Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp 6
Uploaded by
virendra_vyas123Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp 6
Uploaded by
virendra_vyas123Copyright:
Available Formats
ACROPOLIS TECHNICAL CAMPUS, INDORE 452020
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Lab Session No. 006 Page No.1/4 Electronic Devices & Circuits CS - 304 Enrolment No. 0875 Batch No.
Performance Evaluation:
Name
Performing on Extra regular First Submission Second Submission
Grade and Remarks by the Tutor 1. Clarity about the objective of the experiment 2. Clarity about the problem statement 3. Submitted the work in desired format 4. Shown capability to solve the problem 5. Contribution to the team work. Others:
Grade
signature
EXPERIMENT NO. 6 FIXED BIAS BJT BIAS METHOD
Title:
STUDY THE FIXED-BIAS CONFIGURATION OF BIPOLAR TRANSISTOR BIAS METHOD. Aim: To understand the need of biasing. To understand the designing and analysis of the circuit. To understand the effect of themal runaway on the circuit.
OBJECTIVE: After completing the experiment, the student should be able: Find out the Q point. To check the stability of the system. Find out the stability factor.
ACROPOLIS TECHNICAL CAMPUS, INDORE 452020
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Lab Session No. 006 Page No.2/4 Electronic Devices & Circuits Cs - 304 Enrolment No. 0875 Batch No.
Problem Statement:
What is transistor biasing. What is its need. Explain the term thermal stability. Explain the term thermal runaway. What is disadvantage of this methode.
EQUIPMENTS: 1. TAT-01 Trainer kit. 2. Power Supply. 3. Patch cords. 4. Multimeter.
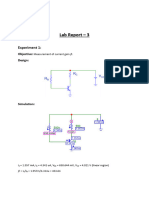
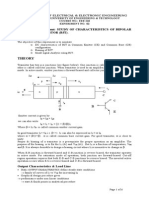
THEORY: The term biasing means establishing a fixed level of current and voltage. For transistor amplifiers, the resulting dc current and voltage establish an operating point on the characteristics that define the region thatll be employed for amplification of the applied signal. Since the operating point is a fixed point on the characteristics, its also called the quiescent point (abbreviated as Q-point). The first biasing method called BASE CURRENT BIAS or sometimes FIXED BIAS. As you recall, it consisted basically of a resistor (RB) connected between the collector supply voltage and the base. Unfortunately, this simple arrangement is quite thermally unstable. If the temperature of the transistor rises for any reason (due to a rise in ambient temperature or due to current flow through it), collector current will increase. This increase in current also causes the dc operating point, sometimes called the quiescent or static point, to move away from its desired position (level). This reaction to temperature is undesirable because it affects amplifier gain (the number of times of amplification). Consider the following circuit diagram.If we first consider the base-emitter loop, Kirchhoffs voltage law gives us VCC IB RB VBE = 0 Or, IB = (VCC VBE) / RB (1) Now, IC = IB .(2) Applying Kirchhoffs voltage law in the clockwise direction around the collectoremitter
ACROPOLIS TECHNICAL CAMPUS, INDORE 452020
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Lab Session No. 006 Page No.3/4 Electronic Devices & Circuits Cs - 304 Enrolment No. 0875 Batch No. loop, we get, VCE + IC RC - VCC = 0 Or, VCE = VCC - IC RC (3) Now, VCE = VC - VE ...(4) Where, VCE = Voltage from collector to emitter VC = Voltage from collector to ground and VE = Voltage from emitter to ground But, in this case, VE = 0V So, VCE = VC (5) Again, VBE = VB - VE ..(6) Or, VBE = VB [ as VE = 0V ] ..(7)
Fig: Fixed Bias BJT CALCULATION:Consider 2N2222 parameter:1) = 75 when VCE = 10V and IC=10V 2) VBE = 0.7V VCC IB RB VBE = 0 Or, IB = (VCC VBE) / RB = Now, IC = IB Where = 75 (When Ic = 10mA and VCE = 10V).
