Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TechDesc R20 040519 p14-34
Uploaded by
SURJIT SINGHOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TechDesc R20 040519 p14-34
Uploaded by
SURJIT SINGHCopyright:
Available Formats
India 180 kVA
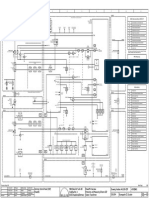
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 6: Circuit Diagram Sheet 6 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
14 of 34
India 180 kVA
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 7: Circuit Diagram Sheet 7 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
15 of 34
India 180 kVA
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 8: Circuit Diagram Sheet 8 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
16 of 34
India 180 kVA
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 9: Circuit Diagram Sheet 9 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
17 of 34
India 180 kVA
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 10: Circuit Diagram Sheet 10 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
18 of 34
India 180 kVA
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 11: Circuit Diagram Sheet 11 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
19 of 34
India 180 kVA
Circuit Diagrams
Figure 12: Circuit Diagram Sheet 12 of 12
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
20 of 34
India 180 kVA
Mechanical Overview
3.4
Mechanical drawings
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
21 of 34
India 180 kVA
Functional Description
4
4.1
Functional Description
Technical Profile
The converter described in this manual is characterized by the type no. U760AC/415AC3-110DC/P180-2/F50. It supplies the AC and DC consumers of the train with electric energy taken from the power line. The converter consists of five main sections: Input section The input section consists of input fuse F01 input EMI choke A101 voltage divider A102 and voltage transducer U101 for measurement of actual input voltage The IVPS (Intermediate circuit Voltage Power Supply) section consists of semicontrolled thyristor bridge A201 choke L201 short circuit module voltage divider A501 and voltage transducer U501 for measurement of actual intermediate circuit voltage voltage divider A502 and voltage transducer U502 for voltage measurement which is indicating earth faults The inverter section consists of inverter A301.1 3 each with an IGBT driver board A01 current transducers T901 903 for measurement of actual output currents with analogue ammeter P902 digital voltmeter P901 for measurement of actual output voltages output filter section: 3 phase chokes L301 303 and capacitors C302.1 6 autotransformer T302 AC-EMI filter module A302 The LVPS (Low voltage power supply) consists of DC/DC module A401 with the chopper unit A01, the IGBT driver A02, the transformer T01, the rectifier A03 and the current sensor U01 DC-EMI filter module A402 The control section consists of converter control unit A710 digital control unit A702 for IVPS LVPS chopper control unit A704 inverter control unit A703 power supply A720
IVPS section
Inverter and output filter section
LVPS section
Control section
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
22 of 34
India 180 kVA
X700 1 Protection Circuit X7 K4 Relays K5 Monitoring RS485 X4 GND fault Internal CAN bus CAN UBatt 15 V Temp AC feedb. T302 Q301 Fan General Fault Disable X3 RS232 X5 X7 Battery A722 A740 2 3 4
A710
Converter Control Board (tt1932-1/33 F)
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
Display Board (tt1823-2/03 A) P903 Q901 15 V DC A703 Inverter Control Board (tt1619-1/68 C) T U301 Volt. A730 Signal sensor Condit. A304 Volt. divider A303 Q302 UCE IL1 IL2 IL3 UAC Q902 M902 3~ S901 S902 Drv. Drv. Drv. L301 R301 L302 L303 Rectif. Bridge T302 A302 L01.1-.3 Fan 2 SCR Control Board (tt1933-1/05 D) T Volt. A770 divider IIC UIC A704 LVPS Control Board (tt1967-2/24 E) UIC UCE T ICharge UBatt M901 3~ Fan 1
F101 blown
Temp. Pre-warning
AC input voltage
A702
UInp
A750
One Phase Filter
F101 A201 Driv. L201
U01
A101 Driv.
