Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HEAT TRANSFER TUTORIAL ON NUCLEAR REACTOR AND THERMAL PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
Unknown uploaderOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HEAT TRANSFER TUTORIAL ON NUCLEAR REACTOR AND THERMAL PROBLEMS
Uploaded by
Unknown uploaderCopyright:
Available Formats
NATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF SINGAPORE Department Mechanical Engineering ME 3122 Heat Transfer TUTORIAL 1- CONDUCTION
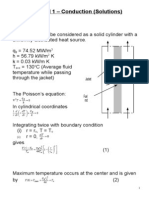
1. Figure 1 shows a typical nuclear reactor used for commercial power production. Heat is generated at the rate of 74.52 MW/m 3 in the long 50 mm OD uranium fuel rods (k = 0.03 kW/mK) which are jacketed by an annulus to permit cooling water to flow. For an average temperature, 130C of cooling water and a convective heat transfer coefficient of 56.79 kW/m2K, determine the maximum temperature of the fuel. [Ans: 534.3C]
Vertical safety rods
Reinforced Shield
Thermal Shield Fuel rods Cooling water passage Cooling tubes Figure 1. Graphite-moderated reactor (Source: General Electric Review)
2. A power transistor is capable of operating at up to 4.5 W. The manufactures specification for the case to ambient thermal resistance of the transistor is 28C/W and the case temperature is not to exceed 75C. To reduce the operating temperature, the transistor is mounted on a black anodized aluminum frame which serves as a heat sink. The frame provides an additional 1500 mm 2 surface area for cooling. In order to minimize the thermal contact resistance between the transistor and the heat sink, and at the same time maintain proper electrical insulation, the surface is first cleaned and coated with thermal grease. A special electrical insulation gasket is then inserted and the transistor is bolted lightly to the frame. In general, for proper thermal contact, resistance is of the order of 0.75C/W. Determine the maximum power at which the transistor can be safely operated if the surrounding walls and air are at 26C and h = 11 W/ m2K. [Ans: 3.09W] 3. One surface of a thin metallic plate (thermal conductivity, k= 245W/m K) has a surface temperature Ts equal to 120C. The other surface is exposed to air at temperature, Ta = 25C. The convective heat transfer coefficient between the surface and the air is 80 W/m 2K. A circular pin fin (diameter, d = 2 mm and length, L = 10 mm) is attached to the surface. Determine, (a) (b) (c) (d) the rate of heat transfer from the surface, the efficiency of the fin, the effectiveness of the fin, and the number of fins required per square meter of primary surface to increase the rate of heat transfer by 100%. [Ans: (a) 0.4645 W, (b) 97.3%, (c) 19.45, (d) 17,245]
4. A thermocouple is introduced into a pipe to measure the temperature of steam flowing through it. The thermocouple junction may be approximated as a sphere. The convection coefficient between the junction surface and the steam is known to be 380 W/m2K and the thermophysical properties of the junction are given as follows: Thermal conductivity, k: 25 W/mK Specific heat, cp: 380 J/kgK Density, : 8000 kg/m3 Determine the diameter of the junction needed for the thermocouple to have a time constant of 1 second. If the junction is at 30C and it is placed inside a tube carrying steam at 250C, how long will it take for the junction to reach 240C? [Ans: 0.75mm, 3.09 sec]
You might also like
- Alternator Working and Its Diagnosing - An Automotive Charging CircuitDocument23 pagesAlternator Working and Its Diagnosing - An Automotive Charging Circuitvijay anandhNo ratings yet
- Heat and TemperatureDocument50 pagesHeat and TemperaturealienlightningNo ratings yet
- Matlab ManualDocument50 pagesMatlab ManualRavi AnandNo ratings yet
- Gravel TestingDocument3 pagesGravel TestingTarun Bhateja100% (1)
- CH 11Document72 pagesCH 11cameronsidwell0% (2)
- ME209 Heat Transfer Solved ProblemsDocument15 pagesME209 Heat Transfer Solved ProblemsWilliam Hernan HenaoNo ratings yet
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Document44 pagesFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315AndrestorpNo ratings yet
- Steam Engineering Principles and Heat TransferDocument99 pagesSteam Engineering Principles and Heat Transferalex mobileNo ratings yet
- 4363 112 Heat TransferDocument6 pages4363 112 Heat Transferyogesh_b_kNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Document AnalysisDocument8 pagesHeat Transfer Document Analysisbhaskar5377No ratings yet
- Mech302-Heat Transfer Homework-7 SolutionsDocument8 pagesMech302-Heat Transfer Homework-7 SolutionsJake OkuyeNo ratings yet
- Thermal Analysis of Electrical Machines Limits and Heat Transfer PrinciplesDocument2 pagesThermal Analysis of Electrical Machines Limits and Heat Transfer PrinciplesAnonymous sAmJfcVNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Practice Questions 1Document2 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer Practice Questions 1Lucky 230503No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2-1Document4 pagesTutorial 2-1chandan rajNo ratings yet
