Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NSN recommended Huawei 2G features sheet
Uploaded by
server_caOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NSN recommended Huawei 2G features sheet
Uploaded by
server_caCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction
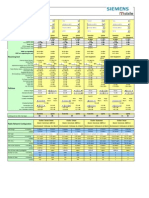
1.1 Purpose This document defines and describes the NSN recommended relevant features used for service projects globally. 1.2 Sheet description Sheet: Basic 2G Huawei Features Optional 2G Huawei Features 1.3 Scope System version 1.4 Revision history v 1.0 v 2.0
cument defines and describes the NSN recommended relevant features used for service projects globally.
Description: Sheet contains NSN recommended Huawei basic features to be evaluated. Column "Feature Relation ": N=new, E=enhanced, M=no change. Sheet contains NSN recommended Huawei optional features to be evaluated. Column "Feature Relation ": N=new, E=enhanced, M=no change.
Huawei GBSS12.0 release
First version of Huawei recommended relevant features documentation issued - GBSS9.0. Second version of Huawei recommended relevant features documentation issued - GBSS12.0. New column "Description " added.
Nokia Siemens Networks GS Managed Services/Capability Management
Notes:
Rev. date: April 8, 2010
Author: Christos Kyriazopoulos
Document owner: Ville Salomaa Ville Salomaa
December 20, 2010 Christos Kyriazopoulos
Basic Huawei Features 2G Feature Name Feature Code
System Improvement GBSS12.0 System Improvement 3GPP Protocol Compliance Radio Service Function Frequency Band Telephone Service (TS11) Emergency Call Service (TS12) Point To Point Short Message Service (TS21,TS22) G3 Fax (TS61,TS62) Bearer Service Mobility Management Location Updating IMSI Detach Paging Authentication HUAWEI I Handover Direct Retry SDCCH Handover Basic Cell Selection Basic Cell Re-selection Connection Management Call Control Assignment and Immediate Assignment Call Reestablishment TCH Re-assignment Radio Resource Management TRX Management Radio Link Management Radio Common Channel Management Radio Dedicated Channel Management Enhanced Channel Assignment Algorithm Operation and Maintenance Configuration Management Performance Management Inventory Management Faulty Management Security Management DBS Topology Maintenance BTS/NodeB Software USB Download O&M of BTS O&M of BSC
GBFD-110001 GBFD-110030 GBFD-110101 GBFD-110201 GBFD-110202 GBFD-110203 GBFD-110204 GBFD-110205 GBFD-110301 GBFD-110302 GBFD-110303 GBFD-110304 GBFD-110601 GBFD-110607 GBFD-110608 GBFD-110401 GBFD-110402 GBFD-110501 GBFD-110502 GBFD-110503 GBFD-112501 GBFD-111001 GBFD-111002 GBFD-111003 GBFD-111004 GBFD-111005 MRFD-210301 MRFD-210302 MRFD-210303 MRFD-210304 MRFD-210305 MRFD-210309 MRFD-210310 GBFD-111202 GBFD-111203
BTS Test Function Integrated Network Management Interface Man Machine Language (MML) Software Management BSC/RNC Software Management BTS/NodeB Software Management Remote Upgrade of the BSC&BTS Software License Management GBSS Network Architecture BTS Combined Cabinet BTS Hybrid Cabinet Group BSC Cabinet/Subrack Sharing Star Topology Chain Topology Tree Topology Connection Inter BSC over IP System Reliability Board Switchover GSM Flow Control Remote EAC Maintenance Operation & Maintenance System One-Key Recovery Reporting the Temperature List of the BTS Equipment Room System Redundancy Operate System Security Management Link aggregation BSC/RNC Resource Sharing Intelligent Shutdown of TRX Due to PSU Failure Basic features Adjustment of Adaptive Timing Advance Processing of Measurement Report Pre-processing of Measurement Report System Information Sending Forced System Information Sending by OMC Supporting Three-Digit MNC Support of Daylight Saving Time SDCCH Dynamic Adjustment Cell Frequency Scan STP (Signaling Transport Point) 14-Digit Signaling Point Code Interface Message Tracing User Signaling Tracing Cell Tracing LAPD Multiplexing at Abis Interface Discontinuous Reception (DRX) BTS Power Management Enhanced Power Control Algorithm Interface Features
GBFD-111207 GBFD-111210 GBFD-116501 MRFD-210401 MRFD-210402 GBFD-111213 MRFD-210403 GBFD-111501 GBFD-111502 GBFD-118801 MRFD-210204 MRFD-210205 MRFD-210206 GBFD-118621 GBFD-111701 GBFD-111705 GBFD-112301 GBFD-111214 GBFD-111211 MRFD-210101 MRFD-210102 MRFD-210103 MRFD-210104 GBFD-117804 GBFD-110901 GBFD-110801 GBFD-110802 GBFD-111101 GBFD-111102 GBFD-111901 GBFD-116101 GBFD-113001 GBFD-112401 GBFD-111806 GBFD-111802 MBFD-210801 MBFD-210802 GBFD-112203 GBFD-111301 GBFD-114802 GBFD-111601 GBFD-110703
Ater Interface 4:1 Multiplexing Gb Interface Function A Interface Circuit Management A Interface Protocol Process A Interface Occupation Rate Monitoring PS Services Features Packet Channel Combination Type Packet System Information MS Types MAC Mode RLC Mode Coding Scheme Networking Control Mode Network Operation Mode Support QoS (Best Effort) Access Assignment Paging Timing Advance Update Power Control Packet Uplink Flow Control Flow Control on Gb Interface Antenna System Solution Connection with TMA (Tower Mounted Amplifier) Remote Electrical Tilt 2-Antenna Receive Diversity Synchronization Mechanism BTS/NodeB Clock BSC/RNC Clock Maintainability and Testing Voice Fault Diagnosis Documentation Documentation
GBFD-111801 GBFD-119001 GBFD-111803 GBFD-111804 GBFD-111805 GBFD-119101 GBFD-119102 GBFD-119103 GBFD-119104 GBFD-119105 GBFD-119106 GBFD-119107 GBFD-119108 GBFD-119109 GBFD-119110 GBFD-119111 GBFD-119112 GBFD-119113 GBFD-119115 GBFD-119116 GBFD-119117 MRFD-210601 MRFD-210602 MRFD-210604 MRFD-210501 MRFD-210502 GBFD-119301 MRFD-210701
Feature Relation N E M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M E E M E M M M M M
Description No description available No description available
P-GSM900 band, E-GSM900 band, R-GSM900 band, DCS1800 band, PCS1900 band, GSM850 band Telephone service is a basic speech service specified in GSM specifications. Huawei GSM BSS supports the emergency call service (TS12) specified in GSM specifications and provid Short Message Service between 2 subscribers. The G3 fax feature is a value-added mobile data service that allows MSs to send and receive the voice f GSM supports the traditional circuit switched data (CSD) services and the data services of multiple rate
When an MS moves from one location area to another, it must register the new location information o The IMSI attach/detach procedure informs the MSC/VLR whether the MS can be reached. Through the paging process, an MS is instructed to access the network to complete call connection. Authentication is a procedure in which the GSM network verifies the validity of the identity of an MS, t Huawei's proprietary handover algorithm. If no TCH is available in the serving cell during the MS access process, the directed retry procedure is pe SDCCH handover is a process in which the MS is handed over from an SDCCH to another SDCCH in an im When an MS is switched on or enters the network coverage area, it scans all the carrier frequencies pe After an MS selects a suitable cell as the serving cell, it continues to monitor all the BCCH carrier freque
Call control is a basic feature for an operator to provide the CS services. With call control, the BSS prov When the MS initiates a call, the BSC needs to assign an SDCCH or a TCH (the TCH is used for signaling) When the MS encounters a radio link failure during the call, the call reestablishment procedure can be TCH re-assignment is a process through which the BSC re-assigns a TCH to the MS, after the assignmen
TRX Management involves the following procedures: 1. The radio resource indication procedure is used Radio link management involves nine procedures: link establishment indication, link establishment req Radio common channel management involves the management of common control channels such as P Radio dedicated channel management involves the assignment, activation, release, management, and Huawei channel allocation algorithm is used to allocate a suitable channel to the radio service and to a
Huawei provides the common configuration management of the MBSC for the GSM Base Station Subsy Performance management involves the periodical collection, gathering, saving, inspection, and analysis With the inventory management feature, the M2000 provides the centralized management of the info The fault management feature supports auto monitoring of the network devices. The operator can lea The security management feature of the BSC6900 involves: User security, Security of OMU operating s The distributed base station (DBS) supports the automatic scan of the RRU topology. The LMT provides This function enables the software upgrade to be performed through the USB disk without using a port The BTS O&M involves the following operations: query, loading, and activation of software versions; qu The O&M of BSC feature provides the following functions: 1. Secure and reliable configuration manage
M M M M E M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M
BTS test function involves site test, baseband test, baseband idle timeslot test, TCH loopback test, tran GBSS products access Huawei mobile integrated network management system (NMS) iManager M2000 MML commands are used for NE operation and maintenance. The BSS supports NE operation and main
Huawei MBSC supports the uniform software management of GBSS and RAN, thus facilitating the remo The BTS/NodeB software management feature enables the operator to remotely manage the software Remote upgrade of BSC software is a process in which the BSC software is remotely upgraded through The license management controls the overall capability (capacity and functions) of the authorized serv
When a single BTS cabinet cannot meet the large capacity requirement, combined cabinets can be use A hybrid cabinet group can combine cabinets of different BTS types in the same cabinet group. With the BSC Cabinet/Subrack Sharing feature, common standardised cabinets and subracks are provid In a star topology, each MBTS is directly connected to the MBSC through a transmission link. In a chain topology a number of BTSs are connencted with each other through transmission links in a se Tree topology is a combination of star and chain topologies. The Connection Inter BSC over IP feature enables operators to use the IP network for inter-BSC interco
For the boards that are configured in the active/standby mode, a switchover can be performed betwee Flow Control implements the detection and precautionary measures to reduce the risks of the BSS ove The EAC board monitors the environment and power supply in the equipment room to ensure the secu This feature reduces the complexity of the backup and recovery of the operating system and of the con With this feature, the temperature in the BTS equipment room can be reported to the BSC at specified The system redundancy feature provides the reliability designs such as the active/standby mode, load The operating system security management feature provides system security management such as ope Link aggregation enables multiple physical links to be bound to form a logical link. That is, multiple links BSC/RNC Resource Sharing provides resource sharing of the control plane and of the user plane. Contro With this function, when one or several PSUs are faulty, the BTS shuts down the power amplifiers of th
To compensate for transmission delay jitter, the MS must transmit signals to the BTS by a certain time Measurement report processing involves measurement report interpolation and filtering. The processing of the MRs is done by the BTS. System information involves main radio network parameters on the Um interface, including network id Forced System Information Sending by OMC is a feature through which the system is made to send sys Huawei BSC starting from BSC6000V900R008 supports three-digit MNC. Daylight Saving Time (DST) is a way of getting more light out of the day by advancing clocks by one hou Dynamic SDCCH conversion is triggered when the requested SDCCH is not allocated to the MS. This pro Cell frequency scan is a feature through which a specific frequency is scanned by using a certain channe The STP feature enables the transfer of signaling messages between signaling points. In an SS7 network, each device is regarded as a signaling point (SP), and each SP has an identical signali Interface message tracing is a feature through which interface messages can be traced in online mode Single user tracing is performed by entering the characteristic identities of the MS on the LMT or the N With the Cell Tracing feature, the signaling of a maximum of 16 users over the A interface, Abis interfac LAPD multiplexing refers to the multiplexing of the LAPD signaling on the E1 timeslots over the Abis int An MS in idle mode detects only the paging channels within a specific paging group. When other paging BTS Power Management supports hierarchical power-off and voltage abnormal protection. The BTS Po Huawei's proprietary power control algorithm.
M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M N M
Huawei BSC supports 4:1 multiplexing on the Ater interface by means of the TC (TRAU). That is, the fou The Gb interface is an interface between the SGSN and the BSS. On this interface, the SGSN communica A Interface Circuit Management, which involves circuit assignment, circuit block, circuit unblock, group The A Interface Protocol Process feature involves the processing of the DTAP and BSSMAP protocols. T This feature monitors the real-time status and usage of the circuits on the A interface and TC resources
According to 3GPP TS 43.064, packet data logical channels are classified into packet broadcast control c Packet system information (PSI) includs all necessary information for the MS to access and operate wit MS types supported by Huawei BSC. Class A, Class B and Class C are suported. The MAC layer defines and allocates the logical channels on the Um interface so that these channels ca The radio link control (RLC) layer is responsible for assembling and disassembling LLC PDUs. By using a Coding Schemes supported. GPRS: CS1-4, EGPRS: MCS1-9. There are three GPRS network control modes: network control 0 (NC0), network control 1 (NC1), and n To coordinate the paging of CS services and PS services, three network operation modes are defined fo Support of QoS mechanisms for BE services. When the MS needs to transmit data, it initiates packet access at the RLC/MAC layer. Based on the ser When the network or MS requests to establish a TBF for data transmission, the GSM/GPRS network as In the GPRS/GSM system, paging consists of PS paging and CS paging. The GPRS timing advance (TA) procedure is used to extract the correct TA value so that the network ca The BSC performs uplink open loop power control and downlink closed loop power control of MS PS se If excessive MSs apply for the GPRS resources within cells or BSCs at the same time, the GPRS resource The BSC supports the downlink flow control of the BVC and MS. It reports associated parameters to the
Installed on the tower top, a TMA is a device for amplifying uplink signals. As an optional component o The RET refers to an antenna system whose tilt is controlled electrically. The 2-antenna receive diversity technique combines the signals received from the two diverse antenna BTS/NodeB support a number of clock sources for synchronisation. BSC/RNC support a number of clock sources for synchronisation.
