Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper 1 and 2 answers
Uploaded by
Hui XiuOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper 1 and 2 answers
Uploaded by
Hui XiuCopyright:
Available Formats
Sec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper 1 answers 1) B 11) C 21) D 31) B 2) C 12) B 22) B 32) D 3) D 13) D 23) A 33)
B 4) A 14) B 24) B 34) D 5) D 15) C 25) C 35) A 6) D 16) D 26) D 36) C 7) C 17) A 27) B 37) A 8) A 18) C 28) C 38) C 9) B 19) A 29) C 39) D 10) C 20) B 30) A 40) B
Sec 4EXP Pure Chemistry Paper 2 answers A1 (a) (b) (c) (d) A2 (a) (b) Carbon dioxide Chromium Silicon dioxide Brass Insert a moist blue red litmus paper into the gas. The gas will turn the litmus paper red and then bleaches it. Sodium burns with a bright orange flame. Sodium burns vigorously with chlorine. / The reaction happens vigorously. (c) (d) 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Legend: Dot: electron of sodium Cross: electron of chlorine [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] Cation- [1] Anion- [1]
(e)(i)
Sodium chloride has a giant ionic structure that consists of strong electrostatic forces of attraction between oppositely-charged ions. A lot of energy is needed to overcome these bonds, hence a high melting point.
[1]
[1] [1]
(e)(ii)
In the molten state, the giant ionic lattice structure is destroyed to release the sodium and chloride ions. These free ions are able to conduct electricity as they move about in the molten liquid.
[1]
A3
(a)
Carbon dioxide. Bubble the gas produced into limewater. A white precipitate is formed in the limewater if the gas is carbon dioxide.
[1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1]
(b)
Observation: A yellow precipitate is formed. Ionic equation: 2I-(aq) + Pb2+(aq) PbI2(s)
(c)
Filter the mixture to obtain the residue (precipitate). Wash the residue with a little distilled water and press it dry between sheets of filter papers.
A4
(a)
Part P: Condenser. Function: It is to condense the hot vapour back into liquid so it can be collected as distillate in the receiving flask.
(b)
First modification: The bulb of the thermometer should be placed near the outlet of the distillating flask. This is to ensure that the thermometer measures the boiling point of the vapour. Second modification: Water should be flowing against the flow of vapour. This is to ensure the presence of a permanent cold surface on which all the vapour will condense back into liquid effectively before it leaves the condenser.
[1] [1]
[1] [1]
(c)
The temperature remains constant.
Substance Y starts to boil and during change of state, temperature [1] remains constant. (d)(i) (d)(ii) A5 (a) (b) (c) X is a volatile liquid. / Boiling point of X is too low. Place the receiving flask in a water bath. Weak acids. Sulfuric acid is a strong acid and it will react with the heating coil which is a metal. Yes. Vinegar is ethanoic acid which is a weak acid. (d) Effervescence will be observed. [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1]
A6
(a)
The atomic radius increases as atomic number increases. 2
[1]
As the atomic number increases, the number of electron shells also increases. (b) Atomic number: 2 Helium (c) A7 (a)(i) (a)(ii) The first ionization energy for sodium is higher than potassium. Therefore it is harder for sodium to lose its outermost electron. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) Cu(s) + ZnSO4(aq) The oxidation state of zinc increases from 0 in zinc to +2 in zinc sulfate. This is oxidation. The oxidation state of copper decreases from +2 in copper(II) sulfate to 0 in copper. This is reduction. Since oxidation and reduction occurs simultaneously, it is a redox reaction. It acts as a catalyst. When the volume of copper(II) sulfate increases, more and more zinc is used in the displacement reaction. There will lesser zinc left to react with sulfuric acid to produce hydrogen gas. Therefore, volume of hydrogen decreases as volume of copper( II) sulfate increases. (c)
[1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [2]
(b)(i) (b)(ii)
[1] [1] [1]
When temperature increases, the zinc atoms and sulfuric acid [1] molecules have greater heat energy and hence gain kinetic energy and move at higher speeds. This increases the frequency of effective collisions between them [1] and thus, rate of reaction increases.
(d)
Number of moles of hydrogen produced = 0.160 / 24.0 0.00667 mol (3sf) Mass of zinc used = 0.00667 x 65 = 0.433 g (3sf)
[1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [1] [2]
B8
(a)(i)
Endothermic. Temperature decreases as the reaction proceeds which means that heat energy is taken in from the surroundings.