U101 Volt. sensor A102 Volt. divider U501 Volt. sensor A501 Volt. divider Volt. U502 sensor Volt. A502 divider
P901 444.4V P902
AC output phase voltages
AC output phase currents
1L1
L01.1-.3
Figure 13: Functional sections and modules of the converter
A202 C301
A01 V01
450 A
L101
3L1 3L2 3L3
AC Input 760/830 V 50Hz (590 -1110 V)
3 phase output 415 V AC 180 kVA 50 Hz A301.3 AC Filter Autotransf. T301
1L2 Semi Controlled SCR Bridge Short Circuit Thyristor A301.1
L102
EMI Module
A301.2 PWM inverter
2L1 2L2
Q301 Single Phase Transformer A720 F701 10 A V701 A402 AC EMI-Filter
1 phase output 110 V AC 500 VA 50 Hz
A401 A02 Driver L01 A01 L02 T01 A03 L03
U01
15 V DC Power Supply
C701
F401 25 A
L01
LB+
DC output 110 V DC 2 kW
LBDC EMI-Filter Low Voltage Power Supply
Functional Description
23 of 34
India 180 kVA
Mechanical Design
4.2
4.2.1
Mechanical Design
Enclosure
The enclosure of the converter is manufactured of stainless steel and its sealing satisfies the international protection class IP55. Access All maintenance and service work can be carried out without removing the power converter. The enclosure can be easily opened even while the unit is in place. Two service covers sideways of the converter allow quick access to all modules of the converter. Access to the inductances is possible via a revision cover at the converters front side. The input and output connections are via stud terminals and are brought out through cut outs for cable entry. An isolated plug-in connector is provided for the connection of the control cable.
Connections
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
24 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
5
5.1
Module Descriptions
Input section and IVPS section
A702 Digital controller unit for IVPS UI UCE UCE Temperature prewarning Overtemperature IIC UIC
S01 75C
A750 1-phase filter
S02 85C
A01.2 Driver
A01.1 Driver
U501 Voltage sensor A502 Voltage divider U201
to converter control unit A710
U101 Voltage sensor A102 Voltage divider V01.1 A101 L101 R01.1 V02.1 C01.1 R02 C01.2 R01.2
L201 +UIC
Current sensor
UI
1L1 1L2
F01
Figure 14: Input section and IVPS section Input EMI choke A101 Input chokes L101 and L102 Thyristor bridge It suspends guided electromagnetic disturbances and thus improves the electromagnetic compatibility of the converter. Input filter chokes The thyristor bridge mainly consists of the two thyristors V01.1 and V01.2 and the two diodes V02.1 and V02.2. It converts the AC input voltage into a DC voltage (= intermediate circuit voltage) L201 smoothes the rectified input voltage Current sensor U201 detects the intermediate circuit current. The output signal of U201 is wired to the SCR control board A702. Short circuit thyristor unit A202 with thyristor V01 works as emergency protection if the DC output (=intermediate circuit) voltage exceeds a specified value. Firing the thyristor shorts the section and thus blows the input fuse outside of the converter (crowbar function). Trigger circuit is A01. L201 limits the current rise. The digital controller unit for IVPS A702 controls and monitors the operation of the thyristor bridge and communicates with the converter control unit A710.
Smoothing choke L201 Current detection
Short Circuit Thyristor Unit A202
Digital controller unit A702 for IVPS
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
{
L102
to inverter section A300, LVPS section A400
V02.2 R01.4
R01.3 V01.2
R01
C01.4
C01.3
V01
C01
Crow A01 bar assy -UIC
A201 Semicontrolled Thyristor Bridge B2HZ
A202 Short circuit thyristor module
25 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
5.2
Inverter section
The inverter modules A301.1, A301.2 and A301.3 transform the filtered input voltage into a system of three AC voltages each with 120 degrees phase shift against the other voltages. Inverter modules A301.1, A301.2, A301.3 Each module is a three single-phase IGBT half bridge with a six-fold driver A01. Each module consists of two individual IGBT's V01 and V02. The connected inverter modules convert the intermediate circuit voltage into a three-phase AC voltage (3 x 415 V/50 Hz). The downstream AC filter consists of chokes L301-L303 and capacitors C302.1-6. The EMI filter is located downstream of the AC filter and consists of the EMI choke L01 and the capacitors C01-10. The output terminals 2L1 and 2L2 provide a phase-to-phase voltage UAC of 110 V / 50 Hz with a power of 500 VA. The output terminals 3L1, 3L2 and 3L3 provide a phase-to-phase voltage UAC of 3 x 415 V / 50 Hz with a power of 180 kVA. The inverter control unit A703 controls and monitors the operations of each inverter module and communicates with the converter control unit A710. It also supplies the IGBTs with the necessary switching signals via the six-fold drivers A01.
