 Gal ipm/s ips2 kn/s Definition 1 ft/(hs) 1 ft/(mins) 1 ft/s2 1 cm/s2 1 in/(mins) 1 in/s2 1 kn/s 1 m/s2 1 mi/(hs) 1 mi/s2 Relation to SI units 8.466 667 105 m/s2 = 5.08 103 m/s2 = 3.048 101 m/s2 = 102 m/s2 4.233 333 104 m/s2 = 2.54 102 m/s2 5.144 444 101 m/s2 = 1 m/s2 = 4.4704 101 m/s2 = 26.8224 m/s2 = 1.609 344 103 m/s2
metre per second squared (SI unit) m/s2 mile per hour per second mile per minute per second mile per second squared standard gravity mph/s mps2 g
mpm/s 1 mi/(mins)
9.806 65 m/s2 = 9.806 65 m/s2
Force
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
19/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Name of unit atomic unit of force dyne (cgs unit) kilogram-force; kilopond; graveforce kip; kip-force milligrave-force, gravet-force newton (SI unit)
Symbol me2c2/a0 dyn gcm/s2
Force Definition
Relation to SI units 8.238 722 06 108 N
[24]
= 105 N = 9.806 65 N = 4.448 221 615 2605 103 N = 9.806 65 mN
kgf; kp; g 1 kg Gf kip; kipf; klbf
g 1 000 lb
mGf; gf 'g' 1 g N
A force capable of giving a mass of one kg an = 1 N = 1 kgm/s2 acceleration of one metre per second, per second.[25] g 1 oz g 1 lb 1 lbft/s2 1 tm/s2 g 1 sh tn = 0.278 013 850 953 7812 N = 4.448 221 615 2605 N = 0.138 254 954 376 N = 1 103 N = 8.896 443 230 521 103 N
ounce-force pound-force poundal sthene (mts unit) ton-force
ozf lbf pdl sn tnf
See also: Conversion between weight (force) and mass
Pressure or mechanical stress
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
20/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Pressure Name of unit atmosphere (standard) atmosphere (technical) bar barye (cgs unit) centimetre of mercury centimetre of water (4 C) foot of mercury (conventional) foot of water (39.2 F) inch of mercury (conventional) inch of water (39.2 F) kilogram-force per square millimetre kip per square inch micron (micrometre) of mercury millimetre of mercury millimetre of water (3.98 C) pascal (SI unit) pize (mts unit) pound per square foot pound per square inch poundal per square foot short ton per square foot torr
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
Symbol atm at bar 1 dyn/cm2 cmHg 1 kgf/cm2
Definition
Relation to SI units 101 325 Pa [26] = 9.806 65 104 Pa
[26]
105 Pa = 0.1 Pa 1.333 22 103 Pa
[26]
13 595.1 kg/m3 1 cm g
cmH2O 999.972 kg/m3 1 cm g ftHg ftH2O inHg inH2O 13 595.1 kg/m3 1 ft g 999.972 kg/m3 1 ft g 13 595.1 kg/m3 1 in g 999.972 kg/m3 1 in g
98.063 8 Pa [26] 40.636 66 103 Pa
[26]
2.988 98 103 Pa
[26]
3.386 389 103 Pa
[26]
249.082 Pa [26] = 9.806 65 106 Pa
[26]
kgf/mm2 1 kgf/mm2 ksi mHg mmHg mmH2O Pa pz psf psi 1 kipf/sq in 13 595.1 kg/m3 1
6.894 757 106 Pa
[26]
m g 0.001 torr 0.133 322 4 Pa [26] 133.3224 Pa [26] = 9.806 38 Pa = 1 Pa [27] = 1 103 Pa = 1 kPa 47.880 26 Pa [26] 6.894 757 103 Pa
[26]
13 595.1 kg/m3 1 mm g 1 torr 999.972 kg/m3 1 mm g = 0.999 972 kgf/m2 N/m2 = kg/(ms2) 1 000 kg/ms2 1 lbf/ft2 1 lbf/in2
pdl/sq ft 1 pdl/sq ft 1 sh tn g / 1 sq ft torr 101 325/760 Pa
1.488 164 Pa [26] 95.760 518 103 Pa 133.322 4 Pa [26]
21/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Torque or moment of force
Name of unit foot-pound force foot-poundal inch-pound force metre kilogram Symbol ft lbf ft pdl in lbf m kg Torque Definition g 1 lb 1 ft 1 lbft2/s2 g 1 lb 1 in N m/ g Relation to SI units = 1.355 817 948 331 4004 Nm = 4.214 011 009 380 48 102 Nm = 0.112 984 829 027 6167 Nm 0.101 971 621 Nm
Newton metre (SI unit) Nm
N m = kgm2/s2 = 1 Nm
Energy
Name of unit British thermal unit (ISO) British thermal unit (International Table) British thermal unit (mean) British thermal unit (thermochemical) British thermal unit (39 F) British thermal unit (59 F) British thermal unit (60 F) British thermal unit (63 F) calorie (International Table) calorie (mean) Symbol Energy Definition 5.8 106 BTU59 F Relation to SI units 6.12 109 J = 1.0545 103 J = 1.055 055 852 62 103 J 1.055 87 103 J 1.054 350 103 J 1.059 67 103 J = 1.054 804 103 J 1.054 68 103 J 1.0546 103 J 4.1868 J
1
barrel of oil equivalent boe
BTUISO 1.0545 103 J BTUIT BTUmean BTUth BTU39 F BTU59 F 1.054 804 103 J BTU60 F BTU63 F calIT calmean
= 4.1868 J 4.190 02 J
to warm one gram of air-free water from 0 C to 100 C @ 1 atm 4.184 J
100 of the energy required
calorie (thermochemical)
calth
= 4.184 J
22/35
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
calorie (3.98 C) calorie (15 C) calorie (20 C) Celsius heat unit (International Table)
cal3.98 C cal15 C cal20 C CHUIT 1 BTUIT 1 K/R 1 atm 1 cm3 4.1855 J
4.2045 J = 4.1855 J 4.1819 J = 1.899 100 534 716 103 J = 0.101 325 J
cubic centimetre of cc atm; atmosphere; standard scc cubic centimetre
cubic foot of cu ft atm; atmosphere; standard 1 atm 1 ft3 scf cubic foot cubic foot of natural gas 1 000 BTUIT
