Professional Documents
Culture Documents
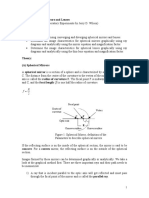
Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics Uses
Uploaded by
Norhisham Mohamed SobriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic: Light: Chapter Highlight: 5.4 Lenses Image Form by Convex Lenses Object Distance Ray Diagram Image Distance Image Characte Ristics Uses
Uploaded by
Norhisham Mohamed SobriCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic : Light : Chapter highlight: 5.
4 lenses Image form by convex lenses Object distance u u= (infiniti) Ray diagram Image Image distance characte ristics Real, Inverted, v=f Reduced in size. Real, inverted, Reduce in size Real, inverted, same size as the object. Real, inverted and magnified Virtual, Upright Magnified Uses Object lens in an astrono mical telescope Camera
u > 2f f < v , 2f u = 2f v = 2f
Upright lens in an earth telescope projector
f < u < 2f v > 2f
u=f v at infinity
Searchlight.
u<f v>f Virtual, Upright Magnified Magnifying lens
Concave lens
Object O F I image F
Object O F I image F
The characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens is not dependent upon the distance of the object from the lens. Characteristics of the image : 1.virtual 2 upright, 3. between the object and the lens 4. smaller in size than the object.
Linear magnification, m
m = Height of image, hi Height of object, ho
OR
m = Image distance , v Object distance , u
Thus
m = hi = v ho u
If m > 1 the size of the image is bigger than the size of the object. If m < 1 the size of an image is smaller than the size of the object. If m = 1 the image size is equals the object size.
Lens equation sign u v f Positive (+) Real Real Convex lens Negative (-) virtual Virtual Concave lens
1 +1 = 1 u v f where u = object distance v = image distance f = focal length
Lens Power power (D) = 1______ focal length (m)
remember ! the unit of focal length is in meter (m)
the unit for power is diopter (D)
Use of Lenses in Optical Devices 1.Magnifying lens
--The object to be magnified must be at a distance that is lesser than the focal length of the lens.
-- characeristic of the image : virtual, magnified, upright and located at the back of the object 2. Camera
--Characteristic of the image : real, inverted and smaller in size 3. Slide projector
-- The slide must be placed between Fand 2F of the projector. -- characteristic of the image : real, magnified and inverted 4. Astronomy telescope
magnification = eye lens power objective lens power = Focal length of the objective lens, fo Focal length of the eye lens , fe fo > fe
--
-- The total distance between the objective lens and eye lens = fo + fm -- Characteristics of the initial image : real, inverted and diminished in size at its focal point -- Characteristics of the final image : virtual, inverted, magnified and located at infinity. 5. Compound microscope
-- fm > fo -- The total distance between the objective lens and eye lens > fo + fm -- Characteristics of the initial image : real, inverted, magnified and is formed at a distance greater than 2F0 -- Characteristics of the final image : virtual, inverted and larger than the object
5.4 UNDERSTANDING LENSES (ACTIVITY)
(50 MINUTES) 1. (a) Draw a labelled diagram to show what is meant by the focal length of a thin converging lens.
(b) The focal length of a concave lens is given as 30 cm. What is the power of the lens ? Power of lens = 1 f(m) =
2.Table 2.1 lists the comparison of the characteristis of the images formed by the convex lens and concave lens.Tick at the appropriate places. (i) (ii) (iii) Characteristics of image Real Virtual Upright Inverted Enlarged Diminished(Smaller in size) Concave Lens Convex Lens
Table 2.1
3.Figure 3.1 shows a small object O is placed at a certain distance away from a thin converging lens. The object distance u is less than the focal length f .By means of a suitable ray diagram, locate the position,the size and the characteristics of the image formed.State one application of such a lens. L
Figure 3.1 *In order to solve the above problem,students can follow the following instructions as a guidance: From the top of the object; (i) Draw an incident ray through the optical centre C passes without Bending. (ii) Draw an incident ray parallel to the principal axis which is refracted by the lens to pass through F. (iii) Extrapolate line (i) and (ii) until both lines intersect. Draw the image at the intersection point.
4. Figure 4.1 shows an object O placed near a converging lens L.
Figure 4.1 (a) On the diagram, draw two rays from the top of the object throygh the lens.use the rays to find the position of the image. Draw the image and label it I. (b) The image produced is a real image.Explain what is meant by a real image.