(a)(ii)
5oC
(a)(iii) No more potassium nitrate can dissolve in the water so temperature did not decrease. B8 (a)(iv) The total energy taken in during bond-breaking is more than the total energy given out during bond-forming. Therefore this is an endothermic reaction and a decrease in temperature occurs. 3
(b)(i)
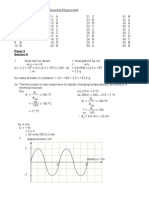
Total energy taken in for bond-breaking = 4(+413) + (+614) + 2(348) = +2962 KJ Total energy given out during bond-forming = 4(-413) + 3(-248) + 2(-330) = -3056 KJ H = (-3056) + (+2962) = -94.0 KJ [1] [1] [1] for correct axis with labels [1] for correct shape of graph C3H4Cl2 [1] for all correct labeling
(b)(ii)
C3H4 + Cl2 H= -94.0KJ
B9
(a)
October Carbon monoxide and PM10.
[1] [1]
(b)
Carbon monoxide reacts almost irreversibly and readily than oxygen with haemoglobin in red blood cells to form carboxy-haemoglobin, a stable compound. This inhibits the transportation of oxygen around the body, leading to dizziness or even death on prolonged exposure.
[1] [1] [2] [1] [1]
(c) (d)
Stay indoors. / Wear a mask when going outdoors. Sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen are pollutants which causes acid rain that damages buildings. These pollutants also cause irritation of the eyes and skin. Therefore it is important to monitor the levels of these pollutants in the air. Sulfur dioxide: Combustion of fossil fuels containing sulfur / Volcanic eruptions Oxides of nitrogen: Reaction of nitrogen and oxygen gas in the air at high temperatures around car engine / Lightning activities.
(e)
[1] [1]
A10
(a)
Platinum / Carbon 4
[1]
Either (b) Electron flow anode All correct [1] Electron flow cathode
(c)
30 40 50 60
16.40 20.80 25.60 25.60
6.60 11.0 15.8 15.8
All correct [1]
(d)
Axis labels [1] Plots and best fit line [1]
(e)
Anode: 4OH-(aq) O2(g) + H2O(l) + 4eCathode: Cu2+(aq) 2e- Cu(s)
[1] [1] [1/2] [1/2]
(f)(i) (f)(ii)
Blue solution. Colourless solution.
(g)(i)
[1]
(g)(ii) A10 Or (a)
Blue.
[1] Axis labels [1] Plots and best fit line [1]
(b) (c)
444 cm3 ( 5cm3) Zn +2HCl ZnCl2 + H2 Number of moles of hydrogen produced =0.500/24.0 =0.0208 mol (3sf)
[1]
Number of moles of hydrochloric acid = 2x0.0208 = 0.0417 mol (3sf) Concentration of hydrochloric acid = 0.0417/0.0500 =0.833 mol.dm3 (3sf) 6
[1]
[1]
(d)(i) (d)(ii)
Total volume 250 cm3 Graph has a greater gradient. Half the total volume of gas will be produced since the number of moles used is halved. The gradient of the graph will be steeper as a higher concentration of acid is used faster initial rate of reaction.
[1] [1]
[1]
(e)
Using zinc strips decreases the total exposed surface area for [1] reactants to act on. This leads to a smaller number of effective collisions per unit time and [1] thus, speed of reaction decreases.
You might also like
- Icse Class 10 March21 Chemistry Question Paper With Solutions 2023Document23 pagesIcse Class 10 March21 Chemistry Question Paper With Solutions 2023Ankit KumarNo ratings yet
- Trial Paper 2 MS PerlisDocument8 pagesTrial Paper 2 MS PerlisZaiton RoslanNo ratings yet
- Getmyunin: Ncert Solution For Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise - 1Document10 pagesGetmyunin: Ncert Solution For Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Exercise - 1Nadim BashirNo ratings yet
- Chem Prepa 1Document10 pagesChem Prepa 1Kubra KhanNo ratings yet
- Form Four (4) Chemistry 233/1 Marking SchemeDocument3 pagesForm Four (4) Chemistry 233/1 Marking SchemeTwinomujuniNo ratings yet
- Exam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1Document10 pagesExam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1asjawolverineNo ratings yet
- Nov 2008Document13 pagesNov 2008dharshanaabNo ratings yet
- HKDSE Chem FX Mock Exam Paper 1 2012 Set 1 Eng AnsDocument10 pagesHKDSE Chem FX Mock Exam Paper 1 2012 Set 1 Eng Ansleung_ting_2No ratings yet
- Tenkasi District Schools .Qu - KeyDocument16 pagesTenkasi District Schools .Qu - Keydevilssworld143No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations NotesDocument13 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations NotesJayanthiNo ratings yet
- Ujian 1 STPM t2.2015Document6 pagesUjian 1 STPM t2.2015Bbiesoth AJNo ratings yet
