Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Unit 10 Basic Layout Operations: Structure
Uploaded by
Akash Kumar DevOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Unit 10 Basic Layout Operations: Structure
Uploaded by
Akash Kumar DevCopyright:
Available Formats
UNIT 10 BASIC LAYOUT OPERATIONS
Structure 10.1 Introduction
Objectives
Basic Layout Operations
10.2 Preparing Surface for Layout 10.3 To Layout Parallel Lines to an Edge 10.4 To Layout Lines at Right Angles 10.5 To Layout Horizontal Lines Using a Surface Gauge 10.6 Laying Out Centre Holes 10.7 To Check the Accuracy of the Centre Layout
10.7.1 10.7.2 Divider Method Lathe Centre Method
10.8 Summary 10.9 Key Words
10.1 INTRODUCTION
The preparation of the work surface and laying out straight lines are the primary operations performed in order to make a layout. Since the accuracy of the finished workpiece depends upon the accuracy of the layout, proper care should be taken during the process. Combination tools are used where the accuracy is not important. Square head is used to lay out horizontal and parallel straight lines. The bevel protractor is used for laying out angles while the centre head is used to layout the centre of round and square workpiece.
Objectives
After studying this unit, you should be able to know how to prepare the work surface for layout, layout straight lines using : � � � the scriber and combination square the surface gauge and surface plate the vernier height gauge and surface plate
locate centre holes by : � � � hermaphrodite calipers centre head surface gauge.
10.2 PREPARING SURFACE FOR LAYOUT
Layout lines must be visually plain. Therefore, the surface of the work is coated with a layout material so that scribed lines are seen easily. The surface must be clean and free from dust, grease, surface scale, oil, etc., otherwise layout material will not stick to it. There are a number of ways of coating the surface for layout. 13
Layout Design for Tool Engineering
(a)
Commercial layout dye or bluing is generally used to coat work surfaces. It is not expensive and dries very fast. Layout dye is generally applied with brush. Chalk may be used into rough surfaces of castings. Copper sulphate solution is used for coating machined surface.
(b) (c)
SAQ 1
Discuss briefly the preparation of surface for layout.
10.3 TO LAYOUT PARALLEL LINES TO AN EDGE
Combination Square Method (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) Hold the workpiece in a vise whenever possible to avoid its motion during operation. Remove all burrs from the edge of the work with a file. Extend the steel rule at the desired distance beyond the body of the square. Always make sure that only half the graduation line can be seen. Hold the base of square tightly against a machined edge with rule flat on the work surface. Hold the scriber at an angle to keep the point against the end of the rule and tilt top of the scriber in a direction where the line is to be scribed. Draw a sharp line along the end of the rule. Move the square a short distance and again scribe along the end of the rule. Continue moving of the square and scribing until the line is complete. Check the location of scribed line.
SAQ 2
How do you lay parallel line to an edge?
10.4 TO LAYOUT LINES AT RIGHT ANGLES
Lines at right angle are laid out by placing the body of square against a machined edge of the work that is at right angle to the first edge. The general steps are as follows : (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) 14 Remove all burrs from the edge of the work with a file. Slide the square along the work until the edge of the rule is at desired distance. Hold the base of the square tightly against the machined edge with the blade of the rule remaining flat on the work surface. Scribe the line by keeping the point of scriber against the edge of the rule. Check the location of scribed line.
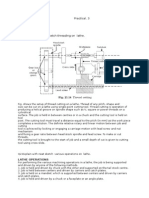
10.4.1 Surface Gauge Method
The work, the base of the surface gauge, the base of the square and the surface plate should be clean when the lines are scribed with surface gauge method. To Set Surface Gauge to a Dimension (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) Clean the top surface of the surface plate. Set the combination square on the surface plate. Loosen the combination square lock nut and make sure that the end of the rule is down against the surface plate. Tighten the lock nut of combination square. Set the surface gauge on the surface plate. Loosen the scriber clamp nut and adjust the scriber so that it is approximately at the desired dimension. Tighten the scriber clamp nut to lock the scriber in position. Turn the surface gauge thumb screw until the scriber point is in the centre of the desired graduation on the rule.
Basic Layout Operations
SAQ 3
Explain the methods of laying out lines at right angles.