= 2.869 204 480 9344 103 J = 1.055 055 852 62 106 J = 77.468 520 985 2288 103 J 1.602 177 33 1019 4.9 1026 J = 107 J = 1.355 817 948 331 4004 J = 4.214 011 009 380 48 102 J = 460.632 569 25 J = 383.556 849 0138 J 4.359 744 1018 J = 2.684 519 537 696 172 792 106 J = 0.112 984 829 027 6167 J
cubic yard of cu yd atmosphere; standard 1 atm 1 yd3 atm; scy cubic yard electronvolt erg (cgs unit) foot-pound force foot-poundal gallon-atmosphere (imperial) gallon-atmosphere (US) eV erg ft lbf ft pdl imp gal atm US gal atm e1V 1 gcm2/s2 g 1 lb 1 ft 1 lbft2/s2 1 atm 1 gal (imp) 1 atm 1 gal (US) me2c2 (= 2 Ry) 1 hp 1 h g 1 lb 1 in
hartree, atomic unit of Eh energy horsepower-hour inch-pound force hph in lbf
joule (SI unit)
The work done when a force of one newton moves the point of its application a = 1 J = 1 mN = 1 kgm2/s2 = distance of one metre in the direction of 1 CV = 1 Ws [25] the force. = 4.1868 103 J
kilocalorie; large calorie
kcal; Cal 1 000 calIT
kilowatt-hour; Board kWh;
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 23/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
of Trade Unit litre-atmosphere quad rydberg therm (E.C.) therm (US) thermie
B.O.T.U. 1 kW 1 h l atm; sl 1 atm 1 L 1015 BTUIT Ry R c 100 000 BTUIT 100 000 BTU59 F th 1 McalIT 7 Gcalth 10 Gcalth 1 Gcalth
= 3.6 106 J = 101.325 J = 1.055 055 852 62 1018 J 2.179 872 1018 J = 105.505 585 262 106 J = 105.4804 106 J = 4.1868 106 J = 29.288 109 J = 41.84 109 J = 4.184 109 J
ton of coal equivalent TCE ton of oil equivalent ton of TNT TOE tTNT
Power or heat flow rate
Power Name of unit atmosphere-cubic centimetre per minute atmosphere-cubic centimetre per second atmosphere-cubic foot per hour atmosphere-cubic foot per minute atmosphere-cubic foot per second BTU (International Table) per hour BTU (International Table) per minute BTU (International Table) per second calorie (International Table) per second erg per second foot-pound-force per hour Symbol atm ccm atm ccs atm cfh atmcfm atm cfs BTUIT/h Definition 1 atm 1 cm3/min 1 atm 1 cm3/s 1 atm 1 cu ft/h 1 atm 1 cu ft/min 1 atm 1 cu ft/s 1 BTUIT/h Relation to SI units = 1.688 75 103 W = 0.101 325 W = 0.797 001 244 704 W = 47.820 074 682 24 W = 2.869 204 480 9344 103 W 0.293 071 W 17.584 264 W = 1.055 055 852 62 103 W = 4.1868 W = 107 W 3.766 161 104 W
24/35
BTUIT/min 1 BTUIT/min BTUIT/s calIT/s erg/s ft lbf/h 1 BTUIT/s 1 calIT/s 1 erg/s 1 ft lbf/h
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
foot-pound-force per minute foot-pound-force per second horsepower (boiler) horsepower (European electrical) horsepower (imperial electrical) horsepower (imperial mechanical) horsepower (metric) litre-atmosphere per minute litre-atmosphere per second lusec poncelet square foot equivalent direct radiation ton of air conditioning ton of refrigeration (imperial) ton of refrigeration (IT) watt (SI unit)
ft lbf/min
1 ft lbf/min
= 2.259 696 580 552 334 102 W = 1.355 817 948 331 4004 W 9.810 657 103 W = 736 W = 746 W = 745.699 871 582 270 22 W = 735.498 75 W = 1.688 75 W = 101.325 W 1.333 104 W = 980.665 W 70.337 057 W 3 504 W
ft lbf/s bhp hp hp hp hp
1 ft lbf/s 34.5 lb/h 970.3 BTUIT/lb 75 kpm/s 746 W 550 ft lbf/s 75 m kgf/s
Latm/min 1 atm 1 L/min Latm/s lusec p 1 atm 1 L/s 1 LmHg/s [14] 100 m kgf/s
sq ft EDR 240 BTUIT/h 2000 lbs of ice melted / 24 h
2240 lb iceIT / 24 h: iceIT = 144F 3.938 875 103 W 2326 J/kg.F 200 lbs iceIT / 24 h: iceIT = 144 2326 J/kg.F W The power which in one second of time gives rise to one joule of energy.[25] 3.516 853 103 W = 1 W = 1 J/s = 1 Nm/s = 1 kgm2/s3
Action
Name of unit Action Symbol Definition Relation to SI units
atomic unit of action au
/2 1.054 571 68 1034 Js[28]
Dynamic viscosity
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
25/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Dynamic viscosity Name of unit pascal second (SI unit) poise (cgs unit) pound per foot hour pound per foot second Symbol Pas P Definition 1 baryes Relation to SI units = 0.1 Pas 4.133 789 104 Pas 1.488 164 Pas 47.880 26 Pas 6,894.757 Pas Ns/m2, kg/(ms) = 1 Pas
lb/(fth) 1 lb/(fth) lb/(fts) 1 lb/(fts)
pound-force second per square foot lbfs/ft2 1 lbfs/ft2 pound-force second per square inch lbfs/in2 1 lbfs/in2
Kinematic viscosity
Kinematic viscosity Name of unit square foot per second Symbol Definition Relation to SI units ft2/s St 1 ft2/s 1 m2/s = 0.092 903 04 m2/s = 1 m2/s
square metre per second (SI unit) m2/s stokes (cgs unit)
104 m2/s = 104 m2/s
Electric current
Electric current Name of unit Symbol ampere (SI base unit) Definition The constant current needed to produce a force of 2 107 newton per metre between two straight parallel conductors of infinite length and negligible circular cross-section placed one metre apart in a vacuum.[8] Relation to SI units
= 1 A = 1 C/s
electromagnetic unit; abampere abamp 10 A (cgs unit) esu per second; statampere (cgs unit) esu/s (0.1 Am/s) / c