AC filter EMI filter
Output terminals 2L1 and 2L2 Output terminals 3L1, 3L2 and 3L3 Inverter control unit A703
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
26 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
UCE
Temperature Overprewarning temperature IL1
A703 Inverter control unit
UCE IL2 UCE IL3
S01 80C
S02 90C
S01 80C
S02 90C
S01 80C
S02 90C
A01 IGBT driver +U IC
R301.1-4 C301.1-3
A01 IGBT driver
A01 IGBT driver
V01
C01.1-3
V01
C01.1-3
V01
C01.1-3
T01 T01 T01
V02
V02
V02
-U IC
A301.1 Inverter
A301.2 Inverter
A301.3 Inverter
A502 Voltage divider
A710 Converter control unit
A302 AC-EMI filter 2L1
L301 L302 L303
Sine wave filter Q901 Q902 P901 M901 3~
{
T301 Q301
C302.1-6
2L2
T302
T901 T902 T903 L01 C01-10
3L1 3L2 3L3
P902
3~ M902
Figure 15: Inverter section
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
27 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
Inverter
The IGBT inverter modules divide the input voltage UIC into separate pulses of constant amplitude, but varying durations (pulse frequency: 3,6 kHz). The variable switching ratio controls the amplitude of the output voltage (sine pulse width modulation, see Figure 16.
Filter output voltage V(t) +VZ Inverter output voltage
-VZ
Figure 16: Generation of sinusoidal alternating voltage by means of sine pulse width modulation. The figure shows the input voltage UDC switched through as square-wave pulses and the inverter output voltage after smoothing by the AC filter (sine curve). Wide voltage pulses +UIC, narrow voltage pulses UIC: amplitude of output voltage close to +UIC Narrow voltage pulses +UIC, wide voltage pulses UIC: amplitude of output voltage close to UIC Voltage pulses of same width for +UIC and UIC: amplitude of output voltage = 0. The combination of three inverter branches like this, which will be triggered with a phase shift of 120, creates a three-phase AC system.
AC filter
Due to the pulse width modulation at a constant pulse frequency, the only oscillation that occurs is harmonic oscillation with the pulse frequency (3,6 kHz) or higher. Even a relatively small-sized filter is sufficient to eliminate this. The filter creates an almost sinusoidal voltage curve from the square-wave voltage pulses of varying length (harmonic distortion factor < 10 % RMS). The alternating voltage UAC at 3 x 415 V / 50 Hz is available to the consumer loads at terminals 3L1, 3L2 and 3L3.
AC output
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
28 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
5.3
Low Voltage Power Supply section
The LVPS converts the intermediate circuit voltage UIC to an DC output voltage of 110 V / 2 kW. It also stabilizes the DC output voltage constant within a specified range irrespective of fluctuations in the intermediate circuit voltage and monitors the total current, in particular limits it to the permissible maximum value. DC/DC module A401 Chopper unit A01 The DC/DC module A401 (LVPS) consists of the IGBT chopper unit A01, the transformer T01 and the rectifier module A03. The chopper unit forms an IGBT full bridge including the two dual IGBT modules V01.1 and V01.2 and the quadruple driver A02. The IGBT driver provides the control signals for the IGBTs. The switching frequency is 20 kHz. The chopper unit A01 switches the filtered intermediate circuit voltage through to the primary winding of the transformer T01 in the form of voltage blocks. The transformer T01 has one primary and two secondary windings (center-tap connection). It transforms the block-shaped AC voltage down to the required output voltage. The rectifier module A03 rectifies the block-shaped AC voltage supplied by the secondary windings of the transformer T01. The ripple-filter choke L03 and the capacitor C02 smooth and dampen the rectified voltage. Furthermore the LVPS has measurement devices for DC output voltage, DC output current and a downstream EMI filter, consisting of the filter choke L01 and the capacitors C01-04. The LVPS chopper control unit A704 controls and monitors the operations of the DC/DC module A401 and communicates with the converter control unit A710. It also supplies the IGBTs with the necessary switching signals via the IGBT driver A01.