ACROPOLIS TECHNICAL CAMPUS, INDORE 452020
Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering Lab Session No. 006 Page No.4/4 Electronic Devices & Circuits Cs - 304 Enrolment No. 0875 Batch No. So, Ic = Now, VRC = IC X RC = VCE = VCC VRC = VBE = PROCEDURE: 1. Make the connections as shown in the practical circuit diagram on TAT-01 board using patch cord. 2. Switch on the power supply. 3. Set onboard power supply to required VCC using POT and voltmeter. 4. Do the calculation part and fill the observation table. 5. Connect VCC to the practical circuit. 6. Measure VBE, VRC and VCE voltages with respect to transistor. 7. Do the calculation of IB, IC, IE and from the observed reading and fill the observation table. OBSERVATION TABLE:-
Transistor (2N2222) Observed values
VBE = VB
IB
IC
VRC
VCE=VC
CONCLUSION: With the help of bserved and calculative values of fixed bias method we can draw the load line and locate the Q point on it.
Prepared by Nasreen Noorani
Date 25/06/13
Modified on
You might also like
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Ecl 302 Electronic Circuits - I and Simulation Lab - Student VersionDocument74 pagesEcl 302 Electronic Circuits - I and Simulation Lab - Student VersionSakthikumar BalasundaramNo ratings yet
- Bjts DC BiasingDocument89 pagesBjts DC BiasingVenugopal ReddyvariNo ratings yet
- Modern Control of DC-Based Power Systems: A Problem-Based ApproachFrom EverandModern Control of DC-Based Power Systems: A Problem-Based ApproachNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document10 pagesModule 3Joseph JohnNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Ee 132Document6 pagesModule 6 - Ee 132JosueNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- BJT Biasing (Complete)Document64 pagesBJT Biasing (Complete)Hung PhamNo ratings yet
- Al-Balqa'a Applied University Al-Huson CollegeDocument5 pagesAl-Balqa'a Applied University Al-Huson CollegeHossam BatainehNo ratings yet
- Electronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8From EverandElectronic Systems: Study Topics in Physics Book 8Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project Common Base TransistorDocument13 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Common Base TransistorKishore BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Module2 PDFDocument16 pagesModule2 PDFSrihari UttanurNo ratings yet
- BJT NotesDocument110 pagesBJT NotesHardesh Chauhan100% (1)
- Physics Investigatory Project: Common Base TransistorDocument13 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Common Base TransistorJoydeep Naskar64% (167)
- Electronic Circuit 1 ManualDocument44 pagesElectronic Circuit 1 ManualEr AnandNo ratings yet
- Lab 5 - Characteristics of A BJT and DC Load LineDocument9 pagesLab 5 - Characteristics of A BJT and DC Load Linevishvajeettiwari96No ratings yet
- Abhishek Lab - 3Document10 pagesAbhishek Lab - 3Abhishek meenaNo ratings yet
- BJT Lab ExperimentDocument7 pagesBJT Lab ExperimentAhmad ShahNo ratings yet
- BJT As An Amplifier: Biasing and Small Signal Model: ECE60L Lecture Notes, Spring 2002Document15 pagesBJT As An Amplifier: Biasing and Small Signal Model: ECE60L Lecture Notes, Spring 2002anon020202100% (1)
- Lecture 17-08-21Document23 pagesLecture 17-08-21R JENILANo ratings yet
- Electronics Circuits Lab ManualDocument109 pagesElectronics Circuits Lab ManualIndische Mädchen100% (2)
- Physics Investigatory Project Common Base TransistorDocument12 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Common Base TransistorAleena MathewNo ratings yet
- Optimize DC Bias CircuitsDocument18 pagesOptimize DC Bias CircuitsJawad Ul Hassan Shah100% (1)