(c) Suggest one instrument which uses a lens in this way. 5. Figure 5.1 shows the position of an image, I of an object, O formed by a convex lens. The height of the object, O is 5cm.If OL = 20cm and OI = 66cm,what is the height of the image? 20cm
66cm Figure 5.1 Image distance u = ; Object distance v = Magnification m = Image distance(v) = Size of image Object distance(u) Size of object =
ASSSESEMENT
OBJECTIVE QUESTION: 1.The image formed by a concave lens is always A upright and diminished. B inverted and magnified. C upright and magnified. D inverted and diminished. 2. An object is placed at a distance of 10.0 cm from a concave lens of focal length 5.0cm.What is the distance of the image from the lens? A 2.5 cm D 5.0 cm B 3.3 cm E 10 cm C 4.8 cm 3. An object of height 1.0 cm is placed infront of a convex lens. An image of height 3.0 cm is formed at a distanceof 24.0 cm from the lens. What is the object distance from the lens? A 6.0 cm C 12.0 cm B 8.0 cm D 24.0 cm 4. The diagram below shows an object placed at a distance u cm from the centre of a convex lens of focal length10 cm.
Which of the following is not correct? U(cm) 3 8 15 25 Characteristics of image Virtual and bigger Virtual and bigger Real and smaller Real and smaller
A B C D
5.The diagram shows an astronomical telescope. It has an objective lens,x,of focal length fx and an eyepiece of focal length fy. x y
Which of the following is correct? A fx = fy. B fx > fy. C fx < fy. STRUCTURED QUESTIONS
1. Figure below shows a compound microscope which consists of two convex lenses X and Y placed at a distance. X is the object lens and Y is the eyepiece, their focal lengths is 10 mm and 30 mm respectively .
(a) (i) Mark the focal point of the object lens X as Fx on the sides of the lens. [1 mark] (ii) Mark the focal point of the object lens Y as Fy on the sides of the lens. [1 mark] (b) (i) On figure above, draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by the [1 mark] object lens. Label this image as Ix. (ii) State three characteristic of the image Ix formed by the object lens X. _______________________________________________________ [3 marks] (c) (i) On figure above draw ray diagram to show the formation of image by the object lens. Label this image as Iy. [1 mark] (ii) State three characteristics of the image Iy formed by the object lens Y. _________________________________________________________ [3 marks]
2. Presbyobia is an inability of the eye to adjust the focusing of far and near objects. This usually happens when we get old, where the ciliary muscle is less
able to change the shape of the eye lens to focus the image on the retina , as shown in figure 2.1 and 2.2.
Figure 2.1
Figure 2.2
As an optician , you have three disigns of lenses A, B and C in your shop. The cross section of A, B and C are shown in figure 2.3.
(i) Choose the most suitable design of lens in Figure 2.3 to correct the sight of a person with presbyopia and explain the suitablility of the design. (ii) Explain why the other two designs are not suitable. (iii) Either low or high refractive index glass can be used to make the lenses. Which type of glass is most suitable to make the lens chosen in (b)(i) ? Give reasons for your choice [10marks]
ANSWER (ACTIVITY)
10
1. (a)
f F is the principal focus. Focal length = f (b) Power = 1/ 0.3m = -3.333D (-ve sign represents a concave lens and +ve sign represents convex lens) 2. Characteristics of image Concave Lens Convex Lens (i) Real Virtual (ii) Upright Inverted (iii) Enlarged Diminished(Smaller in size) 3. L
O u v
The image formed is upright,magnified,virtual and on the same side of the lens behind the object. The application of such a lens is as a magnifying glass.