- SSLC study material for ChemistryDocument28 pagesSSLC study material for ChemistryStudy remix100% (1)
- S5 Chemistry Exam Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesS5 Chemistry Exam Marking Schemelala LuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ElectrolysisDocument8 pagesChapter 4 ElectrolysisPremNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMADocument12 pagesTrial Kedah Chemistry SPM 2013 K2 SKEMACikgu Faizal100% (2)
- Class X NCERT Solutions Chemistry by NTSE GuruDocument5 pagesClass X NCERT Solutions Chemistry by NTSE GuruNTSE GuruNo ratings yet
- RJC 2011 Chem Prelim Paper3ANSDocument12 pagesRJC 2011 Chem Prelim Paper3ANSJean HomeNo ratings yet
- CSEC Chemistry Paper 2 Worked SolutionsDocument6 pagesCSEC Chemistry Paper 2 Worked Solutionskay5christie9081No ratings yet
- ICSE Paper 2008Document8 pagesICSE Paper 2008CGPSC - P&P TutorialNo ratings yet
- Ahs Preliminary Examination 2008 2Document5 pagesAhs Preliminary Examination 2008 2QM007No ratings yet
- ICSE Paper 2008Document12 pagesICSE Paper 2008Geetansh KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Answer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013Document11 pagesAnswer Gerak Gempur Chemistry 2013ryder1man6433No ratings yet
- CLASS - X CHEMISTRY Important QuestionsDocument17 pagesCLASS - X CHEMISTRY Important Questionsvt654009No ratings yet
- P2 Answer SchemeDocument10 pagesP2 Answer Schemesherry_christyNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions With AnswersDocument11 pagesClass 10 Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Important Questions With AnswersASHISHNo ratings yet
- Solution 1:: Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesSolution 1:: Chemical Reactions and EquationsOjasNo ratings yet
- Sec 4E Chem (SPA) MY Marking Scheme 2012Document5 pagesSec 4E Chem (SPA) MY Marking Scheme 2012Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Questions and Answers For NCERT Book XDocument9 pagesQuestions and Answers For NCERT Book XPrabhuPalanichamyNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Model Paper 2018Document9 pagesOlympiad Model Paper 2018deeyamullaNo ratings yet
- Answers For Group VII Problem-Solving QuestionsDocument9 pagesAnswers For Group VII Problem-Solving QuestionsTan Song Kai100% (1)
- CBSE X Scince Notes ch1 Chemical Reaction ADocument3 pagesCBSE X Scince Notes ch1 Chemical Reaction Ajawahar singhNo ratings yet
- 2019 TJC H2 Chem Prelim P3 ANSDocument22 pages2019 TJC H2 Chem Prelim P3 ANSaliciaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Chemistry Question Paper 2018 Solved For Class 10Document13 pagesICSE Chemistry Question Paper 2018 Solved For Class 10Shaurya DhangarNo ratings yet
- 2009 Nov H2 Chemistry Paper 2Document6 pages2009 Nov H2 Chemistry Paper 2nncy_rox3478565No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - QWADocument10 pagesChapter 1 - QWADr.K E Reby RoyNo ratings yet
- Chem PP1, PP2 & PP3 MSDocument19 pagesChem PP1, PP2 & PP3 MSNgechiiNo ratings yet
- 4541-1&2&3 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Document22 pages4541-1&2&3 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Yeow Pow ChooNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 3Document16 pagesLesson 8 - Electrolysis Part 3Dishna KarunasekaraNo ratings yet
- Answer Pelangi 1Document11 pagesAnswer Pelangi 1Yu YanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 9 Electrochemistry Structure and Essay 13-19Document5 pagesCHAPTER 9 Electrochemistry Structure and Essay 13-19peter edwardNo ratings yet
- Science-Class-X-Chapter-1-Chemical-Reactions-And-EquationsDocument6 pagesScience-Class-X-Chapter-1-Chemical-Reactions-And-EquationsorionNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsMadhavi MullickNo ratings yet
- ICSE Paper 2009Document11 pagesICSE Paper 2009CGPSC - P&P TutorialNo ratings yet
- s4 Chemistry Paper 2 Set 4 Marking Guide 1Document13 pagess4 Chemistry Paper 2 Set 4 Marking Guide 1Namuli MercyNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test (Camb-1) October Chemistry MARKS: 25Document3 pagesMonthly Test (Camb-1) October Chemistry MARKS: 25Shahid ArainNo ratings yet