- LAB ReportDocument12 pagesLAB ReportahmadNo ratings yet
- BJT DCDocument19 pagesBJT DCagama1188No ratings yet
- Lab-4 Analog Circuits Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) : Experiment ListDocument4 pagesLab-4 Analog Circuits Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) : Experiment ListRAMOLIYA HARSH MADHUKANTBHAINo ratings yet
- Circuits and Simulation Lab ManualDocument99 pagesCircuits and Simulation Lab Manualkasim_1983No ratings yet
- Electronics I DC Biasing ExamplesDocument13 pagesElectronics I DC Biasing Examplesمحمد كاظم محمدجواد محمود -A-No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Ii) : BJT (DC Analysis)Document17 pagesChapter 3 (Ii) : BJT (DC Analysis)matlela92No ratings yet
- 1EE 415 Lab # 3Document4 pages1EE 415 Lab # 3Ricky TerryNo ratings yet
- S4 EC1 LabDocument87 pagesS4 EC1 LabM N GeethasreeNo ratings yet
- AC analysis on Common Emitter Amplifier AssignmentDocument13 pagesAC analysis on Common Emitter Amplifier Assignmentrandeepa srimanthaNo ratings yet
- Common Collector Circuit DC and AC OperationDocument7 pagesCommon Collector Circuit DC and AC OperationDebbie ComissionNo ratings yet
- AE 1 EQ by Faiz SirDocument16 pagesAE 1 EQ by Faiz SirFaiz RangariNo ratings yet
- BJT Circuits Analysis and DesignDocument60 pagesBJT Circuits Analysis and DesignAdam MoutasemNo ratings yet
- ch4 2Document37 pagesch4 2avishek aviNo ratings yet
- Example DC Analysis of A BJT CircuitDocument6 pagesExample DC Analysis of A BJT CircuitPhạm Văn TưởngNo ratings yet
- BENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 3Document21 pagesBENE1123 - Chapter3 Part 3马铃淑No ratings yet
- Lab Report 7 (Open Ended Lab)Document8 pagesLab Report 7 (Open Ended Lab)Mohammad Fahim Nur0% (1)
- Experiment6 SolutionDocument4 pagesExperiment6 SolutionAsad ShahbazNo ratings yet
- BJT Biasing CircuitDocument40 pagesBJT Biasing Circuitfelix NizeyimanaNo ratings yet
- Example A Small Signal Analysis of A BJT AmpDocument10 pagesExample A Small Signal Analysis of A BJT AmpFilipe da SilveiraNo ratings yet
- AEC LabManualDocument30 pagesAEC LabManualPrateek PaliwalNo ratings yet
- Exp 5Document16 pagesExp 5neelu marturuNo ratings yet
- Ec I (16 M) - Unit IDocument19 pagesEc I (16 M) - Unit IGtecEceNo ratings yet
- Ec 1Document35 pagesEc 1Rekha SharmilyNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Transistor Biasing PDFDocument11 pagesBipolar Transistor Biasing PDFAliza TariqNo ratings yet
- Expt No 7 8Document3 pagesExpt No 7 8c.bhavesh2709No ratings yet
- SIMULATING DEPENDENT SOURCES IN PSPICEDocument39 pagesSIMULATING DEPENDENT SOURCES IN PSPICEIsmat Ara AwalNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 (A) To Study Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Emitter Bias Configuration and Its StabilityDocument14 pagesExperiment 3 (A) To Study Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) Emitter Bias Configuration and Its StabilityNayyab MalikNo ratings yet
- BJT Biasing Circuits Lab ReportDocument11 pagesBJT Biasing Circuits Lab ReportSamz AdrianNo ratings yet
- BJT Bias 2Document21 pagesBJT Bias 2kashi13No ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument46 pagesEDC Lab ManualMOUNIRAGESHNo ratings yet
- BJT DC CHARACTERISTICS LABDocument5 pagesBJT DC CHARACTERISTICS LABKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- BJT DC CHARACTERISTICS LABDocument5 pagesBJT DC CHARACTERISTICS LABHarsh SainiNo ratings yet
- BJT Characteristics & AnalysisDocument6 pagesBJT Characteristics & AnalysisTowsifTaherNo ratings yet
- EC2257-Lab Manual For Circuits and Simulation Integrated LaboratoryDocument38 pagesEC2257-Lab Manual For Circuits and Simulation Integrated Laboratorygokila_dr9897No ratings yet