Transformer T01
Rectifier modules A03 and A04 Output filter EMI filter
LVPS chopper control unit A704
A704 LVPS chopper control unit UCE IPRIM Overtemperature ITOT
UB
to converter control unit A710
S01 100C
A730 Signal conditioning
A02 IGBT driver
A01 IGBT chopper unit +UIC
L01
V01.1
V01.2 T01 A03
T1 L03 L02 V02
+/- 15 V to A702 IVPS digital controller A703 Inverter control unit A704 LVPS control unit A710 converter control unit A740 converter display board A760 1-phase filter A901 Ground fault detection
A720 Power supply
A402 DC-EMI filter
C01 L01 C03
{
U01
LB+
V03
C02
-UIC A401 DC/DC module
C02
C04
LB-
Figure 17: Low voltage power supply A401
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
29 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
5.3.1
Generation of the Low Voltage Power Supply
Figure 18 shows how the DC/DC module A401 generates the stabilized DC output voltage (= 110 V DC) from the intermediate circuit voltage UIC. 1 The input is the intermediate circuit voltage after smoothing by the line coil L01 (1). This voltage is not constant. The diagram shows two different cases: Input voltage at the upper end of the tolerance range (left column) Input voltage at the lower end of the tolerance range (right column) 2 The chopper unit A01 switches the DC voltage through to the primary winding of the transformer T01 in the form of square-wave voltage blocks of alternating polarity. The switching times of the IGBTs are controlled in such a way that the area of these voltage blocks is always constant (pulse-width modulation): Higher input voltage IGBTs conduct for a shorter time [(2), left] Lower input voltage IGBTs conduct for a longer time [(2), right] The transformer T01 converts the block-shaped AC voltage to a different voltage. The form of the voltage curve is retained (3). After rectification by A03, all the square-wave voltage pulses have the same polarity (4). The height and length of the voltage pulses is still dependent on the level of the original input voltage: Higher input voltage higher but shorter voltage pulses (left) Lower input voltage lower but longer voltage pulses (right) The product of the height and length of the voltage pulses (the area of the voltage blocks) is constant, irrespective of the input voltage. The downstream filter then smoothes the voltage by filling in the gaps between the voltage pulses. The maximum value of the voltage drops during this process more for high, short voltage pulses (because there are large gaps to be filled), and less for low, long voltage pulses where the gaps to be filled are only narrow. Observed over a cycle time , the product of the length () and the height of the voltage on the other hand remains constant. The result is a constant output voltage, which is largely independent of the fluctuating input voltage [(5), left and right].
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
30 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
Uin
Uin t t
UCh
UCh t t
USec t
USec t
URect
URect t t
Uout t
Uout t
Figure 18: Generation of constant DC voltage in the Low Voltage Power Supply
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
31 of 34
India 180 kVA
Module Descriptions
5.4
Earth fault detection
The earth fault detection consists of a centre tapped resistor network R1 and R2, which is connected across the negative and positive bus of the intermediate circuit. The centre point of this resistor network is connected to the housing via the resistor R3. The voltage over the resistor R 3 is measured. During regular operation, there is no additional galvanic connection between the housing and the intermediate circuit / output circuit. Thus there is no current through R3. If there is an earth fault (in our example in L3), then the Resistor R3 will be switched parallel to R1 resp. R2 via the earth fault resistance Re, depending on the switching conditions of the IGBT's V5 and V6. The IGBTs V5 and V6 will be switched on and off in the switching frequency of the inverter. There will be an ac current through R3. The earth fault detection recognizes the voltage over R3 and shows an earth fault. There will be detected earth faults at the input circuit, the intermediate circuit as well as at the phases.