Users are likely to complain if crosstalk frequently occurs in the network. Identifying a crosstalk proble No description available
00 band, GSM850 band
SM specifications and provides higher priority for the emergency call service.
send and receive the voice fax. ata services of multiple rates.
new location information on the network. That is, when the MS finds that the LAI stored in the SIM is different from the LAI of the servin an be reached. omplete call connection. y of the identity of an MS, that is, verifies the validity of the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) or Temporary Mobile Subscrib
irected retry procedure is performed in order to set up the call in a TCH of another cell. H to another SDCCH in an immediate assignment. ll the carrier frequencies permitted by the PLMN and selects a suitable cell to camp on. This procedure is called cell selection. r all the BCCH carrier frequencies specified in the neighboring cell frequency list (BA1 list), in order to find a better cell to camp on. This p
th call control, the BSS provides the MS with radio resources and terrestrial circuits for making a call and helps the MSC during the whole he TCH is used for signaling) according to the specific call establishment cause. This procedure is called immediate assignment. After recei blishment procedure can be used to reestablish the radio link connection so that the original call can proceed. he MS, after the assignment of a TCH to the MS fails and the MS returns to the SDCCH.
indication procedure is used to inform the BSC of the interference levels on idle channels on a TRX. 2. The SACCH filling information modi tion, link establishment request, link release indication, link release request, transmission of a transparent L3-message in acknowledged m n control channels such as PCH, RACH, AGCH, NCH, PPCH, PRACH, and PAGCH. Radio common channel management is a basic feature for release, management, and reporting of dedicated channels such as SDCCH, SACCH, and TCH. These procedures work together to establis o the radio service and to adjust the channel as required.
the GSM Base Station Subsystem (GBSS) system and the Radio Access Network (RAN) system. With configuration management, configura ving, inspection, and analysis of the counters regarding management objects, resource bearer functions, and features, thereby helping op ed management of the information about the physical assets and the the software and patch versions of the devices on the network, thu evices. The operator can learn the actual status of the network through the alarm list and log. In addition, the operator can manually enab ecurity of OMU operating system, Data redundancy backup, User authentication failure timeout alarm. topology. The LMT provides the topology maintenance for the distributed base station. The DBS topology maintenance feature provides c SB disk without using a portable computer. tion of software versions; query of site attributes; query of the usage of different resources; transmission performance test; reset in level liable configuration management, 2. Accurate and effective alarm management, 3. Comprehensive counter report, 4. Flexible and configu
est, TCH loopback test, transmission performance test, CRC, and BTS antenna fault detection. tem (NMS) iManager M2000 through the integrated network management interface. ports NE operation and maintenance by running MML commands on the M2000 or LMT.
N, thus facilitating the remote management of the MBSC software and improving the efficiency of software upgrade and data downloadi motely manage the software installation and upgrade of the MBTS. This feature supports enhanced functions such as automatic change of remotely upgraded through the M2000. Multiple BSCs can be upgraded in batches. Remote upgrade of BTS software is a process in which ions) of the authorized services of the authorized NEs (MBSC, BTS, and NodeB). The license management is implemented through the soft
mbined cabinets can be used to expand the capacity. If combined cabinets still cannot meet the capacity requirement, cabinet groups can ame cabinet group. nets and subracks are provided to implement different network elements of Access and Core networks. transmission link. ugh transmission links in a serial manner forming a chain of BTSs. The first BTS in the chain is connected to the BSC. The number of levels o
etwork for inter-BSC interconnection so that the BSCs can communicate with each other directly. Note that the Connection Inter BSC over
er can be performed between the active and standby boards when the active board is faulty. uce the risks of the BSS overload. Once overload occurs, the BSC restricts and controls the incoming services such as prohibiting incoming ent room to ensure the security of physical devices. The Environment Monitor Unit (EMU) board is an enhanced EAC board. It monitors th rating system and of the configuration data of the OMU board. orted to the BSC at specified intervals in a specific period. active/standby mode, load sharing, and redundancy configuration, thus improving the system reliability. ty management such as operating system anti-virus, operating system security enhancement, and operating system patching. al link. That is, multiple links are aggregated to form a link aggregation group (LAG), which can be considered as an independent link in an and of the user plane. Control plane resource sharing is used to share the CPU usage and memory. When the CPU usage of a certain contr n the power amplifiers of the TRXs that consume excessive electricity, based on the power supply capability of the PSUs that work proper
o the BTS by a certain time period in advance. The time period is referred to as a Timing Advance (TA). An MS in dedicated mode must tra n and filtering.
terface, including network identity parameters, cell selection parameters, system control parameters, and network function parameters. B system is made to send system information to a certain cell and the MSs camping on the cell.
advancing clocks by one hour during the summer. allocated to the MS. This procedure involves converting a TCHF to the SDCCH and reverting the SDCCH to the TCHF. ed by using a certain channel to obtain the uplink signal levels on the frequency. Cell frequency scan provides references for engineers to
ch SP has an identical signaling point code (SPC). SPs communicate with each other through SPC. The SPC coding modes vary from one cou n be traced in online mode and reviewed in offline mode. the MS on the LMT or the NMS. The characteristic identities include IMSI, TMSI, MSISDN, and IMEI. the A interface, Abis interface, or Um interface of a specified cell can be traced at a time. 1 timeslots over the Abis interface. ng group. When other paging groups send paging messages to an MS, the MS blocks the receive channel. rmal protection. The BTS Power Management feature enhances power management and self-protection of the BTS, thus improving the re
e TC (TRAU). That is, the four timeslots on the E1 of the A interface can be multiplexed onto a timeslot on the Ater interface by means of erface, the SGSN communicates with the BSS and the MS and performs packet data transfer, mobility management, and session managem block, circuit unblock, group circuit block, group circuit unblock, circuit unequipped, and circuit reset, controls the operation and maintena AP and BSSMAP protocols. The processing of A interface signaling and protocol of Huawei GSM BSS is compliant with international standar A interface and TC resources through performance measurement.
o packet broadcast control channel (PBCCH), packet common control channel (PCCCH), packet data traffic channel (PDTCH), and packet d S to access and operate within a GPRS network.
ce so that these channels can be shared by several MSs. It also maps the LLC frames to the physical channels. When several MSs attempt mbling LLC PDUs. By using a sliding window protocol, the RLC layer exchanges data with the peer entity in acknowledged or unacknowledg
twork control 1 (NC1), and network control 2 (NC2). These modes are described as follows: 1. In NC0 mode, the MS performs autonomou ration modes are defined for the GPRS network: Network Operation Mode I, Network Operation Mode II, Network Operation Mode III.
MAC layer. Based on the service types and the support capability of the MS, the packet access is classified into the following types: 1. One the GSM/GPRS network assigns channels for the TBF or rejects the request based on available network resources and the multislot capab
alue so that the network can correctly receive the radio blocks from the MS. The GPRS TA is classified into two types: 1. Initial TA estimat p power control of MS PS services. me time, the GPRS resources may be insufficient and the uplink may be congested. The uplink flow control is used to control the service r ssociated parameters to the SGSN on a regular basis.
As an optional component of the antenna system, the TMA compensates for the feeder loss caused by a long feeder to improve the uplink
om the two diverse antennas at the receiving end to mitigate multipath interference.
dentifying a crosstalk problem, however, can be difficult if the information related to the crosstalk is not recorded in time. To solve this pr
ifferent from the LAI of the serving cell, it must notify the network to update the stored location area information about the MS. This pro
MSI) or Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI) transmitted over the Um interface.
s called cell selection. nd a better cell to camp on. This procedure is called cell reselection.
d helps the MSC during the whole call handling process. mmediate assignment. After receiving a channel request from the MS, the MSC sends the BSC an Assignment Request message, instructin
he SACCH filling information modification procedure is triggered by the BSC to inform the BTS of the new information to be used as filling ent L3-message in acknowledged mode, reception of a transparent L3-message in acknowledged mode, transmission of a transparent L3-m management is a basic feature for the operators to provide CS speech services. cedures work together to establish, maintain, and release radio links.
iguration management, configuration data can be securely and accurately transmitted to service boards and can then take effect. and features, thereby helping operators understand the overall conditions of the network. This feature enables operators to identify and of the devices on the network, thus providing the operator with a uniform and easy method of inventory management. For example, the f n, the operator can manually enable the board test function, which can help the operator to quickly locate the faulty board.
gy maintenance feature provides convenient OM functions for the DBS. The functions supported by this feature are as follows: 1. The top
n performance test; reset in levels; environment monitoring; alarm shielding; query of ring networking parameters. nter report, 4. Flexible and configurable signaling and user message tracing and commissioning, 5. Classified log management.
ware upgrade and data downloading. With this feature, users can implement the following operations on the M2000: 1. Querying the soft tions such as automatic change of the signaling bandwidth, software download based on the configuration, software download resumptio BTS software is a process in which the BTS software is remotely upgraded through the M2000. Multiple BTSs can be upgraded at a time. t is implemented through the software. To use certain enhanced functions and services, users have to purchase specific licenses.
y requirement, cabinet groups can be used to expand the capacity.
to the BSC. The number of levels of MBTSs in a chain topology should not exceed five.
hat the Connection Inter BSC over IP feature supports only the signaling exchange between BSCs. It does not support the exchange of voi
vices such as prohibiting incoming calls and certain auxiliary functions. In this manner, the load of the BSS quickly restores to the normal s nhanced EAC board. It monitors the environment (through temperature, humidity, water, and smoke sensors), illegal intrusion (through in
ating system patching. dered as an independent link in an upper-layer application perspective. n the CPU usage of a certain control plane unit (CP unit) is too high or when the memory of a certain CP unit is insufficient, a new call is tra ility of the PSUs that work properly. In this manner, the rest of TRXs continue to work normally, thus minimizing the impact of service dis
An MS in dedicated mode must transmit signals in an appropriate TA. Otherwise, the synchronization between the MS and the BTS loses.
nd network function parameters. Based on the received system information, an MS can properly select and access a radio network. Then,
ovides references for engineers to select proper frequencies. The interference of each frequency is important references for network opti
C coding modes vary from one country/area to another. Generally, three coding modes are available, namely, 14-bit, 16-bit, and 24-bit m
n of the BTS, thus improving the reliability of the system and prolonging the lifespan of products and the serving time of the system.
on the Ater interface by means of the TC. In this process, the previous PCM frame of 64 kbit/s can be converted into the TRAU frame of 16 anagement, and session management. The Gb interface is a standard interface. It is mandatory for the GPRS network. ntrols the operation and maintenance on a single circuit or on the entire PCM group circuits for the terrestrial circuit equipment. A Interfa mpliant with international standard protocols, and thus Huawei GSM BSS equipment can interconnect with the MSC from other vendors.
fic channel (PDTCH), and packet dedicated control channel (PDCCH). Huawei BSC supports 3 different combination types of packet channe
nnels. When several MSs attempt to send packet data simultaneously, the MAC layer performs arbitration and provides the collision avoid n acknowledged or unacknowledged mode. The size of the sliding window for GPRS is 64, and that for EGPRS ranges from 64 to 1,024. In
ode, the MS performs autonomous cell reselection without sending measurement reports to the network. 2. In NC1 mode, the MS perform II, Network Operation Mode III.
d into the following types: 1. One phase packet access, 2. Two phase packet access or a single block packet access. resources and the multislot capability of the MS.
nto two types: 1. Initial TA estimation, 2. Continuous TA update. The BSC estimates an initial TA value based on a single access burst reque
rol is used to control the service requests (including paging response messages) that are initiated by the MS and to delay the response to
long feeder to improve the uplink sensitivity and converge.
recorded in time. To solve this problem, the Crosstalk Monitoring feature is introduced. This feature records the information about the ca
formation about the MS. This procedure is called location area update.
ment Request message, instructing the BSC to assign a suitable channel to the MS. The channel to be assigned must meet the requiremen
w information to be used as filling information on SACCHs. 3. The flow control procedure is used for flow control to prevent CCCH overloa transmission of a transparent L3-message in unacknowledged mode, reception of a transparent L3-message in unacknowledged mode, an
s and can then take effect. enables operators to identify and rectify a problem at the earliest possible time, and thereby optimizes the network. management. For example, the feature helps the operator to manage the remaining assets or trace the information about the faulty boa te the faulty board.
feature are as follows: 1. The topology of the distributed base station is displayed in a visualized way, 2. Different colors are used to indic
parameters. ied log management.
n the M2000: 1. Querying the software version and its status, 2. Uploading, downloading, and activating the program files, patch files, and on, software download resumption, download and activation of software in batches, and hot patching. BTSs can be upgraded at a time. urchase specific licenses.
s not support the exchange of voice services or data services between BSCs.
SS quickly restores to the normal state. Flow Control aims at keeping the traffic load within the range of the dimensioned capacity, stabiliz nsors), illegal intrusion (through infrared and door status sensors), and power supply.
unit is insufficient, a new call is transferred to other CP units with low load. If a certain user plane unit (UP unit) is overloaded, a new servi nimizing the impact of service disruption.
tween the MS and the BTS loses. In the GSM system, adjustment of adaptive timing advance is applied to ensure that each MS in dedicate
and access a radio network. Then, it can gain access to all types of service provided by the network. SI is sent by the BSC periodically in all
rtant references for network optimization.
mely, 14-bit, 16-bit, and 24-bit modes. Huawei BSC6900 supports all SPC modes.
serving time of the system.
nverted into the TRAU frame of 16 kbit/s, and therefore reducing the required transmission bandwidth. GPRS network. estrial circuit equipment. A Interface Circuit Management applies to only the TDM network. with the MSC from other vendors.
mbination types of packet channels: Combination 1, Combination 2 and Combination 3.
on and provides the collision avoidance, detection, and recovery procedures. The MAC layer also allows an MS to occupy different timeslo GPRS ranges from 64 to 1,024. In acknowledged mode, each data block in a TBF must be acknowledged by the peer end. If the data block
k. 2. In NC1 mode, the MS performs autonomous cell reselection and sends measurement reports to the network. 3. In NC2 mode, the ne
sed on a single access burst requesting a packet channel. Then, the BSC sends the estimated TA value to the MS through a Packet Uplink A MS and to delay the response to these service requests.
cords the information about the call during which crosstalk occurs in the log and provides an alarm mechanism specific to crosstalk. With
signed must meet the requirements of the MSC and MS, such as the channel type, speech version, and MS frequency capability. This proc
w control to prevent CCCH overload, ACCH overload, and processor overload. 4. The error reporting procedure is triggered by the BTS to re sage in unacknowledged mode, and link error indication.
the network. e information about the faulty board such as the batch number.
Different colors are used to indicate the status of each BBU, RRU, and CRPI link, 3. The BBU or RRU can be selected directly on the display
the program files, patch files, and license files, 3. Using the OMU of the MBSC as the FTP server and transmitting files such as program file
the dimensioned capacity, stabilizing the system operation, and ensuring the highest possible traffic volume.