= 10 A
3.335 641 1010 A
Electric charge
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
26/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Electric charge Name of unit Symbol 10 C Definition Relation to SI units = 10 C 1.602 176 462 1019 C abcoulomb; electromagnetic abC; unit (cgs unit) emu atomic unit of charge au
coulomb faraday milliampere hour statcoulomb; franklin; electrostatic unit (cgs unit)
C F mAh
The amount of electricity carried in one second = 1 C = 1 As of time by one ampere of current.[25] 1 mol NAe 0.001 A 1 h 96 485.3383 C = 3.6 C 3.335 641 1010 C
statC; (0.1 Am) / c Fr; esu
Electric dipole
Electric dipole Name of unit coulomb meter debye Symbol Cm D Definition Relation to SI units 8.478 352 81 1030 Cm[29] =1C1m = 1010 esu = 3.33564095 1030 Cm [30] atomic unit of electric dipole moment ea0
Electromotive force, electric potential difference
Voltage, electromotive force Name Symbol of unit abvolt (cgs abV unit) statvolt (cgs statV unit) volt (SI unit) V 1 108 V Definition Relation to SI units = 1 108 V = 299.792 458 V
c (1 J/Am)
The difference in electric potential across two points along a conducting wire =1V=1 carrying one ampere of constant current when the power dissipated between the W/A = points equals one watt.[25] 1 kgm2/(As3)
Electrical resistance
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 27/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Electrical resistance Name of Symbol unit ohm (SI unit) Definition Relation to SI units
The resistance between two points in a conductor when one volt of electric = 1 = 1 V/A potential difference, applied to these points, produces one ampere of current in = the conductor.[25] 1 kgm2/(A2s3)
Capacitance
Capacitor's ability to store charge Name Symbol of unit farad (SI unit) F Definition The capacitance between two parallel plates that results in one volt of potential difference when charged by one coulomb of electricity.[25] Relation to SI units = 1 F = 1 C/V = 1 A2s4/(kgm2)
Magnetic flux
magnetic flux Name of Symbol unit maxwell (CGS Mx unit) weber Wb (SI unit) 108 Wb[31] Definition Relation to SI units = 1 108 Wb
Magnetic flux which, linking a circuit of one turn, would produce in it an = 1 Wb = 1 electromotive force of 1 volt if it were reduced to zero at a uniform rate in 1 Vs = second.[25] 1 kgm2/(As2)
Magnetic flux density
What physicists call Magnetic field is called Magnetic flux density by electrical engineers and magnetic induction by applied mathematicians and electrical engineers. Name of unit Symbol gauss (CGS unit) G tesla (SI unit) T Definition Wb/m2 Relation to SI units = 1 T = 1 Wb/m2 = 1 kg/(As2) Mx/cm2 = 104 T = 1 104 T [32]
Inductance
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
28/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Inductance Name of Symbol unit henry (SI H unit) Definition Relation to SI units
The inductance of a closed circuit that produces one volt of electromotive force = 1 H = 1 when the current in the circuit varies at a uniform rate of one ampere per Wb/A = [25] second. 1 kgm2/(As)2
Temperature
For more details on this topic, see Conversion of units of temperature. Temperature Name of unit Symbol degree Celsius C degree Delisle De degree Fahrenheit degree Newton degree Rankine degree Raumur F N R; R R K 9/5 F C 9/5 + 32 C K 273.15 Definition Relation to SI units [K] [C] + 273.15 [K] = 373.15 [De] 2/3 [K] ([F] + 459.67) 5/9 [K] = [N] 100/33 + 273.15 [K] [R] 5/9 [K] = [R] 5/4 + 273.15 [K] = ([R] 7.5) 40/21 + 273.15 F GM 25 + 300 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water.[8] [K] [GM] 125/9 + 422.038 1K
degree Rmer R Regulo Gas Mark GM;
kelvin (SI base K unit)
Information entropy
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
29/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Information entropy Name of unit SI unit nat; nip; nepit bit; shannon ban; hartley nibble byte B Symbol J/K nat Definition J/K kB Relation to SI units = 1 J/K = 1.380 650 5(23) 1023 J/K = 1 bit Relation to bits
bit; b; Sh ln(2) k B = 9.569 940 (16) 1024 J/K ban; Hart ln(10) k B = 3.179 065 3(53) 1023 J/K 4 bits 8 bits 1 000 B
= 3.827 976 0(64) 1023 J/K = 22 bit = 7.655 952 (13) 1023 J/K = 7.655 952 (13) 1020 J/K = 7.839 695 (13) 1020 J/K = 23 bit = 8 103 bit = 8000 bit = 213 bit = 8192 bit
kilobyte (decimal) kB
kilobyte (kibibyte) KB; KiB 1 024 B
Often, information entropy is measured in shannons, whereas the (discrete) storage space of digital devices is measured in bits. Thus, uncompressed redundant data occupy more than one bit of storage per shannon of information entropy. The multiples of a bit listed above are usually used with this meaning. Other times the bit is used as a measure of information entropy and is thus a synonym of shannon.