AC R1 R2 DC Input filter Thyristor Bridge R3
V1
V3
V5
V2
V4
V6
Inverter UR3 Control
RE Output Filter
Figure 19: Earth fault detection
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
32 of 34
India 180 kVA
External Controlling Equipment
The external controlling equipment is located on the left lateral service cover (see No. 1 in Figure 20). The detailed view is shown in Figure 21.
N O FAU LT
4
V
2
A
175.0 V
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
AC output voltage meter P901 AC input voltage meter P903 Converter fault display A740 Type plate of converter AC output ammeter P902 Phase selection switch S902 Phase selection switch S901
Figure 20: Left lateral service cover with controlling equipment
Figure 21: Detailed view of external controlling equipment
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
33 of 34
India 180 kVA
ERROR DISPLAY
NO FAULT
DISPLAY OK
Figure 22: Detailed view of converter fault display A740
AC INPUT OK GENERAL FAULT INTERNAL FAULT INVERTER FAULT IVPS/SCR FAULT
TT1823
Descr. in Figure 22 AC INPUT OK GENERAL FAULT INTERNAL FAULT INVERTER FAULT IVPS/SCR FAULT DISPLAY OK
LED Signal name Colour green red red red red yellow AC input voltage Fault of inverter section Fault of LVPS section Phase/ground fault of AC output Fault of IVPS section Heartbeat
LED is on, if AC input voltage is in specified range a fault occurs in the inverter section a fault occurs in the LVPS section an earth fault occurs at the AC output or at the AC input a fault occurs in the IVPS section (thyristor bridge A201) converter fault display A740 is in operation (no fault)
Detailed alphanumeric fault messages of fault display A740 Alphanumeric character N O F A U L T H - B R I D G E I N V E R T E R L V P S T E M H - B R T E M I N V T E M L V P S T E M T 3 0 2 F 0 1 Q 9 0 1 Q 9 0 2 Q 3 0 1 E A R T H F A Description No fault Fault of IVPS section Fault of inverter section Fault of LVPS section Overtemperature in IVPS section Overtemperature in inverter section Overtemperature in LVPS section Overtemperature of autotransformer T302 Fault of fuse F01 Fault of motor-circuit switch Q901 Fault of motor-circuit switch Q902 Fault of circuit breaker Q301 Ground fault
20999_TechDesc_R20_040519.doc
34 of 34
You might also like
- Altivars & Soft Starters - enDocument28 pagesAltivars & Soft Starters - enBudy AndikaNo ratings yet
- SM - MinarcMig 150 - V1Document23 pagesSM - MinarcMig 150 - V1Koguttoo100% (1)
- Max 16841 Ev KitDocument16 pagesMax 16841 Ev KitjorojoroNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: 17-Inch LCD Monitor AL1702Document38 pagesService Manual: 17-Inch LCD Monitor AL1702Abhilash VamanNo ratings yet
- M35&36 Service Manual Parts GuideDocument96 pagesM35&36 Service Manual Parts GuideEugen BratuNo ratings yet
- Ca 3524Document20 pagesCa 3524rmsharma1970No ratings yet
- Telwin Tecnica 150 152 170 168ge Welding Inverter SMDocument21 pagesTelwin Tecnica 150 152 170 168ge Welding Inverter SMdanieltoader69No ratings yet
- Application Note An-985: Six-Output 600V Mgds Simplify 3-Phase Motor DrivesDocument12 pagesApplication Note An-985: Six-Output 600V Mgds Simplify 3-Phase Motor DrivesTaufik InsaniNo ratings yet
- Implementation of A Single-Phase Unipolar Inverter Using DSP TMS320F241Document5 pagesImplementation of A Single-Phase Unipolar Inverter Using DSP TMS320F241Pci ElectronicaNo ratings yet
- Technics Su c909sDocument61 pagesTechnics Su c909sschaiNo ratings yet
- LT1930 FDocument13 pagesLT1930 FZeljko RadonjicNo ratings yet
- Telwin 111 RepairDocument20 pagesTelwin 111 RepairKlavdija CankarNo ratings yet
- TCL TV M35 36 Service ManualDocument96 pagesTCL TV M35 36 Service ManualRituparna Dutta Chowdhury100% (1)