UP unit) is overloaded, a new service is transferred to other UP units with low load.
o ensure that each MS in dedicated mode uses an appropriate TA.
sent by the BSC periodically in all cells of the network.
an MS to occupy different timeslots of several physical channels. The BSC supports two MAC modes: dynamic allocation and extended dy by the peer end. If the data block is unacknowledged, it needs to be retransmitted. The TBF is released only after all the data blocks are tr
e network. 3. In NC2 mode, the network controls cell reselection, and the MS sends measurement reports to the network.
the MS through a Packet Uplink Assignment or a Packet Downlink Assignment message. Before the TA value is updated, the MS transmit
hanism specific to crosstalk. With the Crosstalk Monitoring feature enabled, a call is automatically monitored to check whether crosstalk o
MS frequency capability. This procedure is called assignment.
edure is triggered by the BTS to report detected errors if they cannot be reported by any other procedure.
be selected directly on the display for maintenance.
nsmitting files such as program files and patch files between the FTP server and FTP client, 4. Using the MBSC as the transmission medium
namic allocation and extended dynamic allocation. Dynamic allocation is generally used for the downlink preferred service or neutral serv only after all the data blocks are transmitted and acknowledged. In unacknowledged mode, the data block need not be acknowledged by
rts to the network.
value is updated, the MS transmits data in the uplink based on the initial TA. The MS in packet transfer mode must update the TA value co
ored to check whether crosstalk occurs during the call. If crosstalk occurs, the information about the call, including the calling number, ca
MBSC as the transmission medium to transmit files between the M2000 and the MBTS.
k preferred service or neutral service. Extended dynamic allocation is used for the uplink preferred service to increase the uplink throughp ck need not be acknowledged by the peer end. If a data block is lost or erroneously transmitted, it is replaced with padding bits. The TBF i
mode must update the TA value continuously. The TA value is transmitted on the packet timing advance control channel (PTCCH) that is as
l, including the calling number, called number, serving cell, occupied channel, and serving TRX, is recorded. In this way, maintenance engi
ce to increase the uplink throughput. placed with padding bits. The TBF is released as long as all the data blocks are transmitted. The BSC supports both acknowledged mode an
control channel (PTCCH) that is assigned to the MS.
ed. In this way, maintenance engineers can obtain the data that is crucial to problem identification without simulating the conditions of th
orts both acknowledged mode and unacknowledged mode at the RLC layer. For uplink data transmission, the BSC determines the RLC mo
out simulating the conditions of the call.
n, the BSC determines the RLC mode based on the request of the MS. For downlink data transmission, the BSC determines the RLC mode
he BSC determines the RLC mode ba
Optional Huawei Features 2G Feature Name
Coverage enhancement PBT(Power Boost Technology) Transmit Diversity 4-Way Receiver Diversity Dynamic Transmit Diversity Dynamic PBT(Power Boost Technology) Enhanced EDGE Coverage Voice Capacity Improvement Multi-band Sharing One BSC Enhanced Dual-Band Network Flex MAIO ICC EICC Frequency Efficiency Improvement Frequency Hopping (RF hopping, baseband hopping) BCCH Carrier Frequency Hopping Antenna Frequency Hopping BCCH Dense Frequency Multiplexing Support for E-GSM and R-GSM Frequency Band Network Synchronization Soft-Synchronized Network BTS GPS Synchronization Clock over IP Clock over IP support 1588V2 Synchronous Ethernet Energy Saving HUAWEI III Power Control Algorithm Discontinuous Transmission (DTX)Downlink Discontinuous Transmission (DTX)Uplink TRX Power Amplifier Intelligent Shutdown TRX Power Amplifier Intelligent Shutdown on Timeslot Level Intelligent Combiner Bypass Active Backup Power Control Power Optimization Based on Channel Type PSU Smart Control Enhanced BCCH Power Consumption Optimization Dynamic Cell Power Off TRX Working Voltage Adjustment Multi-Carrier Intelligent Voltage Regulation Weather Adaptive Power Management Abis Transmission Saving
16Kbit RSL and OML on A-bis Interface Flex Abis BTS Local Switch Abis Congestion Trigger HR Distribution A Transmission Saving Flex Ater BSC Local Switch Ater Compression Transmission Hardware Saving TrFO Networking Framework Multi-Cell Function System Reliability Ring Topology TRX Cooperation MSC Pool SGSN Pool Abis Bypass Fast Ring Network Switch Robust Air Interface Signalling Abis Transmission Backup BSC Node Redundancy TC Pool OML Backup High Speed Coverage AFC(Automatic Frequency Correction) Fast Move Handover Chain Cell Handover Multi-site Cell 2G/3G Seamless Coverage GSM / WCDMA Interoperability GSM and TD-SCDMA Interoperability GSM and WCDMA Service Based Handover GSM and WCDMA Load Based Handover GSM and UMTS Cell Reselection Based on MS State Fast UMTS Reselection at GSM CS Call Release BTS Satellite Transmission Satellite Transmission over Abis Interface BSC Satellite Transmission Satellite Transmission over A Interface Satellite Transmission over Ater Interface Satellite Transmission over Pb Interface Satellite Transmission over Gb Interface Big Capacity BSC High Speed Signaling Local Multiple Signaling Points Maintainability
Semi-Permanent Connection End-to-End MS Signaling Tracing Maintenance Mode Alarm Power Control Algorithm Active Power Control Network Security A5/1 and A5/2 Ciphering Algorithm A5/3 Ciphering Algorithm A5/1 Encryption Flow Optimization Encrypted Network Management NAT Beside OM Enhanced Voice Service Enhanced Full Rate Half Rate Speech Dynamic Adjustment Between FR and HR Cell Broadcast Service Short Message Service Cell Broadcast (TS23) Simplified Cell Broadcast CS General Enhancement Automatic Level Control (ALC) Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) Automatic Noise Restraint (ANR) TFO Automatic Noise Compensation (ANC) Enhancement Packet Loss Concealment (EPLC) Voice Quality Index (Uplink VQI) Enhanced Measurement Report (EMR) BTS power lift for handover Dynamic HR/FR Adaptation VQE3.0 KPIs Based on User Experience AMR Package AMR FR AMR HR AMR Power Control AMR FR/HR Dynamic Adjustment AMR Wireless Link Timer AMR Coding Rate Threshold Adaptive Adjustment WB AMR PS QoS Streaming QoS (GBR) QoS ARP&THP PS Active Package Management PoC QoS Conversational QoS PS Service in Priority Cell Reselection of PS Domain
Network-Controlled Cell Reselection (NC2) Intra BSC Network Assisted Cell Change (NACC) Packet SI Status GPRS/EGPRS Service GPRS Network Operation Mode I CS-3/CS-4 EGPRS PDCH Dynamic Adjustment Gb Over FR EGPRS Service Enhancement 11-Bit EGPRS Access Packet Assignment Taken Over by the BTS Extended Uplink TBF Dynamically Adjusting the Uplink MCS Coding Dynamically Adjusting the RRBP Frequency Packet Channel Dispatching Load Sharing Adaptive Adjustment of Uplink and Downlink Channels BSS Paging Coordination PS Handover Early TBF Establishment PS Power Control High Speed Data Service Extended Dynamic Allocation (EDA) MS High Multislot Classes DTM Class11 DTM HMC DTM 14.4kbit/s Circuit Switched Data VIP Service Support Resource Reservation Enhanced Multi Level Precedence and Preemption (EMLPP) Guaranteed Emergency Call Flow Control Based on Cell Priority Terminal Package Network Support SAIC LCS NSS-Based LCS (Cell ID + TA) BSS-Based LCS (Cell ID + TA) Simple Mode LCS (Cell ID + TA) Lb Interface Abis IP Abis over IP Abis IP over E1/T1 Abis MUX A IP
A over IP A IP over E1/T1 UDP MUX for A Transmission TDM/IP Dual Transmission over A Interface Gb IP Gb over IP IP Enhancement IP QOS IP Performance Monitor IP Fault Detection Based on BFD Ethernet OAM PICO Solution Package PICO Automatic Configuration and Planning PICO Synchronization PICO Dual-band Auto-planning PICO USB Encryption PICO Access Control List (ACL) PICO Sleeping Mode PICO Automatic Optimization Easy GSM Solution Package Compact BTS Automatic Configuration and Planning Compact BTS Automatic Capacity Planning Compact BTS Automatic Neighbor Cell Planning and Optimization Compact BTS Timing Power Off Local User Management Public Voice Group Call Service Public Voice Group Call Service Late Broadcast Channel Assignment Single Channel Group Call Originating Talker Identification Group Call EMLPP Fast Group Call Setup Group Call Reliability Enhancing Public Voice Broadcast Service Public Voice Broadcast Service Late Broadcast Channel Assignment GSM-T Relay Handover HUAWEI II Handover Handover Re-establishment RAN Sharing RAN Sharing MOCN Shared Cell IMSI-Based Handover EDGE Evolution MSRD Dual Carriers in Downlink
Uplink EGPRS2-A Downlink EGPRS2-A Latency Reduction Perfomance Analysis Toolkit 2G/3G Neighboring Cell Automatic Optimization Emergency Communications License Control for Urgency Access Control Class (ACC) GSM and UMTS Common Radio Resource Management Based on Iur-g Load Based Handover Enhancement on Iur-g NACC Procedure Optimization Based on Iur-g between GSM and UMTS GSM and UMTS Load Balancing Based on Iur-g GSM and UMTS Traffic Steering Based on Iur-g GSM and UMTS Common Transmission GSM and UMTS Co-Transmission by TDM Switching IP-Based GSM and UMTS Co-Transmission on Base Station Side TDM-Based GSM and UMTS Co-Transmission via Backplane on Base Station Side GSM and UMTS Bandwidth Allocation Uni-Control IP-Based GSM and LTE Co-Transmission on Base Station Side GSM and UMTS and LTE Common Clock GSM and UMTS Common Reference Clock GSM and LTE Common Reference Clock GSM and UMTS and LTE Energy Saving GSM and UMTS Intelligent Shutdown Based on RAT Priority GSM and LTE Seamless Coverage Cell Reselection Between GSM and LTE PS Handover Between GSM and LTE Based on Coverage PS Handover Between GSM and LTE Based on Quality PS Handover Between GSM and LTE Based on Cell Load PS Handover Between GSM and LTE Based on Mode Priority GSM/LTE Service Based PS Handover eNC2 Between GSM and LTE eNACC Between GSM and LTE SRVCC GSM and TD-SCDMA Seamless Coverage Iur-g Interface Between GSM and TD-SCDMA Radio Resource Reserved Handover Between GSM/TD-SCDMA Based on Iur-g Paging Capability Improvement Multiple CCCHs
Feature Code
Feature Relation
M M M M M N M M M M M M M M M M M M M E N M M M M M M M M M M M M M N
Description
GBFD-115901 GBFD-115902 GBFD-115903 GBFD-118101 GBFD-118102 GBFD-118104 GBFD-114401 GBFD-114402 GBFD-117001 GBFD-115801 GBFD-115821 GBFD-113701 GBFD-113702 GBFD-113703 GBFD-118001 GBFD-114901 GBFD-118201 GBFD-510401 GBFD-118606 GBFD-118620 GBFD-118202 GBFD-117601 GBFD-114801 GBFD-114803 GBFD-111602 GBFD-111603 GBFD-111604 GBFD-111605 GBFD-111606 GBFD-111608 GBFD-111609 GBFD-111610 GBFD-111611 GBFD-111612 GBFD-111613
The PBT is a power boost technology. In PBT mode, the two TRXs in the double-tran Transmit diversity can help to improve the quality of the signals received by the MS To suppress Rayleigh fading, four-way receive diversity is implemented in the TRX b Dynamic Transmit Diversity is timeslot-based. Normally, two TRXs in a double-tr Dynamic PBT is timeslot-based. Normally, two TRXs in a double-transceiver unit wo In the existing network, the BSC controls multiple BTSs and manages BTS radio reso
In a multi-band network, in a co-BSC network topology, the GSM850 band, GSM900 The enhanced dual-band network is an improvement on the existing dual-band netw Flex MAIO is a feature through which the BSC dynamically adjusts the MAIO accordi Interference Cancellation Combining. In the actual network, the interference on diff Enhanced Interference Rejection Combining. EICC is developed from ICC. Generally,
With FH, different bursts are transmitted on different frequencies, but the frequenc In GSM, the frequency of the BCCH must remain unchanged, that is, the BCCH cann Antenna frequency hopping provides transmit diversity on the downlink. User data The BCCH dense frequency multiplexing technology is applicable to the network wit E-GSM: UL=880-915 MHz, DL=925-960 MHz; R-GSM: UL=876-915 MHz, DL=921-960
In Soft-Synchronized Network technology the FNs and symbol offsets of the BTSs ar The BTS GPS Synchronization feature enables a BTS clock to be synchronized with th The clock over IP solution is based on the server/client architecture. The IEEE1588 V2 solution uses the same server/client architecture as the clock over The synchronous Ethernet solution has the same basic principles as SDH and PDH n
Huawei III Power Control algorithm involves MR interpolation, MR filtering, calculat The Discontinuous Transmission (DTX) mechanism reduces the interference level an The Discontinuous Transmission (DTX) mechanism reduces the interference level an When the cell is enabled with TRX power amplifier intelligent shutdown, all the TRX TRX power amplifier intelligent shutdown on the timeslot level is supported and the Intelligent Combiner Bypass (ICB) applies to double-transceiver unit. When the non When the mains supply is cut off, the BTS uses the storage battery as a back up pow Power optimization based on channel type refers to the technology that the voltage The PSU smart control feature switches on only the required PSUs and shuts down Huawei introduces enhanced BCCH power consumption optimization, through whic To reduce the power consumption of the whole network, the feature of dynamic ce When the transmit power of the TRX power amplifier decreases, the working voltag The Multi-Carrier Intelligent Voltage Regulation feature is introduced to dynamically Weather adaptive power management determines the proper volume of energy co
GBFD-116701 GBFD-117301 GBFD-117702 GBFD-112013 GBFD-116901 GBFD-117701 GBFD-116902 GBFD-115702 GBFD-114601 GBFD-117801 GBFD-113801 GBFD-117401 GBFD-119701 GBFD-116601 GBFD-117802 GBFD-113721 GBFD-117803 GBFD-113725 GBFD-113726 GBFD-113728 GBFD-510101 GBFD-510102 GBFD-510103 GBFD-510104 GBFD-114301 GBFD-114302 GBFD-114321 GBFD-114322 GBFD-114323 GBFD-114325 GBFD-113901 GBFD-113902 GBFD-113903 GBFD-113904 GBFD-113905 GBFD-115201 GBFD-115301
M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M E M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M
When the function of the 16 kbit/s LAPD signaling link (OML and RSL) is enabled, ea In an actual network, not all the BTSs or cells are busy and not both the PS and CS s BTS local switching is triggered when the BTS detects that the calling MS and the ca When allocating channels, the BSC determines whether to trigger rate adjustment b
Flex Ater is a function based on which Ater resources are allocated according to the BSC local switching is performed on the BSS side without involving NEs on the NSS s Ater Compression Transmission is a technology in which the TransCoder Subrack (TC
The TrFO feature enables the calling MS and called MS to use the same speech codi
Multi-cell function is a function based on which more than three cells (12 at most) a
The BTS ring topology is a special chain or star topology. All the BTSs and the BSC in TRX cooperation means that when a TRX in a cell is faulty, the BSC designates anoth An MSC pool is defined as a group of MSCs handling the traffic generated from one SGSN Pool, also known as Gb Flex, enables multiple SGSNs to form a SGSN pool. A B Abis Bypass is introduced in the network with the chain topology to avoid the probl When a connection in the BTS ring topology is broken, the BTSs that follow the brea FACCH frames and SACCH frames are repeatedly sent to improve the anti-interferen When the active SDH transmission link is faulty due to e.g. a natural disaster, the GB The BSC node redundancy is a function through which two BSCs form a redundancy Huawei GBSS allows other BSCs to connect to the transcoder subracks (TCSs) of a ce The OML is the operation and maintenance link between the BSC and the BTS. Whe
AFC feature is used to compensate the Doppler frequency shift, thus ensuring succe Fast-moving micro cell handover is performed from a micro cell to a macro cell acco Quick handover aims to increase the handover success rate of an MS moving at a hi The multi-site cell feature is a function based on which the multiple subsites that co
The UMTS network and the GSM network will coexist and provide services together The UMTS network and the GSM network will coexist and provide services together The QoS-based service distribution feature is introduced to optimize the utilization In the case of co-existence of 2G and 3G networks, there is a possibility that a netw 2G/3G inter-RAT cell reselection involves the cell reselection from GSM to UMTS an Normally, after an MS terminates a call in a GSM cell, it camps on the GSM cell. Wh
Huawei BSS supports satellite transmission over multiple interfaces. Satellite transm
Huawei BSS supports satellite transmission over multiple interfaces. Satellite transm Huawei BSS supports satellite transmission over multiple interfaces. Satellite transm Huawei BSS supports satellite transmission over multiple interfaces. Satellite transm Huawei BSS supports satellite transmission over multiple interfaces. Satellite transm
Two types of signaling links are available in the SS7 network: 64 kbit/s signaling link The feature of local multiple signaling points enables one physical BSC to function a
GBFD-114701 GBFD-116401 GBFD-116402 GBFD-117602 GBFD-113501 GBFD-113503 GBFD-113521 GBFD-113522 GBFD-113523 GBFD-113301 GBFD-113401 GBFD-113402 GBFD-113601 GBFD-113602 GBFD-115601 GBFD-115602 GBFD-115603 GBFD-115701 GBFD-115703 GBFD-115704 GBFD-116801 GBFD-117501 GBFD-117101 GBFD-115522 GBFD-115705 GBFD-115707 GBFD-115501 GBFD-115502 GBFD-115503 GBFD-115504 GBFD-115505 GBFD-115506 GBFD-115507 GBFD-119901 GBFD-119902 GBFD-119904 GBFD-119905 GBFD-119906 GBFD-119907
M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M N N M M M M M M M M M M M M N
The semipermanent link enables some of the idle E1 timeslots in the BSS system to End-to-end MS signaling tracing is a function based on which the network administr When a network is under certain maintenance operations such as construction, exp
For better results of Power Control, the MS and BTS should transmit signals at a pro
The A5 ciphering algorithm generates a 114-bit ciphering sequence or a 114-bit dec The A5 ciphering algorithm generates a 114-bit ciphering sequence or a 114-bit dec This describes the improvements in A5 ciphering algorithm against security problem The encrypted network management feature is based on the Secure Socket Layer (S With this feature, the Network Address Translation (NAT) firewall is deployed on th
Enhanced full rate (EFR) is adopted. In comparison to FR, EFR optimizes the speech If the full-rate speech codec is used on the Um, Abis, and Ater interfaces, the BSS us This feature enables the dynamic conversion of a FR TCH into HR and vice versa. The Short Message Service Cell Broadcast (SMSCB), cell broadcast service (CBS) for The simplified cell broadcast provides the simple cell broadcast service without the
ALC adjusts the gain of uplink and downlink digital speech signals every 20 ms and c Acoustic echoing refers to a phenomenon in which a calling party can hear not only ANR reduces the background noise in the uplink and downlink speech signals and im To improve the quality of speech signals, Tandem Free Operation (TFO) is introduce ANC adaptively raises the volume of the voice from the other end when the backgro In the communication system, the bit error of the transmission link may be caused b The voice quality index (VQI) feature provides a direct method of measuring the voi GSM will coexist with UMTS for a long time. To obtain better performance of the in BTS power lift for handover function determines whether the BTS of the serving cel Handover between a full-rate TCH and a half-rate TCH performs decision based on h Voice Quality Enhancement. Based on VQE1.0, some optimization is brought into VQ The user experience evaluation system categorizes the factors that affect user expe
AMR is an adaptive multi-rate voice coding/decoding, which is termed full-rate spee AMR is an adaptive multi-rate voice coding/decoding, which is termed full-rate spee The procedure of power control for AMR calls is similar to that for non-AMR calls. In AMR FR/HR Dynamic Adjustment, consists of the AMR TCHF-TCHH handover and th With AMR Wireless Link Timer, we can adjust the values of some parameters to imp The AMR rate adjustment threshold adaptation function enables the BSC to monito The sampling frequency of WB AMR is 16 kHz, and the speech frequency ranges fro
In the case of streaming class, the BSC allocates radio blocks to users according to t This feature describes the QoS attributes of ARP and THP. PS Active Package Management is a feature used to maintain the buffer queue leng PoC (Push-to-talk over Cellular) services belong to the real-time packet services and This feature describes the QoS attributes of BE services. This feature describes the QoS attributes of Conversational service.