10.5 TO LAYOUT HORIZONTAL LINES USING A SURFACE GAUGES
(a) (b) (c) (d) Set the surface gauge to the desired dimension. Place the edge of the work from which the line is to be scribed on the surface plate. Hold the surface gauge down on the surface plate. Draw the surface gauge along the work in the direction of arrow to scribe the line. Push will cause the scriber point to dig into the work which will result in faulty layout. Reset the surface gauge with the combination square rule for each dimension. Layout all the lines which are parallel to the edge resting on surface plate.
(e) (f)
Vernier Height Gauge Method When close tolerance is required, i.e. up to 0.02 mm, a vernier height gauge method should be used. The general steps of the method can be described as : (a) (b) (c) (d) Clean the surface plate and the base of the height gauge thoroughly. Hold the gauge so that scriber point is approximately 45o to the surface being laid out. Press down firmly on the surface or height gauge base. Pull the gauge to maintain an accurate layout. Push will cause the scriber point to dig into the work which results in inaccurate layout lines. 15
Layout Design for Tool Engineering
(e)
If the work is first fastened to the angle plate, all horizontal lines can be laid out as outlined. Therefore, the angle plate can be set on its edge (90o to the base) and the vertical lines can be laid out.
SAQ 4
Explain the various methods to lay horizontal lines.
10.6 LAYING OUT CENTRE HOLES
When the workpiece is to be machined between the centers on a lathe, it is necessary to layout and drill the centre holes before turning the work on a lathe. It is generally more accurate and convenient to drill the lathe centre holes in small round stocks on a lathe. This eliminates the need of laying out the holes. To Locate the Centers of Round Stock By Using Hermaphrodite Calipers (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (a) (b) (c) Place the work in a vise and remove the burrs or sharp edges. Apply layout dye to both ends. Set the hermaphrodite caliper to the approximate radius of the work. Hold the bent leg with thumb below the edge of the work and scribe the arc. Move the bent leg a quarter of a turn and scribe an arc. Repeat the procedure until four arcs are obtained at each end of the work. Mark the centre of the arc using center punch and test the accuracy of the center. Repeat the step 3 to 6 on the other end of the workpiece. Place the work in a vise and remove the burrs or sharp edges. Apply layout dye to both ends. Hold the centre head firmly against the work with the rule remaining flat on the end of the work. Hold the sharp scriber at an angle so that its point touches the edge of the rule. Scribe a line along the edge of the rule. Rotate the centre head by one quarter of turn and scribe the second line. Mark the point where two lines cross each other. Repeat step 3 to 8 on the other end of the work. Test the accuracy of the centre layout. Place the work in a V-block placed on surface plate and remove the burrs or sharp edges with the help of file. Apply layout dye to both the ends.
By Using Center Head
(d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (a) (b) 16
Using Surface Gauge
(c) (d) (e) (f)
Set the scriber point of the surface gauge to the approximate centre of the work. Scribe four lines across the end of the work by rotating it by 90o for each line. Mark the intersection of four lines by centre punch. Test the center for accuracy by the divider or lathe centre method.
Basic Layout Operations
SAQ 5
(a) (b) Explain laying out center hole? Discuss various steps involved in laying out center hole using center head.
10.7 TO CHECK THE ACCURACY OF THE CENTER LAYOUT
It is necessary to check the accuracy of a layout before drilling the hole or machining the work. Also, great care should be taken while laying out lathe center hole. The centre of the hole offsets from the original position if an error occurs during the laying out. Two dividers are used to check the accuracy of the center hole layout. The accuracy of center layout is also checked by rotating the workpiece between the lathe centers.
10.7.1 Divider Method
(a) (b) (c) Place one leg of the divider in light center punch mark. Adjust the divider so that the other leg is on a line and set exactly to the edge of the workpiece. Revolve the divider by one-half turn (to the other end of the same line) and check if the leg of the divider is in the same relation to the edge of the work as in step 2. If not so, lightly move the center punch mark to correct the error. Repeat the step 4 on other scribed line until the punch mark is exactly on center. Deepen the center punch mark in preparation for drilling the center hole. Repeat step 1 to 6 on other end of the workpiece.