- Imprimir Datasheet 1Document14 pagesImprimir Datasheet 1Randy Siancas VelezNo ratings yet
- E560 Aa20 CSDocument7 pagesE560 Aa20 CSMohsen AttaryNo ratings yet
- 1VAL2401 - SG Rev - A ODP Spare Parts Style Guide May 7 - 2010Document9 pages1VAL2401 - SG Rev - A ODP Spare Parts Style Guide May 7 - 2010JEFFERSON ALEJANDRO MURILLO CAPERANo ratings yet
- Digital Benchtop Power Supply Part 1Document4 pagesDigital Benchtop Power Supply Part 1vacsaaNo ratings yet
- LM556/LM556C Dual Timer: General DescriptionDocument6 pagesLM556/LM556C Dual Timer: General DescriptionDaryl ScottNo ratings yet
- LM1575/LM1575HV/LM2575/LM2575HV Series Simple Switcher 1A Step-Down Voltage RegulatorDocument23 pagesLM1575/LM1575HV/LM2575/LM2575HV Series Simple Switcher 1A Step-Down Voltage RegulatorOsman KoçakNo ratings yet
- Alinco DR-138 ServDocument42 pagesAlinco DR-138 ServAzhar Walet67% (3)
- Gradateur CI-Tronic Analogue Power Controller Type ACI 30-1 and ACI 50-1Document8 pagesGradateur CI-Tronic Analogue Power Controller Type ACI 30-1 and ACI 50-1marocainissamNo ratings yet
- Speed Control for Industrial VehiclesDocument37 pagesSpeed Control for Industrial VehiclesVladimir KrivenokNo ratings yet
- Excitation SystemDocument15 pagesExcitation SystemParmeshwar Nath Tripathi67% (3)
- AMS90 - MechatronicsDocument20 pagesAMS90 - MechatronicsMukund FarjandNo ratings yet
- WF 1907Document34 pagesWF 1907Luis Alberto PalaciosNo ratings yet
- Ca3140, Ca3140A: 4.5Mhz, Bimos Operational Amplifier With Mosfet Input/Bipolar Output FeaturesDocument19 pagesCa3140, Ca3140A: 4.5Mhz, Bimos Operational Amplifier With Mosfet Input/Bipolar Output FeaturesRicardo Teixeira de AbreuNo ratings yet
- 750V DC Traction SystemDocument26 pages750V DC Traction SystemShashi Bhusan Singh100% (2)
- Protection Overview Station Transformer CCPDocument1 pageProtection Overview Station Transformer CCPJorge Andres PavónNo ratings yet
- Soft Starters and Variable Speed DrivesDocument36 pagesSoft Starters and Variable Speed DrivesBudy AndikaNo ratings yet
- Service Manual for Minarc 150/150 VRD/151 Welding MachinesDocument27 pagesService Manual for Minarc 150/150 VRD/151 Welding MachinesSimpalean NicolaeNo ratings yet
- CA3140Document20 pagesCA3140Brzata PticaNo ratings yet
- Blazer 400-800 Service ManualDocument34 pagesBlazer 400-800 Service ManualdaossaNo ratings yet
- FT-1802M Technical SupplementDocument34 pagesFT-1802M Technical SupplementBeto Lima0% (1)
- Uc2577 AdjDocument14 pagesUc2577 AdjChandranoola RajuNo ratings yet
- D Escriptio: S FeatureDocument8 pagesD Escriptio: S Featurevsc2012No ratings yet
- HEIDENHAIN Inverter Systems for Machine Tool BuildersDocument48 pagesHEIDENHAIN Inverter Systems for Machine Tool BuildersAstaroth Zion0% (1)
- Altistart 01 TechDocument38 pagesAltistart 01 TechSalim SaadNo ratings yet
- AC/DC Current Transducer AHR-B5 I 500 .. 2000 ADocument4 pagesAC/DC Current Transducer AHR-B5 I 500 .. 2000 ASarafaraz AlamNo ratings yet
- HT7L4811 Non-Isolation Buck LED Lighting Driver With Active PFCDocument12 pagesHT7L4811 Non-Isolation Buck LED Lighting Driver With Active PFCEnéas BaroneNo ratings yet
- Current Loop Control of A Brushless DC Motor With Hall SensorsDocument19 pagesCurrent Loop Control of A Brushless DC Motor With Hall SensorsGautam MonipatroNo ratings yet
- Advanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators UC1524 UC2524 UC3524Document6 pagesAdvanced Regulating Pulse Width Modulators UC1524 UC2524 UC3524Rudy Manuel Huamani FernandezNo ratings yet
- Telwin Tecnica 144-164 Welding-Inverter SMDocument21 pagesTelwin Tecnica 144-164 Welding-Inverter SMAndreea TudoseNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Exercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsFrom EverandExercises in Electronics: Operational Amplifier CircuitsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsFrom EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNo ratings yet