4. (a) L
11
(b) A real image is one that can be projected or captured on a screen. (c) Camera. 5. Size image = 11.5cm
ANSWER (ASSESSMENT) OBJECTIVE QUESTION. 1. A , 2. E, 3. B, 4.C, 5.B STRUCTURED QUESTION 1. (a) (i) & (ii) , (b)(i), (c)(i)
(ii) Real, magnified and inverted (c)(ii) Virtual, magnified and upright. 2. (a) (i) Design B is most suitable [1]
12
- Because it has a diverging and converging ability [1] - Its upper part is a diverging lens which can correct the vision when viewing far object [1] - It diverges the rays further, to make them focused on the retina [1] - Its lower part is a converging lens which can correct the vision when viewing near objects. It converges the rays to make them focused at the retina. [1] (ii) - Design A can only correct the vision when viewing near object, but not far objects. [1] - Design C can only correct the vision when viewing far object , but not near objects. [1] (iii) - High refractive index glass is most suitable. [1] - High refractive index glass can converge or diverge light rays more than low refractive index glass. [1] - Therefore lenses made with high index refractive glass is thinner and l lighter. [1]
13
You might also like
- Compound MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCompound Microscopeaman100% (1)
- Extra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Document5 pagesExtra Questions - Refraction - Lens - Answers - 230610 - 042208Zoha AzizNo ratings yet
- Laboratory E Thin Lenses: Physics 111: Elementary PhysicsDocument8 pagesLaboratory E Thin Lenses: Physics 111: Elementary PhysicsCraigNo ratings yet
- BTL TNVLDocument8 pagesBTL TNVLNguyên Nguyễn XuânNo ratings yet
- Module Science Week 7 10Document2 pagesModule Science Week 7 10Joe CrisologoNo ratings yet
- Lab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesDocument16 pagesLab 10 Spherical Mirrors and LensesOtto ManNo ratings yet
- SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2013 SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2012 LEARNING AREA: 1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS Week / Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities Notes Minimum Requirement & Sources 2/1-4/1 1.1 Understanding Physics A student is able to: • explain what physics is • recognize the physics in everyday objects and natural phenomena Observe everyday objects such as table, a pencil, a mirror etc and discuss hoe they are related to physics concepts. View a video on natural phenomena and discuss how they related to physics concepts. Discuss fields of study in physics such as forces, motion, heta, light etc. JPNP Module Ex: Vernier Callipers And Micrometer Screw Gauge 7/1-11/1 1.2 Understanding base quantities and derived quantities A student is able to: • explain what base quanDocument48 pagesSMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2013 SMK ALOR PONGSU 34300 BAGAN SERAI, PERAK SCHEME OF WORK FOR FORM 4 PHYSICS YEARLY TEACHING PLAN 2012 LEARNING AREA: 1. INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS Week / Date Learning Objective Learning Outcomes Suggested Activities Notes Minimum Requirement & Sources 2/1-4/1 1.1 Understanding Physics A student is able to: • explain what physics is • recognize the physics in everyday objects and natural phenomena Observe everyday objects such as table, a pencil, a mirror etc and discuss hoe they are related to physics concepts. View a video on natural phenomena and discuss how they related to physics concepts. Discuss fields of study in physics such as forces, motion, heta, light etc. JPNP Module Ex: Vernier Callipers And Micrometer Screw Gauge 7/1-11/1 1.2 Understanding base quantities and derived quantities A student is able to: • explain what base quanShu85No ratings yet
- Optical Instruments Part 2 - Compund MicroscopeDocument14 pagesOptical Instruments Part 2 - Compund MicroscopeSolomon Peter SunilNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Physics Chapter 5Document48 pagesForm 4 Physics Chapter 5Misratul A'la Mahyuddin100% (4)
- Determination of The Focal-Length.Document11 pagesDetermination of The Focal-Length.mohammed1998No ratings yet
- Object Concave Mirror: Enforcement Exercise Chapter Light For Final Exam Form 5 Semester 1 2010Document2 pagesObject Concave Mirror: Enforcement Exercise Chapter Light For Final Exam Form 5 Semester 1 2010Mohamad Rizal MukhtarNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign3Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign3Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Q.2. Srlu W3 G10Document6 pagesQ.2. Srlu W3 G10Pamela IndosoNo ratings yet