GBFD-116201 GBFD-116301 GBFD-119801 GBFD-114101 GBFD-510001 GBFD-118901 GBFD-114201 GBFD-113101 GBFD-510002 GBFD-119201 GBFD-119202 GBFD-119203 GBFD-119204 GBFD-119205 GBFD-119302 GBFD-119303 GBFD-119501 GBFD-119305 GBFD-119502 GBFD-119503 GBFD-119504 GBFD-119401 GBFD-119402 GBFD-114151 GBFD-119403 GBFD-119404 GBFD-119405 GBFD-116001 GBFD-115001 GBFD-110521 GBFD-115002 GBFD-118103 GBFD-115401 GBFD-115402 GBFD-115403 GBFD-115404 GBFD-118601 GBFD-118611 GBFD-118604
M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M M N M M M M M M M M M M M M M M N M M M
Network Control Mode 2 (NC2) indicates network-controlled cell reselection. The B Network Assisted Cell Change. The NACC procedure enables the MS to obtain the SI NACC is generally combined with PACKET SI STATUS. The PACKET SI STATUS procedu
General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) is a type of end-to-end packet switched service Network operation mode I supports the paging coordination on the core network (C Coding Scheme 3/4. CS3=14.4 kbps, CS4=20.0 kbps. EGPRS is the Enhanced GPRS. In addition to GMSK, EGPRS also uses the 8 Phase Shif The dynamic PDCH conversion and dynamic PDCH release adjust PDCHs properly ba In Gb over FR mode the physical layer of the Gb interface uses the FR (Frame Relay)
The Packet Channel Request message is a 11-bit access burst. A method to reduce the MS access time. In this way, the packet assignment messag Support of extended uplink TBF. Depending on the network setting, the BSC notifies The BSC adjusts the uplink coding scheme according to the downlink BEP (Bit Error P Dynamic adjustment of transmission interval of the RRBP field is a process in which The BSC obtains the information about all PDCHs in the cell that can be allocated to Dynamic PDCH conversion for load sharing. The BSC determines the maximum number of uplink and downlink channels that ca In BSS paging coordination mode, the BSC determines whether the CS paging messa To achieve the minimum possible time delay, Huawei introduces the PS Handover f The TBF can be allocated before the MS transmits the actual data, thereby reducing PS power control is a technology based on which the transmit power of the MS or B
Extended dynamic allocation is used for the uplink preferred service to increase the The BSC supports MS high multislot class (HMC) channel allocation. For an MS of mu Dual Transfer Mode. Simultaneous CS and PS service. Compared with DTM, class 11 DTM doubles the uplink bandwidth of data services. Compared with DTM, High Multislot Class (HMC) DTM further improves the uplink a Huawei GSM BSS supports the transfer of PS services on individual speech channels
With priority-based resource reservation, the system reserves a certain number of T The Enhanced Multi-Level Precedence and Pre-emption service (eMLPP) is a supple The emergency call guarantee feature is the enhancement of the emergency call fe When the BSC is enabled with the Flow Control Based on Cell Priority feature, the B
Single Antenna Interference Cancellation (SAIC) is used to reduce the impact of inte
Huawei provides services of locating an MS according to the cell ID and TA on both Huawei provides services of locating an MS according to the cell ID and TA on both Based on the current user tracing, the BSC calculates the location information and t The Lb interface is a protocol-defined standard interface for interconnecting the BS
In Abis over IP mode, signaling and speech signals are transmitted over the Abis inte The Abis interface supports IP over E1/T1. Abis multiplexing encapsulates multiple PDUs into one packet, thus reducing the UD
GBFD-118602 GBFD-118622 GBFD-118610 GBFD-118623 GBFD-118603 GBFD-118605 GBFD-118607 GBFD-118609 GBFD-118630 GBFD-510601 GBFD-510602 GBFD-510603 GBFD-510604 GBFD-510605 GBFD-510606 GBFD-510607 GBFD-510701 GBFD-510702 GBFD-510704 GBFD-510705 GBFD-510706 GBFD-510301 GBFD-510303 GBFD-510305 GBFD-510306 GBFD-510307 GBFD-510308 GBFD-510309 GBFD-510302 GBFD-510304 GBFD-510310 GBFD-510501 GBFD-510502 GBFD-118701 GBFD-118702 GBFD-118703 GBFD-510801 GBFD-510802
M M M N M M M M M M M N N N N N M M N
In A over IP mode, signaling and speech signals are transmitted over the A interface The A interface supports IP over E1/T1. UDP Multiplexing for A Transmission is a transport bearer multiplexing technology. A over TDM/IP Dual-Stack Transmission is a feature based on which the BSC uses bo
In Gb over IP mode, signaling and PS signals are transmitted over the Gb interface b
IP performance monitoring (IP PM) is a method of detecting the QoS of the IP trans Bidirectional Forwarding Detection is a means to quickly detect link faults. The ETH OAM (Ethernet Operation, Administration, and Maintenance) provides end
PICO Automatic Configuration and Planning involves automatic configuration of the No description available. PICO BTS supports not only single-band automatic planning but also dual-band auto The USB encryption function enables the encryption of the files in a USB device so t The PICO BTS filters out illegal packets at the receiving ports after analyzing the pac Power consumption is reduced by shutting down the power amplifiers of the TRXs i The M2000 periodically analyzes the uplink and downlink interference-related traffi
The function of automatic frequency planning of Compact BTS enables the automat The automatic capacity and coverage planning of Compact BTS mainly applies to sim Automatic neighboring cell planning applies to the scenario where a BTS is newly de Timing power-off of the compact BTS consists of BTS power-off and BTS sleeping at A feature that allows the management of all users under the compact BTS serving a
M M M M M M M M M M M M M N N M M
A VGCS call is a half-duplex group call that is established in a predefined area for mu When a VGCS/VBS call is established, no radio channels are assigned. If the cell has During VGCS call initiation, the initiator does not seize a dedicated channel; instead Talker identification is a process in which the information about the talking subscrib The eMLPP service provides seven priorities (A, B, 0-4). During call establishment or To initiate a fast VGCS call, an MS sends an Immediate Setup message to request th Enhancement of VGCS consists of fallback and VGCS resource check. Fallback: If the
VBS is a service where one person talks and several persons listen (no limitation on When a VGCS/VBS call is established, no radio channels are assigned. If the cell has If the core network of the traditional GSM system cannot be replaced with the GSM
Huawei's proprietary handover algorithm. In the handover procedure generally, if the BSC does not receive a response from th
RAN Sharing enables multiple operators to share the network resources on the BSS The Multi-Operator Core Network (MOCN) shared cell feature enables multiple ope With the help of this feature, operators can divide a network into multiple areas, w
The definition of Mobile Station Receive Diversity (MSRD) is as follows: An extra ant The dual carriers in downlink feature is an enhanced solution for downlink packet d
GBFD-510803 GBFD-510804 GBFD-510805 GBFD-510901 GBFD-511001 GBFD-511002 GBFD-511101 GBFD-511102 GBFD-511103 GBFD-511104 GBFD-511201 GBFD-511202 GBFD-511203 GBFD-511205 GBFD-511312 GBFD-511204 GBFD-511311 GBFD-511206 GBFD-511301 GBFD-511302 GBFD-511303 GBFD-511304 GBFD-511305 GBFD-511306 GBFD-511307 GBFD-511308 GBFD-511309 GBFD-511401 GBFD-511402 GBFD-511501
M M M M M N M N N N M N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N N M
In the uplink direction, EGPRS2-A increases the data rate by using the 16QAM modu In the downlink direction, EGPRS2-A increases the data rate by using the Turbo code Latency Reduction is a feature that aims to improve latency within GERAN. The Late
Together with the Nastar network optimization tool, Huawei GSM BSS can analyze t
With this feature, telecom operators can temporarily withdraw the license limitatio With the access control (ACC) feature, the BSC can control the number of MSs acce
When the Co-RRM feature is used, the BSC6900 can select the target cell according If the Iur-g interface exists between the UTRAN and the GERAN, the UTRAN-to-GERA The BSC6900 enables the redirection and handover between the GSM and UMTS sy The inter-RAT service distribution is performed in two directions: UMTS to GSM (co
With the 2G/3G Co-Transmission by TDM Switching feature, Huawei SingleRAN equ IP transmission ports and IP transport networks are shared between GSM ad UMTS The GSM and UMTS traffic can be multiplexed onto the same SDH/PDH network thr The GSM and UMTS bandwidth allocation uni-control feature improves the utilizatio GSM LTE co-transmission on the base station side can be based on IP over Ethernet
The common clock solution is supported by Huawei MBTSs sharing a common base The common clock solution is supported by Huawei MBTSs sharing a common base
This feature is applied to the scenario where GSM TRXs and UMTS TRXs, or GSM+UM
Inter-RAT cell reselection between GERAN and EUTRAN involves the cell reselection The inter-RAT handover between the GERAN and the EUTRAN involves inter-RAT ha The inter-RAT handover between the GERAN and the EUTRAN involves inter-RAT ha The inter-RAT handover between the GERAN and the EUTRAN involves inter-RAT ha The inter-RAT handover between the GERAN and the EUTRAN involves inter-RAT ha The inter-RAT handover between the GERAN and the EUTRAN involves inter-RAT ha eNC2 is network-controlled cell reselection between GSM and LTE. Compared with The eNACC between the EUTRAN and GERAN, which is short for External Network A In Single Radio Voice Call Continuity (SRVCC), speech services are implemented in E
Iur-g interface between the RNC and the BSC is used to achieve common measurem The enhanced radio resource reserved handover based on Iur-g applies to the scena
In common cases, one cell is configured with one BCCH physical channel, which is co
the two TRXs in the double-transceiver unit are used as one TRX. After modulation and DA conversion, one signal output is divided into tw f the signals received by the MS and reduce the effect of multipath fading. When Transmit Diversity is enabled, one baseband signal is tra sity is implemented in the TRX board, that is, four receive paths receive the same signal separately. Then, the four RX signals are combined mally, two TRXs in a double-transceiver unit work independently. The two channels with the same timeslot number on the two TRXs in a double-transceiver unit work independently. If required, the two channels of the same timeslot number on the two TRXs work as a ch TSs and manages BTS radio resources, and the BTS handles services. In the case of PS services, the BTS determines whether to use GMSK o
ogy, the GSM850 band, GSM900 band, DCS1800 band, and GSM1900 band use the same BSC, or multiband BTSs are connected to the sam t on the existing dual-band network. It is implemented as follows: physically, two single-band cells are located at the same layer and have mically adjusts the MAIO according to the current interference level of a channel when assigning an MAIO to the channel (note that the BS etwork, the interference on different diversity antennas comes from the same interference source. Therefore, the interference has a cert developed from ICC. Generally, the interfering signals received from multiple antennas are both space correlated (among the antennas) a
nt frequencies, but the frequency remains unchanged for each burst. changed, that is, the BCCH cannot participate in FH. In baseband FH, other channels on the BCCH TRX except the BCCH can participate in F sity on the downlink. User data is coded and interleaved to obtain the transmit signal S. S is divided into S1 and S2, which are then transm is applicable to the network with limited frequency resources. It helps to increase the reusability of BCCH frequencies and reduce the num : UL=876-915 MHz, DL=921-960 MHz.