(d) (e) (f) (g)
10.7.2 Lathe Center Method
(a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) Deepen the center punch marks at both ends and mount the workpiece between the lathe centers. Adjust the lathe center tension so that work can spin freely. Hold a piece of chalk in one hand which is firmed against any part of the lathe. Spin the workpiece by hand and bring the chalk close to the workpiece surface until it lightly marks the high spot. Repeat the step 4 on the other end of workpiece. Fasten the workpiece in a vise, tip the center punch and move the center punch mark toward the chalk mark by hammer. Retest the workpiece between the centers and repeat the steps 3 to 6 until desired accuracy is obtained. 17
Layout Design for Tool Engineering
SAQ 6
Explain the method to check the accuracy of the center layout.
10.8 SUMMARY
The preparation of the work surface and laying out straight lines is the primary operation performed in the layout. Since the accuracy of the finished workpiece depends upon the accuracy of the layout, proper care should be taken during the process. The surface of the work should be coated with a layout material so that scribed lines will be seen easily. The surface must be clean and free from dust, grease, surface scale, oil etc. otherwise layout material will not stick on it. The straight lines are scribed with the aid of scriber and combination square, surface gauge and surface plate, vernier height gauge and surface plate. Combination tool is used where accuracy is not important. Square head is used for laying out horizontal and parallel straight lines. Center holes are located by means of hermaphrodite calipers, center head, and surface gauge. The center head is used to lay out the center of round and square workpieces.
10.9 KEY WORDS
Hermaphrodite Caliper : Hermaphrodite Caliper is used to scribe lines parallel to an edge or shoulder and also to locate the centers of round workpieces. : Combination set is used to lay parallel lines.
Combination Set
18
You might also like
- Unit 11 Layout Work and Safety Issues: StructureDocument11 pagesUnit 11 Layout Work and Safety Issues: StructureakashkumardevNo ratings yet
- Shaping Operations On A Given Mild Steel Work Piece As Per The Figure GivenDocument3 pagesShaping Operations On A Given Mild Steel Work Piece As Per The Figure GivenSangeeth GopanNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Tools For Basic Layout: StructureDocument7 pagesUnit 9 Tools For Basic Layout: StructureAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Carpentry Edited in WordDocument23 pagesCarpentry Edited in WordSJ BatallerNo ratings yet
- MSP - Week 7 8Document7 pagesMSP - Week 7 8John MarkNo ratings yet
- Execution of WorkDocument4 pagesExecution of WorkWalterHuNo ratings yet
- (Metalworking) Welding and MachiningDocument1,767 pages(Metalworking) Welding and MachiningEugeneNo ratings yet
- Reverse Dial Indicator MethodDocument14 pagesReverse Dial Indicator MethodvinothenergyNo ratings yet
- 1112sem2-Me4261 Me4261eDocument4 pages1112sem2-Me4261 Me4261eClarence S. WongNo ratings yet
- 1011sem2 Me4261Document4 pages1011sem2 Me4261Clarence S. WongNo ratings yet
- BumperDocument33 pagesBumperAbhishek VermaNo ratings yet
- Surface Swept by A Toroidal Cutter During 5-Axis MachiningDocument10 pagesSurface Swept by A Toroidal Cutter During 5-Axis MachiningJulen MartinezNo ratings yet
- Testing Machine Tools by Schlesinger Principle - Lathe Machine TestDocument6 pagesTesting Machine Tools by Schlesinger Principle - Lathe Machine TestАлександар ВујаковићNo ratings yet
- MP I SubmissinDocument7 pagesMP I SubmissinAbhijeet PramanikNo ratings yet
- Assembly Instructions For V-2 Rocket: HistoryDocument4 pagesAssembly Instructions For V-2 Rocket: HistoryEmerson URNo ratings yet
- 0910sem2 Me4261Document6 pages0910sem2 Me4261Clarence S. WongNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Job/Experiment No.: Me594/05 2.0 NAME OF EXPERIMENT: Angle Measurement Using Sine Bar & SlipDocument6 pages1.0 Job/Experiment No.: Me594/05 2.0 NAME OF EXPERIMENT: Angle Measurement Using Sine Bar & SlipHimanshu Vasistha0% (1)