- Lecture and Worksheet - LensesDocument13 pagesLecture and Worksheet - LensesJaymar Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Important Questions FinalDocument29 pagesG-10 Physics Important Questions FinalRohan SenapathiNo ratings yet
- Physics Unit 7 Part 2 NotesDocument38 pagesPhysics Unit 7 Part 2 NotesTaylor Waddell-SmithNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Questions #4 - LensDocument4 pagesFinal Exam Questions #4 - Lensanonslu2012No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Light RevDocument24 pagesGrade 10 Light RevDanny BlessyNo ratings yet
- Physics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1Document11 pagesPhysics 30 Lesson 9 Optics - Thin Lenses: Refraction 2 Refraction 1John JohnsonNo ratings yet
- April 2020 Holiday Tuition Form 3 Physics: Category Notes InstructionDocument61 pagesApril 2020 Holiday Tuition Form 3 Physics: Category Notes InstructionDISHONNo ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - Wk6 SLHT 6 (No Answer Key)Document8 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - Wk6 SLHT 6 (No Answer Key)Joy Valerie AricayosNo ratings yet
- 已編輯 - Ch 19 HW set 2 Harder problem on lensesDocument4 pages已編輯 - Ch 19 HW set 2 Harder problem on lenses呆毛是本体No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightDocument9 pagesChapter 7 - Light - Colour and SightHHK88893% (15)
- PhysicsA2 OptionAstrophysics TelescopesDocument27 pagesPhysicsA2 OptionAstrophysics TelescopesILoveBlowingBubblesNo ratings yet
- Mirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Document24 pagesMirrors: Lesson 4 (3 Hours)Donna100% (1)
- Properties of LightDocument10 pagesProperties of LightKesanam SpNo ratings yet
- Physics 72.1 - E08 Image FormationDocument9 pagesPhysics 72.1 - E08 Image FormationTidal SurgesNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15Document7 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15deepak.idea84No ratings yet
- Year End Revision Chapter 5: LightDocument23 pagesYear End Revision Chapter 5: Lightfillyana01No ratings yet
- Lenses in Combination: Determining Focal Lengths and Constructing a Compound MicroscopeDocument4 pagesLenses in Combination: Determining Focal Lengths and Constructing a Compound MicroscopeRA MemijeNo ratings yet
- 10 THDocument3 pages10 THRohitNo ratings yet
- Light and Geometric OpticsDocument53 pagesLight and Geometric OpticsLeah May Tamayo ManayonNo ratings yet
- PPT-3 Chapter 2.2 Concave MirrorsDocument20 pagesPPT-3 Chapter 2.2 Concave MirrorsAreen AlhazaymehNo ratings yet
- Q On LensesDocument3 pagesQ On Lenseszendaya alisiaNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XSyed Ahmed AdeelNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetDocument4 pagesClass 10 - Light Reflection & Refraction-Revision WorksheetFrederic Francois ChopinNo ratings yet
- Salud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021Document12 pagesSalud, Juan Vicente 2017131112 PHYS101L/A2 2/11/2021yyuan ssaludNo ratings yet
- Optics10 PhysicsDocument16 pagesOptics10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Simple MicroscopeDocument9 pagesSimple MicroscopeAlyan Ashraf100% (2)
- Optical Equipment "Lup and Convex Lens ": Practicum Report General PhysicsDocument11 pagesOptical Equipment "Lup and Convex Lens ": Practicum Report General PhysicsJuwita PardedeNo ratings yet
- CURVED MIRRORS EXPLAINEDDocument14 pagesCURVED MIRRORS EXPLAINEDAZORYNo ratings yet
- Physics XII CH 9 CASE STUDY Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument15 pagesPhysics XII CH 9 CASE STUDY Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsNjan KL16么PorottaNo ratings yet
- 0971physics Form 4 Notesa7638e67Document59 pages0971physics Form 4 Notesa7638e67Philemon KeitNo ratings yet
- Year of The YouthDocument13 pagesYear of The YouthJustin A VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Simple MicroscopeDocument10 pagesSimple MicroscopeHabimana HassanNo ratings yet
- Spherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorDocument3 pagesSpherical Mirrors: Concave MirrorLeah ClovisNo ratings yet
- Learning Guide SLM 56Document13 pagesLearning Guide SLM 56Kate Megan ApuliNo ratings yet
- Physics-Form-4-Notes (1) - 1Document60 pagesPhysics-Form-4-Notes (1) - 1NuruNo ratings yet
- PDF 10TH CLASS PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS SSC ABYASA DEEPIKADocument9 pagesPDF 10TH CLASS PHYSICS IMPORTANT QUESTIONS SSC ABYASA DEEPIKAprakashNo ratings yet
- Physics Cl10 Assign1Document2 pagesPhysics Cl10 Assign1Tapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Class X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersDocument9 pagesClass X Science (Physics) Ch10 Question-AnswersAnkur MondalNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsDocument10 pagesActivity 4 7 Mirrors Lenses Motors and GeneratorsMarley Chelsea LevantinoNo ratings yet