- # Ponumber Podt Ven - Code Vend - Name PRD - CodeDocument3 pages# Ponumber Podt Ven - Code Vend - Name PRD - CodeSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- MotivationDocument4 pagesMotivationSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Italian, Swiss, German Industrial Vacuum CleanersDocument2 pagesItalian, Swiss, German Industrial Vacuum CleanersSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Effective Time Management Important Vs UrgentDocument23 pagesEffective Time Management Important Vs Urgentmunisa1961No ratings yet
- WHS EP Housekeeping4Document1 pageWHS EP Housekeeping4SURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- God ChangesDocument1 pageGod ChangesShannon100% (2)
- Chair BillDocument1 pageChair BillSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Angle Grinder Safety ProceduresDocument1 pageAngle Grinder Safety ProceduresSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- And We Say We Work HardDocument13 pagesAnd We Say We Work HardSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Fo No. Code No. Description Qty. Reason Rts NoDocument1 pageFo No. Code No. Description Qty. Reason Rts NoSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Self-Discovery Reflection QuestionsDocument1 pageSelf-Discovery Reflection QuestionsSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- SPECAA22421Document4 pagesSPECAA22421SURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Work Instruction TemplateDocument7 pagesWork Instruction TemplateSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Manpower Status and Productivity Insights for Month of --Month-- 2009Document32 pagesManpower Status and Productivity Insights for Month of --Month-- 2009SURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- ESD Work Instruction WI-OPS-005Document17 pagesESD Work Instruction WI-OPS-005Niv Narkiss75% (4)
- WHS EP Eyeprotection3Document1 pageWHS EP Eyeprotection3SURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Safe Work Procedure (Drill Press)Document2 pagesSafe Work Procedure (Drill Press)SURJIT SINGH100% (1)
- SPECAA22421Document4 pagesSPECAA22421SURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- HeijunkaDocument18 pagesHeijunkamamanbudiNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Training Calendar: Topic Int./ ExtDocument2 pagesTraining Calendar: Topic Int./ ExtSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- View PDFDocument1 pageView PDFSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Epoxy ResinDocument7 pagesEpoxy ResinAtiq JamNo ratings yet
- Hind Rectifiers LTD.: Semiconductor DivisionDocument3 pagesHind Rectifiers LTD.: Semiconductor DivisionSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- SPECAA22421Document4 pagesSPECAA22421SURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- FORCED AIR COOLED ALTERNATOR MOUNTED RECTIFIER TEST REPORTDocument5 pagesFORCED AIR COOLED ALTERNATOR MOUNTED RECTIFIER TEST REPORTSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- From The 6Ms To The 6QsDocument8 pagesFrom The 6Ms To The 6QsSURJIT SINGHNo ratings yet
- All About Diesel LocoDocument293 pagesAll About Diesel LocoDeepak Chauhan100% (9)
- Monthly Safety Report SampleDocument2 pagesMonthly Safety Report SampleSURJIT SINGH82% (33)
- AOAC Official Methods of Analysis for Phosphorus in FertilizersDocument2 pagesAOAC Official Methods of Analysis for Phosphorus in FertilizersDjaloel KhairNo ratings yet