Luminous intensity
The candela is the preferred nomenclature for the SI unit. Luminous intensity Name of unit Symbol Definition The luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540 1012 hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683 watt per steradian.[8] cd The use of candlepower as a unit is discouraged due to its ambiguity. Varies and is poorly reproducible.[33] Approximately 0.981 cd.[14] Relation to SI units = 1 cd
candela (SI base unit); cd candle candlepower cp (new) candlepower (old, precp 1948)
= 1 cd 0.981 cd
Luminance
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
30/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Name of unit candela per square foot candela per square inch
Luminance Symbol cd/ft2 cd/in2 fL L sb
Definition cd/ft2 cd/in2 cd/m2 (1/) cd/ft2 104 cd/m2
Relation to SI units 10.763 910 417 cd/m2 1,550.0031 cd/m2 = 1 cd/m2 3.426 259 0996 cd/m2 1 104 cd/m2
candela per square metre (SI unit); nit (deprecated[14]) cd/m2 footlambert lambert stilb (CGS unit)
(104/) cd/m2 3,183.098 8618 cd/m2
Luminous flux
Luminous flux Name of unit Symbol Definition Relation to SI units lumen (SI unit) lm cdsr = 1 lm = 1 cdsr
Illuminance
Name of unit lumen per square inch lux (SI unit) phot (CGS unit) Illuminance Symbol Definition Relation to SI units lm/ft2 lm/in2 lm/m2 lm/cm2 = 10.763 910 417 lx 1,550.0031 lx = 1 lx = 1 lm/m2 = 1 104 lx lm/in2 lx ph
footcandle; lumen per square foot fc
Radiation - source activity
Radioactivity Name of unit curie rutherford (H) Symbol Ci rd Definition 3.7 1010 Bq 1 MBq Relation to SI units = 3.7 1010 Bq [34] = 1 106 Bq becquerel (SI unit) Bq Number of disintegrations per second = 1 Bq = 1/s
Please note that although becquerel (Bq) and hertz (Hz) both ultimately refer to the same SI base unit (s1), Hz is used only for periodic phenomena, and Bq is only used for stochastic processes associated with radioactivity.[35]
Radiation - exposure
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
31/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Radiation - exposure Name of unit Symbol roentgen R Definition Relation to SI units 1 R 2.58 104 C/kg[31] = 2.58 104 C/kg
The roentgen is not an SI unit and the NIST strongly discourages its continued use.[36]
Radiation - absorbed dose
Radiation - absorbed dose Name of unit Symbol gray (SI unit) Gy rad rad Definition 0.01 Gy[31] Relation to SI units = 0.01 Gy 1 J/kg = 1 m2/s2 [37] = 1 Gy
Radiation - equivalent dose
Radiation - equivalent dose Name of unit sievert (SI unit) Symbol Definition Relation to SI units 0.01 Sv = 0.01 Sv 1 J/kg[35] = 1 Sv Sv Rntgen equivalent man rem
Although the definitions for sievert (Sv) and gray (Gy) would seem to indicate that they measure the same quantities, this is not the case. The effect of receiving a certain dose of radiation (given as Gy) is variable and depends on many factors, thus a new unit was needed to denote the biological effectiveness of that dose on the body; this is known as the equivalent dose and is shown in Sv. The general relationship between absorbed dose and equivalent dose can be represented as H=QD where H is the equivalent dose, D is the absorbed dose, and Q is a dimensionless quality factor. Thus, for any quantity of D measured in Gy, the numerical value for H measured in Sv may be different.[38]
Software tools
Home and office computers come with converters in bundled spreadsheet applications or can access free converters via the Internet. Units and measurements can be easily converted using these tools, but only if the units are explicitly defined and the conversion is compatible (e.g., cmHg to kPa).
General commercial sources of converters
Advanced electronic calculators have unit-conversion functionality. Spreadsheet programs usually provide conversion functions or formulas or the user can write their own. Commercial mathematical, scientific and technical applications often include converters.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 32/35
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In fiction
When a measure is converted to another unit in a fiction work like a novel or film, the value often loses meaning (as in numerology) or gets too many significant digits ("40 miles" turns into "64 km"). For this reason, authors sometimes choose numbers that can be converted easily. Most notably, distances measured in miles often begin with 3 or 5, so the value converted to km also has one significant digit (5 or 8).