- Light Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFDocument18 pagesLight Worksheet Padhleakshay PDFanandatulNo ratings yet
- 23.ray OpticsDocument50 pages23.ray OpticsRakesh Ranjan Mishra100% (1)
- As Sci 10 SLG Week 5 Quarter IiDocument6 pagesAs Sci 10 SLG Week 5 Quarter IiDarwin BondocNo ratings yet
- The Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesFrom EverandThe Lensball Photography Handbook: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Refraction Photography and Creating Stunning ImagesNo ratings yet
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationFrom EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationNo ratings yet
- Hantar K1 4FDocument8 pagesHantar K1 4FNorhisham Mohamed SobriNo ratings yet
- M22 CutiDocument1 pageM22 CutiNorhisham Mohamed SobriNo ratings yet
- Items MathDocument44 pagesItems MathNorhisham Mohamed SobriNo ratings yet
- SMK Sandakan Physics Practical Work Grading FormDocument4 pagesSMK Sandakan Physics Practical Work Grading FormNorhisham Mohamed SobriNo ratings yet
- Uncharted - Golden Abyss Trophy Guide & Road Map - PlaystationTrophiesDocument14 pagesUncharted - Golden Abyss Trophy Guide & Road Map - PlaystationTrophiesJurico AlonzoNo ratings yet
- Main RSIGM Sultan AgungDocument15 pagesMain RSIGM Sultan Agungradiologirsigm sultanagungNo ratings yet
- # Objects That Generate Performance - Nathan Gray - 2014Document91 pages# Objects That Generate Performance - Nathan Gray - 2014trademarcNo ratings yet
- Portrait LPDocument3 pagesPortrait LPapi-534719586No ratings yet
- Visual ArtsDocument6 pagesVisual ArtsMilk BrotherNo ratings yet
- Muybridges - The Human Figure in Motion PDFDocument424 pagesMuybridges - The Human Figure in Motion PDFRobert Foster100% (2)
- PET SpeakingPaperDocument1 pagePET SpeakingPaperMiguel Angel Contreras RuizNo ratings yet
- Gerhard RICHTER. Landscape. Kunstforum Wien. Catálogo en Inglés 2020Document220 pagesGerhard RICHTER. Landscape. Kunstforum Wien. Catálogo en Inglés 2020Adriana Miranda100% (1)
- Sony DSC-H20 PDFDocument120 pagesSony DSC-H20 PDFJorge Alberto VegaNo ratings yet
- Angielski Klasa 7 (Zrobione) Wiosna 2022Document2 pagesAngielski Klasa 7 (Zrobione) Wiosna 2022dawidwiixNo ratings yet
- FOR NO ONE Cifra - The Beatles - CIFRASDocument2 pagesFOR NO ONE Cifra - The Beatles - CIFRASLevi AlvesNo ratings yet
- Cultural Fest Photography Contest IRRDocument1 pageCultural Fest Photography Contest IRRLee SuarezNo ratings yet
- Journalism Questions and Answers Solved MCQsDocument1 pageJournalism Questions and Answers Solved MCQsWahab AfzalNo ratings yet
- Photo Voice TemplateDocument3 pagesPhoto Voice TemplateKatharineSpanishNo ratings yet
- What Are The Etiquettes in A Museum and A GalleryDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Etiquettes in A Museum and A GalleryCARMELA MOSQUEDANo ratings yet
- Marie Kondrat - Is There A Time Fo Alice GuyDocument10 pagesMarie Kondrat - Is There A Time Fo Alice GuyTami WilliamsNo ratings yet
- 365 Days Project GuideDocument2 pages365 Days Project Guidecapt_zoeNo ratings yet
- Ultra-Low Light 2MP EXIR Bullet Camera with 1080p ResolutionDocument3 pagesUltra-Low Light 2MP EXIR Bullet Camera with 1080p ResolutionAhsan KhanNo ratings yet
- EmTech Module 3Document6 pagesEmTech Module 3Roselle AbasNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Hikvision CasvashopDocument28 pagesCatalogo Hikvision CasvashopcybersparkNo ratings yet
- Fashion PhotographerDocument1 pageFashion Photographervividimagingaus1672No ratings yet
- Bill Brandt Perspective of Nudes RevisitDocument49 pagesBill Brandt Perspective of Nudes RevisitEduardo GuariniNo ratings yet
- Email receipt for purchaseDocument31 pagesEmail receipt for purchaseAndrea ClarkNo ratings yet
- How To Take Good Landscape PhotosDocument5 pagesHow To Take Good Landscape Photoscristi13No ratings yet
- Preserving The Traditions of The Masters: Painted Comic Cover: Tonal SketchDocument5 pagesPreserving The Traditions of The Masters: Painted Comic Cover: Tonal SketchJaromir KalabNo ratings yet
- Reality: SurveyDocument260 pagesReality: SurveyCineclub CírculoKinéNo ratings yet
- AF MicroAdjustGuide Desktop PDFDocument19 pagesAF MicroAdjustGuide Desktop PDFCandra Aji SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Annotated Bibliography Final DraftDocument7 pagesAnnotated Bibliography Final Draftapi-495569301No ratings yet
- Photography Compositions PDFDocument156 pagesPhotography Compositions PDFAryan JakharNo ratings yet
- Photograph Like A Thief: Using Imitation and Inspiration To Create Great Images - Glyn DewisDocument5 pagesPhotograph Like A Thief: Using Imitation and Inspiration To Create Great Images - Glyn DewisroritareNo ratings yet