- Diffpairs Cadence App Note 165Document19 pagesDiffpairs Cadence App Note 165Mallappa PatilNo ratings yet
- Instant Download Quickbooks Online For Accounting 1st Edition Glenn Owen Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument29 pagesInstant Download Quickbooks Online For Accounting 1st Edition Glenn Owen Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterdariusluyen586100% (4)
- Make Way For The Algorithms Symbolic Actions and Change in A Regime of KnowingDocument26 pagesMake Way For The Algorithms Symbolic Actions and Change in A Regime of KnowingAbimbola PotterNo ratings yet
- CoolSiC™ MOSFET A Revolution For Power ConversionDocument7 pagesCoolSiC™ MOSFET A Revolution For Power Conversionhope1678481280No ratings yet
- Audio Quality White Paper (YAMAHA)Document76 pagesAudio Quality White Paper (YAMAHA)KennyChoeNo ratings yet
- Dbms Case ToolsDocument1 pageDbms Case ToolsVaibhav AgarwalNo ratings yet
- np6512 SMDocument426 pagesnp6512 SMj1cutterNo ratings yet
- Diksha Rathi - Planetary Combinations For Foreign Travel 1Document101 pagesDiksha Rathi - Planetary Combinations For Foreign Travel 1puneetNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Building A Data Warehouse With Analysis ServicesDocument10 pagesCase Study of Building A Data Warehouse With Analysis ServicesbabussnmcaNo ratings yet
- XRC BasicDocument136 pagesXRC BasicJunior FernandesNo ratings yet
- RICEF MeansDocument42 pagesRICEF MeansAdaikalam Alexander RayappaNo ratings yet
- Basic Prediction Techniques in Modern Video Coding Standards PDFDocument90 pagesBasic Prediction Techniques in Modern Video Coding Standards PDFAndrijaNo ratings yet
- 5539 Project ManagementDocument6 pages5539 Project Managementmeelas123No ratings yet
- PHD Thesis Commerce PDFDocument7 pagesPHD Thesis Commerce PDFufagmcgld100% (1)
- Chapter 3 Public Key Cryptography PrinciplesDocument22 pagesChapter 3 Public Key Cryptography PrinciplesZoe KhanNo ratings yet
- Preboard - Computer Application (165) Class 10 - WatermarkDocument4 pagesPreboard - Computer Application (165) Class 10 - WatermarkJimit PatelNo ratings yet
- Irobot AccessoriesDocument24 pagesIrobot AccessoriesPredatorBDU.com100% (1)
- SAP WEB IDE For SAP HANA Installation Troubleshooting Guide: Public 2021-09-29Document52 pagesSAP WEB IDE For SAP HANA Installation Troubleshooting Guide: Public 2021-09-29Tariq AliNo ratings yet
- SONY IPELA g50 Operation Manual v2-1 enDocument305 pagesSONY IPELA g50 Operation Manual v2-1 enDoruSNo ratings yet
- Covid Bakuna Center RegistryDocument17 pagesCovid Bakuna Center RegistryChris-Goldie LorezoNo ratings yet
- Pa 110 BdaDocument8 pagesPa 110 BdaIvan Arturo Barrientos PreciadoNo ratings yet
- Manual NATRDocument2 pagesManual NATRPaco Ramírez HernándezNo ratings yet
- Data Protection Laws of The World: UkraineDocument8 pagesData Protection Laws of The World: UkraineНаталья Лобкова Переводчик АнглийскогоNo ratings yet
- Packet Loss PDFDocument4 pagesPacket Loss PDFRamiz RzaogluNo ratings yet
- StabilityDocument20 pagesStabilityravalNo ratings yet
- DS52 N FA410Document2 pagesDS52 N FA410Kelvin NgNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Risk Based Auditing PDFDocument99 pagesAn Introduction To Risk Based Auditing PDFadelene100% (2)
- Pgdis and AciseDocument67 pagesPgdis and AcisebhutrotterNo ratings yet
- Hints and Tips For Implementing Storwize V7000 V3.1 30 - JulyDocument35 pagesHints and Tips For Implementing Storwize V7000 V3.1 30 - JulyFerdinand HalimNo ratings yet
- Asus P5B Soporte CPUDocument12 pagesAsus P5B Soporte CPUInfonova RuteNo ratings yet