See also
Accuracy and precision Conversion of units of temperature English units False precision Imperial units International System of Units Mesures usuelles Metric system Natural units Rounding Significant figures SI prefix (e.g. "kilo-" prefix) United States customary units Units (software) Units conversion by factor-label Units of measurement
References
1. ^ jobs (2012-09-14). "The astronomical unit gets fixed : Nature News & Comment" (http://www.nature.com/news/the-astronomical-unit-gets-fixed-1.11416). Nature.com. doi:10.1038/nature.2012.11416 (http://dx.doi.org/10.1038%2Fnature.2012.11416). Retrieved 2013-08-31. 2. ^ "NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty." (http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value? bohrrada0%7Csearch_for=Bohr+radius)(2006). National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved February 22, 2008. 3. ^ a b National Institute of Standards and Technology General Tables of Units of Measurement (http://ts.nist.gov/WeightsAndMeasures/Publications/appxc.cfm) 4. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Lide, D. (Ed.). (1990). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (71st ed). Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press. Section 1. 5. ^ a b National Bureau of Standards. (June 30, 1959). Refinement of values for the yard and the pound. Federal Register, viewed September 20, 2006 at National Geodetic Survey web site (http://www.ngs.noaa.gov/PUBS_LIB/FedRegister/FRdoc59-5442.pdf). 6. ^ The International Astronomical Union and Astronomical Units (http://www.iau.org/public_press/themes/measuring/) 7. ^ Klein, Herbert Arthur. (1988). The Science of Measurement: a Historical Survey. Mineola, NY: Dover Publications 0-4862-5839-4. 8. ^ a b c d e f The International System of Units, Section 2.1 (http://www.bipm.org/en/si/si_brochure/chapter2/2-1/) (8 ed.), Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, 2006, retrieved August 26, 2009 9. ^ International System of Units, (http://www.bipm.org/en/si/si_brochure/chapter4/table8.html) 8th ed. (2006), Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, Section 4.1 Table 8. 10. ^ P. Kenneth Seidelmann, Ed. (1992). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac. Sausalito, CA: University Science Books. p. 716 and s.v. parsec in Glossary. 11. ^ a b c Whitelaw, Ian. (2007). A Measure of All Things: The Story of Man and Measurement (http://books.google.com/books?id=3zgGEWM5-iAC). New York: Macmillan 0-312-37026-1. p. 152. 12. ^ a b De Vinne, Theodore Low (1900). The practice of typography: a treatise on the processes of type-making, the
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 33/35
9/5/13
12. ^ a b De Vinne, Theodore Low (1900). The practice of typography: a treatise on the processes of type-making, the point system, the names, sizes, styles and prices of plain printing types (http://books.google.com/books?id=R4DjphIpLMC) 2nd ed. New York: The Century Co. p. 142150. 13. ^ Pasko, Wesley Washington (1894). American dictionary of printing and bookmaking (http://books.google.com/books?id=Z_QUAAAAIAAJ). (1894). New York: Howard Lockwood. p. 521. 14. ^ a b c d e f Rowlett, Russ (2005), How Many? A Dictionary of Units of Measurement (http://www.unc.edu/~rowlett/units/index.html) 15. ^ Thompson, A. and Taylor, B.N. (2008). Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI). National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 811. p. 57. 16. ^ a b c d e US Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21, Section 101.9, Paragraph (b)(5)(viii) (http://ecfr.gpoaccess.gov/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=ecfr&rgn=div8&view=text&node=21:2.0.1.1.2.1.1.6&idno=21), retrieved August 29, 2009 17. ^ Barry N. Taylor, Ed., NIST Special Publication 330: The International System of Units (SI) (http://physics.nist.gov/Pubs/SP330/sp330.pdf) (2001 Edition), Washington: US Government Printing Office, 43,"The 12th Conference Generale des Poids et Mesures (CGPM)declares that the word litre may be employed as a special name for the cubic decimetre". 18. ^ CODATA Value: atomic unit of mass. (http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value? ttme%7Csearch_for=atomic+unit+of+mass) (2006). National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved 16 September 2008. 19. ^ The Swiss Federal Office for Metrology gives Zentner on a German language web page [1] (http://www.metas.ch/de/scales/systemch.html) and quintal on the English translation of that page [2] (http://www.metas.ch/en/scales/systemch.html); the unit is marked "spcifiquement suisse !" 20. ^ a b Pedersen O. (1983). "Glossary" in Coyne, G., Hoskin, M., and Pedersen, O. Gregorian Reform of the Calendar: Proceedings of the Vatican Conference to Commemorate its 400th Anniversary. Vatican Observatory. Available from Astrophysics Data System. 21. ^ Richards, E.G. (1998), Mapping Time, Oxford University Press, pp. 9495, ISBN 0-19-850413-6 22. ^ Steel, Duncan (2000), Marking Time, John Wiley & Sons, p. 46, ISBN 0-471-29827-1 23. ^ Tom Benson. (2010.) "Mach Number" (http://www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/K-12/airplane/mach.html) in Beginner's Guide to Aeronautics. NASA. 24. ^ CODATA Value: atomic unit of force (http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Constants/). (2006). National Institute of Standards and Technology. Retrieved September 14, 2008. 25. ^ a b c d e f g h i Comit International des Poids et Mesures, Resolution 2 (http://www.bipm.org/en/CIPM/db/1946/2/), 1946, retrieved August 26, 2009 26. ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Barry N. Taylor, (April 1 995), Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) (http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/pdf/sp811.pdf) (NIST Special Publication 811), Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, pp. 5768. 27. ^ Barry N. Taylor, (April 1995), Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) (NIST Special Publication 811), Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, p. 5. 28. ^ International System of Units, (http://www.bipm.org/en/si/si_brochure/chapter4/table7.html) 8th ed. (2006), Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, Section 4.1 Table 7. 29. ^ The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty (http://physics.nist.gov/cgi-bin/cuu/Value?auedm), 2006, retrieved August 26, 2009 30. ^ Robert G. Mortimer Physical chemistry,Academic Press, 2000 ISBN 0-12-508345-9, page 677 31. ^ a b c NIST Guide to SI Units, Appendix B.9 (http://physics.nist.gov/Pubs/SP811/appenB9.html), retrieved August 27, 2009 32. ^ Standard for the Use of the International System of Units (SI): The Modern Metric System IEEE/ASTM SI 101997. (1997). New York and West Conshohocken, PA: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers and American Society for Testing and Materials. Tables A.1 through A.5. 33. ^ The NIST Reference on Constants, Units, and Uncertainty (http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Units/candela.html), retrieved August 28, 2009 34. ^ Ambler Thompson & Barry N. Taylor. (2008). Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI). (http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/pdf/sp811.pdf) Special Publication 811. Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. p. 10. en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units 34/35 ^ a b The International System of Units, Section 2.2.2., Table 3
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
9/5/13
Conversion of units - Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
35. ^ a b The International System of Units, Section 2.2.2., Table 3 (http://www.bipm.org/en/si/si_brochure/chapter2/2-2/table3.html) (8 ed.), Bureau International des Poids et Mesures, 2006, retrieved August 27, 2009 36. ^ The NIST Guide to the SI (Special Publication 811), section 5.2 (http://physics.nist.gov/Pubs/SP811/sec05.html#5.2), 2008, retrieved August 27, 2009 37. ^ Ambler Thompson & Barry N. Taylor. (2008). Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI). (http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/pdf/sp811.pdf) Special Publication 811. Gaithersburg, MD: National Institute of Standards and Technology. p. 5. 38. ^ Comit international des poids et mesures, 2002, Recommendation 2 (http://www.bipm.org/en/CIPM/db/2002/2/), retrieved August 27, 2009
Notes
External links
Statutory Instrument 1995 No. 1804 (http://legislation.gov.uk/uksi/1995/1804) Units of measurement regulations 1995 From legislation.gov.uk (http://legislation.gov.uk) How Many? A dictionary of units of measurement (http://www.unc.edu/~rowlett/units/) NIST: Fundamental physical constants Non-SI units (http://physics.nist.gov/cuu/Document/nonsi_in_1998.pdf) PDF (35.7 KB) NIST Guide to SI Units (http://physics.nist.gov/Pubs/SP811/appenB9.html) Many conversion factors listed. The Unified Code for Units of Measure (http://aurora.rg.iupui.edu/~schadow/units/UCUM/ucum.html) Units, Symbols, and Conversions XML Dictionary (http://www.posc.org/refs/poscUnits20.xml) Units of Measurement Software (http://www.dmoz.org/Science/Reference/Units_of_Measurement/Software//) at the Open Directory Project Units of Measurement Online Conversion (http://www.dmoz.org/Science/Reference/Units_of_Measurement/Online_Conversion//) at the Open Directory Project
Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Conversion_of_units&oldid=570929717" Categories: Units of measurement Metrication Conversion of units of measurement This page was last modified on 31 August 2013 at 10:48. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization.
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Conversion_of_units
35/35
You might also like
- Conversion of Units Is The Conversion Between Different Conversion FactorsDocument19 pagesConversion of Units Is The Conversion Between Different Conversion Factorsnabeelmerchant01No ratings yet
- Conversion of Units Is The Conversion Between DifferentDocument31 pagesConversion of Units Is The Conversion Between DifferentElmerDolendoTorrevillaNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument47 pagesConversion of UnitsTuralNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Units 1234Document25 pagesConversion of Units 1234genetic_genNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument28 pagesConversion of UnitsMoe Myint WinNo ratings yet
- Name of Unit Symbol Relation To SI Units: ÅngströmDocument47 pagesName of Unit Symbol Relation To SI Units: ÅngströmMark Joel BucayuNo ratings yet
- Convert between units of measurementDocument27 pagesConvert between units of measurementEr Pardeep KumarNo ratings yet
- Table Conversion Wikipedia)Document33 pagesTable Conversion Wikipedia)Bobby RedianNo ratings yet
- AreaDocument2 pagesAreaTuralNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion: TechniquesDocument27 pagesUnit Conversion: TechniquesmogazNo ratings yet
- Tables of Conversion FactorsDocument47 pagesTables of Conversion FactorsAshum GoelNo ratings yet
- General Physics I Week 1Document17 pagesGeneral Physics I Week 1Reysel MonteroNo ratings yet
- General Physics (PHYS101) : Golibjon BerdiyorovDocument26 pagesGeneral Physics (PHYS101) : Golibjon BerdiyorovLiuJiewChuanNo ratings yet
- A Dictionary of Units Part 1Document33 pagesA Dictionary of Units Part 1kapil100% (1)
- Clickable Conversion Factors for Engineering CalculationsDocument14 pagesClickable Conversion Factors for Engineering Calculationssaeed65No ratings yet