- AP Orange MCQ+FRQ NewDocument16 pagesAP Orange MCQ+FRQ NewMaya SwailemNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4CH1 1CDocument6 pagesChemistry 4CH1 1CLoki .7thNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry (Answers)Document17 pagesThermochemistry (Answers)Venessa BlingBling ChunNo ratings yet
- 862 Chemistry - Isc SpecimenDocument18 pages862 Chemistry - Isc SpecimenadityaNo ratings yet
- ICSE Paper 2010Document9 pagesICSE Paper 2010CGPSC - P&P TutorialNo ratings yet
- Solutions - Chemical ReactionsDocument8 pagesSolutions - Chemical ReactionschetanNo ratings yet
- Roselyn Trixie M. 10A Mock Test 2 - Chemistry P 2 (07-05-2021)Document16 pagesRoselyn Trixie M. 10A Mock Test 2 - Chemistry P 2 (07-05-2021)Roselyn TrixieNo ratings yet
- 4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Document22 pages4541 123 Skema Kim Trial SPM 2013Robert HicksNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument11 pagesNCERT Solutions For Chemical Reactions and EquationsSuman LataNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument7 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Reactions & EquationsAliBaigNo ratings yet
- Transition Element PropertiesDocument29 pagesTransition Element PropertiesMinaNo ratings yet
- Social ScienceDocument18 pagesSocial Sciencemonika.yogaNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Sec 2EN Holiday HW 2013Document3 pagesSec 2EN Holiday HW 2013Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Visualising FacebookDocument5 pagesVisualising FacebookHui XiuNo ratings yet
- TaiwanDocument9 pagesTaiwanHui XiuNo ratings yet
- QTSS - Sec 4 Exp MYE - Physics AnsDocument4 pagesQTSS - Sec 4 Exp MYE - Physics AnsHui XiuNo ratings yet
- Syria's Civil War Momentum ShiftsDocument18 pagesSyria's Civil War Momentum ShiftsHui XiuNo ratings yet
- SMSS MYE 2012 - 4E - Chemistry - P1 - QPDocument15 pagesSMSS MYE 2012 - 4E - Chemistry - P1 - QPHui XiuNo ratings yet
- Tanjong - Katong - 2011 A Maths Prelim P2Document5 pagesTanjong - Katong - 2011 A Maths Prelim P2Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Bukit Merah - Prelim2011 - AM - 4E5N - P1Document5 pagesBukit Merah - Prelim2011 - AM - 4E5N - P1Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- SMSS MYE 2012 4E Physics P2 QPDocument19 pagesSMSS MYE 2012 4E Physics P2 QPHui XiuNo ratings yet
- SMSS MYE 2012 4E Physics P2 QPDocument19 pagesSMSS MYE 2012 4E Physics P2 QPHui XiuNo ratings yet
- YYSS - 4 Exp Physics 2012 Paper 1Document24 pagesYYSS - 4 Exp Physics 2012 Paper 1Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- A Modest Attempt To Curb The Sale of Firearms Fails: Gun ControlDocument24 pagesA Modest Attempt To Curb The Sale of Firearms Fails: Gun ControlHui XiuNo ratings yet
- Chem - MYE - Marking Scheme - 2012 PDFDocument3 pagesChem - MYE - Marking Scheme - 2012 PDFHui XiuNo ratings yet
- CWD Phy 4e P1 My12Document13 pagesCWD Phy 4e P1 My12Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Bukit Merah - Prelim2011 - AM - 4E5N - P1Document5 pagesBukit Merah - Prelim2011 - AM - 4E5N - P1Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- 2011 BDMS 4E Prelims 2 AM Paper 1Document15 pages2011 BDMS 4E Prelims 2 AM Paper 1Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- CWD Phy 4e P2 My12Document19 pagesCWD Phy 4e P2 My12Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- CWD Phy 4e Ans My12Document6 pagesCWD Phy 4e Ans My12Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- 2012 4E Chem (SPA) P1 MY FinalDocument17 pages2012 4E Chem (SPA) P1 MY FinalHui XiuNo ratings yet
- Chem MYE P1 2012 PDFDocument16 pagesChem MYE P1 2012 PDFHui XiuNo ratings yet
- 2011 BDMS 4E Prelims 2 AM Paper 2Document25 pages2011 BDMS 4E Prelims 2 AM Paper 2Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Chem MYE P2 2012 PDFDocument15 pagesChem MYE P2 2012 PDFHui XiuNo ratings yet
- 4E1 Chem SPA MYE Marking SchemeDocument5 pages4E1 Chem SPA MYE Marking SchemeHui XiuNo ratings yet
- Bio Sec 4 MYEP112Document18 pagesBio Sec 4 MYEP112Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- Sec 4E Chem (SPA) MY Marking Scheme 2012Document5 pagesSec 4E Chem (SPA) MY Marking Scheme 2012Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- 2011 BDMS 4E Prelims 2 AM Paper 1Document15 pages2011 BDMS 4E Prelims 2 AM Paper 1Hui XiuNo ratings yet