nd symbol offsets of the BTSs are adjusted by means of software to synchronize timeslots in the frames. In this case, the BTSs use the plan clock to be synchronized with the GPS clock source. ent architecture. nt architecture as the clock over IP solution. In the IEEE1588 V2 solution, the IPCLK1000 acts as the server, and the Huawei base station is sic principles as SDH and PDH network clock synchronization. That is, a higher-level device encodes clock signals into serial data bit stream
erpolation, MR filtering, calculation FH gain, and calculation of adjustment step based on the FH gain. educes the interference level and improves the system efficiency. During a call, when no speech signals are transferred, the BTS sends on educes the interference level and improves the system efficiency. During a call, when no speech signals are transferred, the MS sends onl ntelligent shutdown, all the TRXs except the one carrying the BCCH can be powered off. That is, the cell can keep providing services for su meslot level is supported and the power consumption of the power amplifier on the timeslot level is zero. There are eight timeslots in a TR transceiver unit. When the non-BCCH TRX is idle, the BCCH TRX is in ICB mode with a capacity of one TRX. The lowest voltage is used by p torage battery as a back up power supply. The battery capacity, however, is limited, and the BSC reduces the power consumption of the B the technology that the voltage is provided for TRX power amplifiers based on different modulation modes of channels so that the BTS p required PSUs and shuts down the redundant PSUs to improve the efficiency of the power system and preserve the lifetime of the power tion optimization, through which the power of the non-BCCH timeslots of BCCH TRX can be reduced. work, the feature of dynamic cell power off is introduced to the multiband network. When the traffic volume is low, the power amplifiers er decreases, the working voltage of the TRX can be lowered in the condition that the power gain of the TRX power amplifier remains alm ure is introduced to dynamically adjust the working voltage of the TRX according to the dynamic changes of the working states of the TRX the proper volume of energy consumption based on the available energy sources (the electric power is generated by the solar battery, no
nk (OML and RSL) is enabled, each signaling link occupies only 16 kbit/s bandwidth at the physical layer, thus saving the transmission reso sy and not both the PS and CS services have a high traffic volume at a specific time. Generally, if the load of one BTS is heavy, the load of o s that the calling MS and the called MS of a call are under the same BTS, in the same BTS group, or in the same local switching area. her to trigger rate adjustment based on the (flex) Abis usage in the cell.
s are allocated according to the channel type during the call establishment. If TCHFs are allocated on the Um interface, 16 kbit/s timeslots hout involving NEs on the NSS side. In other words, the speech signals are not sent to the MSC. hich the TransCoder Subrack (TCS) of the BSC is located remotely and the IP over PPP over Ch-STM-1 transmission mode is used to carry s
MS to use the same speech coding/decoding scheme. Thus, the speech signal is coded at the calling MS and decoded at the called MS only
e than three cells (12 at most) are configured for a single BTS to improve system capacity. Multi-cell function meets the requirement of v
ogy. All the BTSs and the BSC in this topology are connected to form a ring. aulty, the BSC designates another available TRX in the cell to replace the original TRX. the traffic generated from one MSC pool area. A BSC belonging to an MSC pool area is connected to each MSC in the MSC pool. All the M SGSNs to form a SGSN pool. A BSC belonging to an SGSN pool area is connected to all SGSNs in the related SGSN pool. The resources and hain topology to avoid the problem of service disruption on other BTSs upon the power failure of one BTS. With the Abis Bypass feature, a en, the BTSs that follow the breakpoint automatically form a chain in the reverse direction. nt to improve the anti-interference performance of the FACCH link and SACCH link and to increase the possibility of successfully receiving to e.g. a natural disaster, the GBSS automatically switches the terrestrial TDM transmission link over the Abis interface to a backup satelli ch two BSCs form a redundancy group. The two BSCs in a redundancy group work in 1+1 load sharing mode. When one BSC in a redundan anscoder subracks (TCSs) of a certain BSC so that these BSCs share the TC resources. Thus, the TCSs form a TC pool. ween the BSC and the BTS. When the OML is faulty, the BTS cannot work. With this feature, two OMLs can be configured on two independ
uency shift, thus ensuring successful high-speed access of the MSs and meeting the requirements of high-speed mobile communication s a micro cell to a macro cell according to the relative speed of an MS so that the number of handovers can be minimized. ess rate of an MS moving at a high speed and to ensure the call continuity and low call drop rate. Quick handover applies to the scenario w ich the multiple subsites that communicate with the same BBU are logically configured as one cell. In a multi-site cell, a BBU supports a m
st and provide services together for a long time. Therefore, 2G/3G interoperability is introduced into the BSS. The 2G/3G interoperability st and provide services together for a long time. Therefore, 2G/3G interoperability is introduced into the BSS. The 2G/3G interoperability uced to optimize the utilization of resources in 2G and 3G networks. For example, voice services and low-rate data services are distributed here is a possibility that a network is congested due to insufficient resources, whereas the other network has only a light traffic. The inter selection from GSM to UMTS and the cell reselection from UMTS to GSM. Cell reselection is performed mainly by the MS. l, it camps on the GSM cell. When a neighboring UMTS cell meets the requirements for cell reselection, the MS camps on the UMTS cell a
ltiple interfaces. Satellite transmission over Abis interface is widely used.
ltiple interfaces. Satellite transmission over A interface is widely used. ltiple interfaces. Satellite transmission over Ater interface is widely used. ltiple interfaces. Satellite transmission over Pb interface is widely used. ltiple interfaces. Satellite transmission over Gb interface is widely used.
network: 64 kbit/s signaling link and 2 Mbit/s signaling link. The 2 Mbit/s signaling link is also called high-speed signaling link. The BSC uses s one physical BSC to function as multiple logical BSCs. Each logical BSC has an SS7 signaling point code.
1 timeslots in the BSS system to be used to provide transmission paths for subscribers. The paths are used to transmit information such as on which the network administrator traces the activities of each NE when an event occurs. ations such as construction, expansion, upgrade, or commissioning, some NEs may report a large number of alarms. These alarms are aut
should transmit signals at a proper power instead of the maximum power when the connection is initially established. To achieve this, Ac
ering sequence or a 114-bit deciphering sequence based on the 64-bit Kc stored in the MS and the network, and a 22-bit frame number fr ering sequence or a 114-bit deciphering sequence based on the 64-bit Kc stored in the MS and the network, and a 22-bit frame number fr orithm against security problems. The ciphering procedure is optimized on the basis of the characteristics of the Um interface transmissio ed on the Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol, which allows the M2000 to set up an SSL-based TCP transmission channel between the M20 (NAT) firewall is deployed on the LMT side and the M2000 side to maintain the network security without affecting the normal connection
o FR, EFR optimizes the speech codec algorithm and improves the speech quality. , and Ater interfaces, the BSS uses channels of 16 kbit/s for coding and transmission. If the half-rate speech codec is used on the Um, Abis TCH into HR and vice versa.
cell broadcast service (CBS) for short, refers to the information broadcast service for the MSs in the idle state within a specified area know l broadcast service without the CBC system.
peech signals every 20 ms and changes the amplitude of digital speech signals in static or dynamic mode. This keeps the voice level of the a calling party can hear not only the voice of the called party but also his/her own voice when making a call to another MS. The Acoustic E d downlink speech signals and improves the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and speech intelligibility. In this way, the other party of the call can ee Operation (TFO) is introduced to pass by the TC decoder when the originating MS and the terminating MS use the same speech versio the other end when the background noise is loud at the local end. ansmission link may be caused by the mobile terminal, interference between transmission links, or changes in the load of the TRX. When ct method of measuring the voice quality of the radio network. By measuring the uplink VQI and downlink VQI, the voice quality of the ne in better performance of the interoperability between the UMTS network and the GSM network and to obtain more measurement inform ether the BTS of the serving cell transmits signals at the maximum power during a handover. The BSC maximizes the transmit power of th CH performs decision based on handover algorithm II. e optimization is brought into VQE3.0. In VQE3.0, the system can distinguish music and RBT services from noises more accurately, the fun he factors that affect user experience of mobile terminals into five types, with each type defined different KPIs and call history record (CH
g, which is termed full-rate speech version 3 and half-rate speech version 3 in GSM specifications. AMR enables the BTS and the MS to au g, which is termed full-rate speech version 3 and half-rate speech version 3 in GSM specifications. AMR enables the BTS and the MS to au ilar to that for non-AMR calls. In Huawei II power control algorithm and Huawei III power control algorithm, parameters related to AMR p MR TCHF-TCHH handover and the AMR TCHH-TCHF handover. lues of some parameters to improve the robustness of the SACCH frame, enhance the network coverage performance of AMR, and decre ction enables the BSC to monitor the speech quality in real time and to adaptively modify the threshold parameters. Thus, an appropriate he speech frequency ranges from 50 Hz to 7 kHz. Compared with AMR, WB AMR has wide high frequency extension and low frequency ex
o blocks to users according to the GBR of the QoS attributes and ensures that the data transmission rates meet the requirements of strea
maintain the buffer queue length within an appropriate range by discarding data packets in the buffer queue actively. It increases data th he real-time packet services and have strict requirements on bandwidth and transfer delay. The scheduling priority of conversational serv
ational service.
ontrolled cell reselection. The BSC determines whether to perform cell reselection according to the packet measurement report from the enables the MS to obtain the SI of the target cell before the cell reselection. In this way, the period of PS service disruption during a cell r . The PACKET SI STATUS procedure is initiated if the MS does not obtain the complete SI of the target cell through the NACC procedure. Th
d-to-end packet switched service based on the GSM technology. It supports GMSK CS-1 to CS-4. The maximum rate of a single channel is 2 dination on the core network (CN). This function requires the configuration of the Gs interface. For a GPRS-attached MS, the network use
EGPRS also uses the 8 Phase Shift Keying (8PSK) modulation scheme to increase the peak rate of a single channel to 59.2 kbit/s. elease adjust PDCHs properly based on the service requirements and actual network conditions. rface uses the FR (Frame Relay) protocol.
, the packet assignment message is sent by the BTS and thus the MS access delay is reduced by 100 ms. network setting, the BSC notifies in the system information the MS of whether to send the dummy control block when the MS has no othe to the downlink BEP (Bit Error Probability) measurement report sent from the MS. RRBP field is a process in which the BSC transmits downlink data with the RRBP field at different intervals depending on whether an uplin the cell that can be allocated to MSs and determines the maximum number of uplink and downlink PDCHs. This provides a basis for subse
k and downlink channels that can be allocated to the MS according to specific principles. es whether the CS paging message is sent on the PACCH or on the PCH. In GPRS-capable networks, the paging success rate increases when ei introduces the PS Handover feature that can allocate radio resources to the MS in the target cell before the cell reselection is performe he actual data, thereby reducing the service access delay. e transmit power of the MS or BTS is adjusted according to the quality of the link over the Um interface after setup. In this manner, the tr
referred service to increase the uplink throughput. For an MS of multislot classes 32-33, the extended dynamic allocation (EDA) function nnel allocation. For an MS of multislot classes 30-33, the BSC can allocate a maximum of five channels in the uplink or downlink to the MS
nk bandwidth of data services. M further improves the uplink and downlink bandwidth of data services. s on individual speech channels with a high rate of 14.4 kbit/s for transparent data services.
m reserves a certain number of TCHFs for the high-priority users to ensure their QoS. tion service (eMLPP) is a supplementary service offered by the GSM system. When the eMLPP feature is enabled, the MS with a high prio ement of the emergency call feature. With the emergency call guarantee feature, the setup success rate of emergency calls is improved t ed on Cell Priority feature, the BSC preferentially processes the call requests from VIP cells and the paging requests from VIP users on the
sed to reduce the impact of interference on the reception of downlink signals through a signal processing technology.
ng to the cell ID and TA on both the NSS and BSS side. ng to the cell ID and TA on both the NSS and BSS side. s the location information and then sends the location result to the LMT, including the CGI, TA, longitude and latitude of cells, tilt, and err face for interconnecting the BSC and the Serving Mobile Location Center (SMLC).
e transmitted over the Abis interface by using the IP technology. On the Abis interface, the signaling plane uses the LAPD over UDP/IP pro
ne packet, thus reducing the UDP/IP/L2/L1 header transmission overhead and resulting in improved transmission efficiency.
ransmitted over the A interface by using the IP technology. On the A interface, the signaling plane uses the SCCP/M3UA/SCTP/IP protoco
earer multiplexing technology. based on which the BSC uses both TDM and IP to transmit signaling and traffic over the A interface.
smitted over the Gb interface by using IP technology. The BSSGP/NS/UDP/IP protocol stack is used on the Gb interface for transmission.
etecting the QoS of the IP transport network. ickly detect link faults. and Maintenance) provides end-to-end and point-to-point Ethernet link OAM functions. Currently, it complies with two protocols, namel
s automatic configuration of the device data, service data, and some of the transmission parameters.
lanning but also dual-band automatic planning on the mixed 900/1800 MHz and 850/1900 MHz frequency bands. of the files in a USB device so that the files are not displayed as plain text. In this way, the risk of information disclosure due to loss or ste ng ports after analyzing the packets so that they cannot enter the PICO BTS. In this manner, the robustness and anti-attack capability of th e power amplifiers of the TRXs in the cell during the specified period. wnlink interference-related traffic statistics of the PICO BTS. When the working frequency of the PICO BTS is severely interfered, the M200
mpact BTS enables the automatic configuration of device data and service data of the BTS. mpact BTS mainly applies to simple network structure. Initially, the BTS is configured with a single frequency. As the traffic volume increa cenario where a BTS is newly deployed in an existing GSM network. It is necessary only when BTSs have overlapping coverage areas. Auto S power-off and BTS sleeping at night. If there is no traffic or light traffic in a certain period, the power-off and power-on time of the comp nder the compact BTS serving area, e.g. subsciber registration, service provisioning, etc.)
hed in a predefined area for multiple service subscribers to participate in. Simply, VGCS is a service where several persons talk and more nels are assigned. If the cell has a VGCS/VBS subscriber, the subscriber sends a Channel Request message to the network after receiving a ze a dedicated channel; instead, the network regards the initiator as a talker and assigns the initiator a group call channel to establish the ation about the talking subscriber is sent to listening subscribers when a VGCS subscriber talks on the uplink of the group call channel. -4). During call establishment or handover, a group or MS with high priority can be preferentially assigned radio resources or preempt the te Setup message to request the establishment of the VGCS call. resource check. Fallback: If the requirement for service continuity is high, the fallback function is provided in the BTS coverage area when
persons listen (no limitation on the number of listeners). The difference between VGCS and VBS is that only the initiator is allowed to talk nels are assigned. If the cell has a VGCS/VBS subscriber, the subscriber sends a Channel Request message to the network after receiving a annot be replaced with the GSM-R core network, GSM-R services and traditional GSM services can be processed in the same network. Tha
s not receive a response from the MS but receives an Error Indication message from the BTS after sending the Handover Command to the
e network resources on the BSS side while keeping their own subscribers and services. ell feature enables multiple operators to share a cell when using their respective CN equipment. network into multiple areas, which are called handover shared areas, at the BSC based on location areas. In addition, operators can confi
MSRD) is as follows: An extra antenna is configured on the MS to improve the downlink receive performance of the MS. d solution for downlink packet data rate, in which two downlink carriers are supported and the downlink data rate is doubled, that is, the d
rate by using the 16QAM modulation scheme. ata rate by using the Turbo codes and 16 quadrature amplitude modulation (16QAM)/32QAM modulation scheme. latency within GERAN. The Latency Reduction feature can only be enabled in cells that support EDGE.