- Physics Tutorial 1 SolutionsDocument14 pagesPhysics Tutorial 1 SolutionsBonaventure MasekoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument345 pagesPhysicsjoanthanbiederman100% (1)
- Week 2 CE 120-04 FOSDocument48 pagesWeek 2 CE 120-04 FOSdjyo2002.doNo ratings yet
- General Tables of Units of MeasurementDocument20 pagesGeneral Tables of Units of MeasurementhassscribedNo ratings yet
- Topic 2a-Units and Significant FiguresDocument21 pagesTopic 2a-Units and Significant Figuresahmad05673789No ratings yet
- 2Document42 pages2Nhu Nguyen0% (1)
- Conversion of UnitsDocument44 pagesConversion of UnitsYassir Butt100% (1)
- جابتر 1 ,, الدكتور اياد سعد الدين ,,, مهندسون نلتقي فنرتقي ,,S.k.A.H PDFDocument9 pagesجابتر 1 ,, الدكتور اياد سعد الدين ,,, مهندسون نلتقي فنرتقي ,,S.k.A.H PDFAmal Al SayyedNo ratings yet
- Full Conversion TableDocument9 pagesFull Conversion TableAngeloLorenzoSalvadorTamayoNo ratings yet
- Unit of MeasurementDocument4 pagesUnit of MeasurementasmjewelNo ratings yet
- SI Units Conversion Table: AppendixDocument7 pagesSI Units Conversion Table: AppendixMohamedNo ratings yet
- General Information Index: Date Series DescriptionDocument8 pagesGeneral Information Index: Date Series DescriptionRazvan C GoranNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 MeasurementDocument11 pagesCh.2 MeasurementJoanne Aga EslavaNo ratings yet
- Local Media718683439534878413Document76 pagesLocal Media718683439534878413Trisha Mae Fabales Canlas100% (1)
- Pinaka Final NaniDocument68 pagesPinaka Final NaniChristian Jeremiah TevesNo ratings yet
- Reference Data - Metric Conversion ChartDocument20 pagesReference Data - Metric Conversion ChartmshedidNo ratings yet
- Workshop CalculationDocument98 pagesWorkshop CalculationTeguh SetionoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Units of Measurements and Theory of ErrorsDocument15 pagesChapter Two Units of Measurements and Theory of Errorsyared molaNo ratings yet
- Units: Unit Is Internationally Accepted Reference Standard To Measure A Physical QuantityDocument52 pagesUnits: Unit Is Internationally Accepted Reference Standard To Measure A Physical Quantitysusmita waghmareNo ratings yet
- Chiller Refrigeration TonsDocument6 pagesChiller Refrigeration Tonsrogel_ganaNo ratings yet
- PH 110 Chapters 1 To 4Document94 pagesPH 110 Chapters 1 To 4Utailo Chaling'angaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Konversi Satuan InternasionalDocument13 pagesDaftar Konversi Satuan InternasionalDimas Jalu PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Basics, Terms, Explanations: SI UnitsDocument2 pagesBasics, Terms, Explanations: SI UnitsINTRAVEcom Industrial AutomationNo ratings yet
- Chock FastDocument49 pagesChock Fasthasancihan19032880No ratings yet
- CH 02Document16 pagesCH 02alejandra258No ratings yet
- 1 IntroDocument26 pages1 IntroJerry PratamaNo ratings yet
- CH 03Document45 pagesCH 03Titser LaarniNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion ChartDocument5 pagesUnit Conversion Chartrosid_alhusnaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 MeasurementDocument13 pagesModule 2 MeasurementEric LucesNo ratings yet
- Engg. Hydrology TYS Exp 240Document18 pagesEngg. Hydrology TYS Exp 240BIJAY KRISHNA DASNo ratings yet
- Unit Konversi SatuanDocument4 pagesUnit Konversi SatuanAdela ShofiaNo ratings yet
- Friction Head Loss in PipesDocument9 pagesFriction Head Loss in PipesnattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- BASIC FORMULAS FOR CONVERSION, AREA, PERIMETER AND VOLUMEDocument8 pagesBASIC FORMULAS FOR CONVERSION, AREA, PERIMETER AND VOLUMEAr Raymar Balisi ArabesNo ratings yet
- AP Physics Notes - IntroductionDocument5 pagesAP Physics Notes - IntroductionAndy HeNo ratings yet
- ES 15 Module 1Document21 pagesES 15 Module 1Verenice FuentesNo ratings yet
- Sheet ch1 PropDocument9 pagesSheet ch1 PropMohammad Yahya AzabNo ratings yet
- LESSON 2.4 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS v2Document43 pagesLESSON 2.4 UNITS OF MEASUREMENTS v2Reign CallosNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (10)
- Building Fire Safety SAMFSDocument2 pagesBuilding Fire Safety SAMFSmarx0506No ratings yet
- Payments on disputed sums risks minimizedDocument3 pagesPayments on disputed sums risks minimizedmarx0506No ratings yet
- Cost Consultant - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesCost Consultant - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506No ratings yet
- Priced Bill of Quantities - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesPriced Bill of Quantities - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506No ratings yet
- Earned Value Management TopicsDocument10 pagesEarned Value Management Topicsmarx0506No ratings yet
- Change Order For Construction Contracts - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesChange Order For Construction Contracts - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506100% (1)
- Additional PreliminariesDocument2 pagesAdditional Preliminariesmarx0506No ratings yet
- Tender Analysis and RecommendationsDocument18 pagesTender Analysis and Recommendationsmarx0506No ratings yet
- Piotr Nowaczyk FIDICDocument32 pagesPiotr Nowaczyk FIDICmarx0506No ratings yet
- Priced Bill of Quantities - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesPriced Bill of Quantities - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506No ratings yet
- Final Certificate For Construction Contracts - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesFinal Certificate For Construction Contracts - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506No ratings yet