- 2012 4E P2 Chem (SPA) MY FinalDocument17 pages2012 4E P2 Chem (SPA) MY FinalHui XiuNo ratings yet
- VT Banana FrozenDocument1 pageVT Banana FrozenHui XiuNo ratings yet
- GP ToneDocument3 pagesGP ToneHui XiuNo ratings yet
- 2.what Scrap Metal Is ThisDocument2 pages2.what Scrap Metal Is ThisRakesh Ranjan MishraNo ratings yet
- Cublen D 5113: PhosphonatesDocument2 pagesCublen D 5113: PhosphonatesrichardNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Chemistry Assignment 7 Elements of Group 16,17,18Document4 pages12 TH Chemistry Assignment 7 Elements of Group 16,17,18ritesh sakhareNo ratings yet
- 03 Neutralization Reactions Worksheet KeyDocument2 pages03 Neutralization Reactions Worksheet KeyFrancesca Penaranda17% (6)
- Chemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam) Chemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)Document4 pagesChemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam) Chemistry 17 (Second Long Sample Exam)AcademicBMNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4Document3 pagesExperiment 4Siti Rahmah YahyaNo ratings yet
- HSAB Principle ExplainedDocument14 pagesHSAB Principle Explainedneha yarrapothuNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument20 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelequakeroatsNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - Titration of Soda - Citric AcidDocument9 pagesLab 3 - Titration of Soda - Citric AcidAndrea Satira100% (1)
- CHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023Document36 pagesCHM 101 - General Chemistry-1-Lecture Note - 2023bangysmashiNo ratings yet
- 2207 - Biuret TestDocument2 pages2207 - Biuret TestSubhashree SadangiNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1027 (Amount of Substance)Document38 pagesChemsheets AS 1027 (Amount of Substance)R100% (1)
- Daftar Obat High Alert 2021Document1 pageDaftar Obat High Alert 2021Prima OktaviaNo ratings yet
- Tubular and Immersion HeatersDocument16 pagesTubular and Immersion HeatersEliasNo ratings yet
- Metal Corrosion Causes and PreventionDocument23 pagesMetal Corrosion Causes and PreventionAman NikhareNo ratings yet
- Address: Brgy. Gredu, Panabo City Telephone No.: (084) 628-4830Document2 pagesAddress: Brgy. Gredu, Panabo City Telephone No.: (084) 628-4830Mickoy D. EbagagNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of SoapsDocument2 pagesThe Chemistry of Soapsscribduserz99No ratings yet
- Group 7 The Halogens KLASSDocument12 pagesGroup 7 The Halogens KLASSKimberly LinderholmNo ratings yet
- CHEM101 - Exam 1 - Version B - Final - AnswersDocument7 pagesCHEM101 - Exam 1 - Version B - Final - AnswersSaudi ArabiaNo ratings yet
- QuantitativeDocument87 pagesQuantitativeMohamed DahmaneNo ratings yet
- The Determination of Iron (II) by Redox Titration: Experiment 15Document1 pageThe Determination of Iron (II) by Redox Titration: Experiment 15AdewaleNo ratings yet
- The Uses of Sulphuric AcidDocument9 pagesThe Uses of Sulphuric AcidsupercandidNo ratings yet
- Fontargen AJ PDFDocument282 pagesFontargen AJ PDFantonyNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 21 Answer SchemeDocument9 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 21 Answer SchemeNicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Chemsheets AS 1053 Hess Law 4 MixtureDocument1 pageChemsheets AS 1053 Hess Law 4 Mixturemy religion is hwang minhyunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Textbook Answers Chapter 5Document20 pagesChemistry - Textbook Answers Chapter 5angelina_boseNo ratings yet
- Corrosion & Control - Module3Document38 pagesCorrosion & Control - Module3lalithkumaran LNo ratings yet
- Color Coding The Periodic Table - InstructionsDocument2 pagesColor Coding The Periodic Table - InstructionsVictoria LowmanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Combination: Chapter # 02Document10 pagesChemical Combination: Chapter # 02Hina RabbaniNo ratings yet
- A2 FPS P4 PDFDocument21 pagesA2 FPS P4 PDFHaris AwanNo ratings yet