- Use of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables Are PermittedDocument4 pagesUse of Heat and Mass Transfer Data Books, Steam Tables Are Permitted3rajaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer ProblemsDocument3 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer ProblemsRiyasNo ratings yet
- Cycle Test 1 Set1Document6 pagesCycle Test 1 Set1logeshboy007No ratings yet
- Tutorial SheetDocument5 pagesTutorial Sheetpradeep.kumarNo ratings yet
- HT (Tute Sheets)Document8 pagesHT (Tute Sheets)Jagdeep PundirNo ratings yet
- Sheet Ch.1Document4 pagesSheet Ch.1Ahmed KingNo ratings yet
- Practice Problem Set 1 - Three Heat Transfer TechniquesDocument4 pagesPractice Problem Set 1 - Three Heat Transfer TechniquesDan Mc0% (1)
- Mech302 Heat Transfer Homework SolutionsDocument13 pagesMech302 Heat Transfer Homework SolutionschurvaloooNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2Yik Vui KongNo ratings yet
- 8S 2105 Mepc22 1Document2 pages8S 2105 Mepc22 1Challa YachendraNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Tutorial Conduction ConvectionDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Tutorial Conduction Convectionpushkal0% (2)
- Chn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Document2 pagesChn-201 Tutorial 2 - Autumn 16-17-1Prashant RajNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer (HT) QueDocument6 pagesHeat Transfer (HT) QueAshutosh KushwanshiNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D EDocument4 pagesHeat and Mass Transfer (MCC 15102) Assignmnet - 1: A F B C D ERotten AppleNo ratings yet
- G4 - Sample ExamsDocument8 pagesG4 - Sample ExamsLeeSM JacobNo ratings yet
- JNTU Old Question Papers 2007Document8 pagesJNTU Old Question Papers 2007Srinivasa Rao G100% (3)
- MEHB323 Tutorial Assignment 6Document2 pagesMEHB323 Tutorial Assignment 6SattishZeeNo ratings yet
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sathyabama University-Aeronautical Engineering 6th Sem Heat Transfer Sample Paper 1Document4 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - Sathyabama University-Aeronautical Engineering 6th Sem Heat Transfer Sample Paper 1manipsgNo ratings yet
- Files-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315Document44 pagesFiles-5-Exams Quizzes Examples Problems Me315TortelliniTimNo ratings yet
- Seminar 3 Transport PhenomenaDocument6 pagesSeminar 3 Transport PhenomenaAlexandraNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document4 pagesAssignment 2Roshan ShanmughanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Examples and Exercises (Part III) NewDocument12 pagesChapter 3 - Examples and Exercises (Part III) NewtemesgenNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Guru PrakashNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8Document3 pagesTutorial 8CHANDAN RAJNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Processes and Calculations in ME-341 Thermal Engineering AssignmentDocument5 pagesHeat Transfer Processes and Calculations in ME-341 Thermal Engineering AssignmentFeeling_so_flyNo ratings yet
- 02-12-2011Document2 pages02-12-2011charulapNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1AdarshpatankarNo ratings yet
- rr320306 Heat TransferDocument8 pagesrr320306 Heat TransferSrinivasa Rao G100% (2)
- Ass 7Document4 pagesAss 7Puneet MeenaNo ratings yet
- MAE 4171: Principles of Heat Transfer Solution-Assignment #1Document4 pagesMAE 4171: Principles of Heat Transfer Solution-Assignment #1Bo100% (5)
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDocument4 pages9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Me52102 - HMT Sheet - I Conduction Jul-Dec'23Document3 pagesMe52102 - HMT Sheet - I Conduction Jul-Dec'23HarshNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Heat TransferDocument5 pagesAssignment 2 Heat TransferolenbearNo ratings yet
- Questions Transport Phenomenon PDFDocument5 pagesQuestions Transport Phenomenon PDFvinay13579No ratings yet
- 1492Document15 pages1492_Anggyaa_No ratings yet
- Heat Transfer (MEE - 306) RCS (Makeup) (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Document3 pagesHeat Transfer (MEE - 306) RCS (Makeup) (EngineeringDuniya - Com)Sanjay ShreeshaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Tutorial Assignment SolutionsDocument3 pagesHeat Transfer Tutorial Assignment SolutionsNirmal ChandraNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Nmu UniversityDocument4 pagesHeat Transfer Nmu UniversityKetan V. JoshiNo ratings yet
- Quiz HT104: ProblemsDocument20 pagesQuiz HT104: ProblemsZERINA ŠKULJNo ratings yet
- Figure 1 Schematic of A Hair DryerDocument2 pagesFigure 1 Schematic of A Hair DryerIcy45No ratings yet