- Construction Contract - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesConstruction Contract - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506No ratings yet
- Provisional Sum EOT ClaimsDocument5 pagesProvisional Sum EOT Claimsmarx0506No ratings yet
- Provisional Sum - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesProvisional Sum - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506No ratings yet
- E Procurement PDFDocument3 pagesE Procurement PDFmarx0506No ratings yet
- Architect's Instruction - Designing Buildings WikiDocument4 pagesArchitect's Instruction - Designing Buildings Wikimarx0506100% (1)
- Procurement PDFDocument8 pagesProcurement PDFmarx0506No ratings yet
- Latent DefectDocument2 pagesLatent Defectmarx0506No ratings yet
- Understanding Liquidated Damages ClausesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Liquidated Damages Clausesmarx0506100% (1)
- Understanding Liquidated Damages ClausesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Liquidated Damages Clausesmarx0506100% (1)
- New FIDIC - Checklist & GuidelinesDocument45 pagesNew FIDIC - Checklist & Guidelinesb16579% (14)
- Understanding Liquidated Damages ClausesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Liquidated Damages Clausesmarx0506100% (1)
- Extension of Time and Liquidated DamagesDocument19 pagesExtension of Time and Liquidated DamagesWan Hakim Wan YaacobNo ratings yet
- SCSI Guide To Life Cycle CostingDocument23 pagesSCSI Guide To Life Cycle Costingmarx0506100% (1)
- Latent DefectDocument2 pagesLatent Defectmarx0506No ratings yet
- Construction Contracts Checklist enDocument15 pagesConstruction Contracts Checklist enmarx0506No ratings yet
- FIDICDocument2 pagesFIDICmarx0506No ratings yet
- BCCD Fact Sheet2014Document2 pagesBCCD Fact Sheet2014marx05060% (1)
- Happens To Be A Uniform Ellipsoid: Chapter 16 Gauss' LawDocument7 pagesHappens To Be A Uniform Ellipsoid: Chapter 16 Gauss' LawSamuel PakianathanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Parameter Identification of The Universal Robots UR5 PDFDocument7 pagesDynamic Parameter Identification of The Universal Robots UR5 PDFAyman DamounNo ratings yet
- Eelab Exp8Document12 pagesEelab Exp8Leona Arreza Huerte100% (1)
- Slope stability analysis for access tunnel portalDocument3 pagesSlope stability analysis for access tunnel portal2685866No ratings yet
- Nanometer Scale Multilayer Coatings Achieve Extreme HardnessDocument12 pagesNanometer Scale Multilayer Coatings Achieve Extreme HardnessBojan PodgornikNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsDocument90 pagesLaboratory Manual For Ac Electrical CircuitsLharie Mae BecinaNo ratings yet
- ABB Motors Technical Data SheetDocument1 pageABB Motors Technical Data SheetAgung AfrizalNo ratings yet
- Table 6-Peak Solar Heat Gain Thru Ordinary GlassDocument1 pageTable 6-Peak Solar Heat Gain Thru Ordinary GlassADsuperman100% (1)
- @structural Steel Design - A Practice Oriented ApproachDocument9 pages@structural Steel Design - A Practice Oriented ApproachFRANCISCO CUBA H.No ratings yet
- Profile of Albert EinsteinDocument4 pagesProfile of Albert Einsteinfirstman31No ratings yet
- Low Angle XRDDocument11 pagesLow Angle XRDKoushik PonnuruNo ratings yet
- MSC - Adams TutorialDocument17 pagesMSC - Adams Tutorialjuandpg0% (1)
- Catalogo Raycap Baja TensionDocument250 pagesCatalogo Raycap Baja TensionDomingo RuizNo ratings yet
- 1-Classification of Waves-16-02-2023Document12 pages1-Classification of Waves-16-02-2023efewfwedawasNo ratings yet
- Forane 22 Saturation Pressure Temperature DataDocument1 pageForane 22 Saturation Pressure Temperature Datavineeth100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project: Electromagnetic InductionDocument16 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Electromagnetic InductionRajesh ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- IAL - Physics - SB2 - Teaching Plans - 7BDocument10 pagesIAL - Physics - SB2 - Teaching Plans - 7BsalmaNo ratings yet
- Noise Level Calculations: Example #1Document2 pagesNoise Level Calculations: Example #1Susheel WankhedeNo ratings yet
- The Relevance of YS/UTS RatioDocument21 pagesThe Relevance of YS/UTS RatiocarrespmNo ratings yet
- Tarea 1 MunsonDocument4 pagesTarea 1 MunsonAlexander JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Physics of Electromagnetic Calorimeters Based On Crystal ScintillatorsDocument49 pagesPhysics of Electromagnetic Calorimeters Based On Crystal ScintillatorsVigneshRamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 VibrationDocument83 pagesChapter 9 Vibration胡宇晟No ratings yet
- Literal Equations Name ProjectDocument4 pagesLiteral Equations Name Projectapi-297789948No ratings yet
- Transformers:: " Transformers Are The Heart of The Alternating Current System." - William Stanley Jr.Document13 pagesTransformers:: " Transformers Are The Heart of The Alternating Current System." - William Stanley Jr.SRIRAM SATHISHNo ratings yet
- Lewis Structures Molecular Geometry and Polarity 1A KEYDocument3 pagesLewis Structures Molecular Geometry and Polarity 1A KEYrsleoNo ratings yet
- Energy Balance CalculationDocument2 pagesEnergy Balance CalculationSzelee KuekNo ratings yet
- Papagiannakis Solutions For Text BookDocument112 pagesPapagiannakis Solutions For Text BookRishiKaithala100% (2)
- New Regulations For Geotech GermanyDocument10 pagesNew Regulations For Geotech GermanySâu HeoNo ratings yet
- Kid-sized humanoid robot design paperDocument4 pagesKid-sized humanoid robot design paperHimanshu VermaNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Atom Position on X-Ray Diffraction IntensitiesDocument29 pagesThe Effect of Atom Position on X-Ray Diffraction IntensitiesJorge De Jesus Torres ReyesNo ratings yet