- The Vital Role of Quantum Cryptography in IoT Network SecurityDocument15 pagesThe Vital Role of Quantum Cryptography in IoT Network SecurityAllanki Sanyasi RaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Functional Analysis - Goetz GrammelDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Functional Analysis - Goetz GrammelLaura RadoiNo ratings yet
- Murakami - Analysis of Stress Intensity Factors of Modes I, II and III For Inclined Surface Cracks of Arbitrary ShapeDocument14 pagesMurakami - Analysis of Stress Intensity Factors of Modes I, II and III For Inclined Surface Cracks of Arbitrary ShapeDavid C HouserNo ratings yet
- Advanced parallel techniques for supercomputer performanceDocument32 pagesAdvanced parallel techniques for supercomputer performanceSpin FotonioNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Sample For AnalysisDocument27 pagesPreparation of Sample For Analysisapi-26215965100% (2)
- 1 - Logic GatesDocument7 pages1 - Logic GatesAlfred GaleaNo ratings yet
- KSH - Korn Shell TutorialDocument5 pagesKSH - Korn Shell Tutorialramaniqbal123No ratings yet
- Fourier SeriesDocument16 pagesFourier Seriesvolly666No ratings yet
- Fire Magic 2019 Catalog PDFDocument56 pagesFire Magic 2019 Catalog PDFgallegos7386No ratings yet
- Primo Theory Volume 5 Secured - Unlocked PDFDocument60 pagesPrimo Theory Volume 5 Secured - Unlocked PDFmsmali100% (1)
- Digital Logic GatesDocument41 pagesDigital Logic Gatessurafel5248No ratings yet
- Entry Test Preparation Test No.2 (ECAT)Document3 pagesEntry Test Preparation Test No.2 (ECAT)NAEEM UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Salesforce Object Relationships: What Is Lookup Relationship in SalesforceDocument4 pagesSalesforce Object Relationships: What Is Lookup Relationship in SalesforceYash Patel-YashuNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Computer Simulation Methods: Harvey Gould, Jan Tobochnik, and Wolfgang Christian July 31, 2005Document8 pagesAn Introduction To Computer Simulation Methods: Harvey Gould, Jan Tobochnik, and Wolfgang Christian July 31, 2005Maria Juliana Ruiz MantillaNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Tips: 40 Shorthand SymbolsDocument3 pagesNote Taking Tips: 40 Shorthand Symbolstinesh9402No ratings yet
- FVM - CFDDocument44 pagesFVM - CFDgrkguptaNo ratings yet
- 2011 REV SAE Suspension Kiszco PDFDocument112 pages2011 REV SAE Suspension Kiszco PDFRushik KudaleNo ratings yet
- Euphonix - An OverviewDocument5 pagesEuphonix - An OverviewNathan BreedloveNo ratings yet
- Newtonian Mechanics (Physics Chap 2)Document46 pagesNewtonian Mechanics (Physics Chap 2)anon_815277876No ratings yet
- HPLC: A GUIDE TO HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHYDocument90 pagesHPLC: A GUIDE TO HIGH PERFORMANCE LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHYRakesh Kotta100% (1)
- IntertekWhitepaper Surface Area and Porosity Pharmaceutical PDFDocument7 pagesIntertekWhitepaper Surface Area and Porosity Pharmaceutical PDFJosé Antonio Michea GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Grade8 UseDocument31 pagesGrade8 UseSabino Alfonso RalaNo ratings yet
- Lec 6Document15 pagesLec 6Katevarapu Venkateswara RaoNo ratings yet
- Experiment #1 Audio MonitorDocument7 pagesExperiment #1 Audio MonitorDaniel CafuNo ratings yet
- Lab Scope Certificate ISO 17025-2017Document33 pagesLab Scope Certificate ISO 17025-2017Khan SattrakulvongNo ratings yet
- Schlenk Line Techniques: Liquid NDocument15 pagesSchlenk Line Techniques: Liquid NMarinoChavarroCordobaNo ratings yet
- College Department Course: B.E Course Code 18CSL67 Student Name USN Mini Project Title Under Taken at Internal Guide SynopsisDocument3 pagesCollege Department Course: B.E Course Code 18CSL67 Student Name USN Mini Project Title Under Taken at Internal Guide Synopsismohit kunduNo ratings yet