, Huawei GSM BSS can analyze the 2G/3G neighboring cell configuration based on numerous measurement reports (MRs) from MSs, show
y withdraw the license limitation in the case of a sudden increase in traffic volume due to natural disasters, holidays, or a faulty BSC in the ontrol the number of MSs accessing the network at a certain time by allowing only the MSs of a certain ACC class to access the network.
select the target cell according to the traffic load in the cell before initiating an inter-RAT handover. the GERAN, the UTRAN-to-GERAN NACC procedure is an optimized NACC procedure. In this case, the UE obtains the SI of the target cell d between the GSM and UMTS systems based on the load condition and difference in each network. In this way, the two networks in the sa wo directions: UMTS to GSM (controlled by the RNC) and GSM to UMTS (controlled by the BSC). As a result of load-based system redirectio
feature, Huawei SingleRAN equipment uses the TDM timeslot cross connection function to enable the SDH to be shared by the GSM traff shared between GSM ad UMTS. the same SDH/PDH network through the TDM timeslot cross-connect function. Through the fractional ATM or fractional IP function, the R ol feature improves the utilization efficiency of transmission resources while ensuring the fairness of transmission bandwidth allocation be an be based on IP over Ethernet or IP over E1/T1.
MBTSs sharing a common baseband unit (BBU). MBTSs sharing a common baseband unit (BBU).
RXs and UMTS TRXs, or GSM+UMTS dual-mode TRXs, are in the same BTS cabinet, and uses the same BBU and groups of storage batteries
RAN involves the cell reselection from GERAN to EUTRAN and the cell reselection from EUTRAN to GERAN. Cell reselection is performed m e EUTRAN involves inter-RAT handover from the GERAN to the EUTRAN and inter-RAT handover from the EUTRAN to the GERAN. This fea e EUTRAN involves inter-RAT handover from the GERAN to the EUTRAN and inter-RAT handover from the EUTRAN to the GERAN. This fea e EUTRAN involves inter-RAT handover from the GERAN to the EUTRAN and inter-RAT handover from the EUTRAN to the GERAN. This fea e EUTRAN involves inter-RAT handover from the GERAN to the EUTRAN and inter-RAT handover from the EUTRAN to the GERAN. This fea e EUTRAN involves inter-RAT handover from the GERAN to the EUTRAN and inter-RAT handover from the EUTRAN to the GERAN. This fea n GSM and LTE. Compared with the autonomous cell reselection of the MS, the network-controlled cell reselection comprehensively cons h is short for External Network Assisted Cell Change, functions as follows: In NC0/NC1 mode and packet transfer mode, if an MS determine h services are implemented in EUTRAN packet network, so technically the SRVCC feature can be regarded as a real LTE VoIP technique. Th
d to achieve common measurement and information exchange between 2G and 3G networks. sed on Iur-g applies to the scenarios where the GSM and TD-SCDMA networks provide coverage for the same area. The enhanced radio re
CCH physical channel, which is configured on timeslot 0 of the BCCH TRX. The feature of Multiple CCCHs (GBFD-511501 Multiple CCCHs) al
one signal output is divided into two RF signals. These two signals are amplified and then combined to form one signal. As the two signals nabled, one baseband signal is transmitted through two RF channels. The combined signals in the multipath transmission are optimized. T n, the four RX signals are combined into one according to the specified algorithm. In this way, a strong useful signal is obtained, and the up meslot number on the two TRXs can work as a channel group if required. That is, the two channels can be converted into a channel mber on the two TRXs work as a channel group. That is, the two channels can be converted into a channel group, and the channel group in etermines whether to use GMSK or 8PSK modulation scheme according to the service type of the BSC. In 8PSK modulation scheme, the m
nd BTSs are connected to the same BSC. ocated at the same layer and have the same priority but different coverage areas; logically, the two cells serve as neighboring cells of each O to the channel (note that the BSC assigns an MAIO to only a channel under activation). In this way, the BSC assigns the MAIO with the m refore, the interference has a certain correlation. ICC uses this correlation to eliminate some interference. correlated (among the antennas) and time correlated. The difference between ICC and EICC is that ICC considers only space correlation to
cept the BCCH can participate in FH to obtain FH gains. In RF FH, the transmit frequency of each TRX changes. Therefore, the BCCH TRX ca S1 and S2, which are then transmitted through different antennas. H frequencies and reduce the number of frequencies used by the BCCHs. Therefore, more frequencies can be used at the FH layer.
In this case, the BTSs use the planned FNs and symbol offsets to achieve synchronization.
er, and the Huawei base station is embedded with the synchronization client. The clock over IP solution and the IEEE1588 V2 solution diffe k signals into serial data bit streams and a lower-level device receives the serial data bit streams from the physical layer to extract and tra
are transferred, the BTS sends only comfort noises periodically to the peer end. are transferred, the MS sends only comfort noises periodically to the peer end. can keep providing services for subscribers even if the TRXs are shut down. o. There are eight timeslots in a TRX. If only one timeslot has traffic and the other seven timeslots are idle, the power amplifier is working X. The lowest voltage is used by power amplifier on the BCCH TRX, and the output power of a single power amplifier on the BCCH TRX is 1 s the power consumption of the BTS by shutting down some TRXs or decreasing the maximum transmit power of the TRX to prolong the b odes of channels so that the BTS power consumption can be decreased. preserve the lifetime of the power system.
lume is low, the power amplifiers of all the TRXs in the DCS1800 cells are shut down and the GSM900 cells provide services for all the sub TRX power amplifier remains almost the same. In this way, the power consumption of the TRX power amplifier and the overall power con s of the working states of the TRX. Through this feature, the BTS power consumption is significantly reduced. generated by the solar battery, not by the algorithm or storage battery). The general principle is to keep balance between energy consum
thus saving the transmission resources on the Abis interface. d of one BTS is heavy, the load of other BTSs is light; if the traffic volume of the PS service is high, that of the CS service is low, and vice ver e same local switching area.
e Um interface, 16 kbit/s timeslots are used on the Ater interface. If TCHHs are allocated on the Um interface, 8 kbit/s timeslots are used
nsmission mode is used to carry signals when the Ater interface is in TDM transmission mode.
and decoded at the called MS only once.
ction meets the requirement of various networking scenarios, especially the dual-band networking.
ch MSC in the MSC pool. All the MSCs in the MSC pool implement load balancing and resource sharing for even distribution of traffic in th ed SGSN pool. The resources and load are shared by all the SGSNs in the pool, thus balancing the traffic load and reducing inter-SGSN han S. With the Abis Bypass feature, a bypass transmission link is formed within the BTS that is powered off to transfer data to other BTSs foll
ossibility of successfully receiving the signaling messages by the MS and BSC. e Abis interface to a backup satellite transmission link, thus maintaining the normal operation of the network. ode. When one BSC in a redundancy group is faulty or all the signaling links on the A interface are faulty, the other BSC in this group takes
an be configured on two independent E1s (one for each). When the active OML is faulty, the BTS uses the standby OML.
h-speed mobile communication services. an be minimized. handover applies to the scenario where an MS moves fast along an urban backbone road, a selected route, or a high-speed railroad. The t multi-site cell, a BBU supports a maximum of six subsites, and each subsite supports a maximum of six TRXs.
e BSS. The 2G/3G interoperability involves inter-RAT handover and inter-RAT cell reselection between GSM and UMTS. e BSS. The 2G/3G interoperability involves inter-RAT handover and inter-RAT cell reselection between GSM and UMTS. w-rate data services are distributed to the 2G network, whereas high-rate data services are distributed to the 3G network to achieve high p rk has only a light traffic. The inter-RAT load-based handover in connected state feature is introduced to solve this problem. mainly by the MS. the MS camps on the UMTS cell after the cell reselection. Before initiating the UMTS cell reselection, the MS must receive system inform
-speed signaling link. The BSC uses the high-speed signaling links when the signaling load of the system is high.
ed to transmit information such as business hall information, alarm information on the BTS AC power supply, and other maintenance infor
er of alarms. These alarms are automatically cleared after the maintenance operations are complete. Maintenance mode alarm feature ca
lly established. To achieve this, Active Power Control should be enabled.
ork, and a 22-bit frame number from the current pulse stream. ork, and a 22-bit frame number from the current pulse stream. cs of the Um interface transmission in GSM, and thereby enhances transmission security and network bugging defense. mission channel between the M2000 server and an NE. t affecting the normal connections between devices.
ech codec is used on the Um, Abis, and Ater interfaces, the BSS uses channels of 8 kbit/s for coding and transmission. Thus, when half-rate
state within a specified area known as the cell broadcast area.
e. This keeps the voice level of the entire network within an appropriate range, prevents volume fluctuation for the two parties during a ca call to another MS. The Acoustic Echo Cancellation (AEC) feature of the BSC is implemented by the DSP of the DPU board. The DSP analyze way, the other party of the call can clearly hear the voice. g MS use the same speech version. The speech signal is coded at the originating MS and decoded at the terminating MS, and is transpare
nges in the load of the TRX. When bit error occurs in voice transmission, at least one frame is lost before it arrives at the decoder, and thu nk VQI, the voice quality of the network is quantified, which provides a reference for future network optimization. obtain more measurement information about the neighboring cells, a new type of measurement report (MR), that is, the enhanced meas aximizes the transmit power of the BTS before sending a handover command to the MS. The BSC does not adjust the BTS power during th
m noises more accurately, the function of real-time speech monitoring over the network is supported, the ACLP feature is added, and the ent KPIs and call history record (CHR) information.
enables the BTS and the MS to automatically select an appropriate coding/decoding rate from the specified ACS according to the interfere enables the BTS and the MS to automatically select an appropriate coding/decoding rate from the specified ACS according to the interfere hm, parameters related to AMR power control are configured separately from those related to non-AMR power control. The AMR calls an
e performance of AMR, and decrease the call drop rate. parameters. Thus, an appropriate AMR codec mode can always be selected for the call. cy extension and low frequency extension. Thus, WB AMR can provide better speech quality. In the GSM system, WB AMR specifies five sp
es meet the requirements of streaming class. If streaming services support resource preemption, high-priority streaming services can pree
queue actively. It increases data throughput and reduces service delay at the price of buffer utilization. ng priority of conversational services and PoC services is higher than other services. The bandwidth requirement of PoC services is guaran
ket measurement report from the MS, the current load in the serving cell and in the neighboring cells. S service disruption during a cell reselection is shortened. ll through the NACC procedure. The combination of these two procedures ensures the normal operation of PS services, thus reducing the
imum rate of a single channel is 20 kbit/s. PRS-attached MS, the network uses the same paging channel for transmitting PS and CS paging messages. Thus, the MS needs to monitor channel to 59.2 kbit/s.
ol block when the MS has no other block to transmit in extended TBF mode. This is an enhanced feature of the extended uplink TBF, as de
ls depending on whether an uplink TBF exists and whether the delayed release of the downlink TBF is performed at an early stage or at a Hs. This provides a basis for subsequent PDCH allocation.
paging success rate increases when BSS paging coordination is enabled. re the cell reselection is performed. Thus, the delay is shortened to not more than 150 ms. In addition, the PS Handover feature considers
after setup. In this manner, the transmit power is reduced without affecting the link quality, thus reducing the network interference and e
ynamic allocation (EDA) function must be used if the MS requires more than three channels in the uplink. n the uplink or downlink to the MS.
enabled, the MS with a high priority has advantages in terms of the call setup rate, call completion capability, and service continuity. Wh e of emergency calls is improved to the greatest extent. ng requests from VIP users on the CN side if the BSC is overloaded.
g technology.
e and latitude of cells, tilt, and error.
ne uses the LAPD over UDP/IP protocol stack and the user plane uses the PTRAU over UDP/IP protocol stack for transmission.
nsmission efficiency.
the SCCP/M3UA/SCTP/IP protocol stack and the user plane uses the RTP/UDP/IP protocol stack for transmission. The function of transcod
he Gb interface for transmission.
mplies with two protocols, namely, IEEE 802.1ag and IEEE 802.3ah.
mation disclosure due to loss or stealing of the files in the USB device is reduced. ess and anti-attack capability of the PICO BTS are improved.
S is severely interfered, the M2000 instructs the PICO BTS to restart uplink and downlink frequency scanning. Based on the frequency sca
uency. As the traffic volume increases, the system may activate another frequency by performing the automatic capacity and coverage pla overlapping coverage areas. Automatic neighboring cell optimization is a feature with which the M2000 automatically starts the BTS neig ff and power-on time of the compact BTS can be configured on the BSC. Also during night the BTS is put in sleeping mode.
re several persons talk and more persons listen. e to the network after receiving a notification message. Then, the network assigns the VGCS/VBS channel to this cell through the notificat roup call channel to establish the VGCS call. Thus, the dedicated channels can be saved. group call channel to the talker. Compared with t plink of the group call channel. ed radio resources or preempt the radio resources seized by an MS with low priority.
ded in the BTS coverage area when the BTS is out of service because of transmission failure. VGCS resource check: Periodical VGCS resourc
only the initiator is allowed to talk during a VBS call and other members are always in the listening state. e to the network after receiving a notification message. Then, the network assigns the VGCS/VBS channel to this cell through the notificat ocessed in the same network. That is, the BSC implements the function of forwarding GSM-R services.
ng the Handover Command to the MS, the BSC regards that call drop occurs and then initiates the release procedure. After Handover Re-e
s. In addition, operators can configure the mapping between the IMSI ranges and the handover shared areas to limit the areas to which a
ance of the MS. data rate is doubled, that is, the downlink data rate of the EGPRS system is increased from 473.6 kbit/s to 947.2 kbit/s.
ent reports (MRs) from MSs, show the analysis result on the map, and find out missing or redundant 3G neighboring cells for the GSM ser
ers, holidays, or a faulty BSC in the BSC Pool scenario. For each release version of BSC6900, the operation personnel have three chances t ACC class to access the network.
E obtains the SI of the target cell directly over the Iur-g interface. is way, the two networks in the same coverage area can have similar load conditions, thus reducing the risk of access congestion. ult of load-based system redirection and handover, the CS services will mainly be handled by the GSM network whereas the high-rate data
DH to be shared by the GSM traffic and UMTS traffic.