- Cadabadi - T1 - Taller ConduccionDocument5 pagesCadabadi - T1 - Taller ConduccionAndres FigueroaNo ratings yet
- EjerciciosDocument24 pagesEjerciciosMarjorieNo ratings yet
- HMT 2marksDocument85 pagesHMT 2marksyogesh sNo ratings yet
- Mae 3314 HW 4Document1 pageMae 3314 HW 4john_andrews_1234No ratings yet
- Mms Assignment No. 1 Session 16171Document7 pagesMms Assignment No. 1 Session 16171Gurjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5-1Document2 pagesTutorial 5-1chandan rajNo ratings yet
- Heat TransferDocument2 pagesHeat TransferAmal JoyNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- GEK2013 Real Estate FinanceDocument20 pagesGEK2013 Real Estate FinanceUnknown uploaderNo ratings yet
- ME3281 Term PaperDocument11 pagesME3281 Term PaperUnknown uploaderNo ratings yet
- ME3281 Lab Question PaperDocument4 pagesME3281 Lab Question PaperUnknown uploaderNo ratings yet
- Sec 4NA Math EOY Prac PaperDocument6 pagesSec 4NA Math EOY Prac PaperUnknown uploaderNo ratings yet
- ME2113-2010SEM1 Past Year PaperDocument7 pagesME2113-2010SEM1 Past Year PaperUnknown uploaderNo ratings yet
- Tensile and Hardness Tests ExplainedDocument22 pagesTensile and Hardness Tests ExplainedUnknown uploader100% (1)
- ME3122 Tutorial 1 - Conduction-SolutionsDocument9 pagesME3122 Tutorial 1 - Conduction-SolutionsUnknown uploaderNo ratings yet
- Kompresibilitas OkDocument9 pagesKompresibilitas OkFeby RochmaniahNo ratings yet
- Catan YHINFDocument4 pagesCatan YHINFX RagaNo ratings yet
- Notes On Circuital Representation of Two-Conductor Transmission LinesDocument32 pagesNotes On Circuital Representation of Two-Conductor Transmission LinesLuigi ReveruzziNo ratings yet
- Holip 201207110500417645Document105 pagesHolip 201207110500417645Jose Sanchez Palma100% (2)
- Chapter 1, B, Introduction To Heat TransferDocument68 pagesChapter 1, B, Introduction To Heat Transfer01094255175 01094255175No ratings yet
- Surge Arrester - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument2 pagesSurge Arrester - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaMuhammad Nico PermanaNo ratings yet
- ASTM C127 - Specific Gravity and Absorption of Coarse AggregateDocument5 pagesASTM C127 - Specific Gravity and Absorption of Coarse AggregateIsaac ArturoNo ratings yet
- PYL 100 2016 QMLect 02 ProbContEqDocument15 pagesPYL 100 2016 QMLect 02 ProbContEqPulkit AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Samsung Aqv12 PDFDocument51 pagesSamsung Aqv12 PDFTol SirtNo ratings yet
- Hydrophore Sequencing Relay HSR2: 2 Outputs HSR3: 3 OutputsDocument1 pageHydrophore Sequencing Relay HSR2: 2 Outputs HSR3: 3 Outputsmezo catNo ratings yet
- 10th Class PhysicsDocument2 pages10th Class Physicsricha sonyNo ratings yet
- Thessaloniki EstablishmentDocument220 pagesThessaloniki Establishmentzedbolete6704No ratings yet
- Practical Properties of Rogowski Coil ConstructionDocument6 pagesPractical Properties of Rogowski Coil ConstructionDavid Halomoan MalauNo ratings yet
- Effect of Lean Primaryzone Operation On Emissions and Stability of Non-Premixed CombustorsDocument12 pagesEffect of Lean Primaryzone Operation On Emissions and Stability of Non-Premixed Combustorsmechmuthu1No ratings yet
- Technical information on transformer definitions and classificationsDocument1 pageTechnical information on transformer definitions and classificationsAnonymous zUO8ZEmNo ratings yet
- Non-Standard Models and The Sociology of Cosmology (Lopez Corredoira)Document41 pagesNon-Standard Models and The Sociology of Cosmology (Lopez Corredoira)Dr Abhas MitraNo ratings yet
- 'Ulyhfrq: Instruction ManualDocument36 pages'Ulyhfrq: Instruction ManualAndri kuswandiNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Design Tables: Appendix 2Document6 pagesMagnetics Design Tables: Appendix 2Gopichand GaddamNo ratings yet
- In Uence of Falling Height and Plate Size On Surface Stiffness Evaluated by LWDDocument9 pagesIn Uence of Falling Height and Plate Size On Surface Stiffness Evaluated by LWDAshish WaliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Basic Aerodynamic-The Physics of AtmosphereDocument26 pagesChapter 1-Basic Aerodynamic-The Physics of Atmospherezuliana_ismail8564100% (1)
- CHAPTER1 EnergyStorage Pea3450Document52 pagesCHAPTER1 EnergyStorage Pea3450Mateus BonettiNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, Pilani Campus (Raj.)Document3 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science Pilani, Pilani Campus (Raj.)Arihant JainNo ratings yet
- Absolute Maximum Ratings Semitrans M Power MOSFET Modules SKM 151 A4RDocument5 pagesAbsolute Maximum Ratings Semitrans M Power MOSFET Modules SKM 151 A4RChaovalit Jitsinthu100% (1)
- Modular Lead Exit - Info SheetDocument2 pagesModular Lead Exit - Info SheetSunil GurubaxaniNo ratings yet
- Mitsubishi MSZ Fd25 35vahDocument2 pagesMitsubishi MSZ Fd25 35vahZachary TaylorNo ratings yet