- Common Terms and Definitions: Basic DimensionDocument9 pagesCommon Terms and Definitions: Basic Dimensionswap dNo ratings yet
- Sheet Metal Duct Layout BookDocument40 pagesSheet Metal Duct Layout BookRyan Murray77% (13)
- Jig - Horizontal Boring JigDocument3 pagesJig - Horizontal Boring Jigcorneliu.modilcaNo ratings yet
- Plane Table Surveying TechniquesDocument29 pagesPlane Table Surveying TechniquesIbrahim MohmandNo ratings yet
- Machining Processes Used To Produce Various Shapes: MillingDocument28 pagesMachining Processes Used To Produce Various Shapes: MillingSuleiman SaidNo ratings yet
- Step Fitting Construction Guide - Tools, Process & QuestionsDocument6 pagesStep Fitting Construction Guide - Tools, Process & QuestionsTejesh MannemNo ratings yet
- Surface Finish Guide for Engineering DrawingsDocument163 pagesSurface Finish Guide for Engineering DrawingsGilbert ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Dividing Head IndexingDocument40 pagesDividing Head IndexingChristopher Ruben100% (3)
- Exp No 9 ShaperDocument5 pagesExp No 9 ShaperM IRFANNo ratings yet
- Drawing Instruments and Their Uses 2020Document7 pagesDrawing Instruments and Their Uses 2020Gibson MwaleNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING DRAWING GUIDEDocument20 pagesENGINEERING DRAWING GUIDEranydiNo ratings yet
- Machining Worksheet DJJ30082Document11 pagesMachining Worksheet DJJ30082zairil izuwan0% (1)
- Manufacturing Engineering 2Document7 pagesManufacturing Engineering 2Study SuccessNo ratings yet
- Industrial Arts:Carpentry (Prepare Stakeout Building Lines) Learner's MaterialDocument10 pagesIndustrial Arts:Carpentry (Prepare Stakeout Building Lines) Learner's MaterialJojie D. RamosNo ratings yet
- Machining FixedDocument512 pagesMachining FixedstephendixNo ratings yet
- 5.EMM Lab ManualDocument38 pages5.EMM Lab ManualRakeshkumarcegNo ratings yet
- Explain Drilling, Boring, Reaming, Counterboring, Countersinking and Spot Facing OperationsDocument7 pagesExplain Drilling, Boring, Reaming, Counterboring, Countersinking and Spot Facing OperationsNishit ParmarNo ratings yet
- Mee 221 Orthog Sept 2021Document46 pagesMee 221 Orthog Sept 2021Igi NelsonNo ratings yet
- Plane Table SurveyingDocument18 pagesPlane Table SurveyingAshish6300100% (3)
- Chapter 4 - Angular Measurements PDFDocument11 pagesChapter 4 - Angular Measurements PDFIbrahim AlghoulNo ratings yet
- MEE101 Engineering Graphics Tutorial BookDocument23 pagesMEE101 Engineering Graphics Tutorial Bookk4r7hyNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Lab Report: Threaded Hinge ClampDocument18 pagesManufacturing Lab Report: Threaded Hinge ClampTaylor WorthingtonNo ratings yet
- Parametric Spur GearDocument11 pagesParametric Spur GearGoutam AcharjeeNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil EngineeringDocument6 pagesDepartment of Civil EngineeringNaa WinNo ratings yet
- Survey QPDocument10 pagesSurvey QPRanjith KumarNo ratings yet
- Rim and Face AlignmentDocument8 pagesRim and Face Alignmentnazir305No ratings yet
- Tle 9 Quiz BeeDocument42 pagesTle 9 Quiz Beeanon_176509991No ratings yet
- Ntroduction TO Ngineering Rawing: Chapter DetailsDocument12 pagesNtroduction TO Ngineering Rawing: Chapter DetailsflorenceprasadNo ratings yet
- Perform a Precision Shaft Alignment Using the Rim & Face MethodDocument10 pagesPerform a Precision Shaft Alignment Using the Rim & Face Methodmohamed elejmiNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering 121 - Spring 2020: Grading (Cut & Fill)Document5 pagesCivil Engineering 121 - Spring 2020: Grading (Cut & Fill)Nouman SabirNo ratings yet
- Land Grading Survey Design and PlanningDocument5 pagesLand Grading Survey Design and PlanningtizazuNo ratings yet
- Wooden Medallion Installation Techniques.Document19 pagesWooden Medallion Installation Techniques.maliankaduNo ratings yet
- Plane Table SurveyingDocument22 pagesPlane Table SurveyingParth AnajwalaNo ratings yet
- A Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsFrom EverandA Guide to Making a Leather Wallet - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making Wallets and BillfoldsNo ratings yet