TM or fractional IP function, the RNC and NodeB can map ATM cells or IP packets onto several E1 timeslots. TDM timeslots can be shared nsmission bandwidth allocation between GSM and UMTS.
BU and groups of storage batteries. If the mains power supply fails and thus the base station is provided with power by storage batteries,
N. Cell reselection is performed mainly by the MS. he EUTRAN to the GERAN. This feature supports coverage-based handover. he EUTRAN to the GERAN. This feature supports quality-based handover. he EUTRAN to the GERAN. This feature supports load-based handover. he EUTRAN to the GERAN. This feature supports handover based on priority of neighbour cells. he EUTRAN to the GERAN. This feature supports service-based handover. eselection comprehensively considers such factors as the receive level and load status in the serving cell and the neighboring cells so that transfer mode, if an MS determines to perform cell reselection, it requests the system information (SI) about the target cell from the BSC. d as a real LTE VoIP technique. The SRVCC feature enables the speech services that are carried on the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) to b
same area. The enhanced radio resource reserved handover procedure consists of the standard handover procedure between GSM and T
(GBFD-511501 Multiple CCCHs) also allows one to configure timeslots 2, 4, and 6 of the BCCH TRX as BCCH physical channels.
orm one signal. As the two signals are aligned in phase, the transmit power is amplified and the downlink signal strength is increased. ath transmission are optimized. Thus, the impact of Rayleigh fading on the MS is reduced. seful signal is obtained, and the uplink gain is enhanced. can be converted into a channel group, and the channel group into two independent channels. This balances cost, capacity, and cov el group, and the channel group into two independent channels. This balances cost, capacity, and coverage. Dynamic PBT increases resou n 8PSK modulation scheme, the maximum transmit power of a TRX is improved through enhanced EDGE coverage so that the maximum o
s serve as neighboring cells of each other and form a cell group, namely, one overlaid cell and one underlaid cell. The enhanced dual-band e BSC assigns the MAIO with the minimum interference to the channel, and the channel experiences the minimum interference in the BTS
onsiders only space correlation to eliminate interference whereas EICC considers both space correlation and time correlation to suppress
nges. Therefore, the BCCH TRX cannot participate in RF FH.
an be used at the FH layer.
and the IEEE1588 V2 solution differ with respect to the clock synchronization procedure and the frame format. As for the frame format, t e physical layer to extract and trace the higher-level clock.
e, the power amplifier is working only in the timeslot with the traffic, and is shut down in the other seven timeslots. wer amplifier on the BCCH TRX is 15 W/10 W. After Power Boost Technology (PBT) is used on the BCCH TRX, the transmit power on top of power of the TRX to prolong the battery discharge time.
ells provide services for all the subscribers, so that the power consumption of the whole network is reduced. When the traffic volume incr mplifier and the overall power consumption of the BTS are also reduced. balance between energy consumption and generation, to prevent power failures and energy wastes at the same time.
the CS service is low, and vice versa. Flex Abis (Flexible Abis) enables the sharing of the Abis interface transmission resources among diffe
rface, 8 kbit/s timeslots are used on the Ater interface.
or even distribution of traffic in the MSC pool, thus reducing inter-MSC handovers and providing redundancy. load and reducing inter-SGSN handovers. to transfer data to other BTSs following the faulty BTS on the chain. Thus, the power failure of a BTS will not affect the normal services on
the other BSC in this group takes over the voice and data services.
he standby OML.
ute, or a high-speed railroad. The target cell must be a chain neighboring cell of the serving cell.
SM and UMTS. SM and UMTS. o the 3G network to achieve high peak throughput. solve this problem.
e MS must receive system information and calculate cell reselection parameters. When the Fast 3G Reselection at 2G CS Call Release feat
pply, and other maintenance information.
aintenance mode alarm feature can manage these alarms. This avoids the impacts of such alarms on normal network monitoring and imp
ugging defense.
transmission. Thus, when half-rate speech channels are used, a channel of 16 kbit/s on the terrestrial interface Abis can be used to carry t
tion for the two parties during a call, and prevents voice distortion. of the DPU board. The DSP analyzes the uplink and downlink digital voice signals, searches for acoustic echoes in the uplink speech signals
terminating MS, and is transparently transmitted between the TCs at the two ends. Thus, the process of encoding and decoding by the T
it arrives at the decoder, and thus the voice quality deteriorates. EPLC predicts the information contained in the missing frame by using t
t (MR), that is, the enhanced measurement report (EMR), is introduced. not adjust the BTS power during the handover to ensure the success of the handover.
he ACLP feature is added, and the AEC, ALC, ANC, and ANR features are enhanced.
fied ACS according to the interference level in the radio environment. FR: 4.75 kbit/s, 5.15 kbit/s, 5.90 kbit/s, 6.70 kbit/s, 7.40 kbit/s, 7.95 fied ACS according to the interference level in the radio environment. HR: 4.75 kbit/s, 5.15 kbit/s, 5.90 kbit/s, 6.70 kbit/s, 7.40 kbit/s, 7.95 R power control. The AMR calls and non-AMR calls can adopt different power control strategies.
system, WB AMR specifies five speech coding rates. In addition, WB AMR occupies only full-rate channels. Rates: 6.60 kbit/s, 8.85 kbit/s,
riority streaming services can preempt the radio blocks of low-priority streaming services when radio resources are insufficient. This ensu
uirement of PoC services is guaranteed by the GBR mechanism of streaming class. To meet the low transfer delay requirement of PoC ser
n of PS services, thus reducing the service delay or disruption.
s. Thus, the MS needs to monitor only one paging channel. If a PDCH is assigned to the MS, the network can use this PDCH for transmittin
e of the extended uplink TBF, as described in 3GPP TS 44.060 (Release 6). If the MS does not send the dummy control block when it has no
erformed at an early stage or at a late stage. Thus, the speed of establishing an uplink TBF on the downlink is increased.
he PS Handover feature considers factors such as signal level and load of the neighboring cells before cell reselection is performed. This e
ng the network interference and expanding the network capacity.
ability, and service continuity. When TCHs are insufficient, for example, during traffic peak hours, the calls with a higher priority can preem
stack for transmission.
smission. The function of transcoding from TRAU to PCM is taken over by the MGW from the TCS.
nning. Based on the frequency scanning result, the M2000 selects the frequency with the minimum interference as the working frequency
tomatic capacity and coverage planning of Compact BTS and distribute transmit power between the two frequencies. 0 automatically starts the BTS neighboring cell optimization after determining that a neighboring cell is redundant or missing by analyzing in sleeping mode.
el to this cell through the notification response procedure. If the assignment of the VGCS/VBS channel is delayed when a VGCS/VBS call is nel to the talker. Compared with the normal VGCS call initiation, the initiation of a VGCS call through only one channel saves TCHs and A-
rce check: Periodical VGCS resource checks are performed on the BSC and BTS to eliminate inconsistent VGCS calls. At present, the VGCS r
el to this cell through the notification response procedure. If the assignment of the VGCS/VBS channel is delayed when a VGCS/VBS call is
se procedure. After Handover Re-establishment is enabled, the BSC initiates the procedure for re-establishing the connection at the data l
areas to limit the areas to which an MS can be handed over. In this way, the MS can be handed over to only the cells in the handover shar
to 947.2 kbit/s.
neighboring cells for the GSM serving cell.
n personnel have three chances to enable this feature. The validity period is seven days each time.
risk of access congestion. etwork whereas the high-rate data services will mainly be handled by the UMTS network.
lots. TDM timeslots can be shared by the GU networks on the Abis and Iub interfaces respectively.
with power by storage batteries, operators can automatically shut down GSM TRXs (or UMTS TRXs) or stop providing GSM services (or UM
l and the neighboring cells so that the MS can reselect a proper cell. In this way, the loads in the cells can be balanced. bout the target cell from the BSC. Then, the BSC sends the requested SI through the Cell Change Notification (CCN) procedure. According Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) to be handed over to the GERAN. A UE accesses the IMS to maintain the speech service through circuit swit
er procedure between GSM and TD-SCDMA and the radio resource reservation procedure. The radio resource reservation procedure is ac
CH physical channels.
k signal strength is increased.
balances cost, capacity, and coverage. age. Dynamic PBT increases resource utilization and assists in expanding the coverage. E coverage so that the maximum output power of high-rate PS services is the same as that of CS services. In this way, the average output p
laid cell. The enhanced dual-band network algorithm enables channel sharing and load balancing between the two cells in the cell group. minimum interference in the BTS. and time correlation to suppress and eliminate interference.
ormat. As for the frame format, the clock over IP solution complies with the Huawei proprietary standard, whereas the IEEE1588 V2 solu
n timeslots. RX, the transmit power on top of the cabinet of the BCCH TRX is the same as that of a single power amplifier, that is, 60 W/40 W.
uced. When the traffic volume increases, the cells that have been shut down are enabled again, thus meeting the requirement for traffic v
the same time.
ansmission resources among different BTSs, cells, and services, and thus improves the resource utilization. Flex Abis is a mode of allocatin
l not affect the normal services on the subsequent BTSs on the chain.
election at 2G CS Call Release feature is activated, the BSS determines the best neighboring UMTS cell based on the measurement inform
rmal network monitoring and improves network OM efficiency.
terface Abis can be used to carry two speech services.
choes in the uplink speech signals, and suppresses the acoustic echoes.
f encoding and decoding by the TC is eliminated to improve the quality of the speech signal.
ed in the missing frame by using the information contained in the good frames and by considering the correlation between the previous f
bit/s, 6.70 kbit/s, 7.40 kbit/s, 7.95 kbit/s, 10.2 kbit/s, 12.2 kbit/s. bit/s, 6.70 kbit/s, 7.40 kbit/s, 7.95 kbit/s.
els. Rates: 6.60 kbit/s, 8.85 kbit/s, 12.65 kbit/s, 15.85 kbit/s, 23.85 kbit/s.
sources are insufficient. This ensures that high-priority services can preferentially use radio resources. If streaming services do not suppor
sfer delay requirement of PoC services, the BSC takes many optimization measures, such as preferentially scheduling PoC services, using a
can use this PDCH for transmitting CS paging messages to the MS.
mmy control block when it has no other block to transmit to the network in extended TBF mode, the message flow on the Um interface c
nk is increased.
ell reselection is performed. This ensures a high success rate of the PS handover and great data throughput in the target cell, thus improvi
lls with a higher priority can preempt the resources of the calls with a lower priority.
ference as the working frequency of the PICO BTS. Through the automatic optimization of the working frequency, the PICO BTS avoids th
o frequencies. edundant or missing by analyzing MRs.
delayed when a VGCS/VBS call is established, the radio channel resources can be saved effectively and the congestion rate of the radio ch y one channel saves TCHs and A-interface circuits.
VGCS calls. At present, the VGCS resource check function can be used to solve the problem that a VGCS call exists on the BTS side but doe
delayed when a VGCS/VBS call is established, the radio channel resources can be saved effectively and the congestion rate of the radio ch
shing the connection at the data link layer of the Um interface on the source channel. If the connection re-establishment is successful, th
only the cells in the handover shared area that maps to the IMSI of the MS.
top providing GSM services (or UMTS services) by using the function of Active Backup Power Control according to the priorities of the GSM
n be balanced. ation (CCN) procedure. According to the SI about the target cell, the MS accelerates the packet service access in the target cell. In this way peech service through circuit switch in the GERAN or packet switch in the EUTRAN. The SRVCC feature supports only handover of speech
source reservation procedure is achieved through the information exchange over the Iur-g interface between the BSC and the RNC. That i
. In this way, the average output power of high-rate PS services in 8PSK modulation scheme is the same as that of CS services.
en the two cells in the cell group.
rd, whereas the IEEE1588 V2 solution complies with the IEEE1588 V2 standard.
lifier, that is, 60 W/40 W.
eting the requirement for traffic volume.
on. Flex Abis is a mode of allocating the Abis interface transmission resources. That is, the Abis interface transmission resources form a re
ased on the measurement information on the neighboring UMTS cells after the call termination in a GSM cell. Then, the BSS sends the fre
orrelation between the previous frames and subsequent frames of the missing frame. In this way, the voice quality is improved.
streaming services do not support resource preemption, the GBRs are decreased; when radio resources become sufficient, the GBRs are
ly scheduling PoC services, using a low-rate coding scheme, and using the policy of balanced channel allocation between uplink and down
essage flow on the Um interface can be decreased, thus increasing the performance of the MS and the BSC and reducing the MS power co
put in the target cell, thus improving the QoS.
requency, the PICO BTS avoids the use of the frequency with severe interference so that the speech quality and traffic KPIs are improved
the congestion rate of the radio channel can be decreased.
call exists on the BTS side but does not exist on the BSC side.
the congestion rate of the radio channel can be decreased.
re-establishment is successful, the MS resumes the call without a call drop.
cording to the priorities of the GSM network and UMTS network.
ccess in the target cell. In this way, the period of PS service disruption during a cell reselection is shortened. upports only handover of speech services from EUTRAN to GERAN. It is available only when the EUTRAN and the GERAN cover the same a
ween the BSC and the RNC. That is, the BSC reserves a channel for the MS to be handed over from the TD-SCDMA network. In this way, th
as that of CS services.
transmission resources form a resource pool that is shared by the CS service and PS service (including idle timeslots) among different cel
M cell. Then, the BSS sends the frequency information on the neighboring UMTS cell through a Channel Release message to the MS to inst
oice quality is improved.
s become sufficient, the GBRs are restored to the negotiated values. When the BSC needs to decrease or restore GBRs, it requests the SGS
ocation between uplink and downlink.
BSC and reducing the MS power consumption.
ality and traffic KPIs are improved significantly in the coverage area. Thus, the handover success rate increases and the call drop rate decre
N and the GERAN cover the same area.
D-SCDMA network. In this way, the BSC performs the radio resource reservation procedure that originally involves the Core Network (CN
dle timeslots) among different cells and BTSs.
Release message to the MS to instruct it to camp on the UMTS cell. In this way, the MS camps on a UMTS cell without calculating cell rese
r restore GBRs, it requests the SGSN to modify the GBRs through the PFM procedures.
reases and the call drop rate decreases in the coverage area.
ly involves the Core Network (CN) in advance. In this case, delay caused by handovers between GSM and TD-SCDMA is reduced, and the h
S cell without calculating cell reselection parameters, thus accelerating cell reselection.
d TD-SCDMA is reduced, and the handover success rate is improved.
You might also like
- NodeB Application PartDocument94 pagesNodeB Application Parttusarkar85No ratings yet
- Training Document WRAN13.0 BSC6900 (V900R013C00) LBO Feature Description-20110212-A-1.0Document38 pagesTraining Document WRAN13.0 BSC6900 (V900R013C00) LBO Feature Description-20110212-A-1.0Sedjali Ali-MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Huawei RNC Capacity DimensionDocument17 pagesHuawei RNC Capacity DimensionMuhammad Qasim NazirNo ratings yet
- Cross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionFrom EverandCross-Layer Resource Allocation in Wireless Communications: Techniques and Models from PHY and MAC Layer InteractionNo ratings yet
- CAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkFrom EverandCAMEL: Intelligent Networks for the GSM, GPRS and UMTS NetworkRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- BSC6900 GSM Initial Integration Procedure (V900R013C00 - 04)Document172 pagesBSC6900 GSM Initial Integration Procedure (V900R013C00 - 04)touaiti2009100% (1)
- Number of Triggered Procedures: CS FallbackDocument4 pagesNumber of Triggered Procedures: CS Fallbackarslan arifNo ratings yet
- 00396605-BSC6680 MML Command Reference (V300R006 - 04)Document1,685 pages00396605-BSC6680 MML Command Reference (V300R006 - 04)Patrick PiresNo ratings yet
- Paging Strategy and Lac OptimizationDocument10 pagesPaging Strategy and Lac Optimizationkaijage kishekyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Outage Detection and CompensationDocument44 pagesCell Outage Detection and CompensationAhmed YunesNo ratings yet
- Network Impact Report 2016 04Document273 pagesNetwork Impact Report 2016 04juliosantanaNo ratings yet
- NodeB Parameter ReferenceDocument1,413 pagesNodeB Parameter ReferenceJackson A. PlusNo ratings yet
- Lte Blind HoDocument7 pagesLte Blind Homanish_chaturvedi_19No ratings yet
- BSC6900 UMTS Parameter Reference (V900R012C01 - 03)Document931 pagesBSC6900 UMTS Parameter Reference (V900R012C01 - 03)snsingh_ecNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for Improving ASR SecurityDocument22 pagesGuidelines for Improving ASR Securitysureshkumar1912No ratings yet
- AMR Voice Quality Based On PLVADocument10 pagesAMR Voice Quality Based On PLVAahmadzubair28No ratings yet
- Key Performance Guarantee Steps For UMTS Swapping V2.0Document58 pagesKey Performance Guarantee Steps For UMTS Swapping V2.0Ronald SimamoraNo ratings yet
- Wireless Router PDFDocument61 pagesWireless Router PDFBenhar ImadNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 GU V900R015C00SPC529 Used Reserved Parameter ListDocument1,145 pagesBSC6900 GU V900R015C00SPC529 Used Reserved Parameter ListJonathan Ruiz DakerNo ratings yet
- Huawei Dual Cell HSDPA Technology White Paper V1 (1) .0 (20100128)Document21 pagesHuawei Dual Cell HSDPA Technology White Paper V1 (1) .0 (20100128)Salvador Cristobal LLanca100% (2)
- ERAN7.0 Capacity Monitoring Guide (05) (PDF) - enDocument39 pagesERAN7.0 Capacity Monitoring Guide (05) (PDF) - ensigitNo ratings yet
- Ciphering Feature Parameter Description: GSM Bss GBSS14.0Document34 pagesCiphering Feature Parameter Description: GSM Bss GBSS14.0Gunvant ParmarNo ratings yet
- ENodeB V100R003C00SPC420 Performance Counter Reference (PDF) - enDocument594 pagesENodeB V100R003C00SPC420 Performance Counter Reference (PDF) - enWael AlkodamiNo ratings yet
- Network Lacractac Audit and NormalizationDocument2 pagesNetwork Lacractac Audit and NormalizationfazadoNo ratings yet
- BSC6900 UMTS Guide To Avoiding Network Problems (V900R012) - 20110524-A-V1.40Document173 pagesBSC6900 UMTS Guide To Avoiding Network Problems (V900R012) - 20110524-A-V1.40Anonymous g8YR8b9No ratings yet
- Configuring RF UnitsDocument1 pageConfiguring RF Unitsnaeem05No ratings yet
- HUAWEI - Statistics Data Analysis and Optimization V 4.0Document154 pagesHUAWEI - Statistics Data Analysis and Optimization V 4.0Abdel SbeitiNo ratings yet
- TS-3GBTS-SW-0120 Feature RAN1849 BTS Licensing - Logical Target ID For Flexi BTSDocument7 pagesTS-3GBTS-SW-0120 Feature RAN1849 BTS Licensing - Logical Target ID For Flexi BTSAndrés F. Hernández SenegalNo ratings yet
- Concentric Cell Main ParameterDocument15 pagesConcentric Cell Main ParameterMahdi Khansari100% (1)
- GSM BSS Handover Success Rate Optimization ManualDocument30 pagesGSM BSS Handover Success Rate Optimization ManualSri Datta Sameer AchantaNo ratings yet
- CSFB QoS (GBSS16.0 - 01)Document42 pagesCSFB QoS (GBSS16.0 - 01)Wael AlkodamiNo ratings yet
- RAN17 SignalingDocument156 pagesRAN17 SignalingNinh Văn TrưởngNo ratings yet
- Soft-Synchronized Network (GBSS16.0 01)Document122 pagesSoft-Synchronized Network (GBSS16.0 01)Wael AlkodamiNo ratings yet
- Material For BSC6900 GSM Parameter Changes (V900R018C10 Vs V900R016C00)Document25 pagesMaterial For BSC6900 GSM Parameter Changes (V900R018C10 Vs V900R016C00)Diego Germán Domínguez HurtadoNo ratings yet
- TEMS Discovery Device 12.1.3 Release NoteDocument45 pagesTEMS Discovery Device 12.1.3 Release NoteCEM LOGSNo ratings yet
- 2G To 3G Reselection PDFDocument94 pages2G To 3G Reselection PDFhekriNo ratings yet
- Faizal Akbar Griya Prima Tonasa D1/7 Kel - Pai Kec. Biringkanaya Makassar PhoneDocument3 pagesFaizal Akbar Griya Prima Tonasa D1/7 Kel - Pai Kec. Biringkanaya Makassar PhoneAriefSuryoWidodoNo ratings yet
- 2G Handover Analysis and ImprovementDocument13 pages2G Handover Analysis and Improvementtadjouamina100% (1)
- Examples of MML Message Parse FunctionsDocument4 pagesExamples of MML Message Parse FunctionsMohamed MostafaNo ratings yet
- 2G TCH Traffic and Congestion: NOVATEL - IT - Algeria - Internal - Document - V032016 RNO - DepartementDocument16 pages2G TCH Traffic and Congestion: NOVATEL - IT - Algeria - Internal - Document - V032016 RNO - DepartementtadjouaminaNo ratings yet
- Udit Narayan Singh - RANDocument3 pagesUdit Narayan Singh - RANUdit Narayan SinghNo ratings yet
- RL FailureDocument2 pagesRL FailureGunawan HendroNo ratings yet
- CSSR AnalysisDocument14 pagesCSSR AnalysisAhmed OmerNo ratings yet
- Huawei GSM DBS3900Document74 pagesHuawei GSM DBS3900إدريس طاهيريNo ratings yet
- Aspiro Instruction Manual 2RU BCG.00075 - ABDocument103 pagesAspiro Instruction Manual 2RU BCG.00075 - ABJack SmitNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Reconfigure Switch for CS and PS HHODocument13 pagesAsynchronous Reconfigure Switch for CS and PS HHOKHAZANENo ratings yet
- 3900 Series & 5900 Series Base Station Installation Guides-Wireless Network Info Community-Huawei ConnectDocument7 pages3900 Series & 5900 Series Base Station Installation Guides-Wireless Network Info Community-Huawei ConnectDavid TombeNo ratings yet
- (RF) Call Drops On Traffic Channel HuaweiDocument4 pages(RF) Call Drops On Traffic Channel Huaweikarthir26No ratings yet
- CS Fallback (ERAN12.1 03)Document314 pagesCS Fallback (ERAN12.1 03)CosminDNo ratings yet
- 2G TrafficDocument29 pages2G Trafficalhboosh alatrashNo ratings yet
- Guide to ZTE BSS Operation Quick GuideDocument81 pagesGuide to ZTE BSS Operation Quick Guidesuharto MoestahalNo ratings yet
- Configuring Dynamic CE Resource ManagementDocument1 pageConfiguring Dynamic CE Resource Managementnitin_vfNo ratings yet
- Huawei Co MPT Bts3900Document2 pagesHuawei Co MPT Bts3900Himanshu ButalaNo ratings yet
- Guide For Expanding FACH Bandwidth From 36K To 72KDocument5 pagesGuide For Expanding FACH Bandwidth From 36K To 72KVikrant Singh100% (2)
- 4 - OMO133030 BSC6900 GSM V9R13 Power Control Algorithm and Parameters ISSUE 1.01Document71 pages4 - OMO133030 BSC6900 GSM V9R13 Power Control Algorithm and Parameters ISSUE 1.01Abdel Sbeiti100% (1)
- Huawei 3G optimization resultsDocument4 pagesHuawei 3G optimization resultsmuh47irNo ratings yet
- Critical Alarms For Huawei GSMDocument37 pagesCritical Alarms For Huawei GSManandkusNo ratings yet
- 02 01 Mn3530eu35mn 0002 Utran Radio Netw ParamDocument61 pages02 01 Mn3530eu35mn 0002 Utran Radio Netw Paramserver_caNo ratings yet
- 2G Huawei Performance MonitoringDocument70 pages2G Huawei Performance Monitoringserver_ca67% (3)
- Lenovo 3000 N200 Hardware Maintenance ManualDocument107 pagesLenovo 3000 N200 Hardware Maintenance ManualnickypanzeNo ratings yet
- 01 Mn3530eu35mn 0001 Introduction PDFDocument82 pages01 Mn3530eu35mn 0001 Introduction PDFserver_caNo ratings yet
- 2G Huawei Database Object StructureDocument192 pages2G Huawei Database Object Structureserver_ca0% (1)
- 2G Huawei Recommended ParametersDocument42 pages2G Huawei Recommended Parametersserver_ca100% (1)
- 2G Huawei Site SolutionDocument31 pages2G Huawei Site SolutionAnshul Singhal100% (1)
- 2GDocument12 pages2Gserver_caNo ratings yet
- 2G Huawei RefarmingDocument25 pages2G Huawei RefarmingVito Wahyudi75% (4)
- BSC6900 V900R013C00 Performance Counter Reference SummaryDocument3 pagesBSC6900 V900R013C00 Performance Counter Reference Summaryserver_caNo ratings yet
- 2G Huawei NSNDocument199 pages2G Huawei NSNYasir Adin SaputroNo ratings yet
- Diffserv-The Scalable End-To-End Quality of Service ModelDocument19 pagesDiffserv-The Scalable End-To-End Quality of Service ModelijundiNo ratings yet
- Final IHFDocument6 pagesFinal IHFserver_caNo ratings yet
- TWM Gap V1 (1) .0Document160 pagesTWM Gap V1 (1) .0ddddlaNo ratings yet
- 2RF Sites Configuration Guidelines RAS06Document17 pages2RF Sites Configuration Guidelines RAS06server_caNo ratings yet
- Coverage Eva PDFDocument1 pageCoverage Eva PDFserver_caNo ratings yet
- 3.basic Traffic CasesDocument10 pages3.basic Traffic CasesVikas MishraNo ratings yet
- Gazelle S1020i: L2 Manageable Industrial SwitchDocument2 pagesGazelle S1020i: L2 Manageable Industrial SwitchMaz MoektiNo ratings yet
- 5GTF Test Plan AI v1p1Document38 pages5GTF Test Plan AI v1p1savyNo ratings yet
- Compatibilidade de PlacasDocument3 pagesCompatibilidade de PlacasWendson SilvaNo ratings yet
- Huawei IP Router Portfolio-Sample - ADocument1 pageHuawei IP Router Portfolio-Sample - ATarek DeghedyNo ratings yet
- BGP 3Document100 pagesBGP 3maheshNo ratings yet
- School of Engineering Wireless Communication Lab 1: Wireless LAN (WLAN)Document7 pagesSchool of Engineering Wireless Communication Lab 1: Wireless LAN (WLAN)Liecell CabalesNo ratings yet
- IManager M2000 V200R013 Basic Feature Description (GSM&UMTS<E)Document176 pagesIManager M2000 V200R013 Basic Feature Description (GSM&UMTS<E)Christopher BennettNo ratings yet
- Brocade Fabric OS v6.3.0cDocument61 pagesBrocade Fabric OS v6.3.0cMustafa BenmaghaNo ratings yet
- Security Attacks Against The Availability of LTE Mobile Networks PDFDocument9 pagesSecurity Attacks Against The Availability of LTE Mobile Networks PDFNikNo ratings yet
- Manual-108M Router PDFDocument47 pagesManual-108M Router PDFCalin Paul-DoruNo ratings yet
- Challenge Inno EDHEC Bouygues Telecom 17 Janv - English VFDocument32 pagesChallenge Inno EDHEC Bouygues Telecom 17 Janv - English VFDeepam LakhotiyaNo ratings yet
- 1Document12 pages1Nguyễn Ngọc ViệtNo ratings yet
- m120 PicDocument140 pagesm120 Picsebax123No ratings yet
- 5G Air Interface - Session2Document13 pages5G Air Interface - Session2蔣文彬No ratings yet
- GSM Frequency AllocationsDocument27 pagesGSM Frequency AllocationsukccoodNo ratings yet
- MA5600T&MA5603T&MA5608T V800R016C10 Feature Guide 02 PDFDocument2,232 pagesMA5600T&MA5603T&MA5608T V800R016C10 Feature Guide 02 PDFMonowarul Alam MonirNo ratings yet
- Asa 914 General Config PDFDocument1,396 pagesAsa 914 General Config PDFgerardNo ratings yet
- OTN/SDH/Packet Convergence 10G/40G/100G Oriented Platform ASON/T-SDN Based ArchitectureDocument2 pagesOTN/SDH/Packet Convergence 10G/40G/100G Oriented Platform ASON/T-SDN Based ArchitectureEze Alexander IkNo ratings yet
- T REC G.984.4 200911 I!Amd2!PDF EDocument164 pagesT REC G.984.4 200911 I!Amd2!PDF EAnonymous GK9mHwnrNo ratings yet
- Kswan-Bw RFP - 4Document94 pagesKswan-Bw RFP - 4Chethan GowdaNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument5 pagesProject ReportPrakhar RastogiNo ratings yet
- QBII SrtmunDocument15 pagesQBII Srtmunskill courseNo ratings yet
- IPv6 global unicast addresses quizDocument40 pagesIPv6 global unicast addresses quizAdilson PedroNo ratings yet
- ASA 5585X in DataCenterDocument8 pagesASA 5585X in DataCenterNgo Trung KienNo ratings yet
- 35 Lte Eran7.0 Ul Comp FeatureDocument36 pages35 Lte Eran7.0 Ul Comp FeaturePhan An100% (1)
- View PDU Contents Cisco Packet TracerDocument2 pagesView PDU Contents Cisco Packet TracerMijail Denis Zavala LlancoNo ratings yet
- 8.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A Router PDFDocument6 pages8.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Basic DHCPv4 On A Router PDFJed Efraim Espanillo50% (2)
- 16 Mme AdminDocument284 pages16 Mme AdminFrost IceNo ratings yet
- V5.2 InterfaceDocument3 pagesV5.2 Interfacesunilsharma2002No ratings yet