- Blocks with Options: Quick & Easy Quilts with Color & Size VariationsFrom EverandBlocks with Options: Quick & Easy Quilts with Color & Size VariationsNo ratings yet
- Practical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemFrom EverandPractical Stair Building and Handrailing: By the square section and falling line systemNo ratings yet
- Mel311 Part IIIDocument52 pagesMel311 Part IIIAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Rac ExpDocument44 pagesRac ExpAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Project MangemntDocument26 pagesProject MangemntAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Anna University Exam Paper Theory of Metal Cutting: Production EngineeringDocument3 pagesAnna University Exam Paper Theory of Metal Cutting: Production EngineeringAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Success InterviewDocument11 pagesSuccess InterviewAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Legacy Tcl/Tk TrainingDocument61 pagesLegacy Tcl/Tk TrainingAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- BHEL's Bowl Mills and Their FeaturesDocument12 pagesBHEL's Bowl Mills and Their FeaturesAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- 02MA751 Foundry Technology Dec Jan 2006Document1 page02MA751 Foundry Technology Dec Jan 2006Akash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- TQM - Notes Anna UniversityDocument86 pagesTQM - Notes Anna UniversityMohsin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Book1 HTMLDocument3 pagesBook1 HTMLAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- TataDocument2 pagesTataAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper InfosysDocument19 pagesSample Paper InfosysPankaj GuptaNo ratings yet
- PS-N AC-63 Number of Votes Vast Male Female Others Total From 7am To 9 Am 9 Am To 11 Am 11 Am To 1 PM 1 PM To 3 PM 3 PM To 5 PM 5 PM To 6 PMDocument1 pagePS-N AC-63 Number of Votes Vast Male Female Others Total From 7am To 9 Am 9 Am To 11 Am 11 Am To 1 PM 1 PM To 3 PM 3 PM To 5 PM 5 PM To 6 PMAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Production and Operations ManagementDocument21 pagesProduction and Operations ManagementGaurav218100% (4)
- New Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationDocument40 pagesNew Microsoft Office PowerPoint PresentationAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Cast Iron Properties and Types in 40 CharactersDocument34 pagesCast Iron Properties and Types in 40 CharactersMKPashaPasha100% (1)
- Powered by Amplitud3'Zz ... in CsDocument1 pagePowered by Amplitud3'Zz ... in CsAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Upload 1Document28 pagesUpload 1Akash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Defects PointDocument8 pagesDefects PointAnkit SenNo ratings yet
- 06 Strengthening MechanismsDocument63 pages06 Strengthening Mechanismspranavkumarparit100% (2)
- IEEE Copyright FormDocument2 pagesIEEE Copyright FormMatías IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Daemon ProcessDocument1 pageDaemon ProcessAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Principles of Ic EnginesDocument15 pagesPrinciples of Ic EnginesIvan KopićNo ratings yet
- S S - A L: Tress AND Train Xial OadingDocument11 pagesS S - A L: Tress AND Train Xial OadingAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of MaterialsDocument9 pagesBehaviour of MaterialsAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- GATE 2014: Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering 2014Document2 pagesGATE 2014: Graduate Aptitude Test in Engineering 2014Akash Kumar DevNo ratings yet
- The Codemasters Software Company Limited Software License AgreementDocument4 pagesThe Codemasters Software Company Limited Software License AgreementJigar TrivediNo ratings yet
- 1 Stress Strain SMDocument48 pages1 Stress Strain SMappuanandhNo ratings yet
- Win Configure Updated Title "Recommended Settings Updated"Document2 pagesWin Configure Updated Title "Recommended Settings Updated"dams6797No ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument3 pagesNew Text DocumentAkash Kumar DevNo ratings yet